Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


STRRAT is a type of malicious software known as a remote access trojan (RAT). It gives attackers the ability to gain full control over a victim's computer system, enabling them to steal confidential information, spy on their activities, and drop other malware. STRRAT has been in operation since 2020 and is regularly updated to increase its complexity and make it more difficult to detect.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
STRRAT is a Java-based malware that has been active since at least mid-2020. It is intended for a number of malicious purposes, including exfiltrating data from users’ browsers and email clients, keylogging, stealing files, as well as dropping additional malware. The creators of STRRAT are unknown, yet the continued evolution of the malware suggests that the developers behind it are constantly working to improve its capabilities.
The use of Java, a language that has largely lost its popularity over the past decade, does not prevent STRRAT from infecting numerous machines across the globe every year. Although the early versions of the malware required the presence of Java Runtime Environment (JRE) on the victim’s computer, the newer ones can do without it. Instead, they scan the system and install the JRE software downloaded from one of the remote servers.
While STRRAT continues to be distributed using simple .jar files, there are also instances of weaponized .pdfs and .xlsbs. Some attackers also use the polyglot technique to spread the malware (CVE-2020-1464). Specifically, they can combine two file formats (e.g., .msi and .jar) to circumvent security systems. Such files are usually sent as attachments to emails disguised as legitimate documents, including receipts and invoices, as part of spam or phishing campaigns.
Similar to other remote access trojans, such as XWorm and AsyncRAT, STRRAT enables criminals to engage in:
Additionally, it can act as a reverse proxy server for attackers, listen for incoming RDP connections, as well as execute cmd and PowerShell commands. The malware can download and install new updates from a remote server, allowing it to receive the latest features and capabilities, and to evade detection by antivirus software.
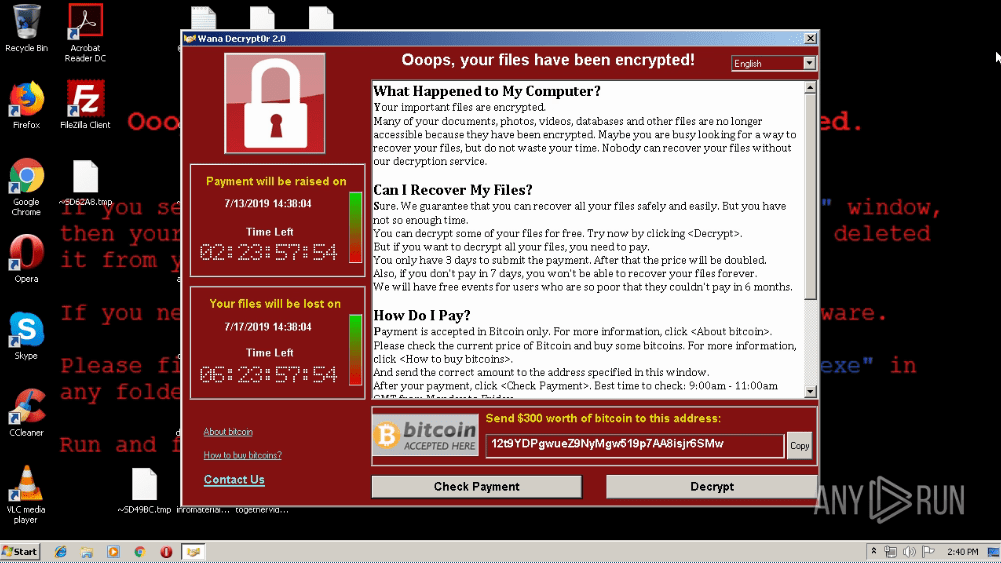
Another notable feature of STRRAT is its “crimson” module, which makes an attempt at encrypting victims’ files by adding the .crimson extension to them. Yet, by manually removing this extension, users can once again access their files. Basically, STRRAT poorly imitates the behavior of full-scale ransomware, such as WannaCry.
In terms of obfuscation, the latest version of the malware, namely the 1.6 one, employs two commercial obfuscators, Zelix KlassMaster (ZKM) and Allatori. One of the ways that STRRAT achieves persistence is by creating a scheduled task, masked under the name of a legitimate process such as "Skype.exe." In addition to creating a scheduled task, STRRAT also changes the autorun value and writes itself into the startup menu. This ensures that the malware will launch again after the operating system is rebooted.
STRRAT is capable of easily gaining elevated privileges on the system, which gives more power to the attacker. You can learn more about the techniques used by STRRAT by reading the article STRRAT: Malware Analysis of a JAR archive.
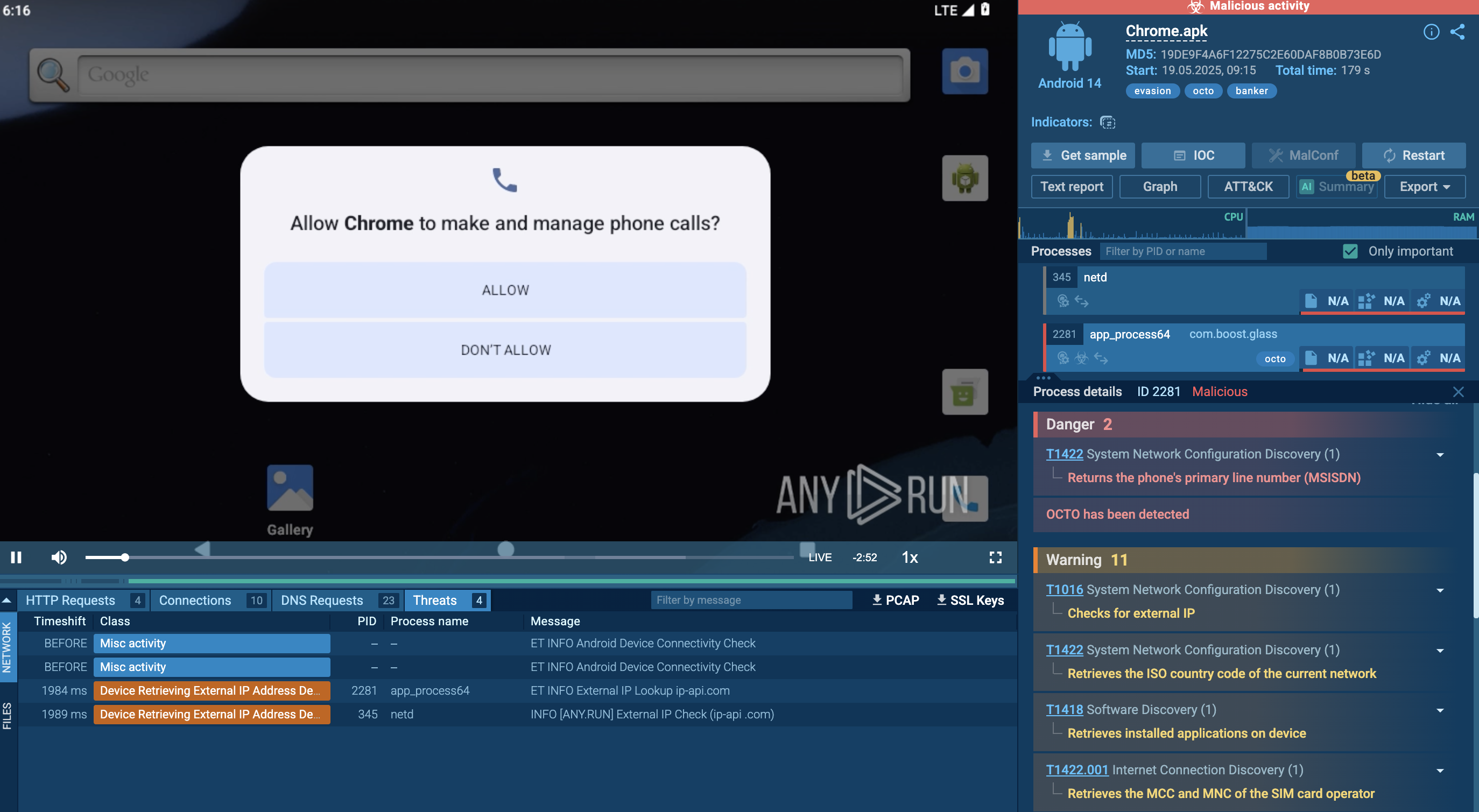
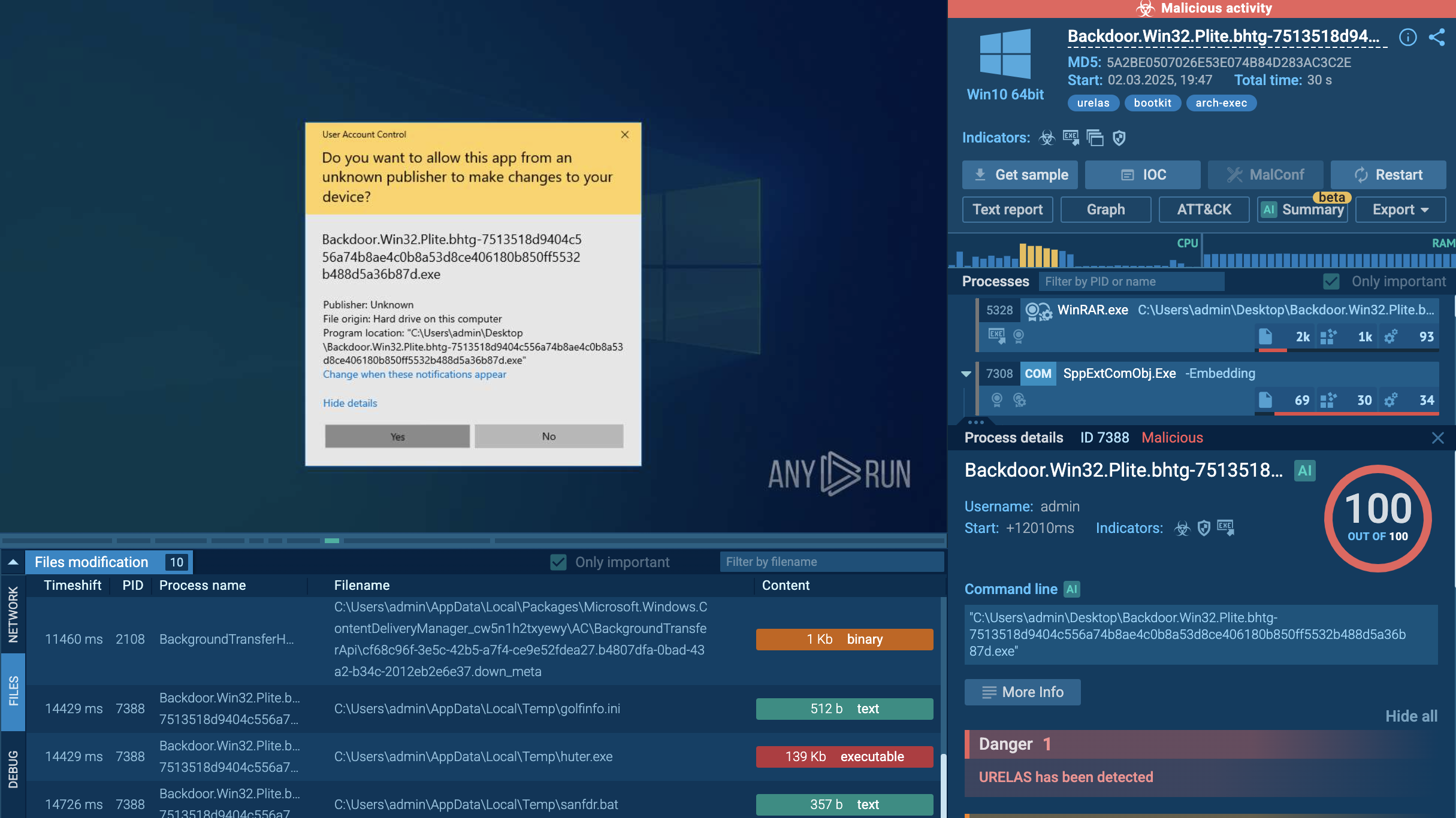
To get a better understanding of the techniques used by the malware and collect its IOCs, STRRAT can be uploaded to the ANY.RUN interactive sandbox.
Upon execution, STRRAT drops DLL files onto the disk and initiates a persistent task that runs every 30 minutes via the task scheduler. This task spawns a new process that generates WMI queries for system information. The malware then starts a benign Windows application that serves as a launchpad for an embedded malicious payload, in this case, Formbook.
Read a detailed analysis of STRRAT in our blog.
