Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


WhiteSnake is a stealer with advanced remote access capabilities. The attackers using this malicious software can control infected computers and carry out different malicious activities, including stealing sensitive files and data, recording audio, and logging keystrokes. WhiteSnake is sold on underground forums and often spreads through phishing emails.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2023
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2023
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 828
828
 0
0

 495
495
 0
0

 2760
2760
 0
0
WhiteSnake is a stealer malware whose activity was first observed in early 2023. This malware is designed to infiltrate computer systems and exfiltrate a variety of sensitive information to the attacker’s servers, including saved passwords, autofill information, and browsing history.
WhiteSnake operates as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS), a business model where the developers offer the malware to other cybercriminals for a fee. In the case of WhiteSnake, the developers provide a subscription service for several hundred dollars.
According to the threat intelligence researcher @RussianPanda9xx, the malware’s notable feature is the support of different payload formats like BAT, MSI, SCR, etc.
The distribution and sale of WhiteSnake primarily occurs on DarkWeb forums and Telegram. The availability of the malware contributes to its spread and increases its potential impact.
WhiteSnake has been distributed through various vectors like phishing campaigns, where unsuspecting users are tricked into downloading the malware, and even through open-source repositories.
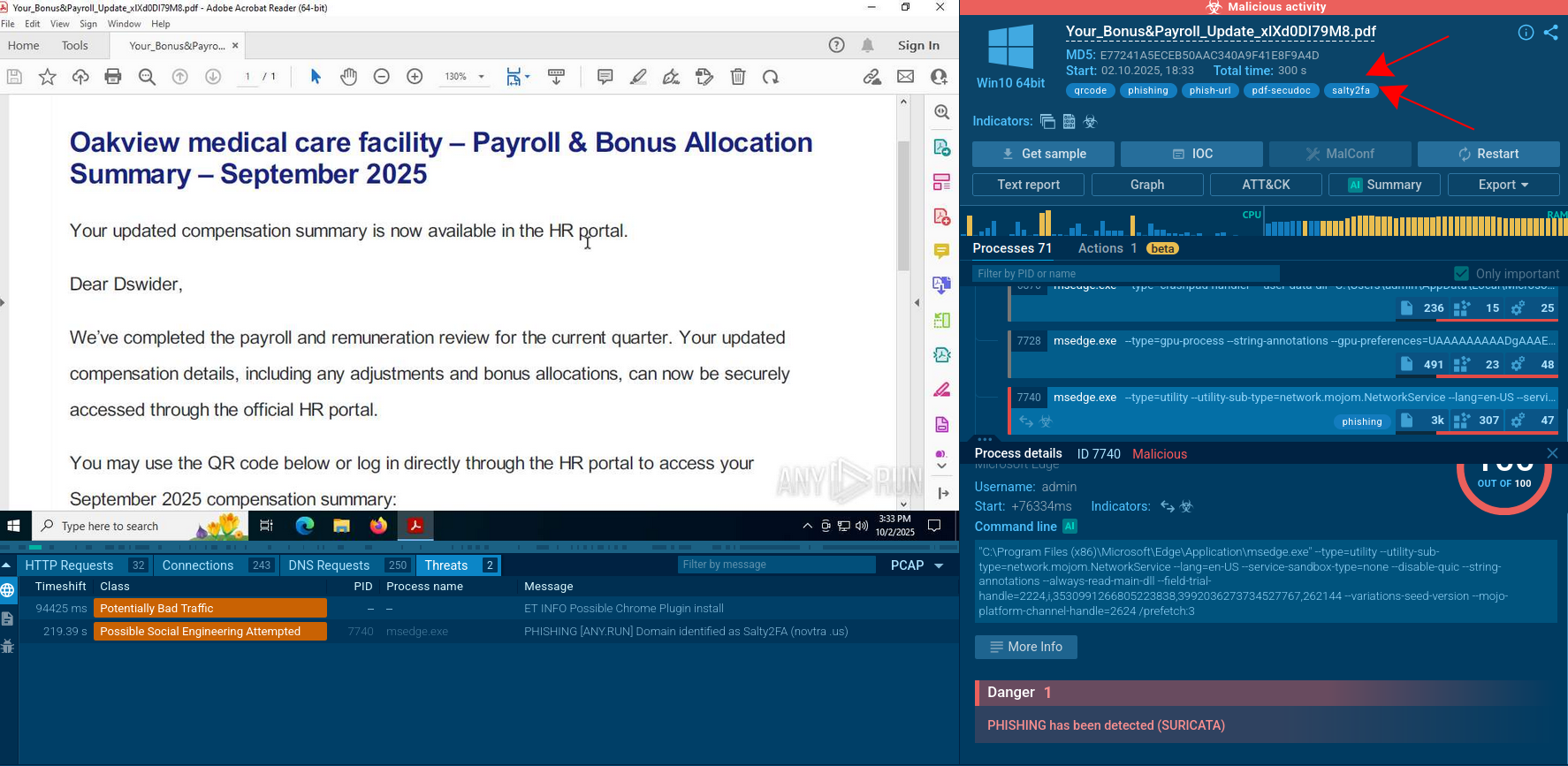
Let’s upload a sample of WhiteSnake to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
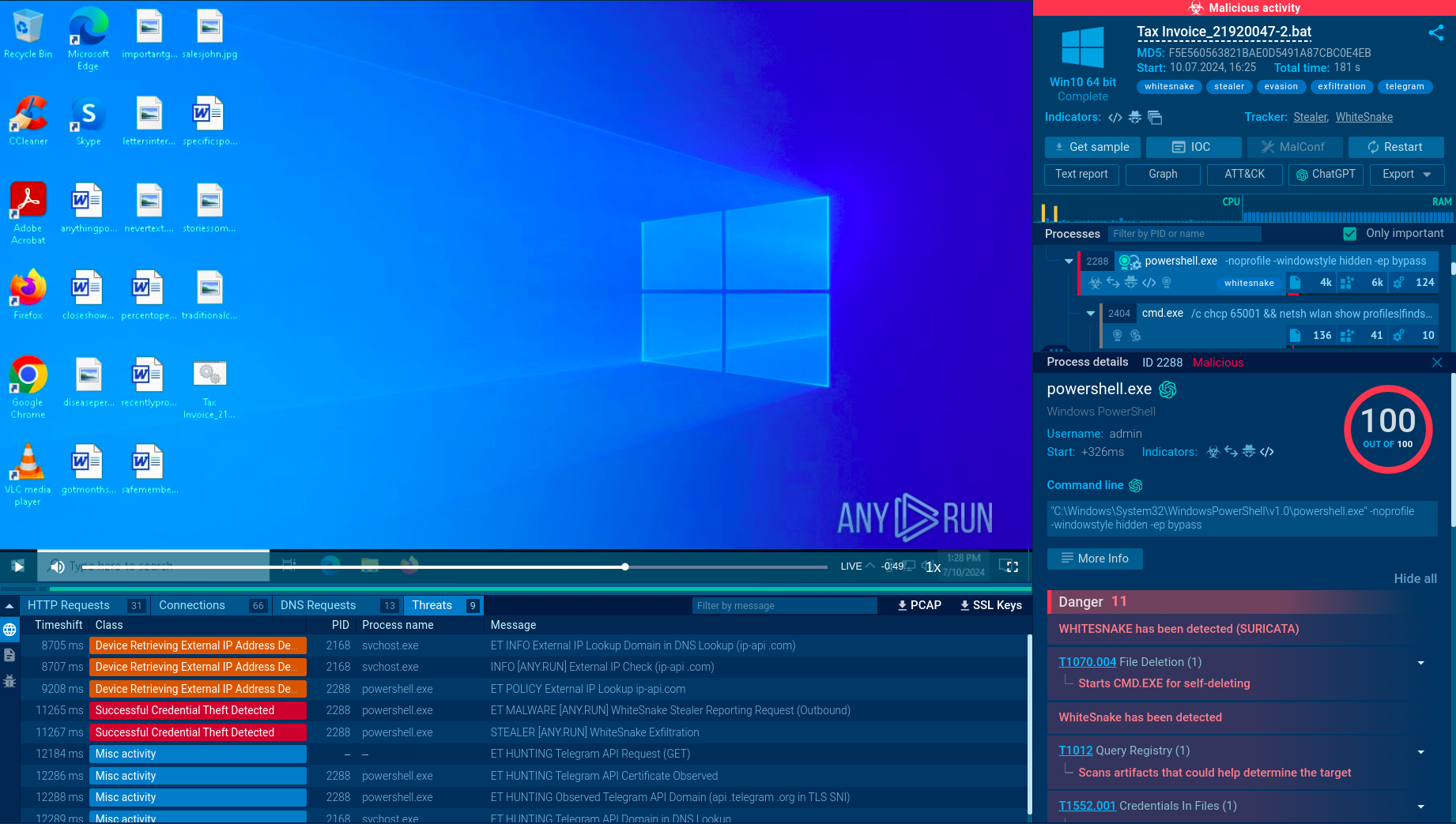 WhiteSnake analysis in ANY.RUN sandbox
WhiteSnake analysis in ANY.RUN sandbox
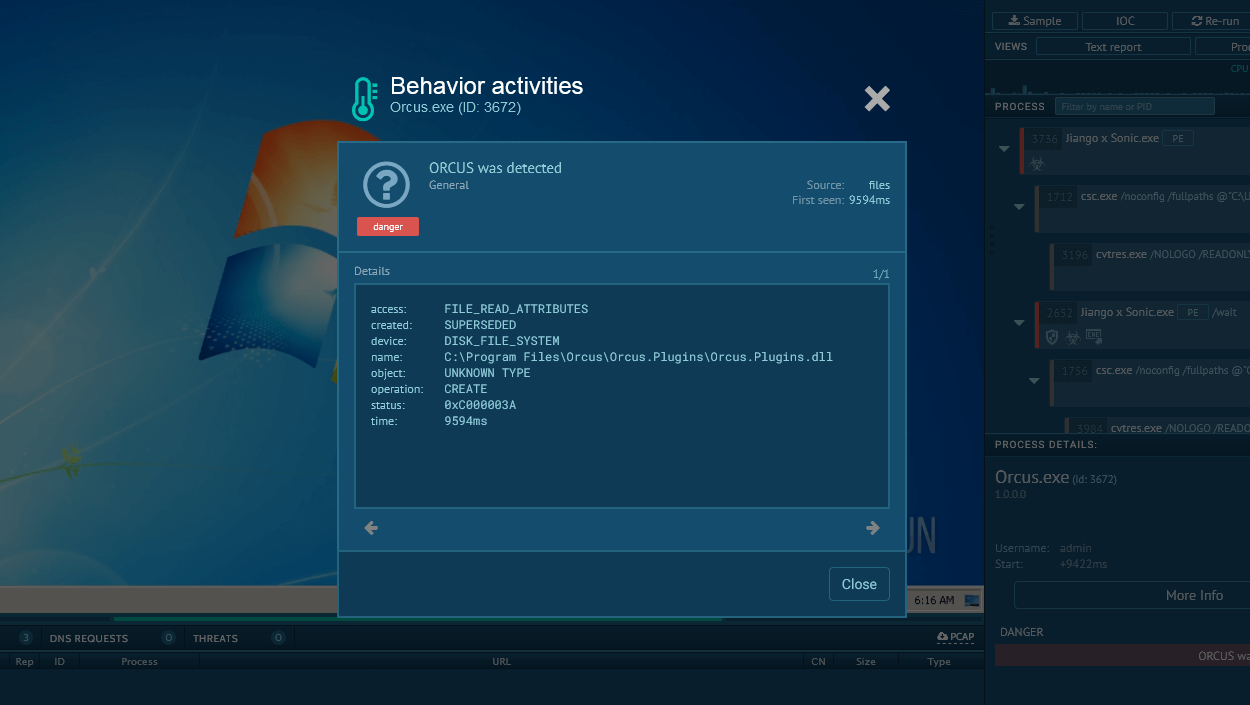
WhiteSnake first performs anti-VM checks to detect if it is running in a virtual environment or sandbox. It does this by querying the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) to retrieve the "Manufacturer" and "Model" properties of the system. It then checks if any of these properties contain strings associated with virtual machines or sandboxes, such as "virtual," "vmware," "virtualbox," etc. If any of these strings are detected, the malware will exit to avoid analysis.
