Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases
Trojans are a group of malicious programs distinguished by their ability to masquerade as benign software. Depending on their type, trojans possess a variety of capabilities, ranging from maintaining full remote control over the victim’s machine to stealing data and files, as well as dropping other malware. At the same time, the main functionality of each trojan family can differ significantly depending on its type. The most common trojan infection chain starts with a phishing email.

 443
443
 0
0

 2320
2320
 0
0

 4485
4485
 0
0
According to the standard trojan malware definition, it is malicious software that pretends to be legitimate in order to deceive victims into downloading and executing it.
However, attackers now frequently distribute trojans via loaders, and as a result, advanced disguises are unnecessary and may not go beyond simply mimicking the name of a legitimate process. Additionally, trojan attacks often make use of social engineering tactics, spoofing, and phishing to persuade the user to take the desired action.
The most common purpose for these malicious programs is to gain unauthorized access to a user's computer and extract sensitive files and data, including credit card information and private email addresses. Trojans are often used to distribute other types of threats, including ransomware that encrypts users’ files and demanding payment for their decryption.
The core functionality of such malware can vary significantly depending on its type (e.g., remote access trojan or trojan spyware). However, the most common features include:
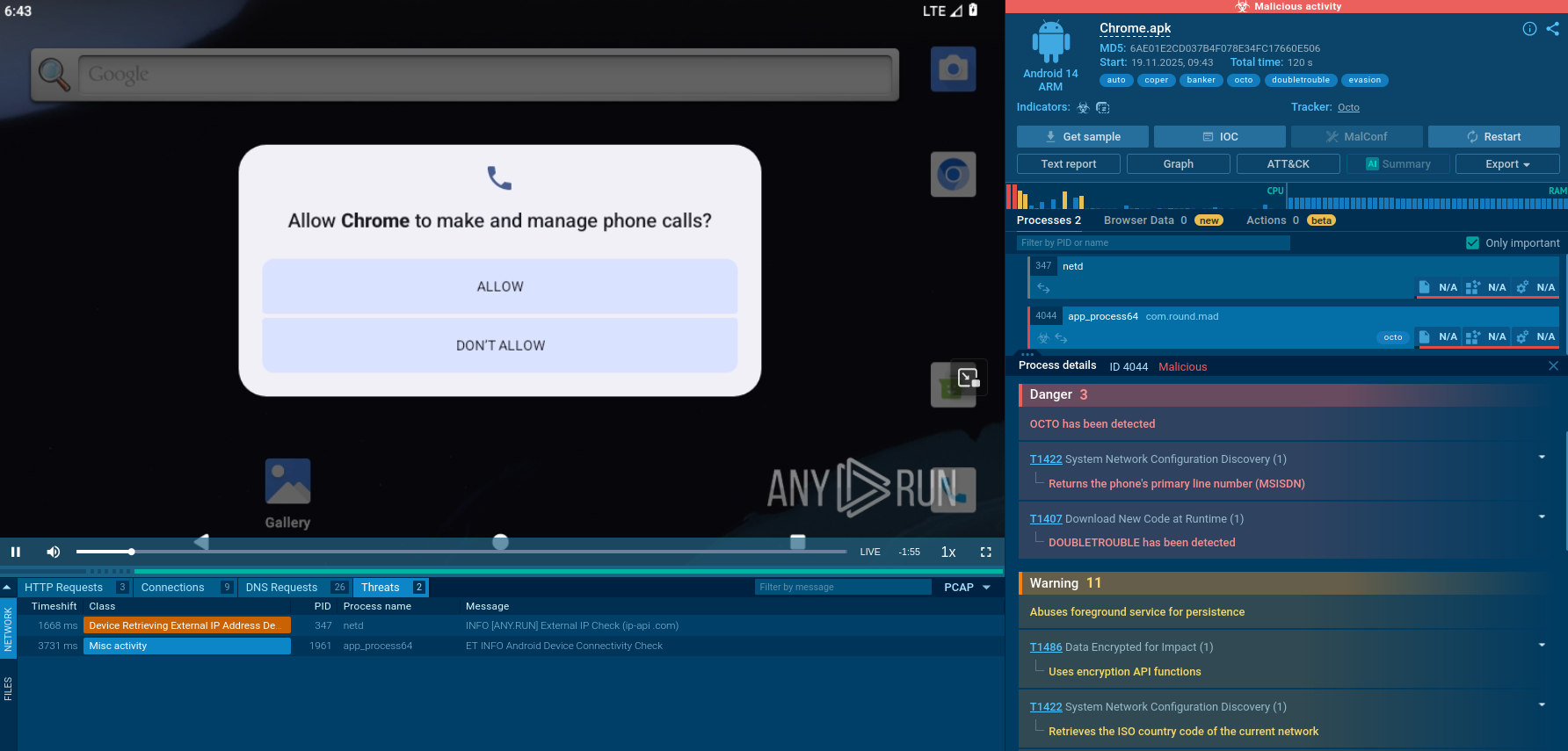
Some types of this computer virus can target specific spheres. For instance, banking trojan malware is designed to steal banking credentials and other sensitive financial information, such as credit card and social security numbers. They can also be used to take over a user's online banking account and perform fraudulent transactions.
Attackers have devised a variety of methods for infiltrating computers to deploy a trojan virus, including email attachments, infected websites, and file sharing platforms. When a user interacts with these sources by downloading and executing a malicious file, the trojan can be installed on their device without their knowledge.
Email phishing campaigns remain the most common vector of infection. Social engineering plays a significant part in how criminals manage to carry out successful attacks involving trojans.
Their tactics may include sending out thousands of spam emails on the part of a trusted entity, such as an actual brand or government organization, or using intimidation to scare the victim and persuade them to perform harmful actions.
For instance, criminals behind one of the phishing campaigns aimed at spreading the STRRAT trojan targeted individuals on behalf of the MAERSK shipping corporation.
A typical trojan malware infection chain follows these steps:
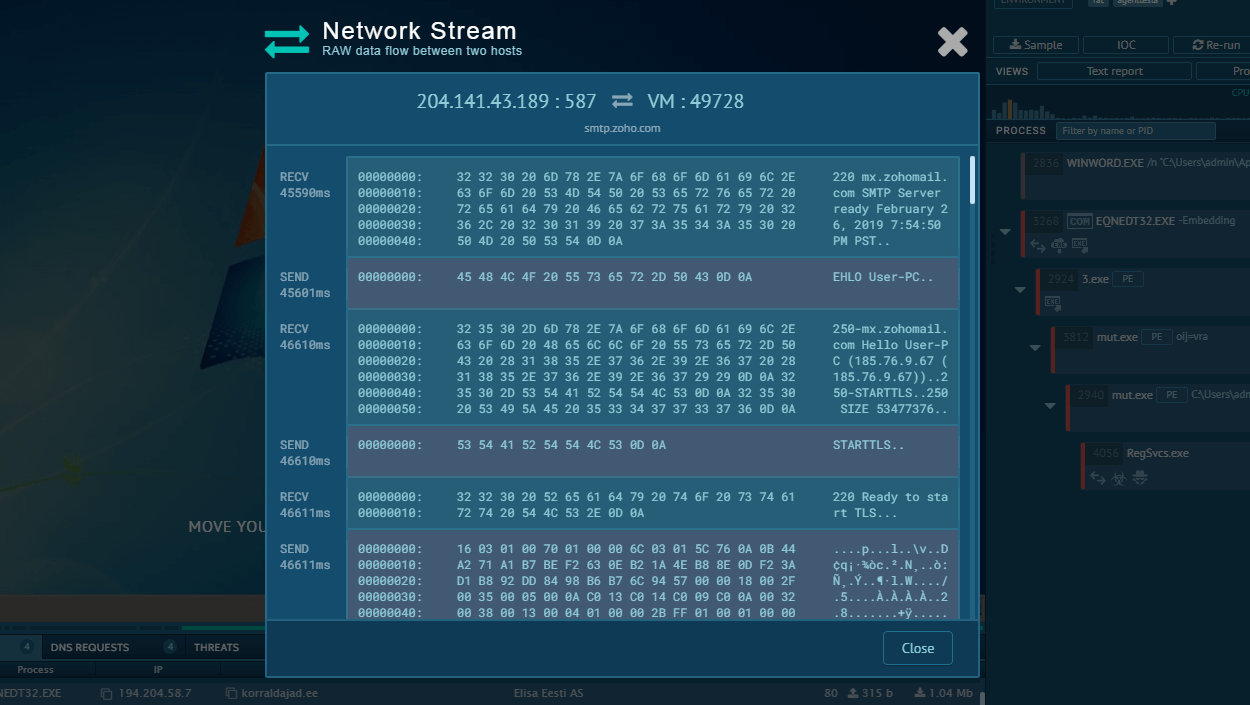
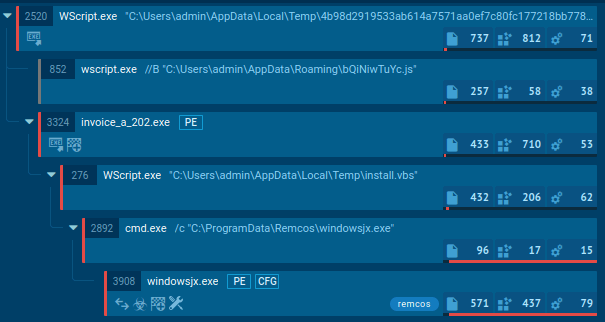 Execution processes of Remcos displayed by the ANY.RUN malware sandbox
Execution processes of Remcos displayed by the ANY.RUN malware sandbox
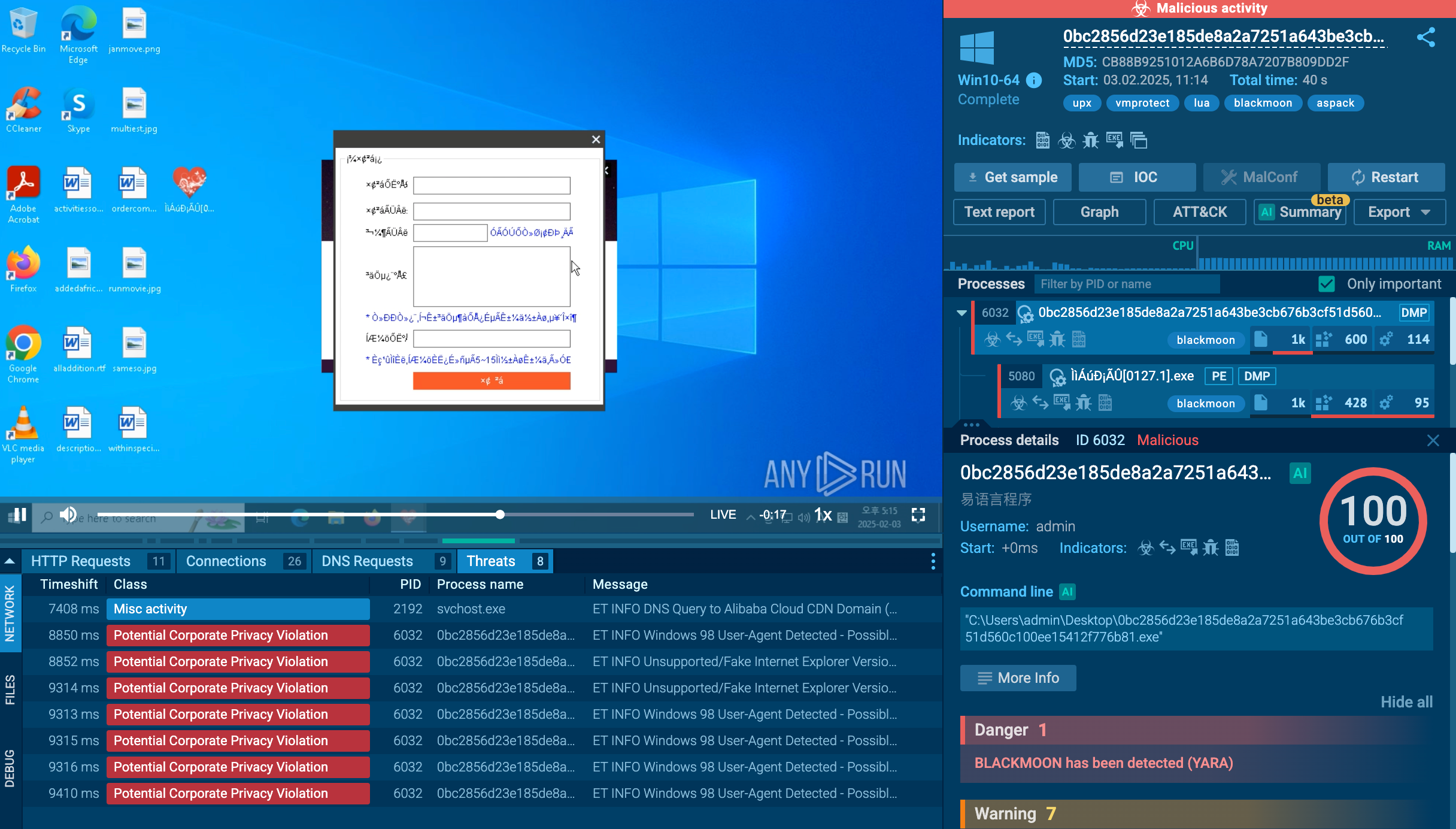
Using the Remcos trojan as an example, we can trace this entire process in action by uploading a sample of this malware to the ANY.RUN interactive malware sandbox.
