Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


The Jigsaw ransomware, initially detected in 2016, encrypts files on compromised systems and requires a ransom payment in Bitcoin. If the ransom is not paid, the malware starts deleting files, increasing the pressure on victims to comply. Its source code is publicly accessible, allowing various threat actors to customize and repurpose the malware for different objectives.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2016
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2016
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
Jigsaw ransomware, initially detected in 2016, is a form of malware designed to encrypt files on a victim's system and extort a ransom payment in Bitcoin to restore access.
The creators of Jigsaw incorporate themes and visuals from the horror movie Saw, utilizing threatening messages inspired by the film to pressure victims into complying with the ransom demands.
If the victim does not pay the ransom, Jigsaw begins deleting files from the infected system, increasing the urgency for victims to act. This approach not only encrypts valuable data but also introduces a time-sensitive element that can cause significant distress and data loss.
The original malware is no longer active, as researchers were able to quickly develop decryption tools. However, Jigsaw's source code is openly available, allowing different threat actors to modify and adapt the malware for various purposes, including data theft.
Jigsaw has a range of capabilities which vary across different variants.
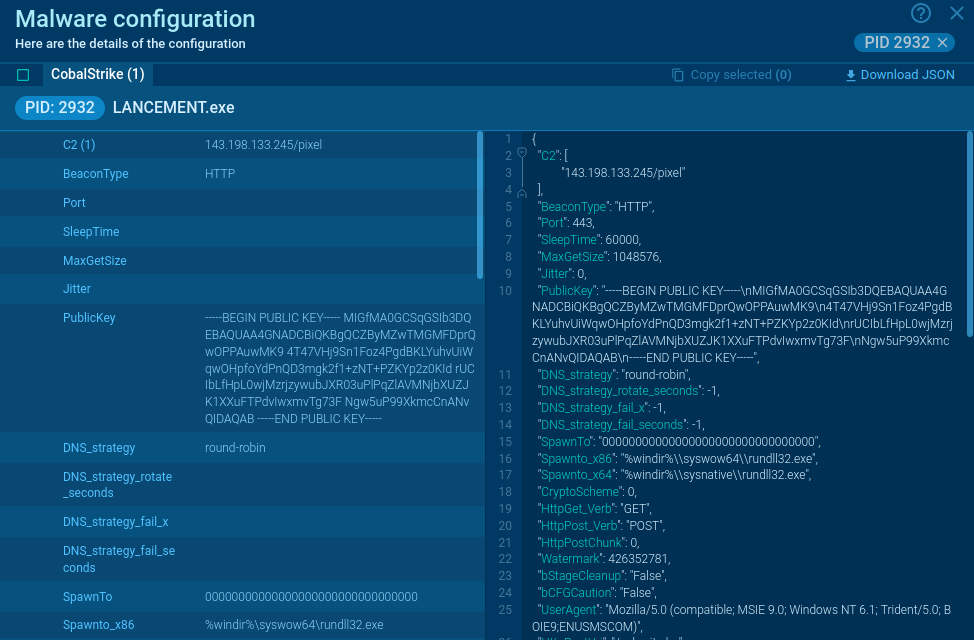
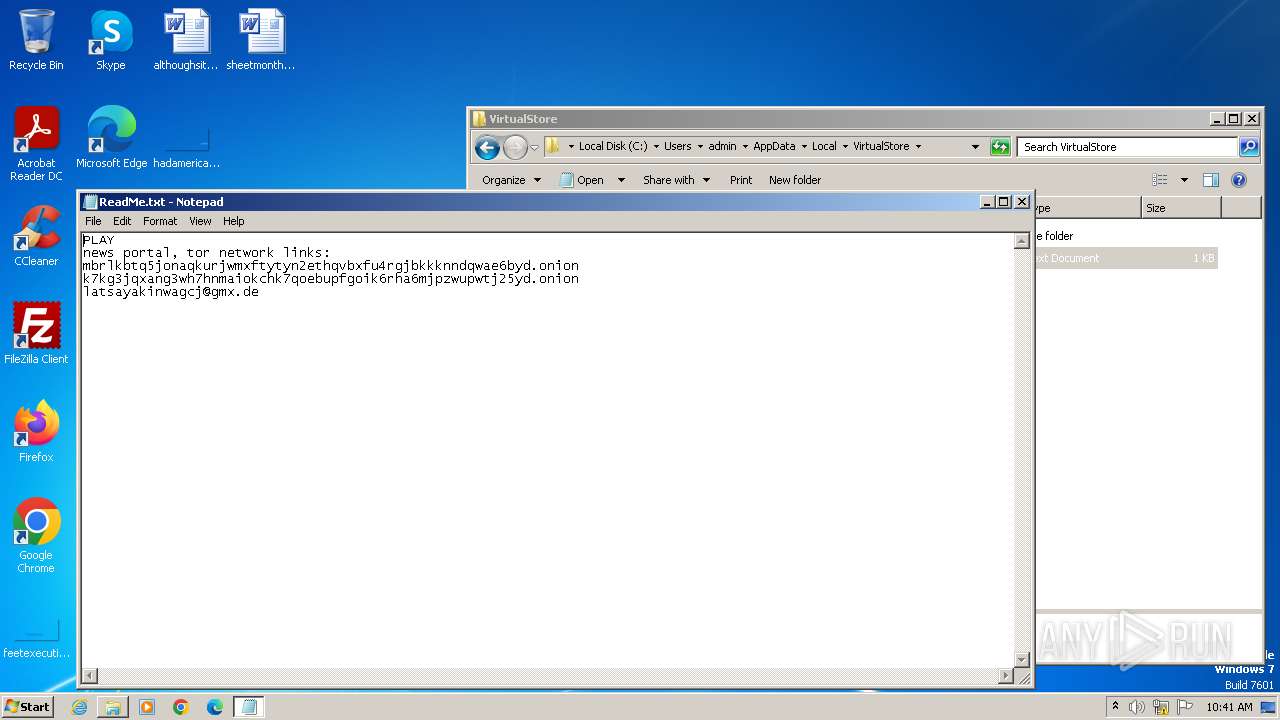
 Analysis of Jigsaw inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox threat context
Analysis of Jigsaw inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox threat context
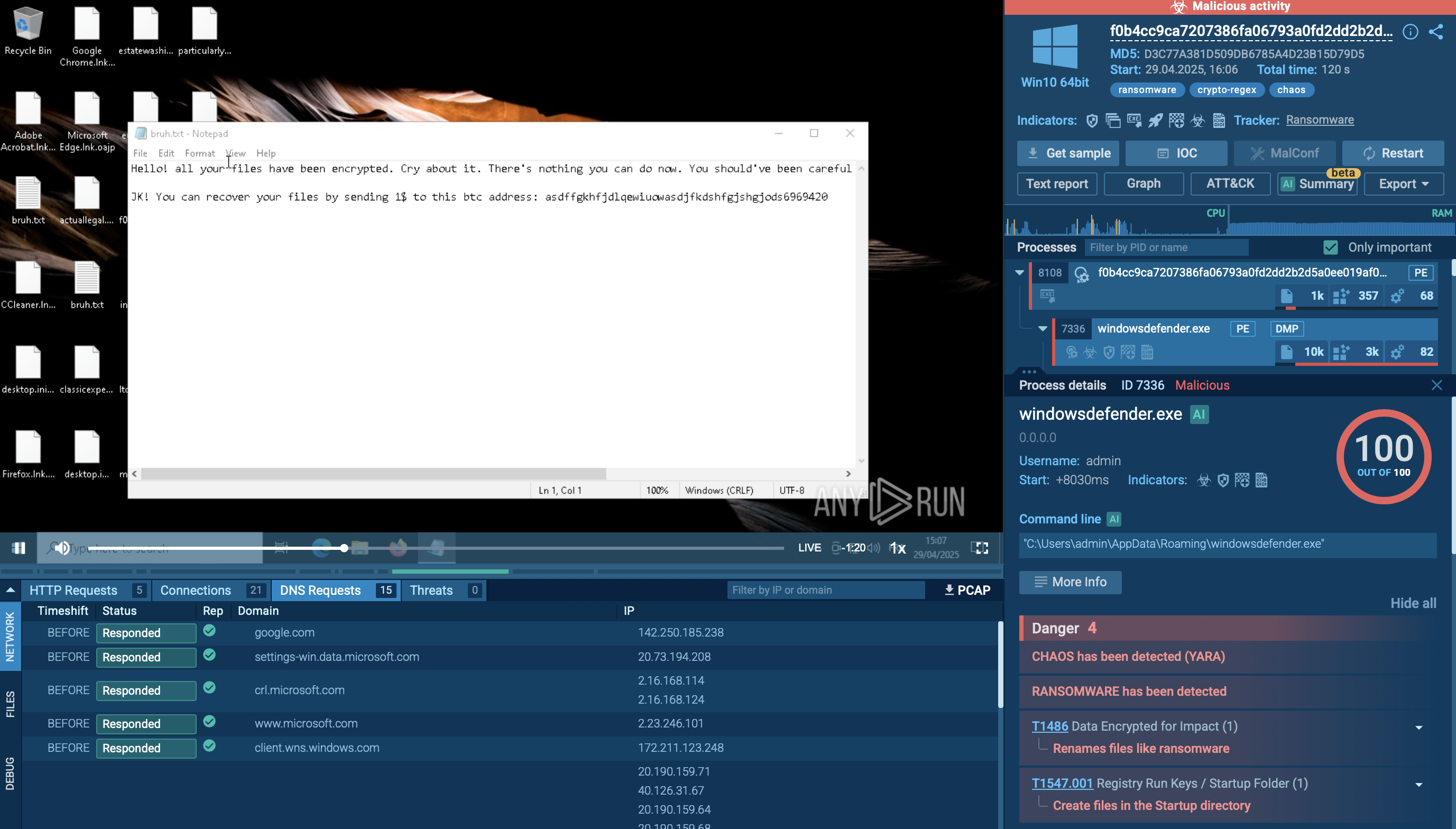
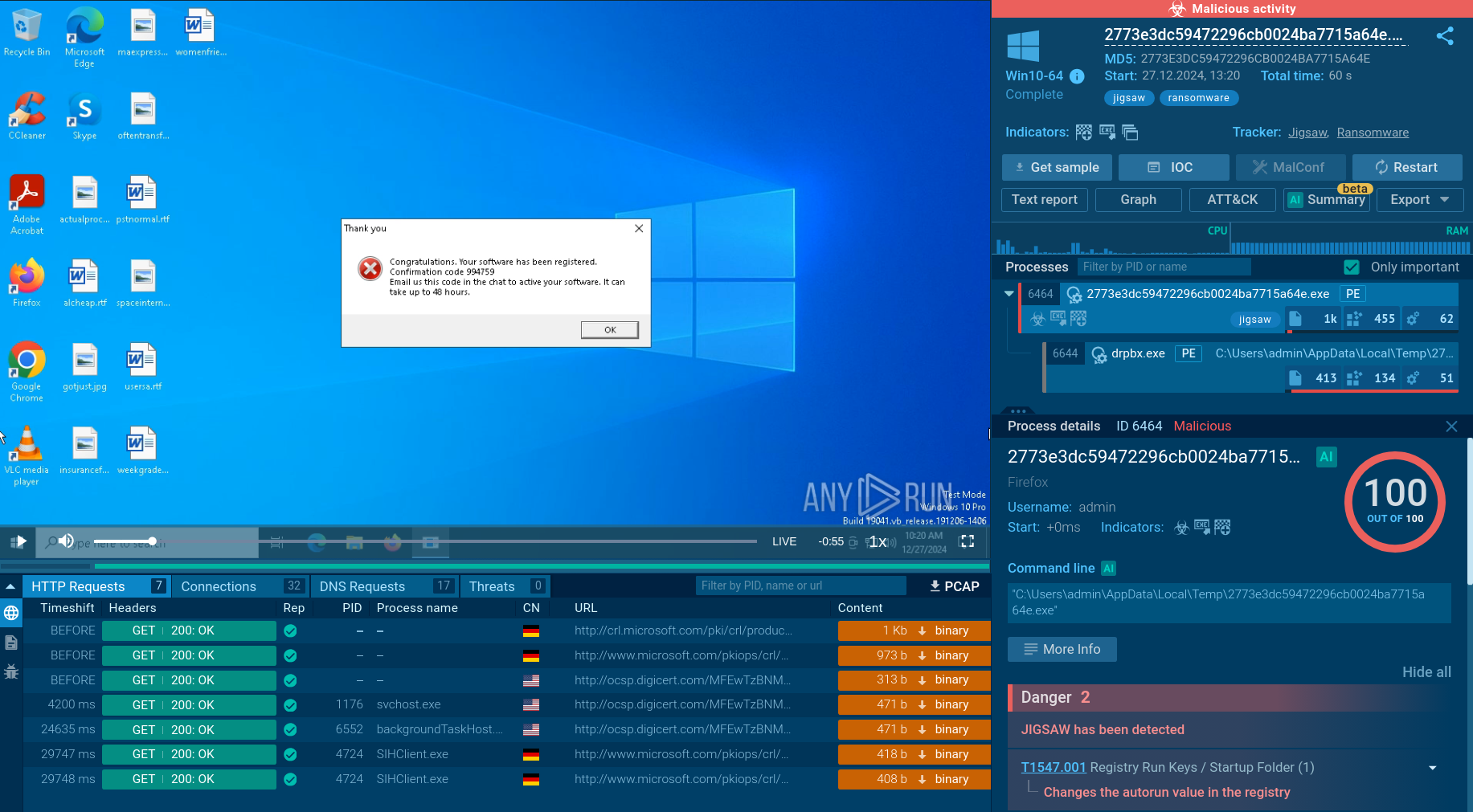
The execution process of Jigsaw ransomware involves several critical steps to ensure the encryption of files and the extortion of victims. Upon infecting a system, the malware begins by encrypting the files and displaying a ransom note with payment instructions. The