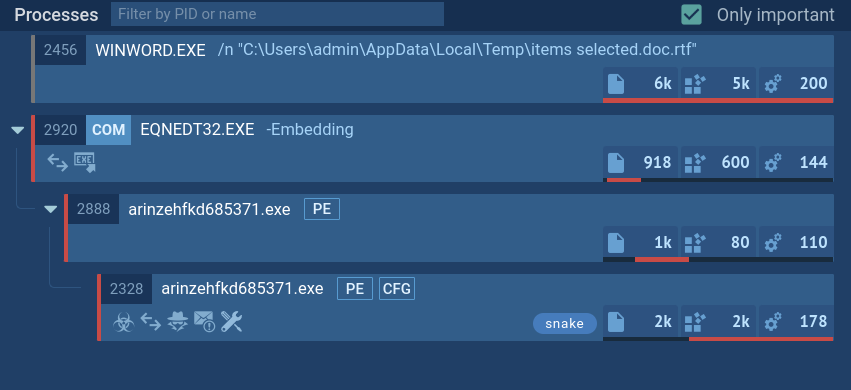
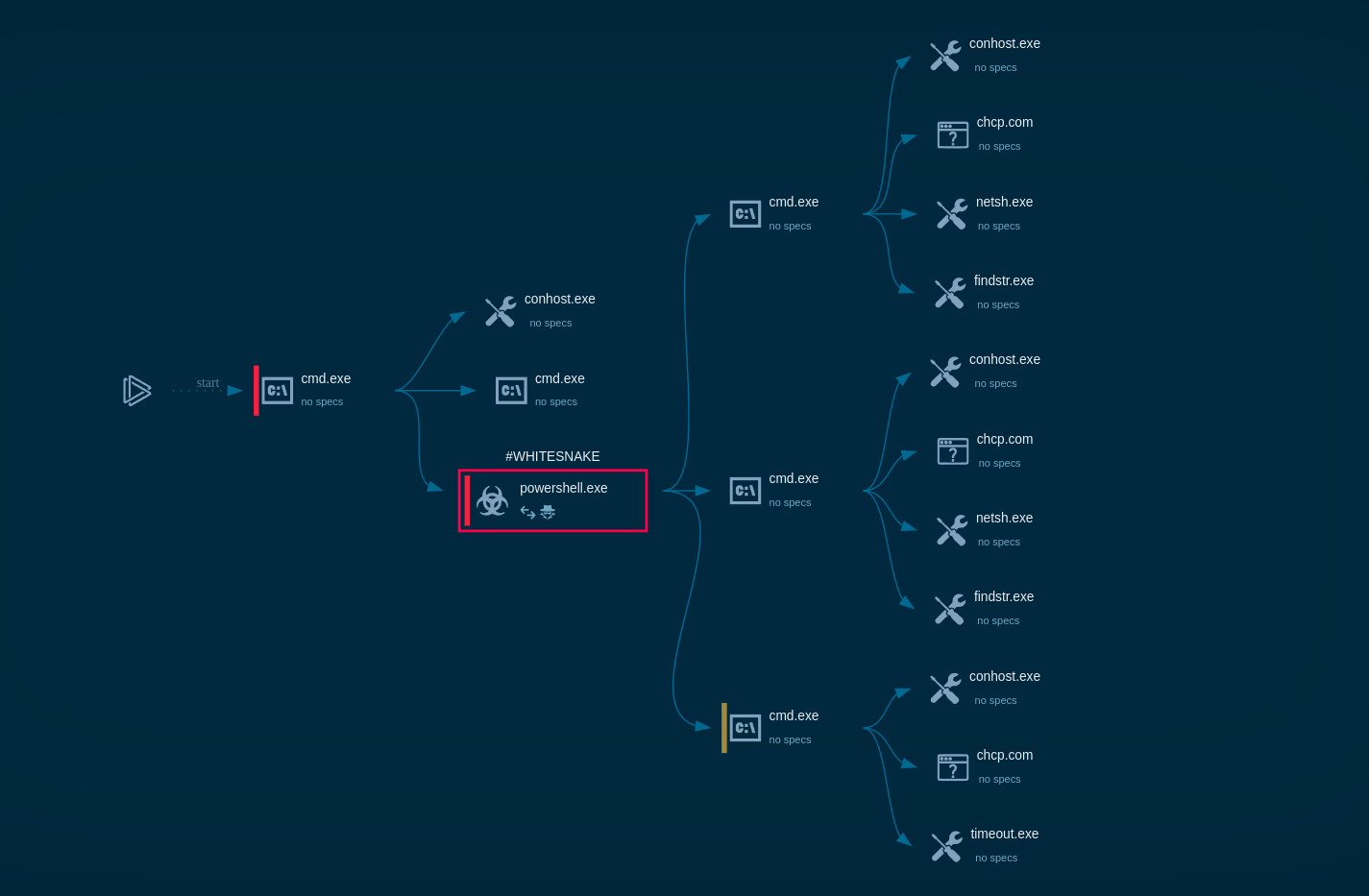 WhiteSnake process graph demonstrated by ANY.RUN sandbox
WhiteSnake process graph demonstrated by ANY.RUN sandbox
The malware in our task performs system discovery and uses the command line to display information about available Wi-Fi networks, including SSID, BSSID, and signal strength. It also checks if a mutex (a synchronization object) is already present to prevent multiple instances of the malware from running simultaneously. In our sample, the mutex is "lcy9igxycx."
Then WhiteSnake proceeds to gather sensitive information from the infected system. This includes:
The gathered information is then encrypted and uploaded to one of the attacker-controlled servers specified in the malware's configuration.
Let’s sum up what the WhiteSnake stealer is capable of. Thanks to its remote command execution functionality. attackers can remotely control the infected system and perform various malicious activities that include:
One of the key features of this malware is its use of mutex to avoid running on systems that have already been infected. This helps prevent detection and conflict with other instances of the malware.
It is also designed to avoid analysis in a sandbox or virtual machine. The malware includes anti-VM functionality that allows it to detect when it is running in a virtual environment and stop its operation.
WhiteSnake can maintain persistence on the infected system. It automatically runs via a scheduled task, ensuring that it remains active even after the system is restarted.
As mentioned, WhiteSnake is distributed through various methods. However, as with most stealers, including Stealc and Amadey, phishing emails with malicious attachments and links constitute the most widespread vector of attack. In one campaign, criminals leveraged fake documents masquerading as official correspondence from a government agency.
In another attack, threat actors attempted to spread the WhiteSnake stealer through the open-source Python Package Index repository. Attackers uploaded malicious code hoping it would be downloaded and executed by unsuspecting users.
Given that WhiteSnake is a MaaS, available for purchase to various criminals, it is likely that new methods of distributing this threat will be used by criminals in the future.
WhiteSnake is a relatively new but serious cybersecurity threat for organizations worldwide. To prevent infection, it's important to have good security measures in place. One important part of a strong security plan is using a malware analysis sandbox.
ANY.RUN’s interactive sandbox has many features that make analyzing malware easier and faster. It can: