Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


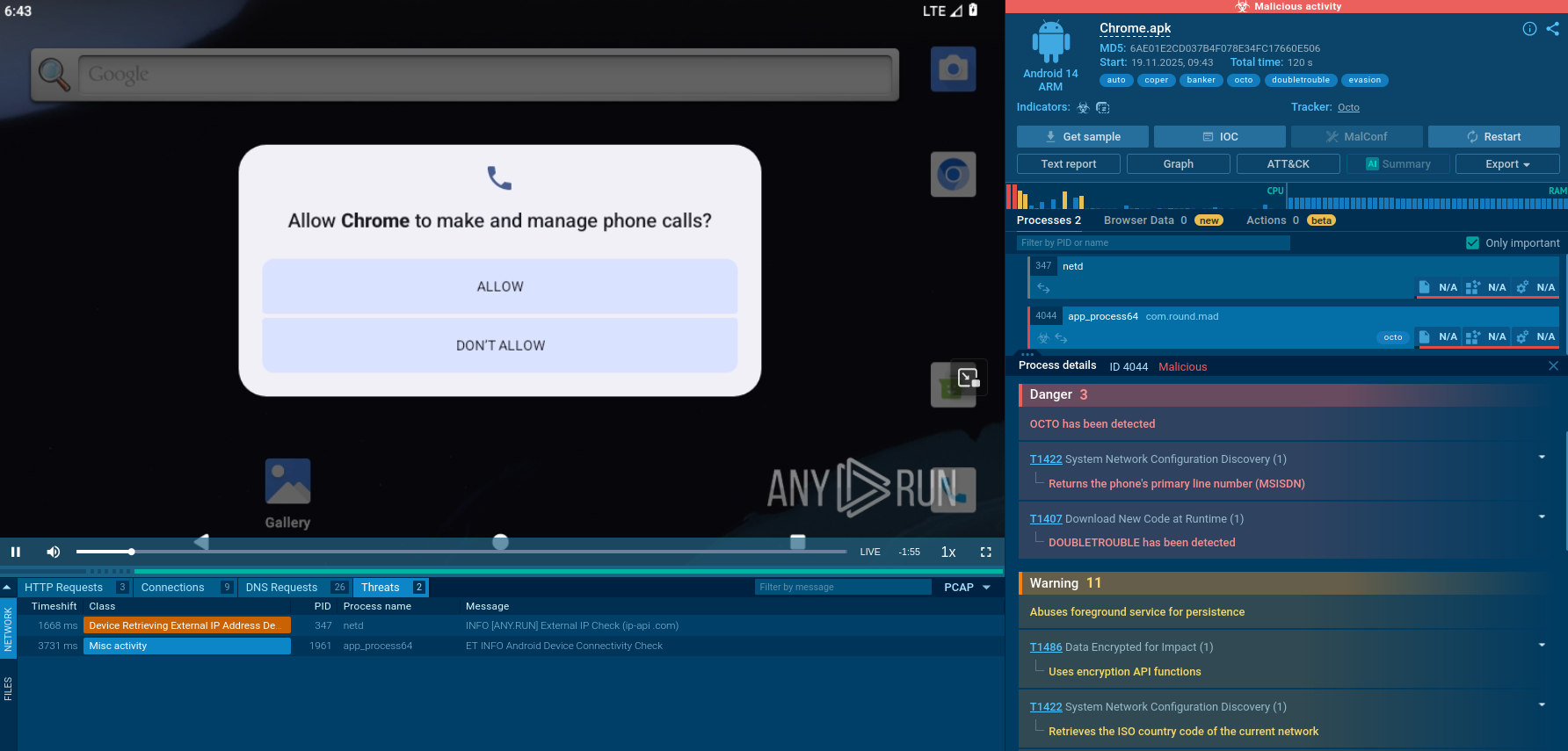
Danabot is an advanced banking Trojan malware that was designed to steal financial information from victims. Out of the Trojans in the wild, this is one of the most advanced thanks to the modular design and a complex delivery method.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
6 May, 2018
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
6 May, 2018
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Danabot is a banking trojan that was spotted in the wild in 2018. Danabot differs from competing Trojans thanks to its robust delivery system and modular design. Since its first appearance, Danabot has obtained high popularity among cybercriminals and became an active threat in multiple regions of the world.