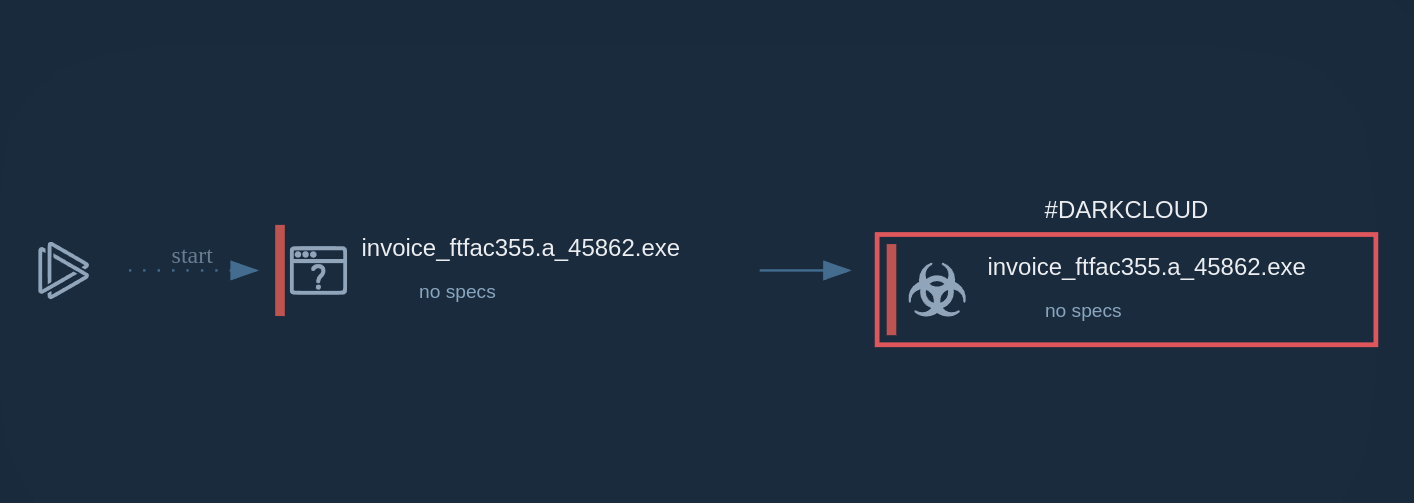
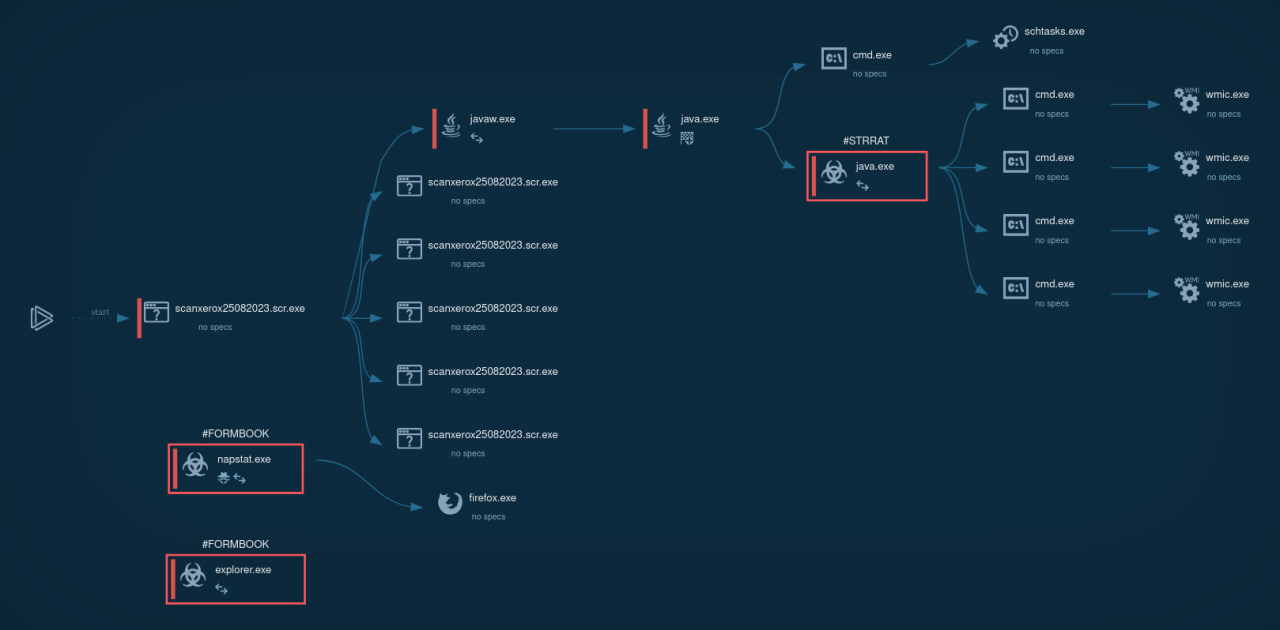 STRRAT's process tree
STRRAT's process tree
Phishing email campaigns remain the go-to method for threat actors to launch attacks using STRRAT against victims. Such emails typically mimic the branding and logos of trusted organizations, making them appear legitimate.
For instance, one of the documented cases related to STRRAT involved a fake email from the MAERSK shipping company. By unknowingly downloading and opening files attached to these emails, victims can kick off a chain reaction resulting in attackers gaining full control over their computers.
The STRRAT malware has proven to be a persistent challenge over the past 3 years. Individual users and SMEs are the groups primarily targeted by threat actors who use this malware. This puts an emphasis on the importance of having a reliable and fast tool like ANY.RUN for scanning suspicious links and files. The service generates comprehensive reports on the behavior of any sample in seconds and provides a conclusive verdict on whether a certain file or URL is malicious or not.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!.