Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Hancitor was created in 2014 to drop other malware on infected machines. It is also known as Tordal and Chanitor. This malware is available as a service which makes it accessible tools to criminals and contributes to the popularity of this virus.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
2 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
2 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 396
396
 0
0

 2171
2171
 0
0

 4243
4243
 0
0
Hancitor, sometimes called Tordal and Chanitor is a loader designed to install other malware on the victim’s PC – most often it’s either Pony, Vawtrak, or DELoader. The malware has been around since 2014 and it is distributed to other users as a service by the original creators via malspam.
This malware can’t be considered dangerous since even Microsoft's built-in antivirus Windows Defender can detect it. On top of that, being distributed in malspam campaigns, in a lot of cases emails don’t even reach their targets, being intercepted by spam filters. In essence, the only people truly in danger of getting infected by Hancitor, are those who still utilize older Windows versions like Windows seven or earlier and who either don’t have or disabled their antivirus software. Curiously, despite such a limited “target audience”, Hancitor creators continue to update this malware and it is still very active to this day.
Creators of Hancitor provide their loader as a service to other criminals, helping to install various malware on the target PCs. The people behind Hancitor are extremely active and organized. Some researchers suspect that they work full business weeks since the surge of Hancitor attacks usually takes place on business days and falls off on the weekends, which suggests that the hackers responsible have a work structure and a schedule.
Despite that, Hancitor loader has not changed very much since 2016 and to this day relies on very simple execution and evasion techniques which makes its detection and prevention relatively easy, especially for corporate targets with adequate levels of cybersecurity.
According to the Hancitor analysis, the 2016 version of the malware had 66 functions and had the size of 20 480 bytes while the 2018 version is made up of 51 functions that amount to the size of 20 992 bytes. One of the main differences between the versions is the lack of connectivity check functionality in the 2018 iteration. As such, the older iteration of Hancitor would try to connect to Google.com during execution to check for connections whereas the never iteration fully omits this step. The newer version also makes use of the RC4 encryption and contains some updated commands.
Not unlike other malware, Hancitor Trojan uses several attack vectors to maximize the success rate. Hancitor creators have exploited uncommon API abuse and PowerShell methods among others to ensure the successful infection.