The Remcos trojan can be delivered in different forms. In our case, the entire infection chain starts with an executable file, which, once launched, initiates a VBS script that runs a command line and drops an executable file. This file is the main payload, which carries out malicious activities such as stealing information, changing the autorun value in the registry, and connecting to the C2 server.
The threat landscape is changing by the hour and the popular trojans today may be gone forever tomorrow. To stay in the know about the latest trends in malware, as well as collect fresh indicators of compromise and samples, use ANY.RUN’s Tracker.
Here are some of the most active trojan families according to the service:
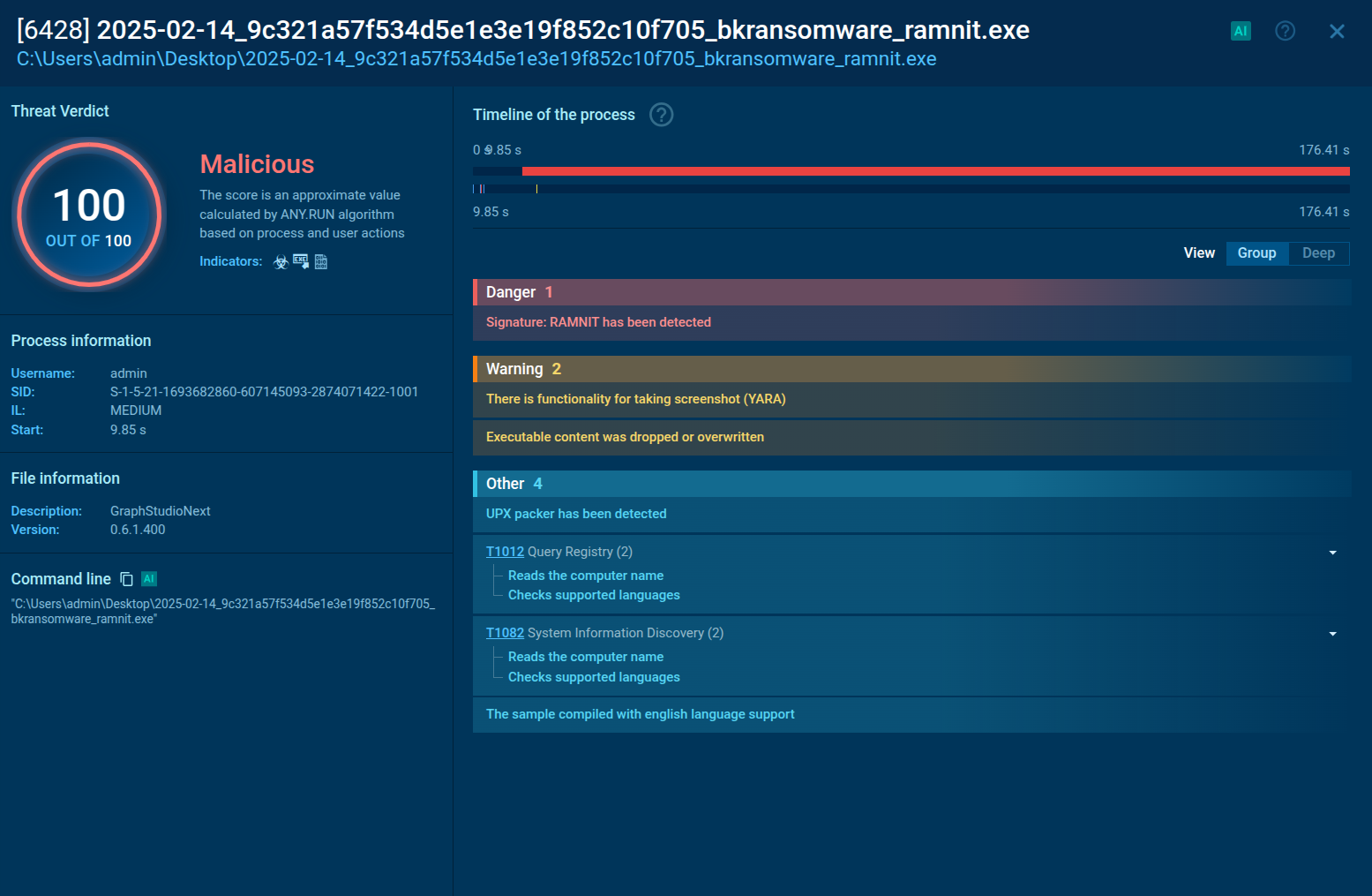
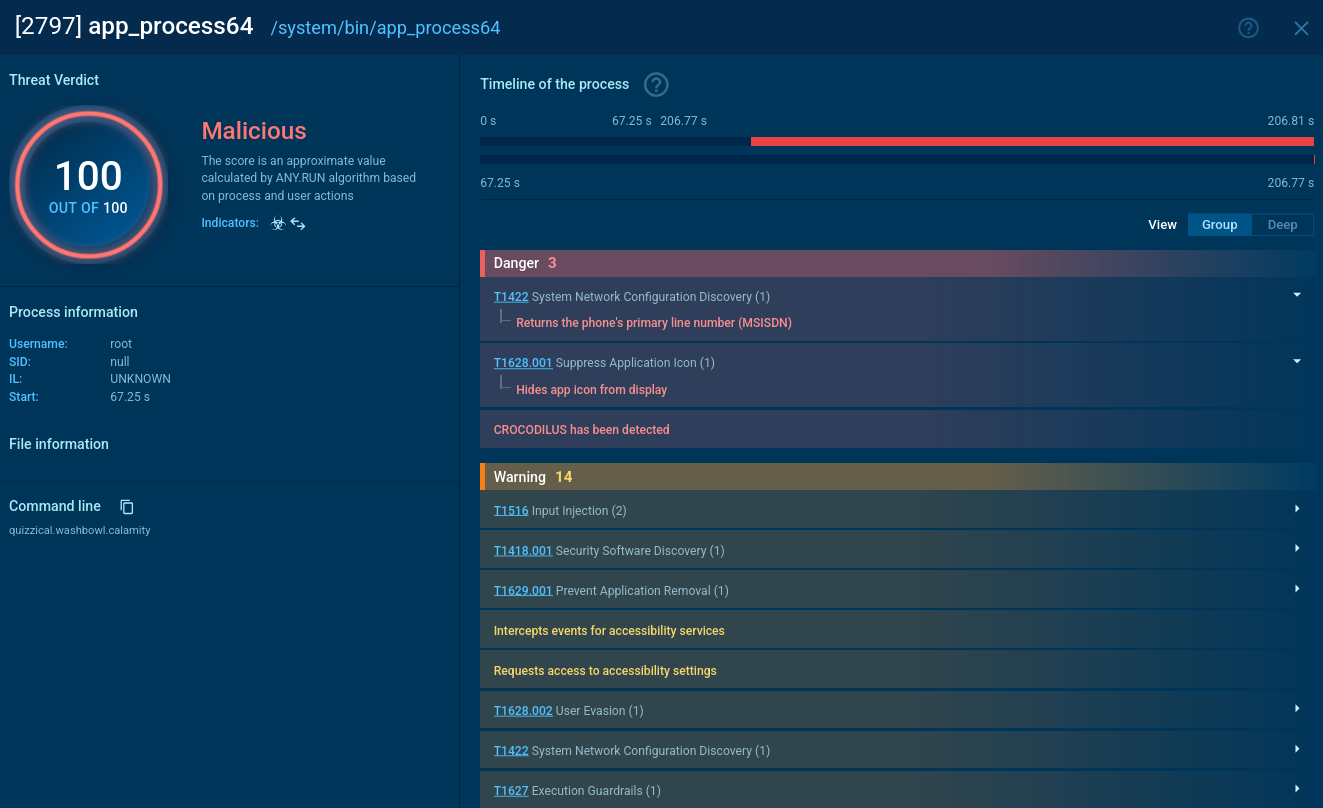
Despite the prevalence of trojan viruses, detecting them can be extremely challenging. They often use sophisticated techniques to evade detection from antivirus programs, making them a serious threat to cybersecurity.
Yet, uploading any suspicious file or link to the ANY.RUN malware sandbox can help you quickly discover if the sample under inspection is a trojan, another type of malware, or a completely safe file. The service also shows the entire execution path of the sample and displays its network traffic activity.
Additionally, ANY.RUN enables you to interact with files, links, and the infected system in a safe VM environment like you would on a normal computer.
You can also use the sandbox to gain the information needed to ensure timely malware trojan removal.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!