This malware is constantly updated by the creators, helping the Trojan continue to gain popularity in the hacking community. Danabot is written using the Delphi programming language carries several credential theft functions.
When first documented, Danabot malware was being used by just one actor who carried out a campaign against Australian companies. Since then, other malicious actors have started utilizing this malware and expanded the geography of attacks to Europe and North America.
In particular, the Danabot trojan was seen in attacks in Poland, Germany, Italy, Austria, and the US. Particularly, the US campaigns were carried out on a large scale, indicating that the malware is evolving and developing.
As far as the function set of this malware is concerned, Danabot can be classified as a banking trojan, though some of its features suggest that it is becoming a more versatile malware. Danabot is constructed out of three main components. The loader is a program created to download the main payload. The main component, which is installed by the loader, is configured to download the modules that the attacker can specify. Finally, once installed, the modules provide the functionality, which can vary depending on which modules were chosen by the ill-wisher in a particular campaign.
The malware can take screenshots, grant attackers remote control of the victims’ machine, collect system information, steal credentials, and record lists of files stored on infected PCs. Once collected, all information recorded by Danabot is sent to the control server in an encrypted form. Danabot aims to steal sensitive information that can be leveraged by the attackers later, therefore instead of confirming the victim head-on and demanding a ransom. This malware tries to stay hidden and collect valuable data over time. Some of the smaller distribution campaigns featuring Danabot were well made in terms of clever social engineering and carried on with the same philosophy of a more subtle approach.
In addition, researchers noticed that the attackers utilizing Danabot ventured beyond banking credentials theft and started utilizing this banking malware to host other spam and malicious campaigns, using the infected machines of their victims. What’s more, Danabot creators are thought to be collaborating with the group behind a different banking trojan – GootKit. Danabot was recorded as being used to distribute this type of threat. This case is a first for both malicious programs since neither has been distributed or distributed by other malware before.
