Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

Gh0st RAT is a malware with advanced trojan functionality that enables attackers to establish full control over the victim’s system. The spying capabilities of Gh0st RAT made it a go-to tool for numerous criminal groups in high-profile attacks against government and corporate organizations. The most common vector of attack involving this malware begins with spam and phishing emails.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2008
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2008
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 807
807
 0
0

 488
488
 0
0

 2743
2743
 0
0
Gh0st RAT is one of the long-standing members of the global threat landscape. Launched in 2008, it remains in full operation to this day. The RAT part in the malware’s name stands for Remote Access Trojan, meaning that it provides attackers with the capacity to control the victim’s machine and manipulate it.
The original developers of Gh0st RAT were from China. However, due to the open-source nature of its code, criminals from many other countries have created their iterations of the malicious software. As a result, there are many versions of this trojan with varying sets of features.
If you're interested in exploring variants of Gh0st, we recommend reading our article about Gh0stBins, Gh0stBins, Chinese RAT: Malware Analysis, Protocol Description, RDP Stream Recovery.
The most notable aspect of Gh0st RAT is that it has been utilized by criminal groups linked to the Chinese government. For instance, in 2009, the malware was used to target Tibetan organizations. There were also instances of attacks on businesses in various fields, including healthcare and banking.
The standard set of features of Gh0st RAT includes the following:
To persist on the system, Gh0st RAT adds registry entries that allow it to automatically execute itself on every system startup. The malware can scan the system to determine if it is running