ransom note typically includes a countdown timer, indicating the time remaining before files start being deleted.
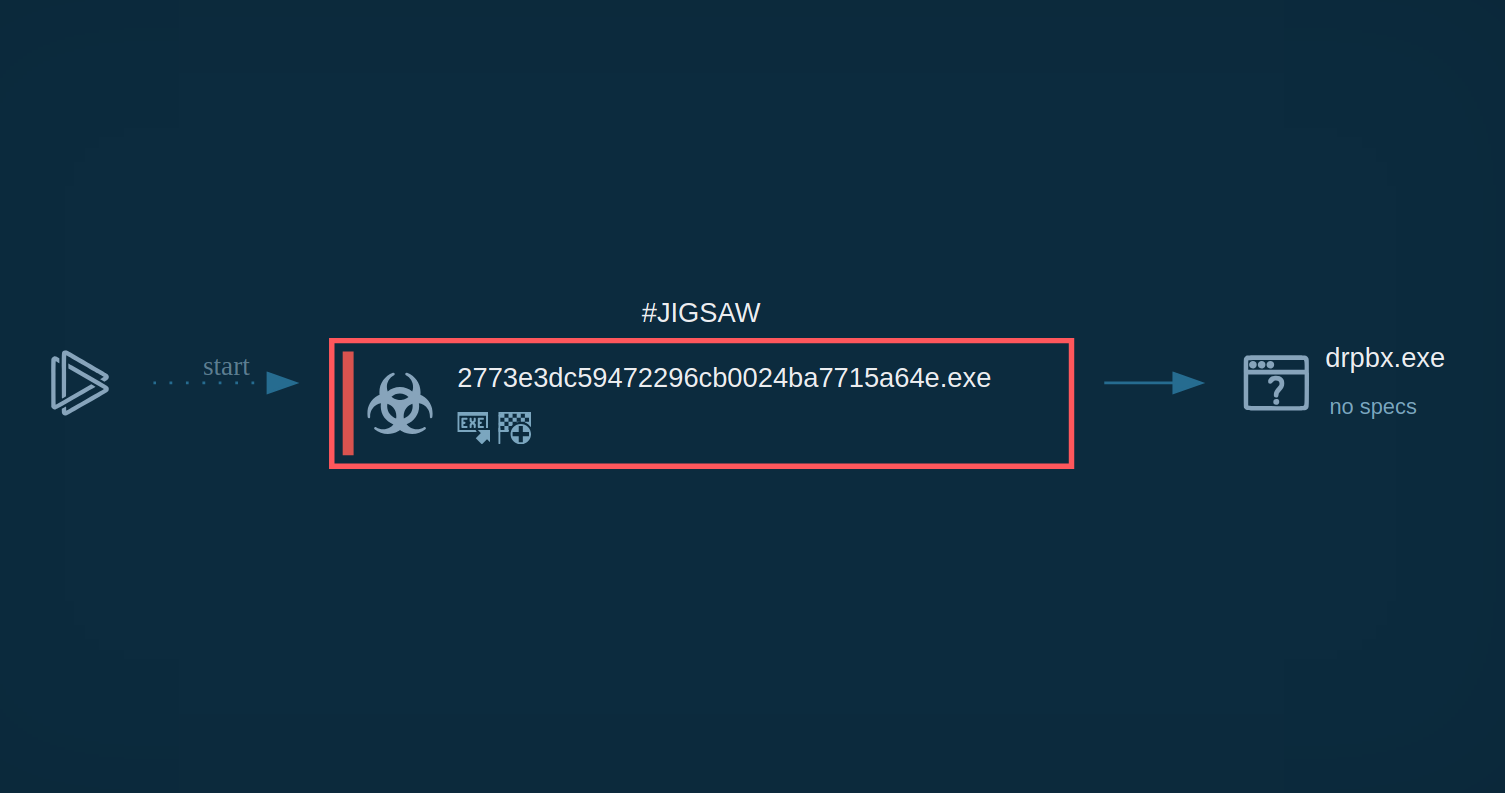 Process graph showing the execution of a Jigsaw sample
Process graph showing the execution of a Jigsaw sample
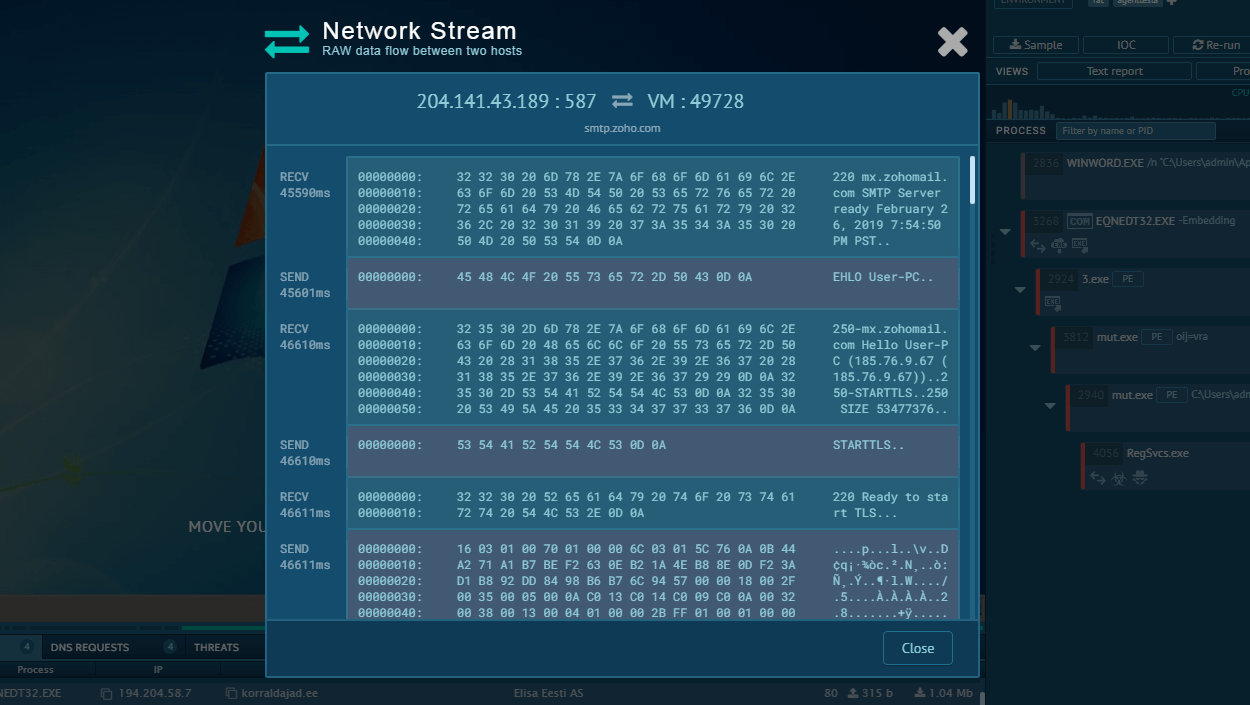
To verify that the ransom has been paid, Jigsaw queries a Bitcoin wallet address via HTTP requests. If the malware detects that the required funds have been deposited, it triggers the decryption process, restoring access to the encrypted files.
