Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


The Godfather malware is an Android banking Trojan capable of bypassing MFA that targets mobile banking and cryptocurrency applications. Known for its ability to evade detection and mimic legitimate software, it poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations by stealing sensitive data and enabling financial fraud.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
25 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
25 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 868
868
 0
0

 515
515
 0
0

 2802
2802
 0
0
Godfather is a rebranded and evolved variant of the Anubis trojan, first identified in 2022. It primarily targets Android devices, exploiting their accessibility services and employing innovative techniques such as on-device virtualization to hijack legitimate apps. This malware is designed to steal sensitive information, including banking credentials, two-factor authentication codes, and cryptocurrency wallet data.
It mimics legitimate applications and uses advanced obfuscation techniques to avoid detection. Once installed, it overlays fake login screens on top of banking and cryptocurrency apps to harvest user credentials. Godfather is actively maintained and frequently updated, making it a persistent and evolving threat.
It employs a number of vectors of system infiltration and spread:
Godfather primarily targets users in Europe, the U.S., and Canada, but its campaigns have also affected regions in Asia and the Middle East.
Both individual consumers and businesses, particularly those with mobile banking operations or cryptocurrency holdings, are at risk. Enterprises with employees using personal devices for corporate access (BYOD) are especially vulnerable due to the malware’s ability to compromise mobile endpoints.
Once installed, Godfather can severely compromise an Android device by:
Similar to other Android malware like Salvador Stealer and Spynote, Godfather can be used to:
The consequences for businesses tend not to be limited by serious financial losses and reputational damage due to the exposure of sensitive customer or corporate data but escalate to operational disruption and regulatory fines.
Godfather operates by impersonating legitimate applications, such as Google Protect, to gain user trust. It requests permissions to access device storage, SMS, contacts, and accessibility services. Once granted, it:
Watch a sample of Godfather detonated in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to analyze its execution chain and gather data for detecting the trojan and protecting your organization.
View sandbox analysis of Godfather
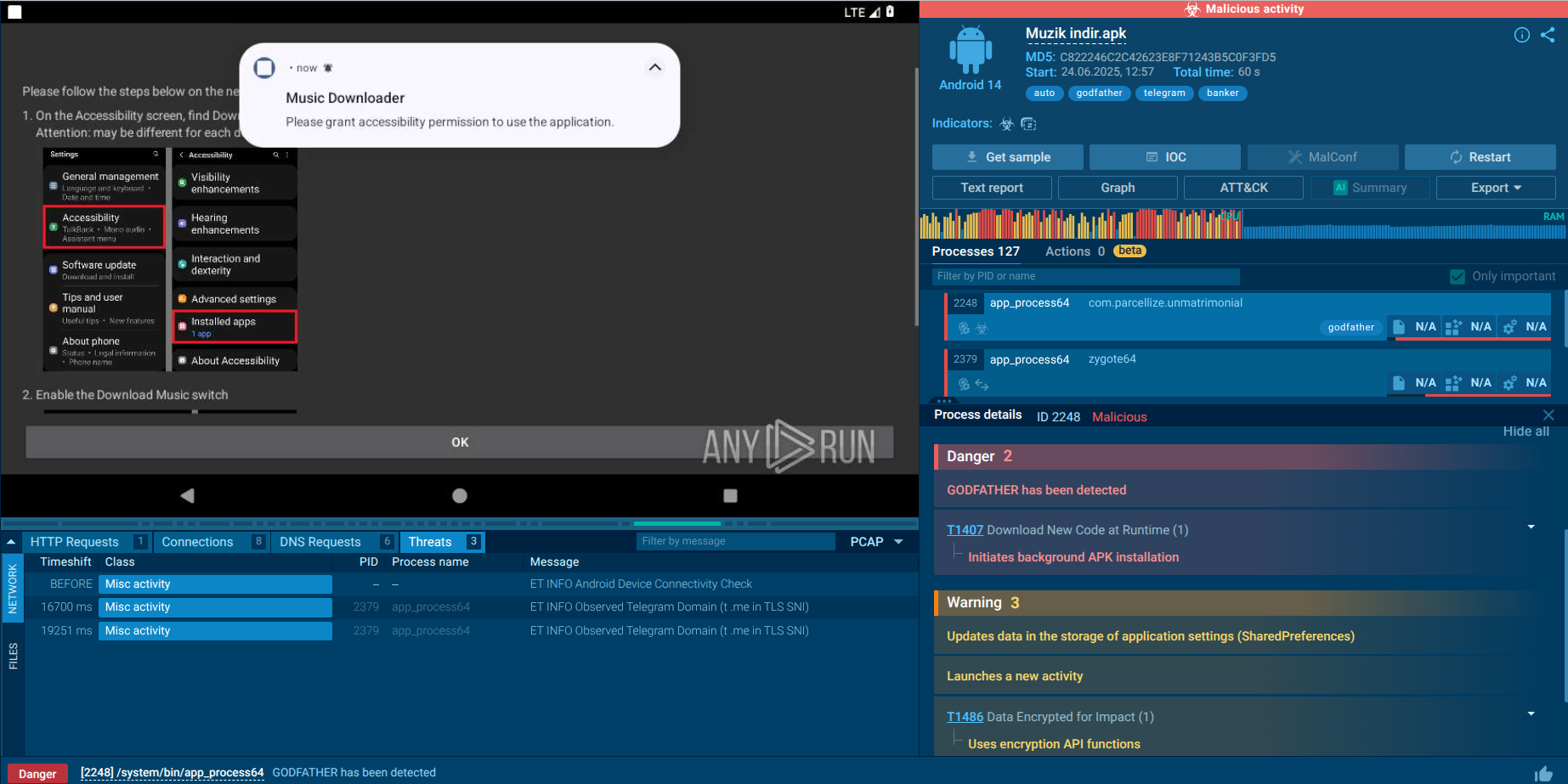 Godfather malware analysis in the Sandbox
Godfather malware analysis in the Sandbox
In this sample, Godfather begins its execution with a dropper disguised as a legitimate-looking app, such as “Müzik İndir,” a fake music downloader. Once launched, it shows a prompt claiming a plug-in is needed. In the background, it silently installs a second-stage APK without user consent.
