Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


HijackLoader is a modular malware acting as a vehicle for distributing different types of malicious software on compromised systems. It gained prominence during the summer of 2023 and has since been used in multiple attacks against organizations from various sectors, including hospitality businesses.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2023
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2023
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 412
412
 0
0

 2216
2216
 0
0

 4315
4315
 0
0
HijackLoader is a loader malware that possesses strong evasion capabilities, allowing it to bypass mainstream security solutions. It has been observed to deliver numerous persistent malware families, such as DanaBot and the RedLine stealer.
Most of the known attacks involving HijackLoader began with phishing emails. As of the end of 2023, it continues to be an active threat. The modular design of the malware is one of the key factors behind its popularity. It enables HijackLoader to ensure a more flexible approach to deployment on the infected system and further execution of the final payloads.
HijackLoader is notorious for its ability to evade detection. One way it does this is by utilizing a modified Windows C Runtime (CRT) function to gain a foothold on the device.
During the initial stage, HijackLoader also ascertains whether the final payload is embedded in the binary or has to be downloaded from external sources. It does this through the use of an array of DWORD values.
It can also check if the device is connected to the Internet by attempting to connect to legitimate websites. The network connectivity check is a clever strategy that allows HijackLoader to remain undetected while the network is unavailable. In a similar fashion, the malware can delay the execution of different parts of its code to once again avoid early detection.
To make it more difficult for reverse engineers to analyze its code, the malware uses dynamic API loading via a custom hashing method. This makes it harder to locate the specific API calls used during execution.
HijackLoader’s AVDATA module is designed specifically for the purpose of identifying security software installed on the system and adjusting its operation depending on the results of its scanning.
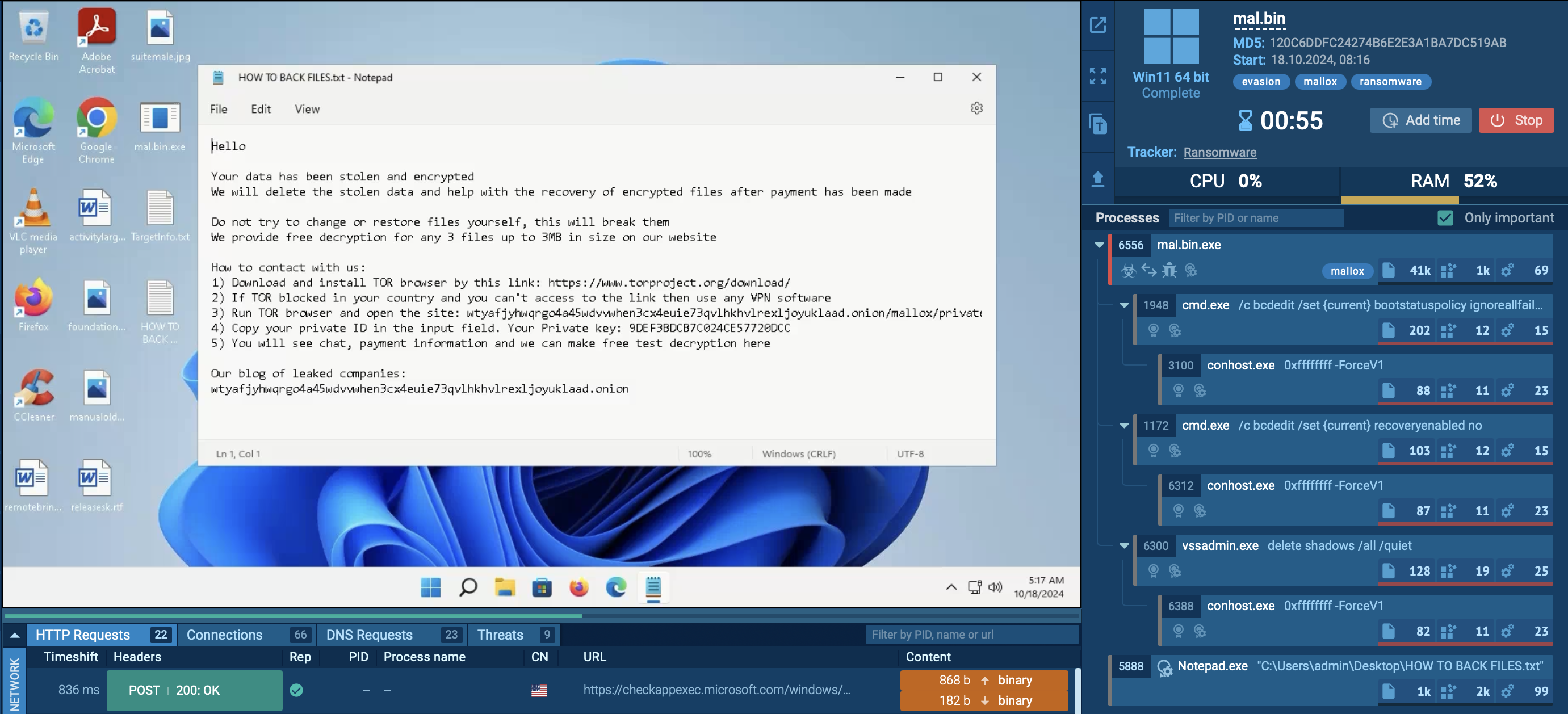
Let’s take a closer look at the execution flow of a HijackLoader sample by uploading it to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
HijackLoader is a typical loader, and its execution flow is also straightforward and simple. This simplicity allows malware to remain less active inside infected systems, making it more challenging to detect. However, it can still attract attention in certain cases.
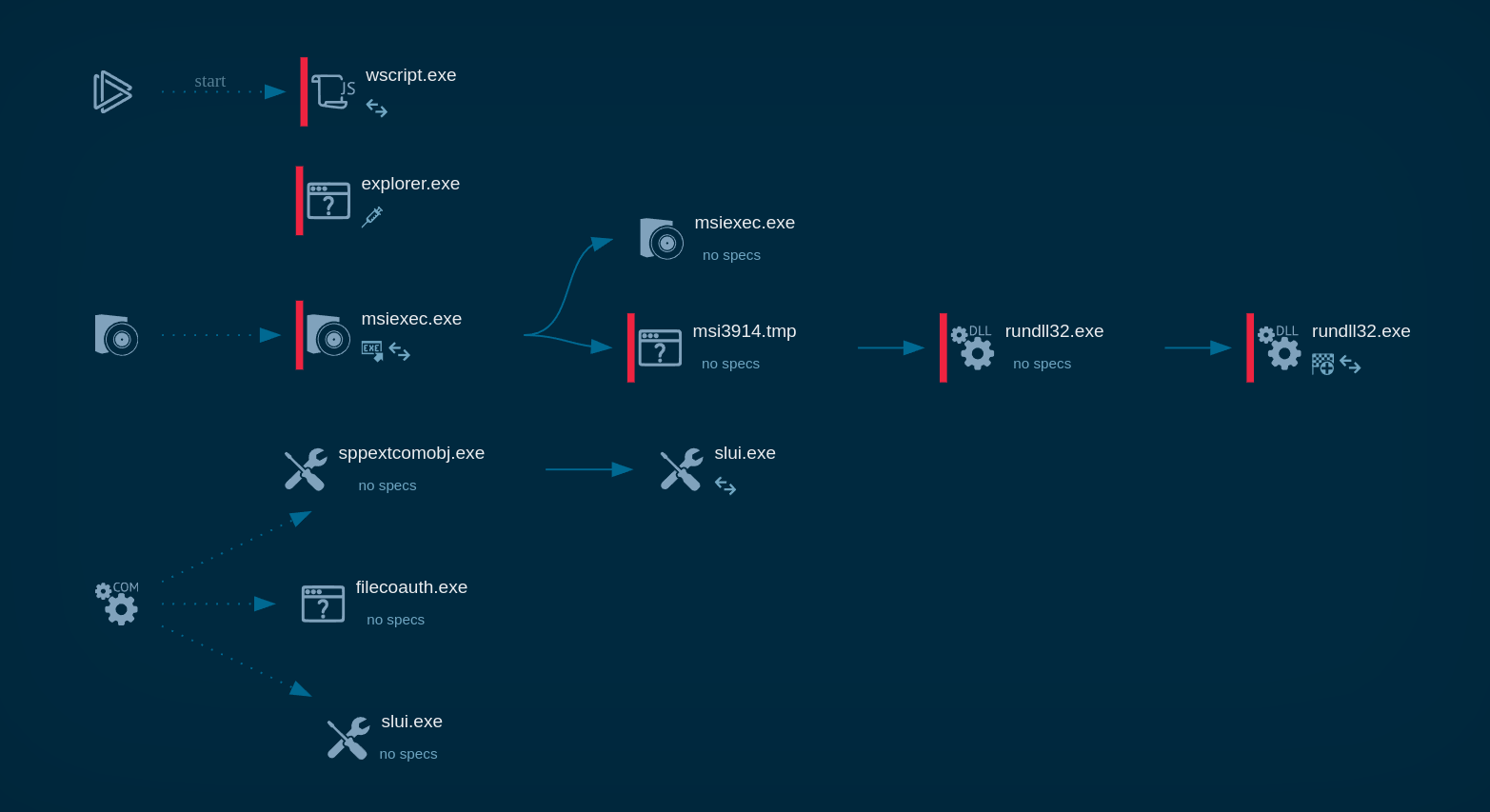
In our example, the loader leveraged the CMD utility to stay under the radar. It, in turn, initiates the MSBuild process, which downloads and runs the Phonk which downloads the miner. HijackLoader demonstrates evasion capabilities that aid in staying undetected by certain security solutions.
Analyze malware for free in a fully interactive cloud sandbox – sign up now!
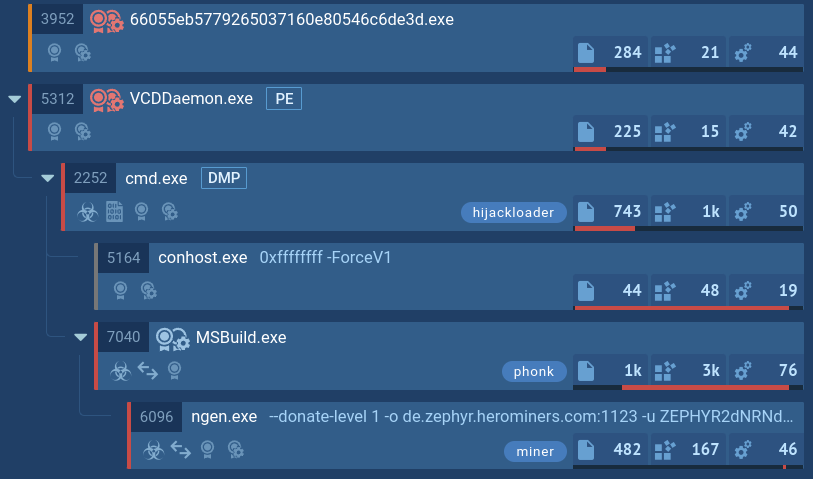 HijackLoader's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
HijackLoader's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
The preferred method of infiltration among the attackers behind HijackLoader is phishing attacks, where cybercriminals craft emails that appear to be from legitimate sources, hoping to trick recipients into opening malicious attachments or clicking on infected links.
In one notable instance, hotels were targeted with emails from fake clients claiming to be staying at the hotel and requesting staff to download a file containing information on their allergy. Once opened, the file kickstarted the infection chain resulting in the deployment of HijackLoader on the victim’s device.
Keeping your infrastructure safe from a HijackLoader infection requires a proactive cybersecurity approach. An indispensable part of it is a reliable malware analysis sandbox like ANY.RUN.
With ANY.RUN, you can example incoming emails to determine any malicious intent behind them with ease. The service’s interactive cloud environment enables you to effectively investigate even the most intricate phishing campaigns and uncover multi-stage attacks in no time. The service delivers comprehensive text reports encompassing detailed information about the submitted files and links, including fresh IOCs.
Adopt a proactive cybersecurity approach by leveraging ANY.RUN.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!