Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

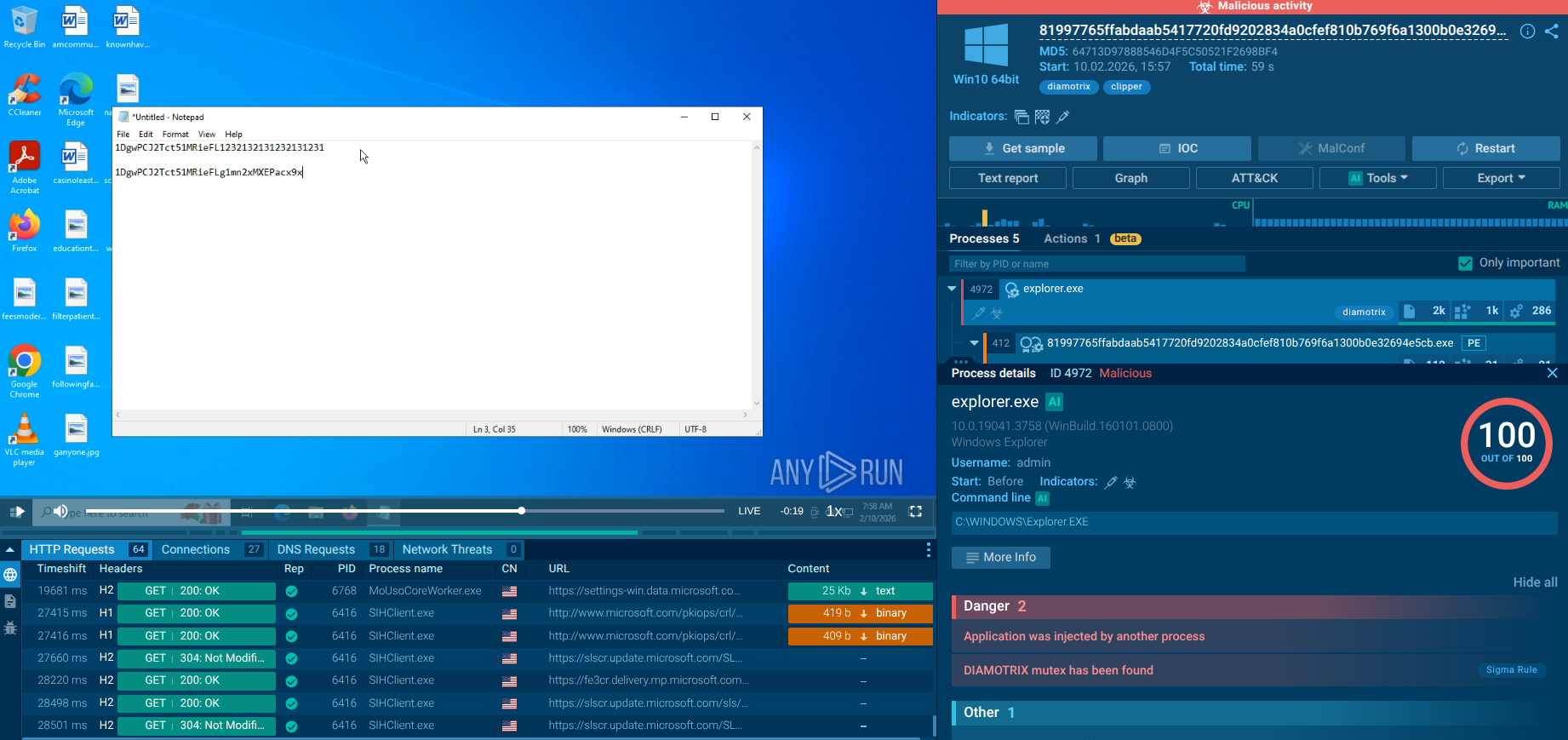
Hawkeye often gets installed in a bundle with other malware. This is a Trojan and keylogger that is used to retrieve private information such as passwords and login credentials. This is an advanced malware that features strong anti-evasion functions.
|
Keylogger
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2013
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2013
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 857
857
 0
0

 508
508
 0
0

 2788
2788
 0
0
Hawkeye, also known as Predator Pain, is a dangerous trojan and keylogger - a malware used to steal information from PCs. It has very advanced detection evasion and information stealing functionality. Hawkeye can be combined with other malicious software to steal passwords from email clients and web browsers.
Available as a service on the dark web, Hawkeye can be used even by non-technically savvy attackers. In addition, this malware is known to have been advertised for some time on the general Internet on its own website, which today is unavailable. What’s more, the creators of Hawkeye have developed a unique business model in which intermediaries are used for reselling the malware.
Hawkeye keylogger is capable of stealing a variety of information from the victim's PC, including passwords from mail clients, web browsers, and bitcoin wallet information, as ransomware does. Furthermore, this malware can take screenshots, have a keylogger functionality, and retrieve data from the Internet download manager to employ JDownloader to steal passwords.
Predator Pain targets victims worldwide, but its attacks are being registered most often in the countries with the wealthiest economies, according to the GPD data, such as the USA, Canada, Italy, and others.
Hawkeye keylogger employs a sophisticated technique to stay hidden from the antiviruses called process hollowing. In essence, the Trojan generates a new instance of a harmless process to swap the native code with a malicious one subsequently. The 8 version of Hawkeye keylogger is different from previous iterations of the malware. Instead of running the main malicious code as a new process, the latest build injects the payload into MSBuild.exe, RegAsm.exe, and VBC.exe, which are a part of the .NET framework, enabling the virus to further disguises itself as a real and harmless process.
Another difference between the newest Predator Pain version from the older ones is that instead of being written in C, now it uses .NET and calls the native Windows API directly.
The primary function of the Hawkeye keylogger is to record the key and mouse presses along with window context and clipboard data. In addition, the malware has special modules that allow it to derive information from certain applications, including a popular video game Minecraft, the FTP client FileZilla and others.
Somewhat standardly, Predator Pain utilizes real BrowserPassView and MailPassView tools to save data from browsers and emails. In addition, the malware is able to activate and take control of the webcam if the infected machine has one connected.