inside a virtual machine and if antivirus software is installed. These actions help it hide its behavior from security analysts and avoid detection. It also utilizes encryption to obfuscate its functions.
Essentially, Gh0st operates similarly to other RAT malware families, such as njRAT and DCrat.
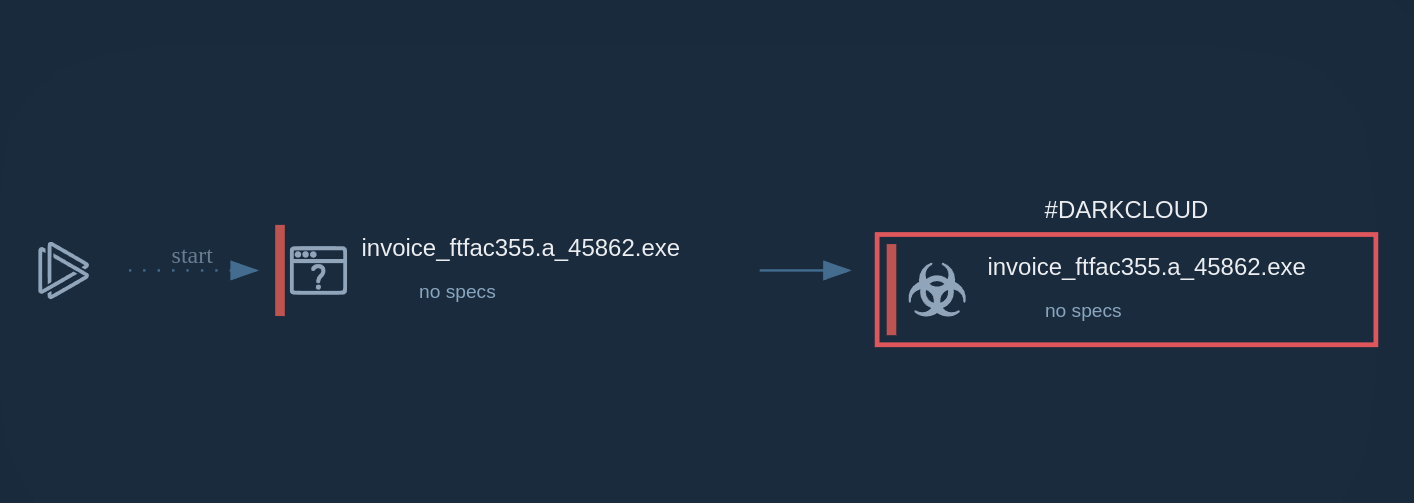
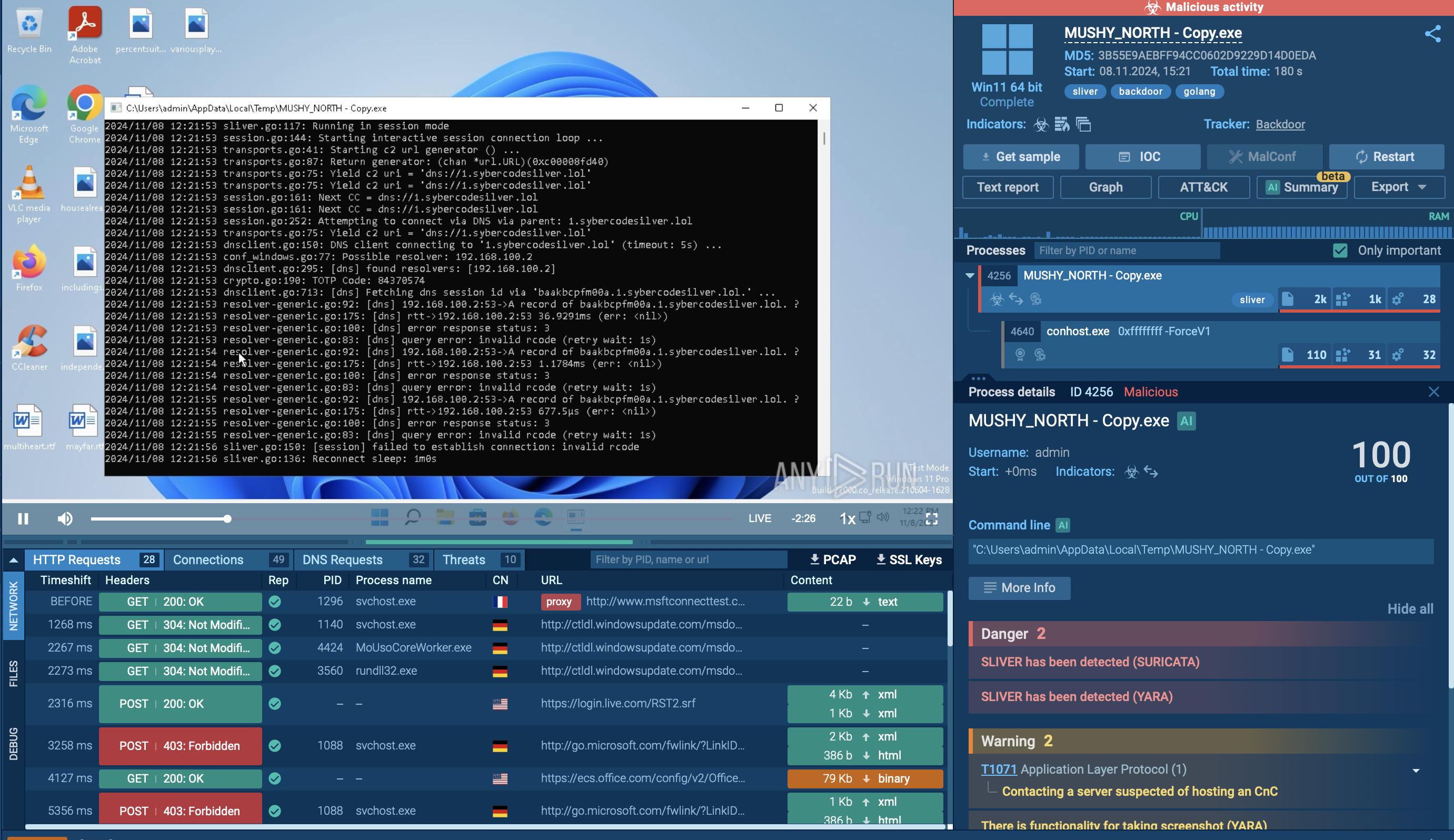
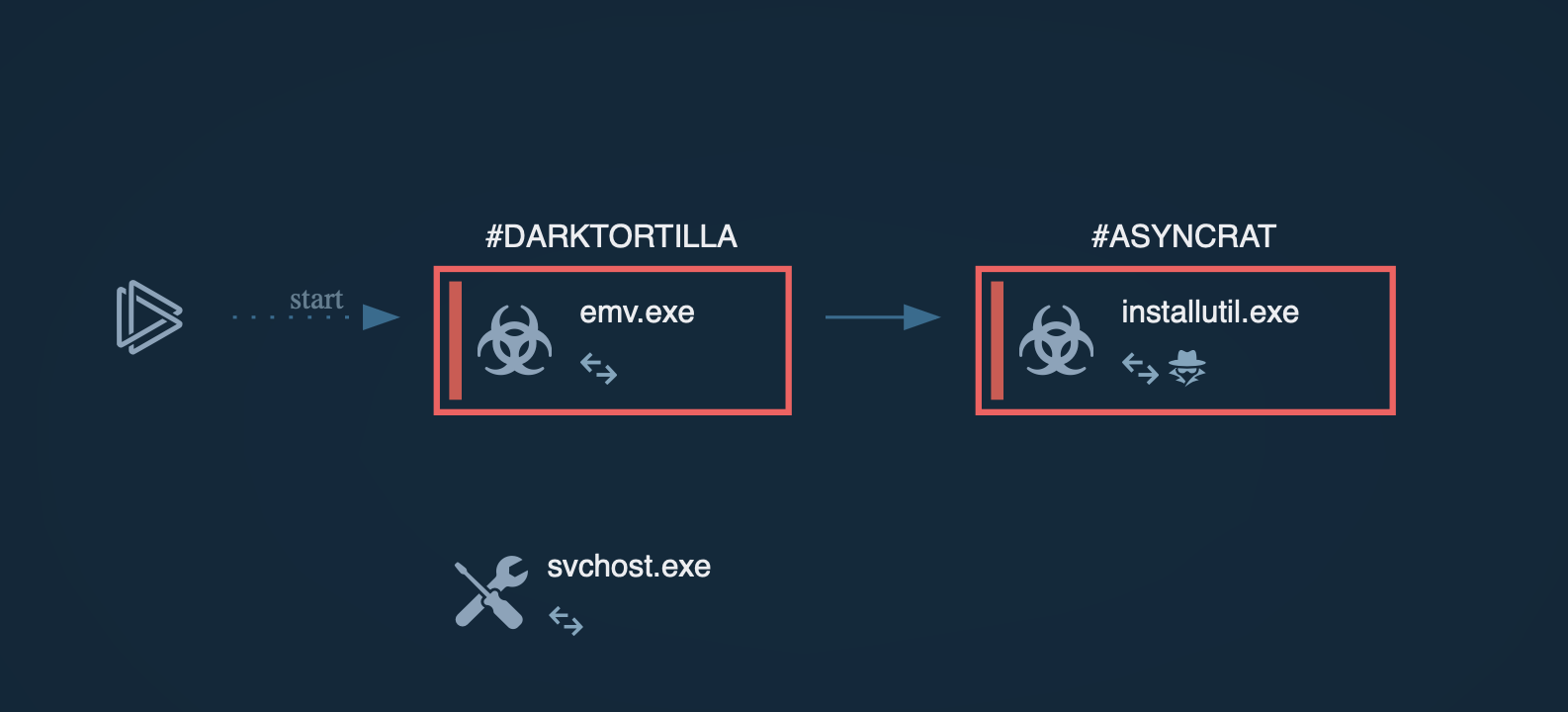
By uploading a sample of Gh0st RAT to ANY.RUN, an interactive sandbox for malware analysis, we can observe its malicious processes in detail and collect IOCs.
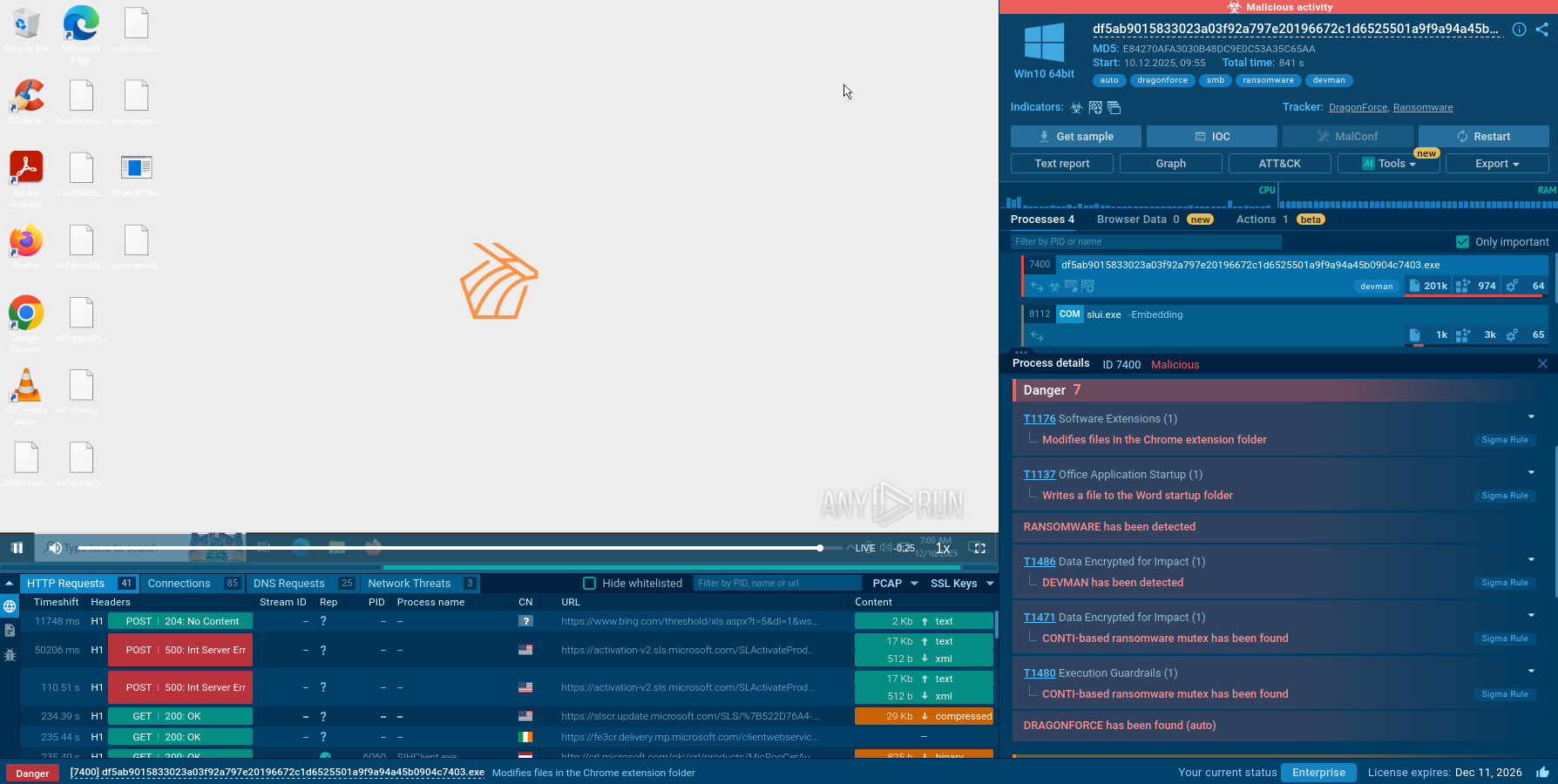
The execution process of the Gh0st Stealer typically begins with a user inadvertently downloading or executing a malicious file, often disguised as legitimate software or attached to phishing emails. Once executed, the malware establishes a connection to a remote command and control (C2) server, allowing the attacker to remotely control the infected system. This malware utilizes various system tools for execution, such as CMD in our example.
Gh0st Stealer then begins its data theft operations, scanning the system for sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and financial data. Captured data is exfiltrated back to the attacker's server, where it can be used for malicious purposes or sold on the dark web. The malware may also maintain persistence on the compromised system, allowing for continued data theft and remote control capabilities. In our task stealer use steganography techniques in order to prevent the detection of hidden information – It hides an encrypted DLL file inside a downloaded JPEG image.
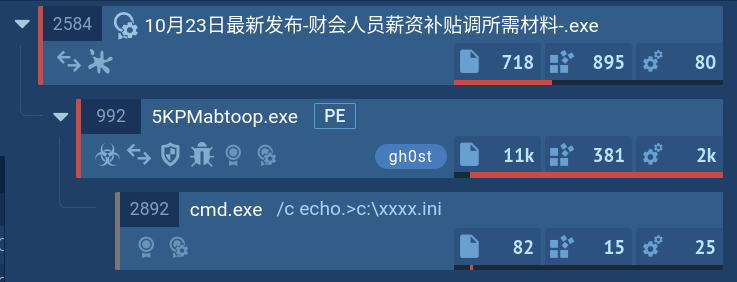 Gh0st process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Gh0st process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
To collect up-to-date intelligence on Gh0st RAT, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can efficiently gather relevant data on threats like Gh0st RAT.
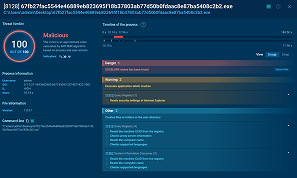
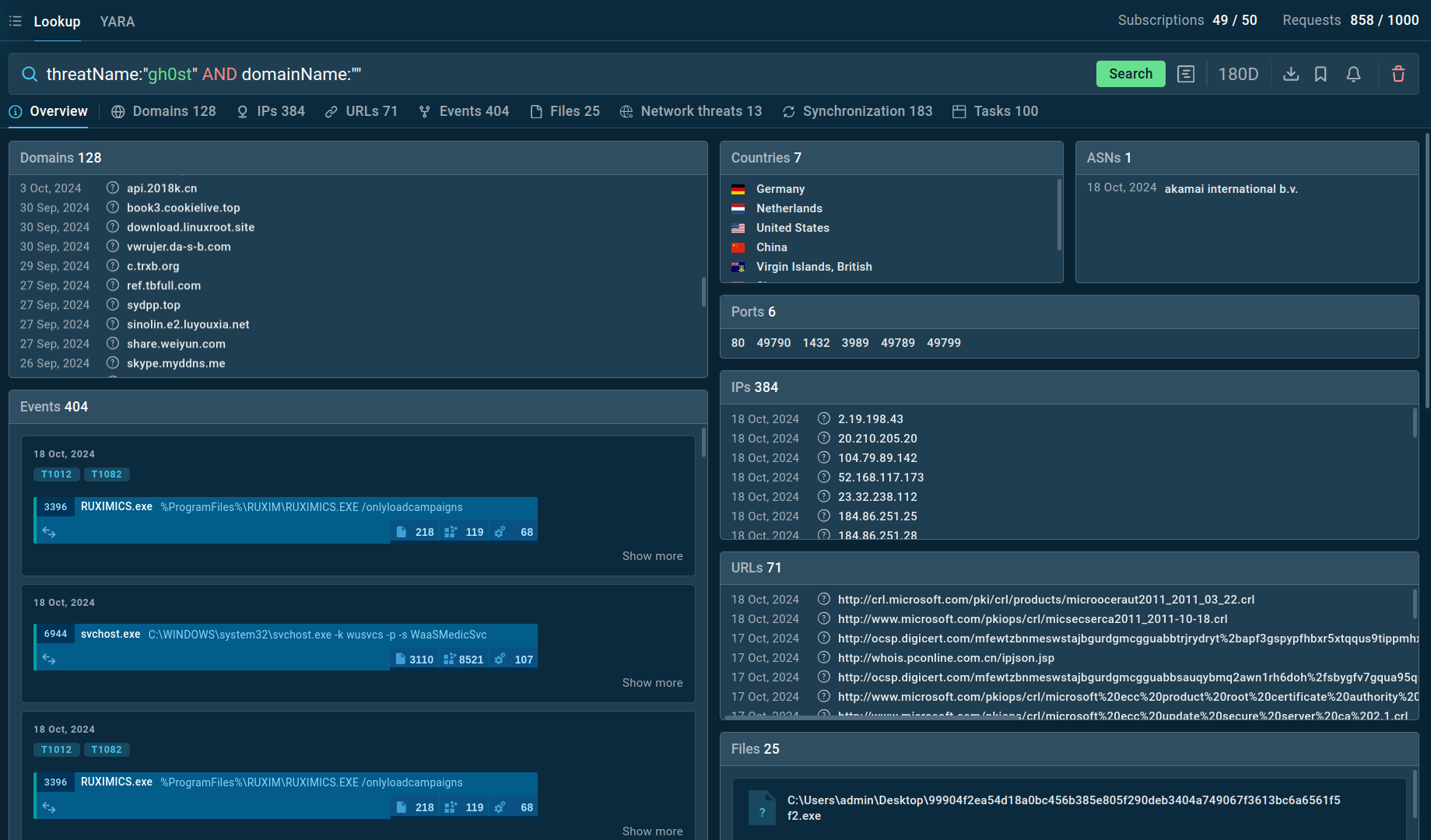 Search results for Gh0st RAT in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Gh0st RAT in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"gh0st" AND domainName:"" will generate a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from Gh0st RAT samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
As mentioned earlier, Gh0st RAT is often used in targeted campaigns against government organizations and businesses. In order to carry out them successfully, attackers implement the method of spear phishing.
This involves composing emails that are similar to those sent by legitimate entities to trick the victim into downloading a malicious attachment or clicking on an unsafe link.
Gh0stRAT is a veteran RAT with an open-source code that continues to be used by both individuals and organized groups in attacks around the world. Due to the fact that phishing campaigns constitute the key starting point of infection, businesses need to exercise extra vigilance when handling suspicious emails.
By analyzing all files and emails from unknown senders in ANY.RUN, companies can quickly identify whether they were targeted by criminals. The service offers conclusive verdicts on the malicious activities of samples and generates comprehensive reports, containing IOCs and configs to ensure future detection.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!