After installation, the malware redirects the victim to Accessibility settings. It asks the user to activate a new service named “Music Downloader.” If granted, this gives the malware full control to simulate taps, read screen content, and overlay fake elements on top of real apps.
In this specific sample, the malware does not use virtualization. However, other Godfather variants have been seen using frameworks like VirtualApp and Xposed. These allow them to sandbox and clone real banking apps, intercepting user input, screen data, and network activity in real time.
When virtualization is used, the malware launches genuine banking apps inside its controlled environment. The user sees the real interface, but everything is monitored and manipulated silently in the background. This enables seamless data theft and transaction fraud.
Godfather stores its configuration in shared preferences, including AES-encrypted and Base64-encoded C2 URLs. Campaigns typically target hundreds of apps, with many focused on Turkish financial institutions. Importantly, Godfather has been found distributed through the official Google Play Store. It often mimicked popular apps like MYT Music to bypass detection and reach a wider audience, as reported by Malwarebytes and other security vendors.
Like its predecessor, the Anubis banking trojan, Godfather is offered as malware-as-a-service, which helps explain the wide range of capabilities and variations seen across different campaigns.
Threat intelligence provides context, indicators of compromise (IOCs), and TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures) used by Godfather operators. It is critical in combating Godfather by:
Use ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup to find more Godfather public analyses in the Interactive Sandbox, watch the malware’s behavior in the network and on device, collect IOCs and IOBs.
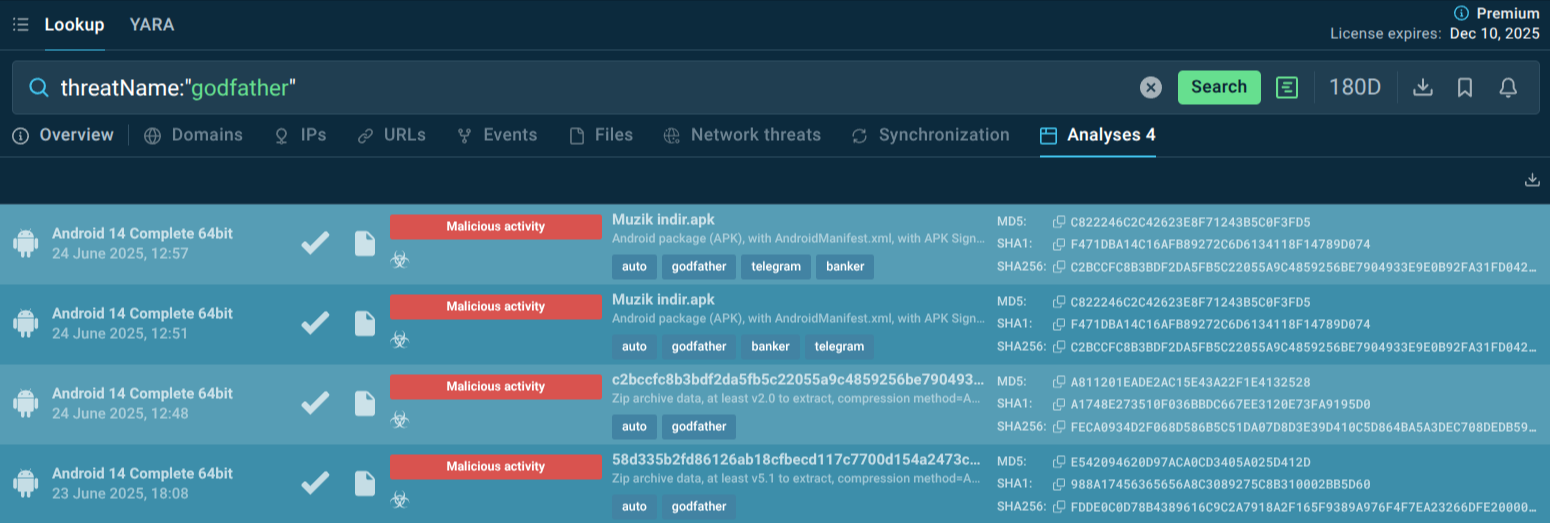 Godfather samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
Godfather samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
You can also explore other malware targeting financial services users by searching the malware type “banker” in TI Lookup.