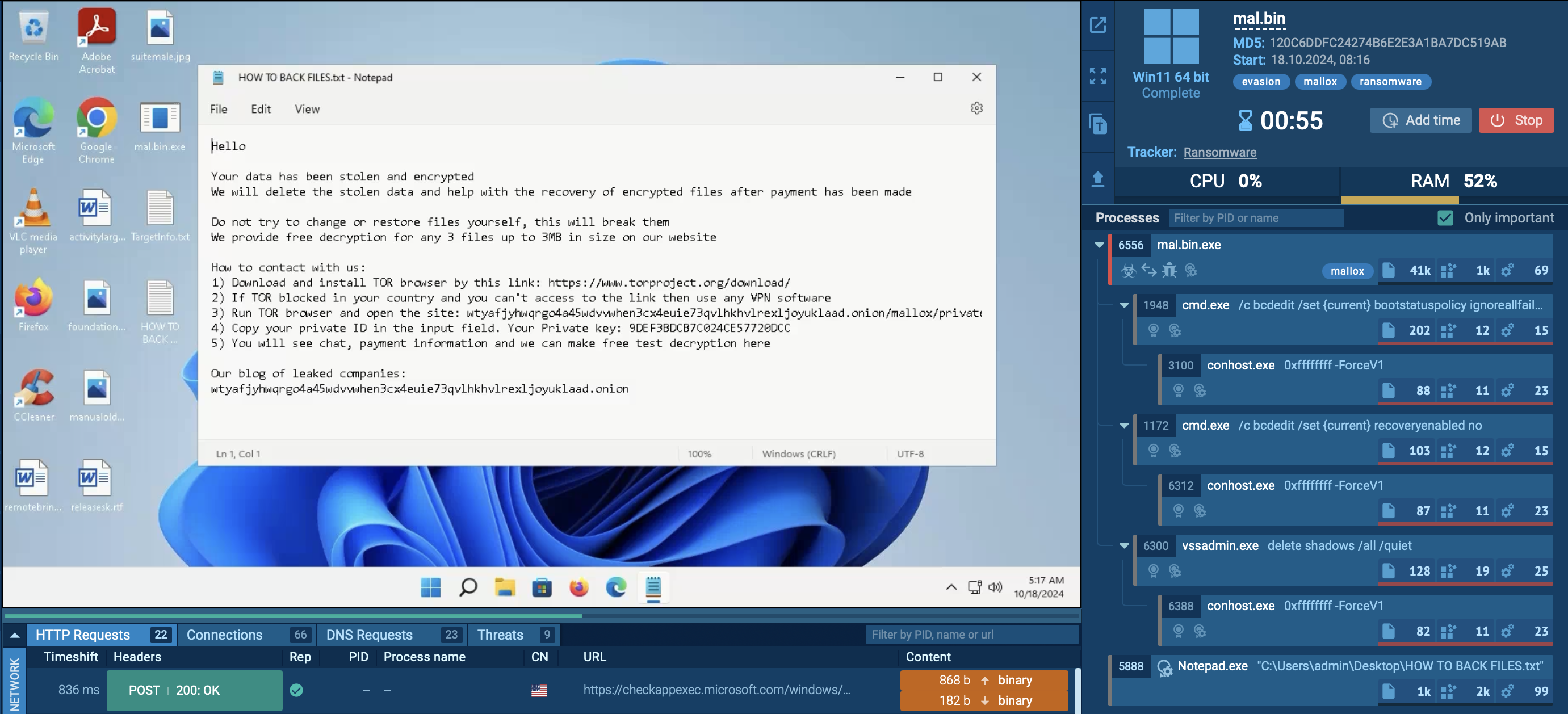
To prevent detection and analysis, Hawkeye comes equipped with a series of anti-evasion tools besides processes hollowing. For instance, the malware sets a delay before being executed, which helps it trick some of the automated sandbox analysis tools. It also comes equipped with a technique that targets specific antivirus processes and stops them from executing and blocks access to several domains used by antivirus programs for updating.
What’s more, the malware takes active steps to prevent the victim from disabling its own processes by taking control over command prompt, registry editor, and task manager. At the same time, Hawkeye constantly scans the computer for other malicious programs and instantly deletes them if found.
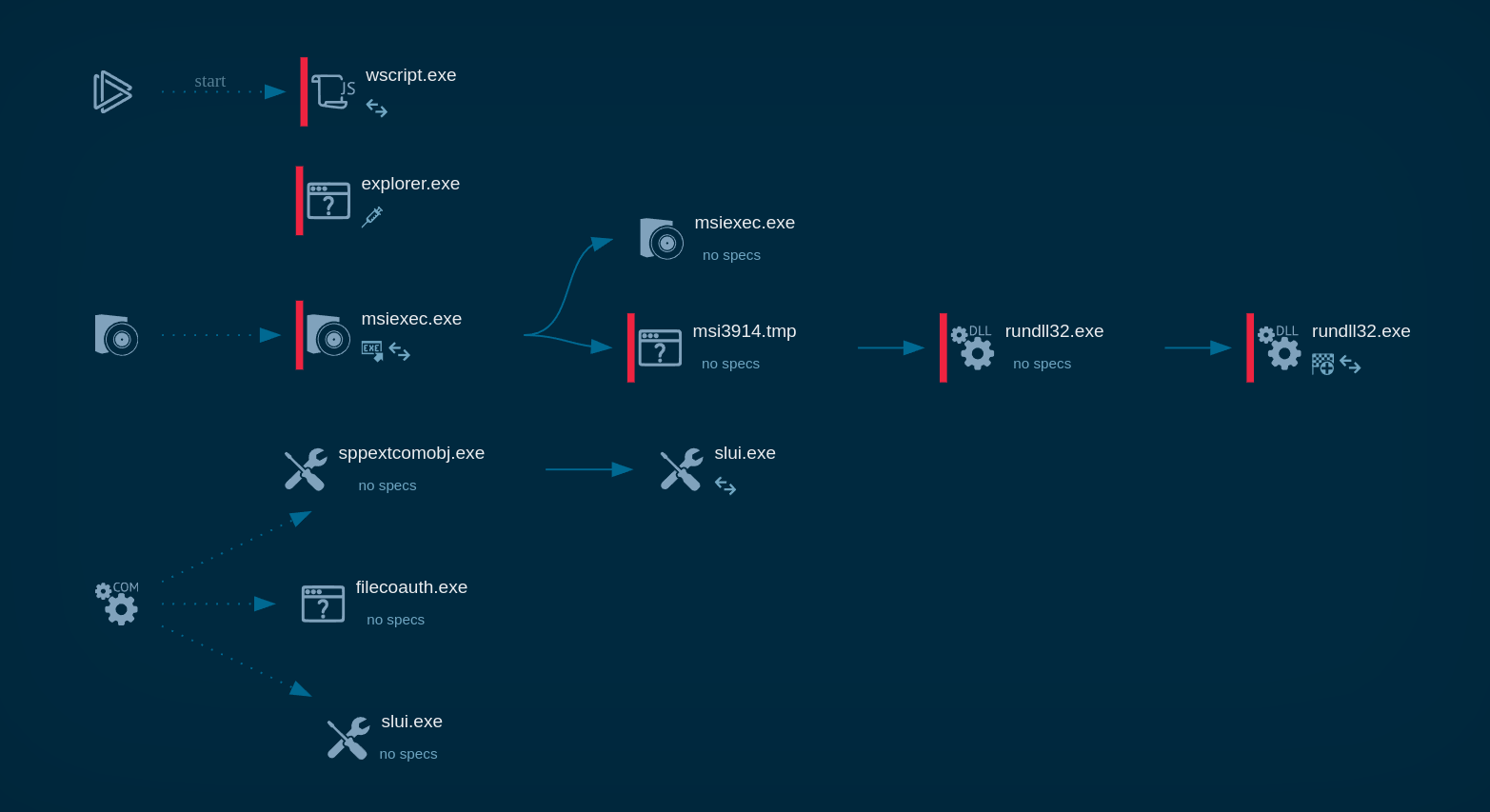
The execution process of the Predator Pain keylogger can be reviewed in a lot of detail in a video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service

Figure 1. a visual process graph generated by ANY.RUN allows reviewing the lifecycle of the Hawkeye quickly
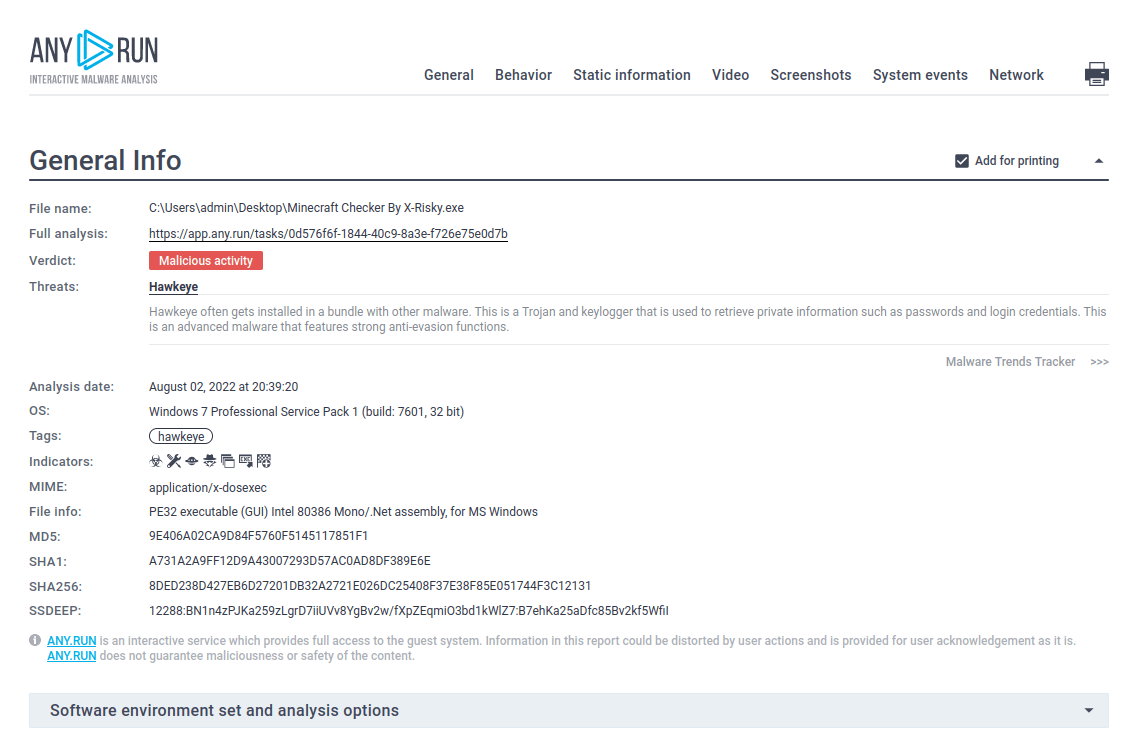
Figure 2. ANY.RUN also allows researchers to generate customizable text reports which are a great way to present the analysis results
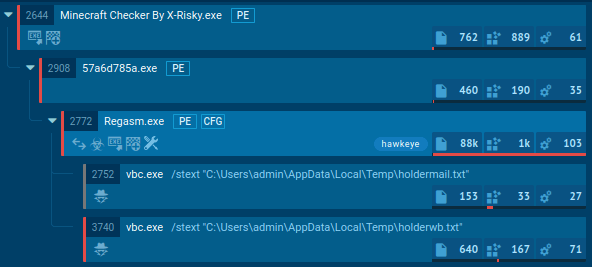
Figure 3. Execution processes of Hawkeye as displayed by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service
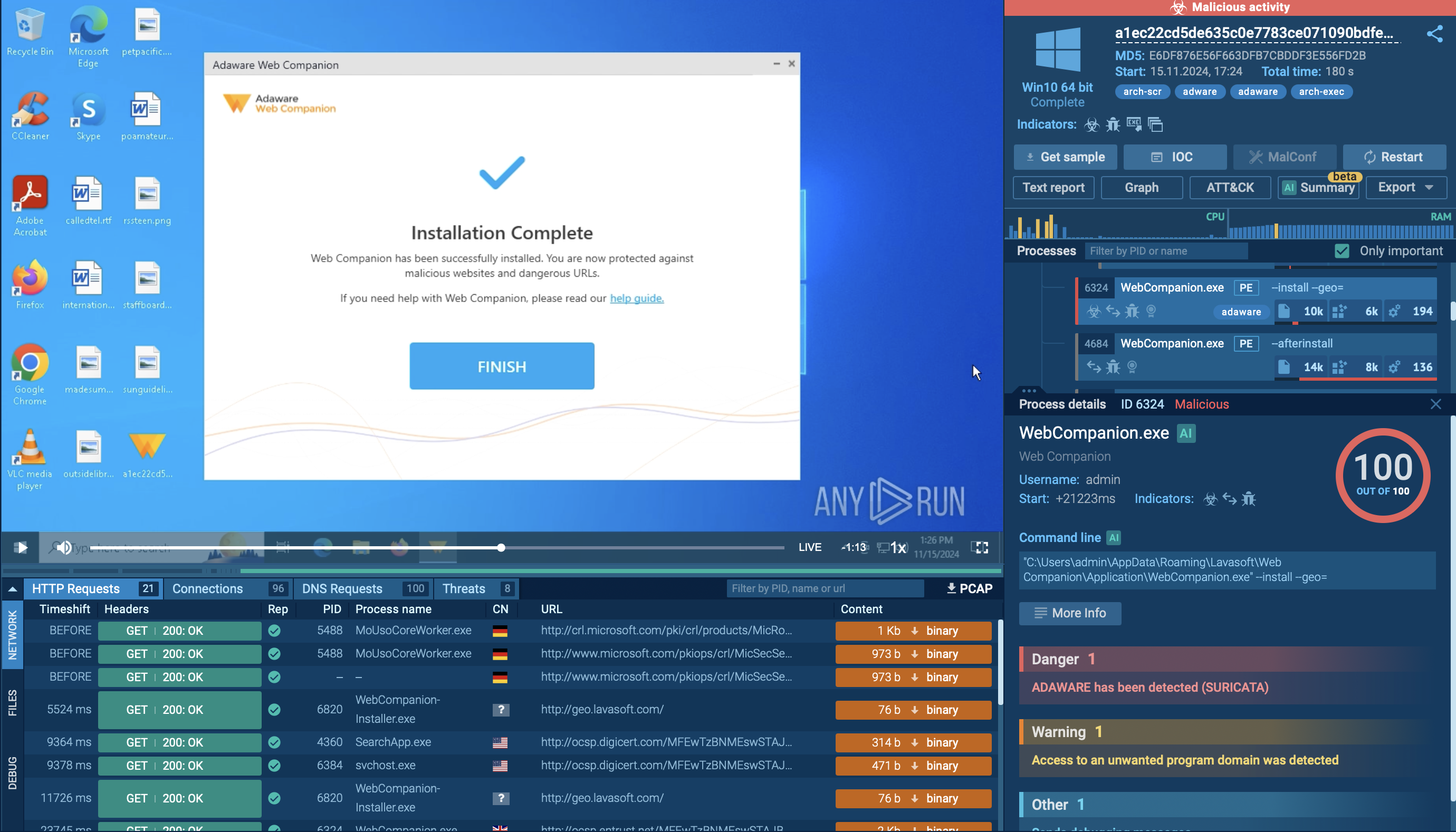
Hawkeye keylogger often reaches users' devices through phishing emails, most commonly as a malicious Microsoft Office file, such as Docx file. After the user opens the downloaded file, it either asks the user to enable macros or uses vulnerabilities to download and execute the main payload. In most cases, it downloads itself into the %AppData% folder. To maintain its presence, the malware adds itself to the autorun registry. It also uses process hollowing to hide its code in legitimate processes. For example, the 8 version of Hawkeye, presented in this task from our simulation, injects itself into MSBuild.exe, RegAsm.exe, or VBC.exe. Before sending information to the control server, Hawkeye saves stolen data in Tmp files into the %Temp% folder. Usually, these Tmp files are deleted after the information is sent to a control server.
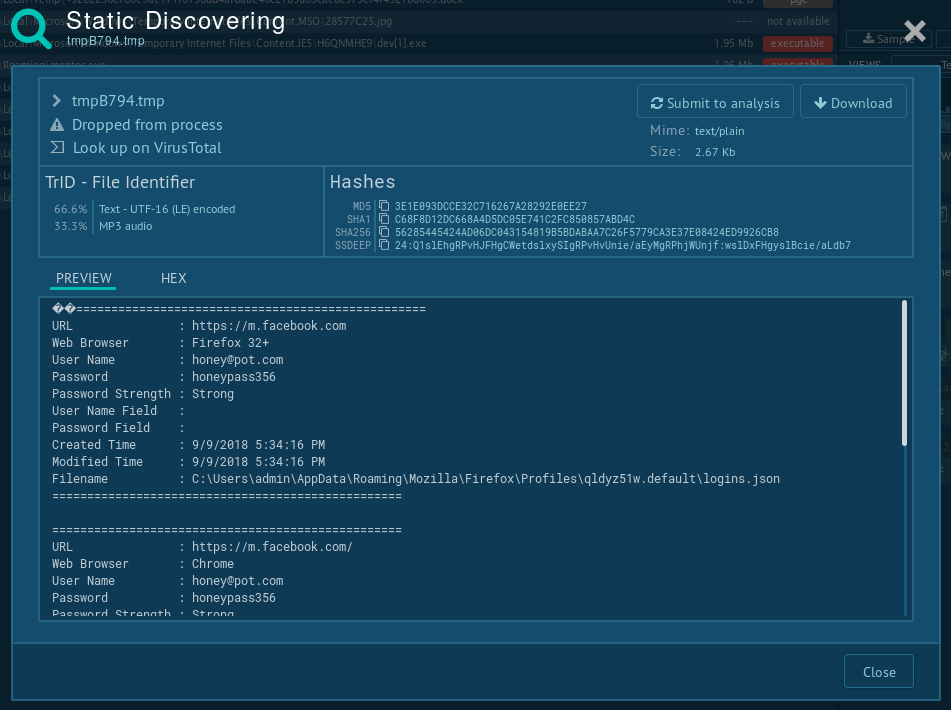
Figure 4. Information saved in .TMP file
Following some common online hygiene guidelines is a good way to stay safe from getting infected with Hawkeye. In addition, users should be careful when downloading free software from unknown or suspicious websites and carefully check the URLs when downloading any software in general.
In addition, after receiving a suspicious email or an email from an unidentified sender, users should be cautious when downloading attachments. Although the opened document prompts the user to enable macros or activate the editing, users must never follow these instructions as they most likely indicate the file's malicious nature.
Hawkeye trojan uses multiple distribution methods, including packaging within free downloadable programs or disguised as legitimate software. Hawkeye can also be installed on the victim’s PC manually if the attacker gains remote or physical access to the machine.
However, the most commonly used distribution method is email phishing, the same as ransomware, where the malware is distributed as a malicious attachment, usually a Microsoft Word document. The technique is used by different malware, including Ursnif and Raccoon. Known phishing campaigns usually revolve around notifications regarding an issue with a real product, quotation requests, payment orders, or random or personal, disturbing topics aimed at tricking the victim into downloading the attachment.