In January 2019, researchers noticed a new version of the Danabot trojan in the wild. The investigation confirmed the new samples to be the evolution of Danabot, with a different C2 communication protocol that began to use multiple encryption layers and proved very complex. In the new variant, AES and RSA encryption algorithms were employed in particular. On top of that, the core design of the malware was also changed, as the loader was made responsible for downloading all the modules along with the main component. The researchers believe a technique was used to avoid detection on a network level that the attackers could have invented after reading existing analysis material on Danabot.
It should be noted that Danabot features several evasion techniques designed to make research as complicated as possible. For one, the banking malware is loaded with many lines of junk code, implemented solely to mislead the researchers. The malware also uses encryption and Windows API function hashing to fool automated sandboxes and researchers and prevent them from uncovering the true nature of the code.
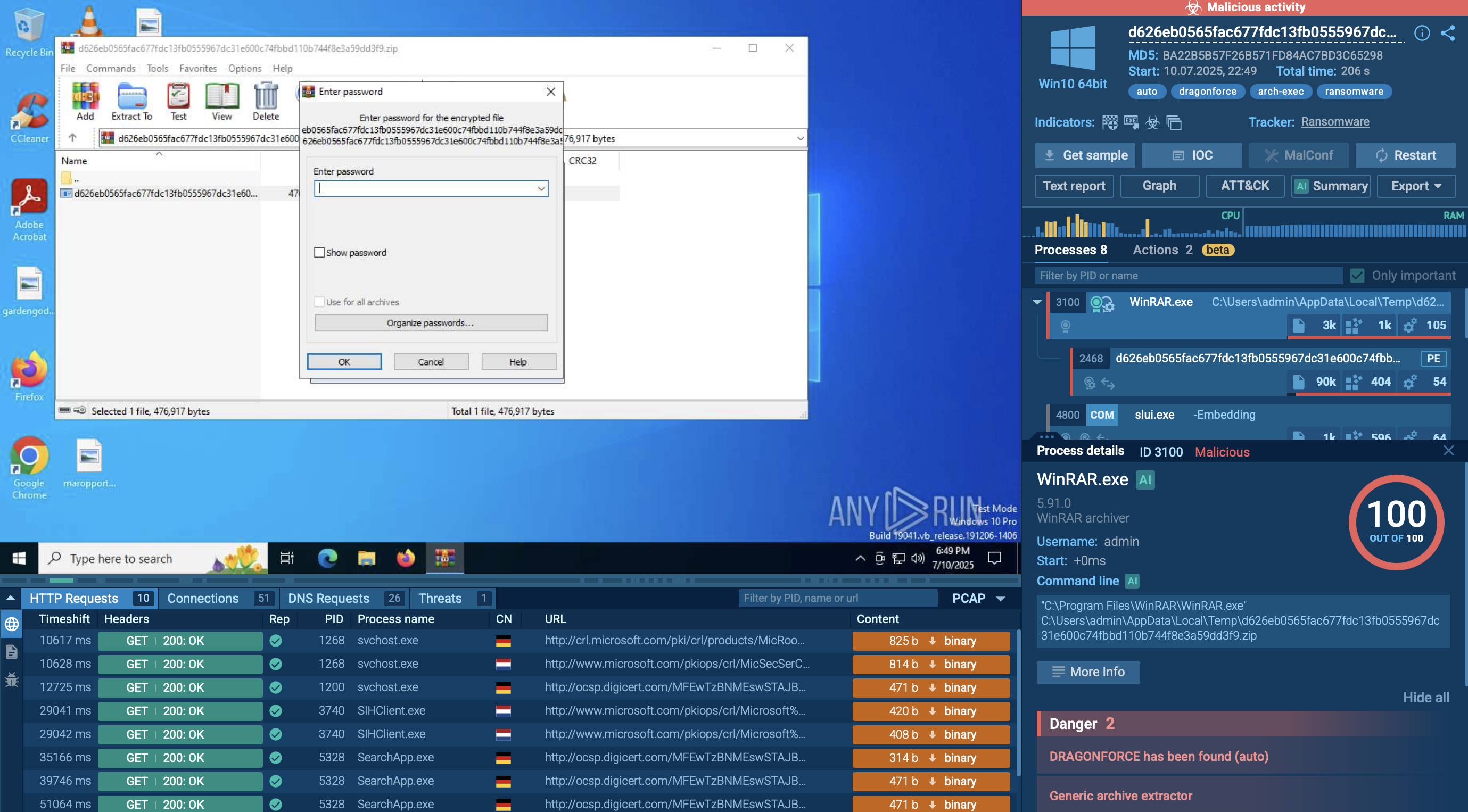
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service enables us to take a look at Danabot in action.
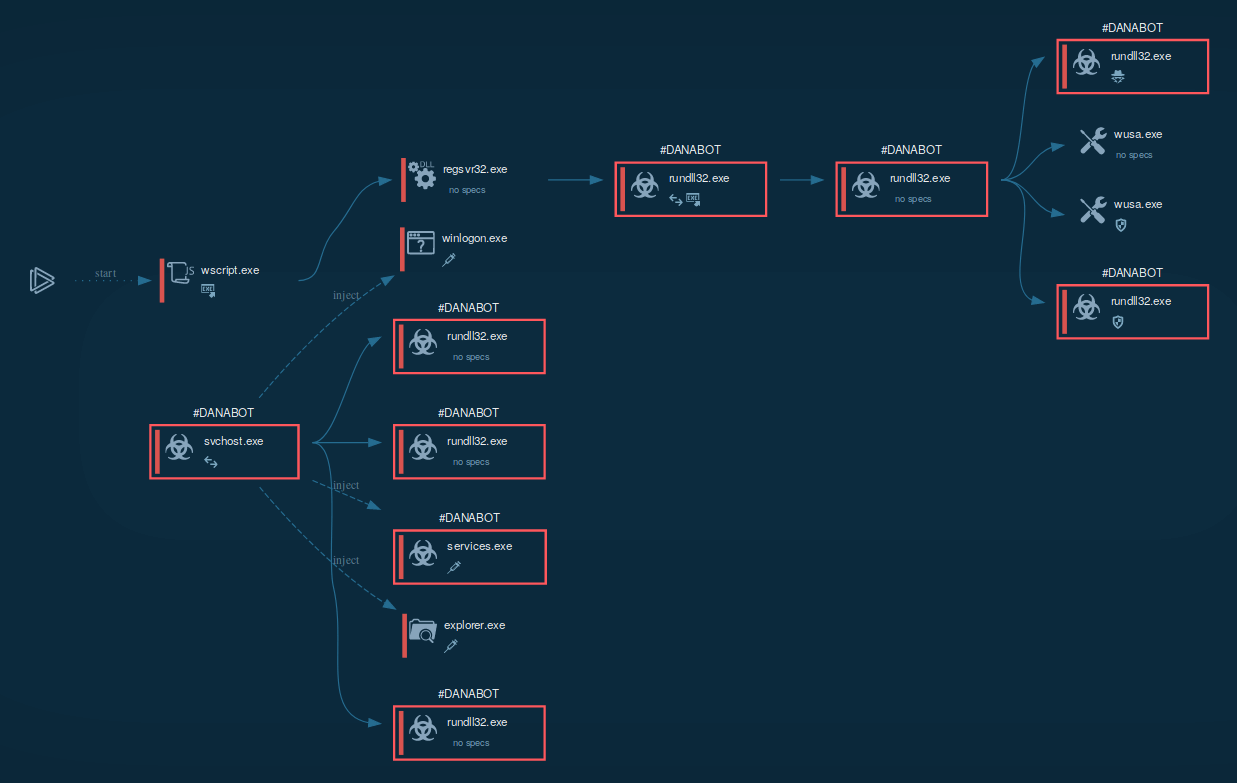
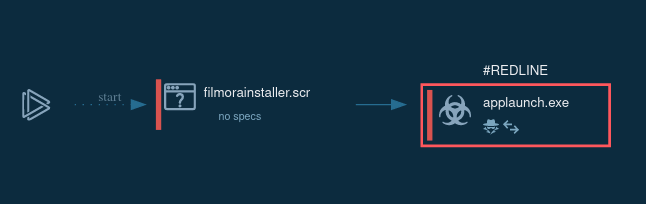
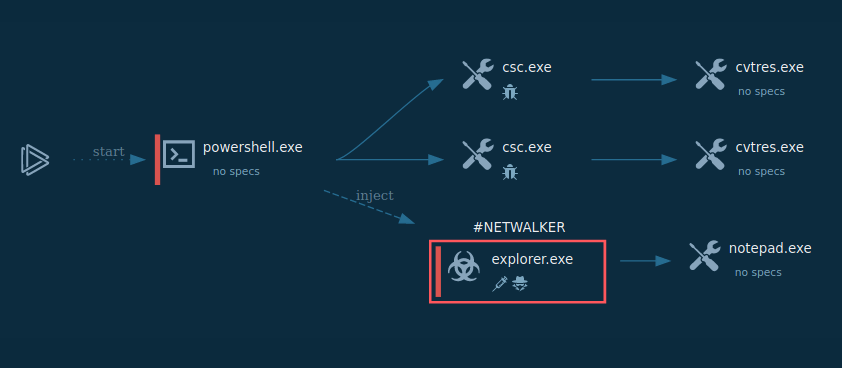
Figure 1: A process graph generated by ANY.RUN for the convenience of the researchers
Figure 2: The text report generated by ANY.RUN is created to allow easy sharing of the study results
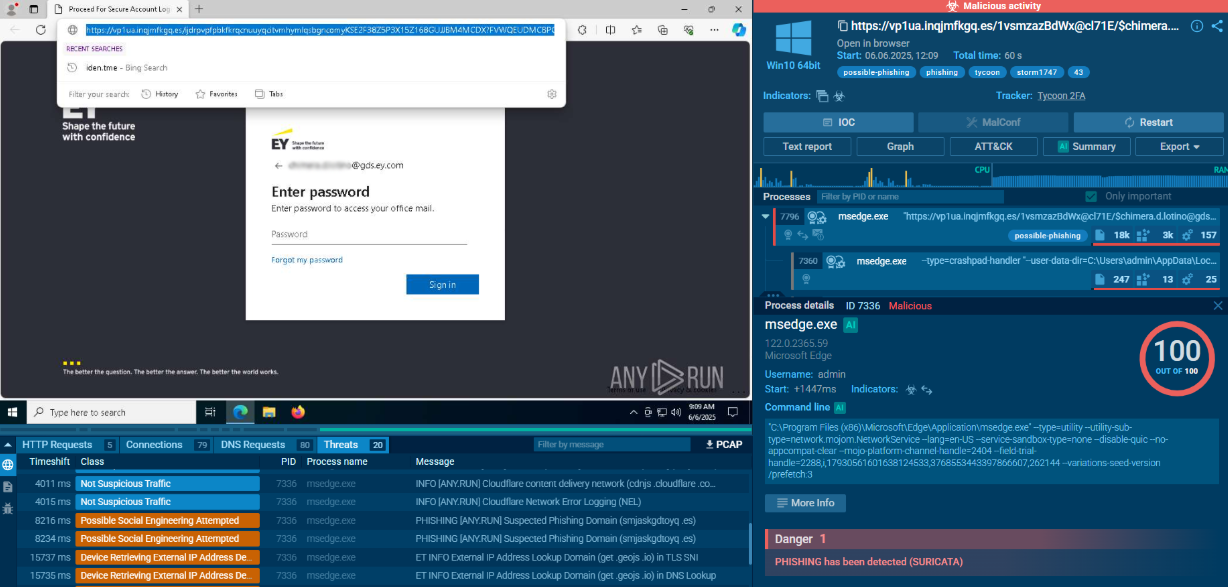
Typically Danabot trojan infects devices according to the following scenario. First of all, the downloader establishes a connection with the C2 server and downloads an executable file with a DLL file, which can be either 32-bit or 64-bit based on the infected OS version.
After that, Danabot begins stealing information from the infected OS. The banking malware bypasses user access control by using a DLL hijacking vulnerability in the Windows Update Standalone Installer (wusa.exe). This allows Danabot to create services and execute the injection into system processes. After all of these steps, Danabot receives full system control.
Danabot is distributed in email spam campaigns targeting organizations and using social engineering to trick victims into downloading malicious documents the same scenario as
Danabot is also known to get into PCs with another malware called Hancitor. Email campaigns featuring Danabot were considered well crafted by some researchers, who noted that social engineering involved seemed very effective.
In older samples of Danabot, the loader component used HTTP protocol to communicate with the control server, whereas the main component utilized the binary protocol. In more recent iterations, both components started to communicate with the C2 server over TCP port 443 using TLS instead.
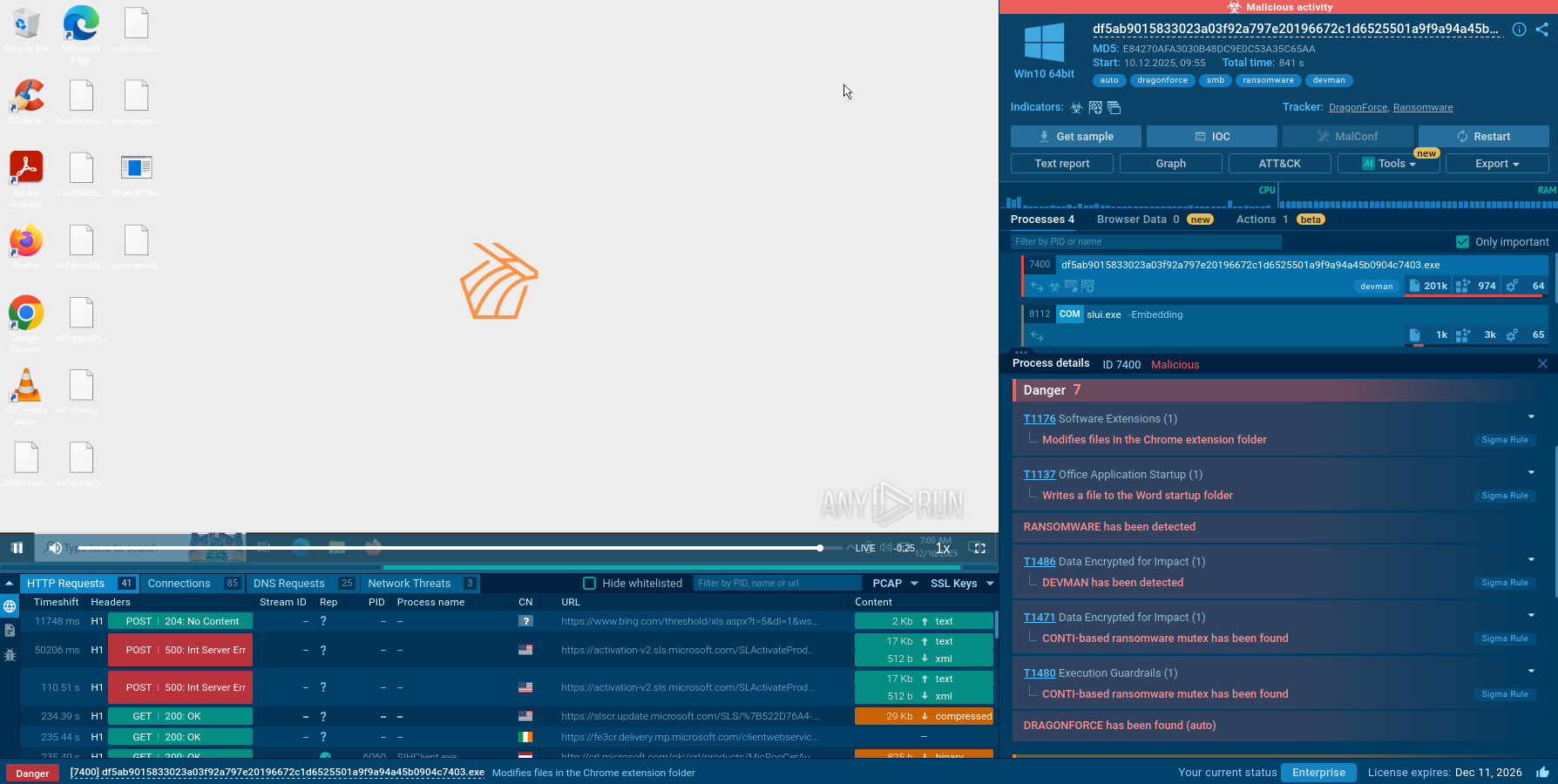
ANY.RUN uses Suricata IDS rule sets, so if malware trying to communicate with C&C servers, it will be detected. To look at what threats were detected, click on the "Threats" section of the "Network" tab.
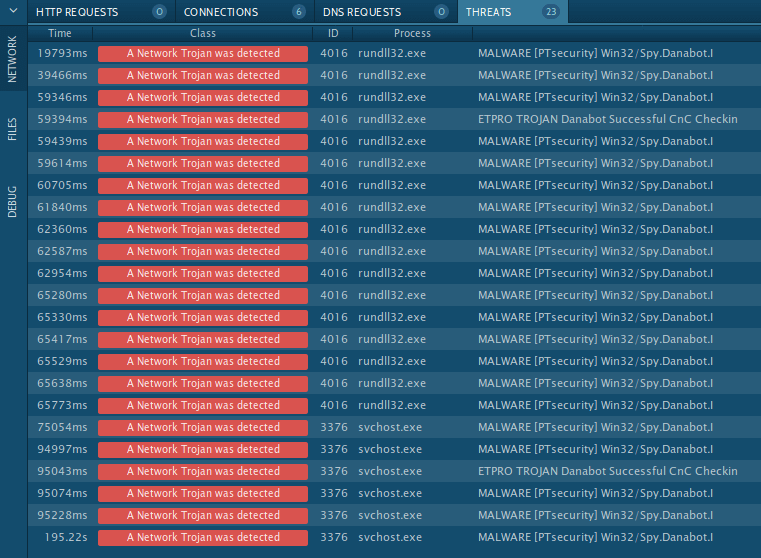 Figure 3: Danabot's network threats
Figure 3: Danabot's network threats
Danabot is a very sophisticated malicious program used as a banking trojan and more. Targeting organizations across multiple continents, Danabot malware poses a high threat to businesses thanks to robust distribution methods and cutting-edge anti-evasion and persistence techniques.
In addition, the module nature of this banking malware allows attackers to fine-tune their campaigns, customizing them for every potential victim. All these traits combined helped make Danabot a very popular banking trojan that is only continuing to gain traction in the criminal community and further expand the geography of attacks.
To establish a reliable cyber defense, security professionals can utilize malware hunting and analysis services such as ANY.RUN, which allows to dissect malware samples and thoroughly study their behavior and architecture.