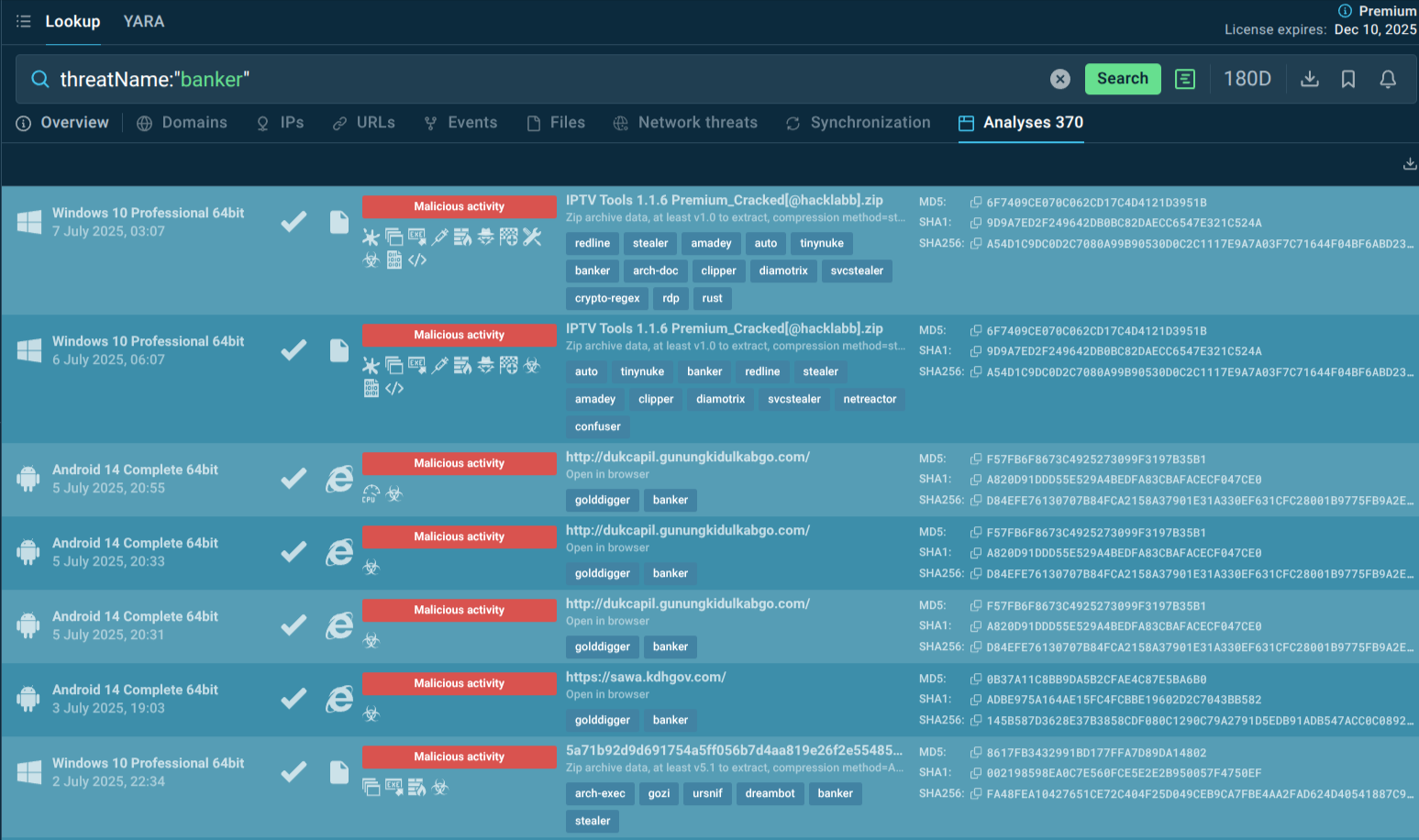 Banking trojan samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
Banking trojan samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
Regular research helps analysts follow the emerging threat patterns and build proactive protection of business assets.
Godfather is a highly adaptive and dangerous mobile malware that exploits users’ trust and weaknesses in mobile security. With the right mix of mobile protection tools, user education, and actionable threat intelligence, organizations and individuals can reduce their exposure and respond swiftly to potential infections.
Gather fresh actionable threat intelligence via ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup: start with 50 trial requests.