The distribution methods for Jigsaw ransomware have evolved significantly since its inception. Initially, the malware was spread through fake software executables that mimicked legitimate programs. These executables were designed to trick users into downloading and running the malicious files, leading to infection.
However, newer variants of Jigsaw utilize a broader range of distribution channels. Some of the most common methods include:
Each threat actor may utilize their own channel of distribution, making it challenging to predict and defend against the spread of Jigsaw ransomware.
To gather information about Jigsaw ransomware and collect relevant intelligence, utilize Threat Intelligence Lookup.
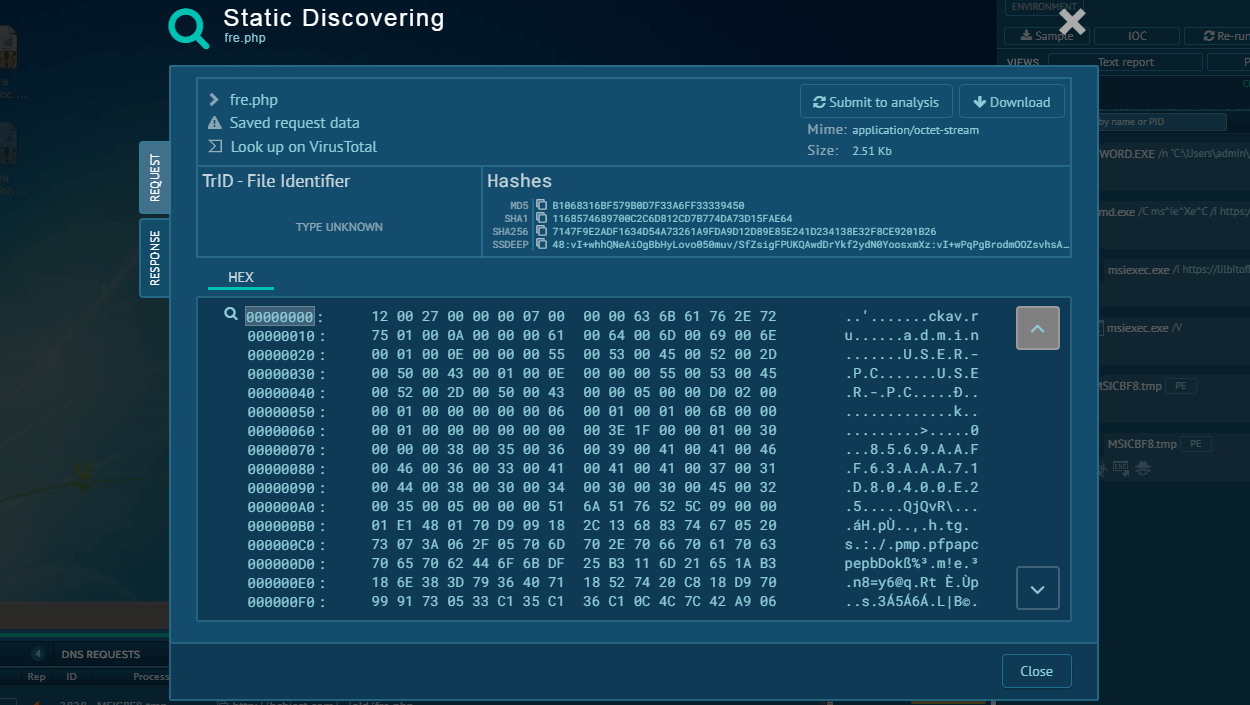
This service provides access to a comprehensive database containing insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 search parameters, users can find specific data related to threats, including IP addresses, domains, file names, and process artifacts.
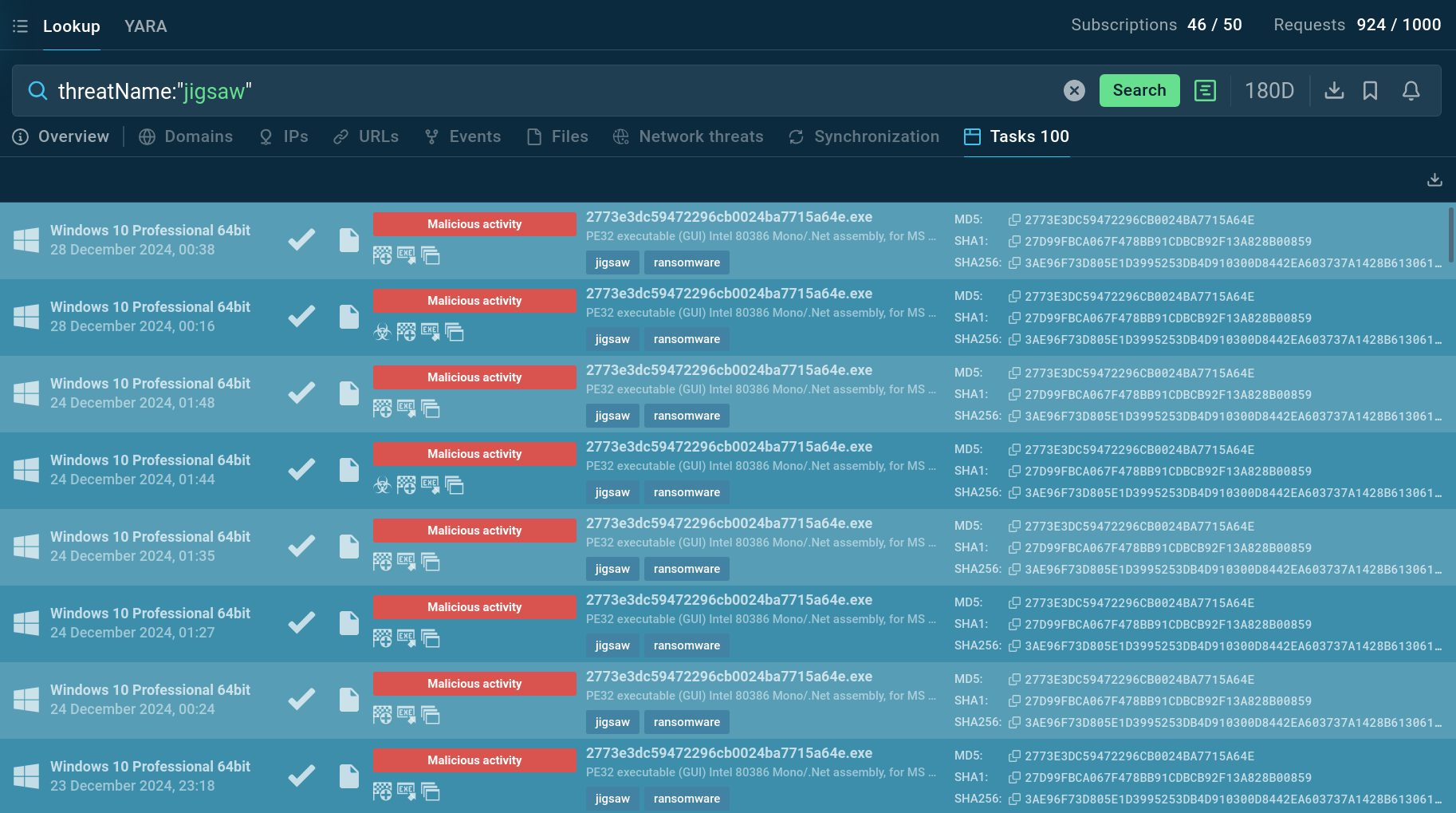 TI Lookup helps you enrich your investigations with additional threat context
TI Lookup helps you enrich your investigations with additional threat context
For example, you can search for Jigsaw by its name or related artifacts. A query like threatName:"Jigsaw" will retrieve all associated samples and sandbox results relevant to this ransomware. This tool is invaluable for staying informed about the latest variants and indicators of Jigsaw, helping security professionals to better understand and mitigate the threat.
Although the Jigsaw ransomware no longer presents a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape, as it did in 2016, access to its source code makes it a potential security risk to organizations. To prevent possible infections with Jigsaw, it is important to implement comprehensive security measures, including proactive sandbox analysis.
Use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to quickly examine suspicious files and URLs to identify threats early and address them before they have a chance to compromise your infrastructure.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to access unlimited analysis!