In most cases, the Microsoft Office opens the document with a warning, and Hawkeye displays a message prompting to enable editing. Thus, the user must interact with to make the trojan start the execution process. However, in some other cases, the malware uses Microsoft Office exploits, allowing Hawkeye to start the execution without any user interaction.
Some versions of this malware create files that allow analysts to say for sure that this is Hawkeye. First, click on the malicious process in the process tree and then click the "More info" button. Then, in the upper-right corner of the "Events" panel, switch from "Friendly" to "Raw." Now you see all operations with files that were performed by a chosen process. Often, this malware family tries to create files with "Reborn" in their names. And based on that type, you can determine that it is Hawkeye.
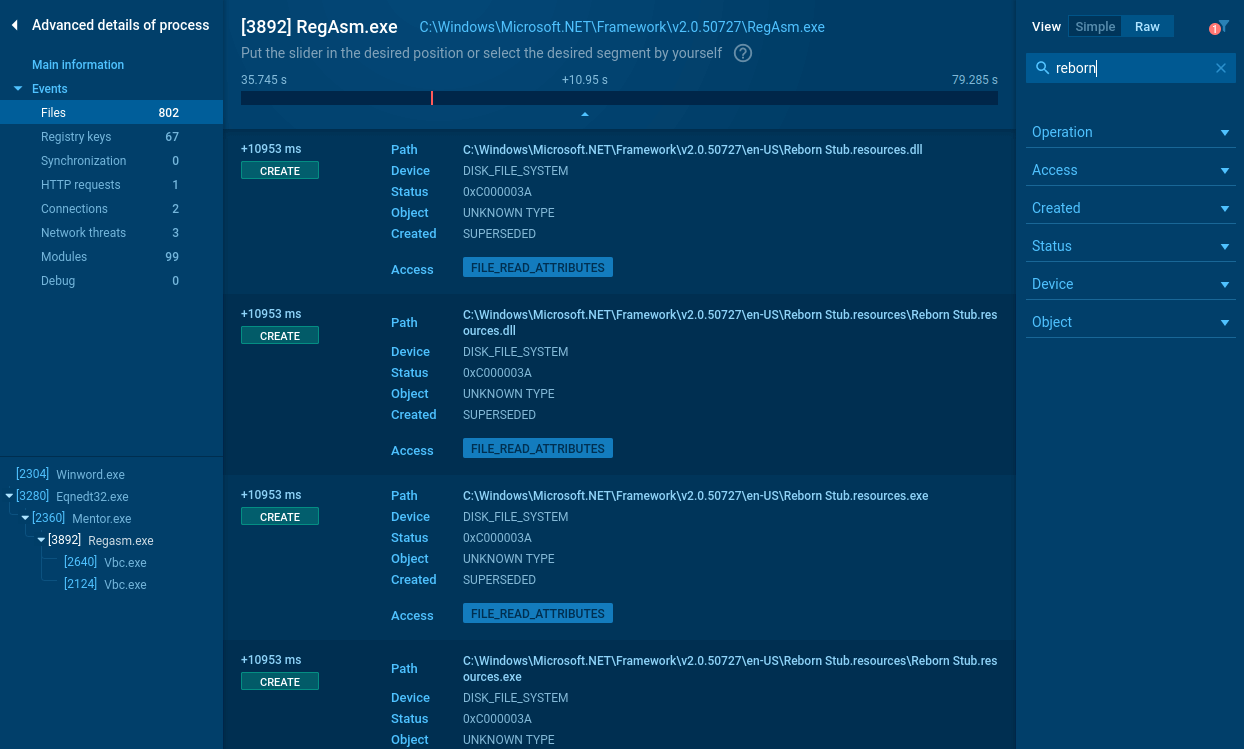 Figure 5: Files created by Hawkeye
Figure 5: Files created by Hawkeye
Carrying extremely advanced anti-evasion techniques and robust info-stealing functionality, Hawkeye presents a danger to corporations and individuals all around the globe. Unfortunately, the distribution of malware as a service allows even non-technically savvy cybercriminals to set up effective attack campaigns, contributing to the overall popularity of the virus.
Furthermore, Hawkeye trojan uses a set of special techniques to complicate the analysis and trick automated analysis services and confuse the development of countermeasures.
However, interactive analysis services like ANY.RUN gives researchers the ability to examine malware even as elusive as Hawkeye is and conduct effective studies.