Over the last two years, over 80 variations of Hancitor were detected in the wild. Usually, a new variation would be created simply to define a new variable for a different campaign, while at other times the basic functions of the loader were completely changed and rewritten. However, such instances were rather rare, and highly rewritten samples didn’t stick around for long. Some researchers believe that in such instances the malware authors were testing different approaches and keeping track of the infection rate to determine what changes should remain and which innovations should go.
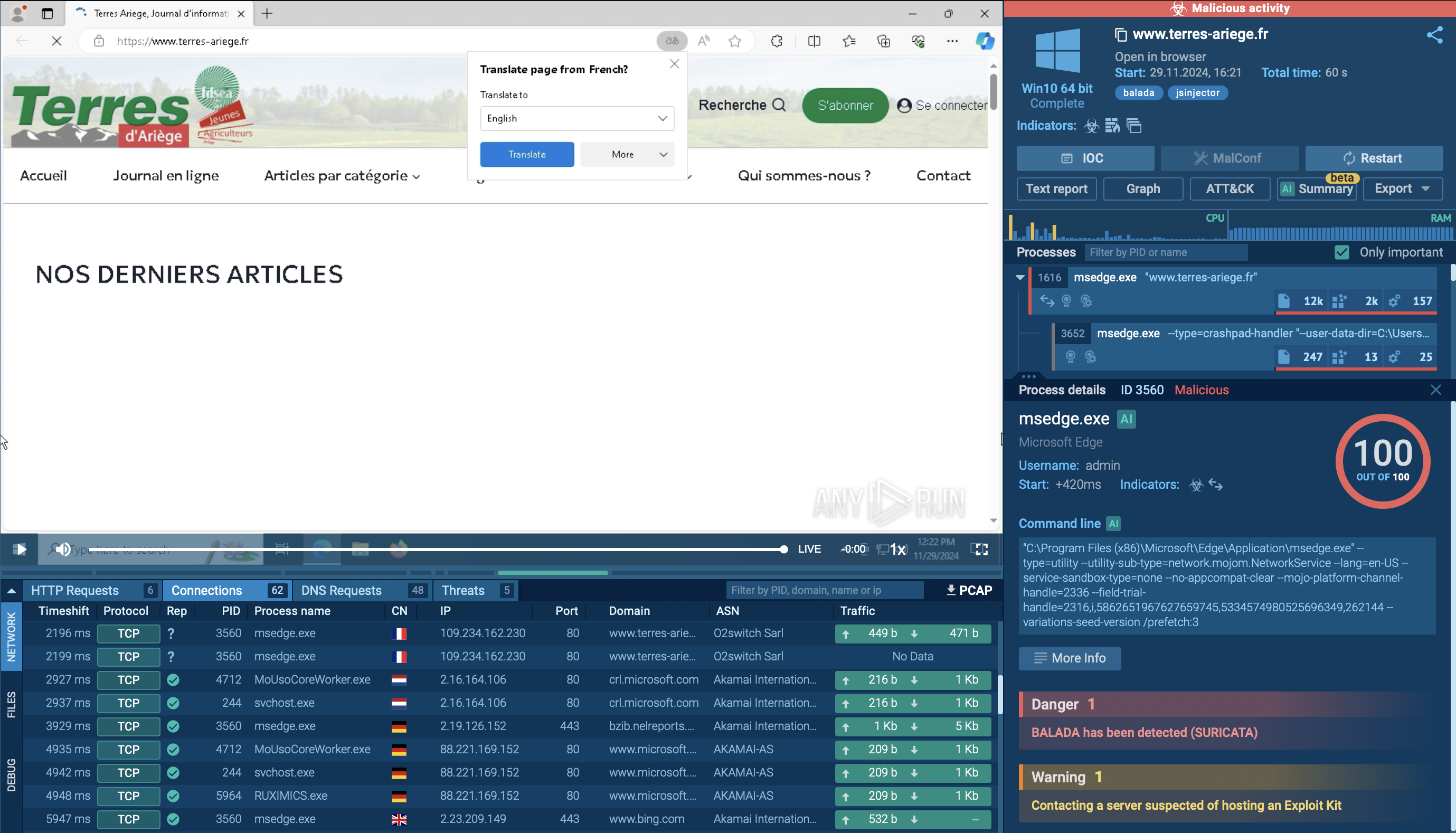
A video recorded on the ANY.RUN malware hunting service displays the execution process for Hancitor analysis.
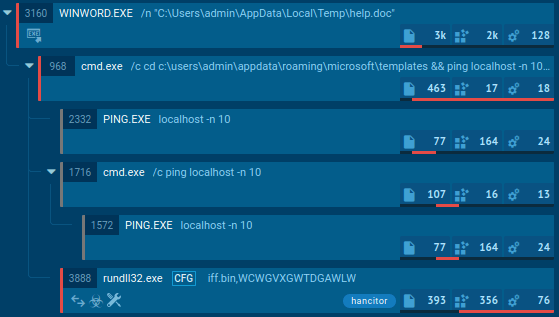
Figure 1: A visual graph of Hancitor execution processes generated by ANY.RUN
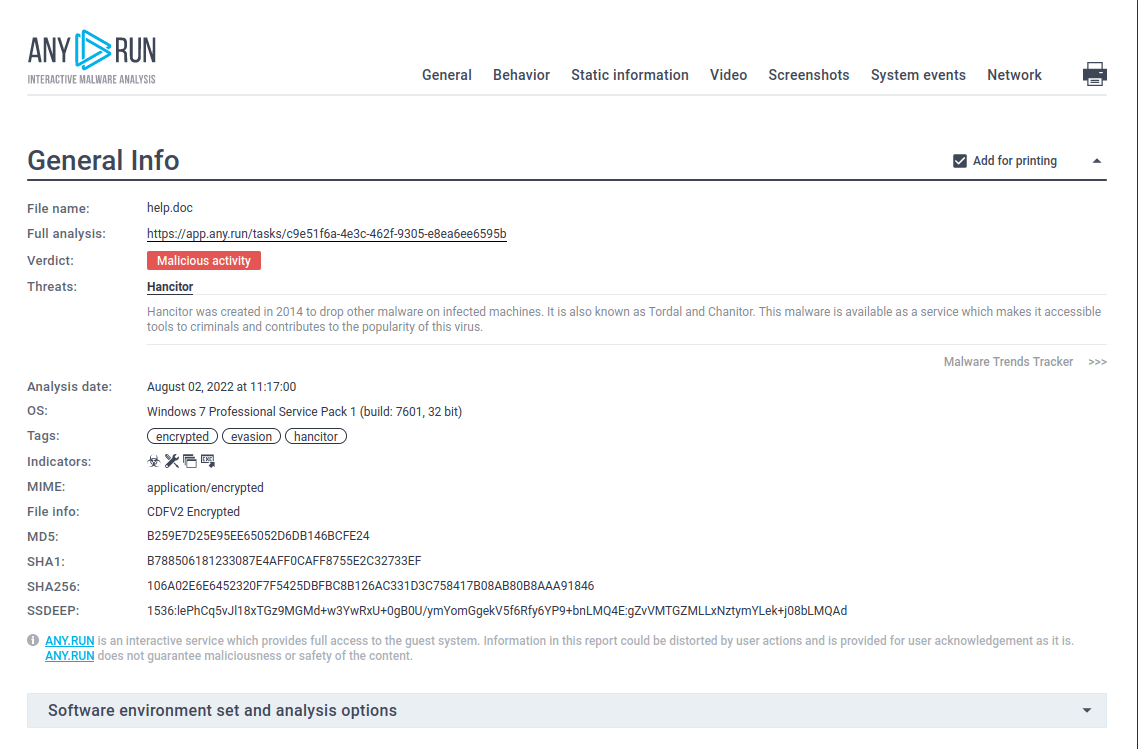
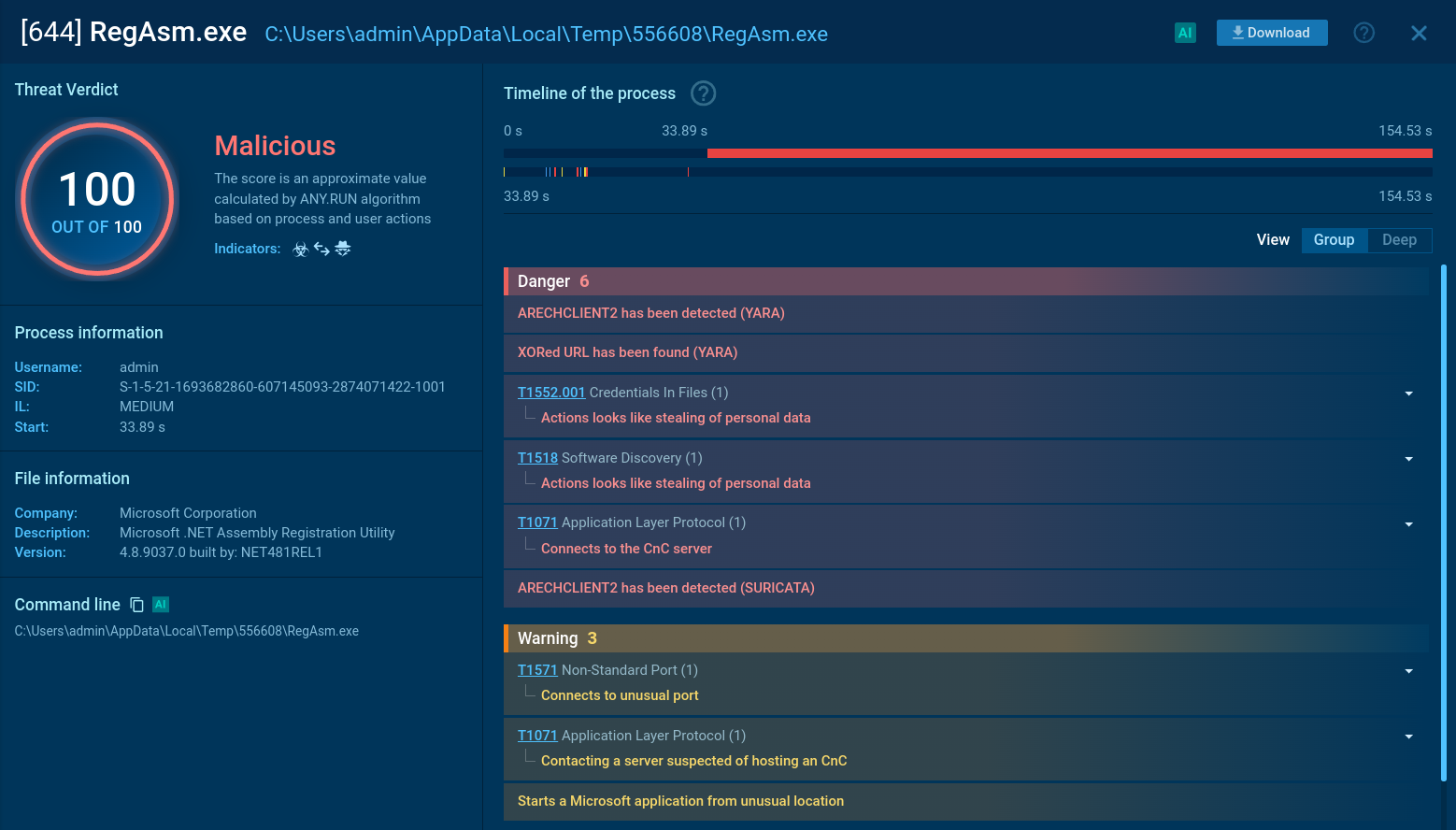
Figure 2: A customizable text report shown here was generated in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service
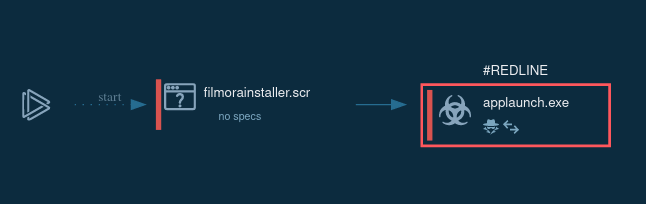
Because of its main purpose, the execution of Hancitor doesn't look that impressive. Since the most common vector of attack to infect users' devices is malicious spam campaigns, Hancitor mostly gets into devices with Microsoft Office files. Once the user downloads and opens the malicious file, the malware either use the lure to trick the victim into enabling macros or uses an exploit. After that Hancitor will be either downloaded from the C2 server or dropped from an Office file. The next step is its execution during which the malware downloads the main payload, usually a trojan such as Pony, Vawtrak, or DELoader.
Based on the Hancitor analysis, the trojan is usually distributed in malspam campaigns as a maldoc, malicious Microsoft Office file attachment. However, since most organizations started improving their cybersecurity measures some campaigns distributing Hancitor contain a link pointing at the website from where this loader is downloaded.
In the case of distribution using .DOC attachments, the user must first download the file and then activate macros, ignoring multiple security warnings. Malware authors use lures to trick users into doing that. Some phishing emails contain an invoice or a fake payment-related document, trying to make the user download it. In addition, attackers provide instructions to enable macros. If the user complies, malicious macros will download Hancitor or it will be dropped from the maldoc.
In some malspam campaigns, Hancitor was delivered to victims with .RTF maldocs which used an exploit to run the PowerShell command which downloaded the loader to the computer.
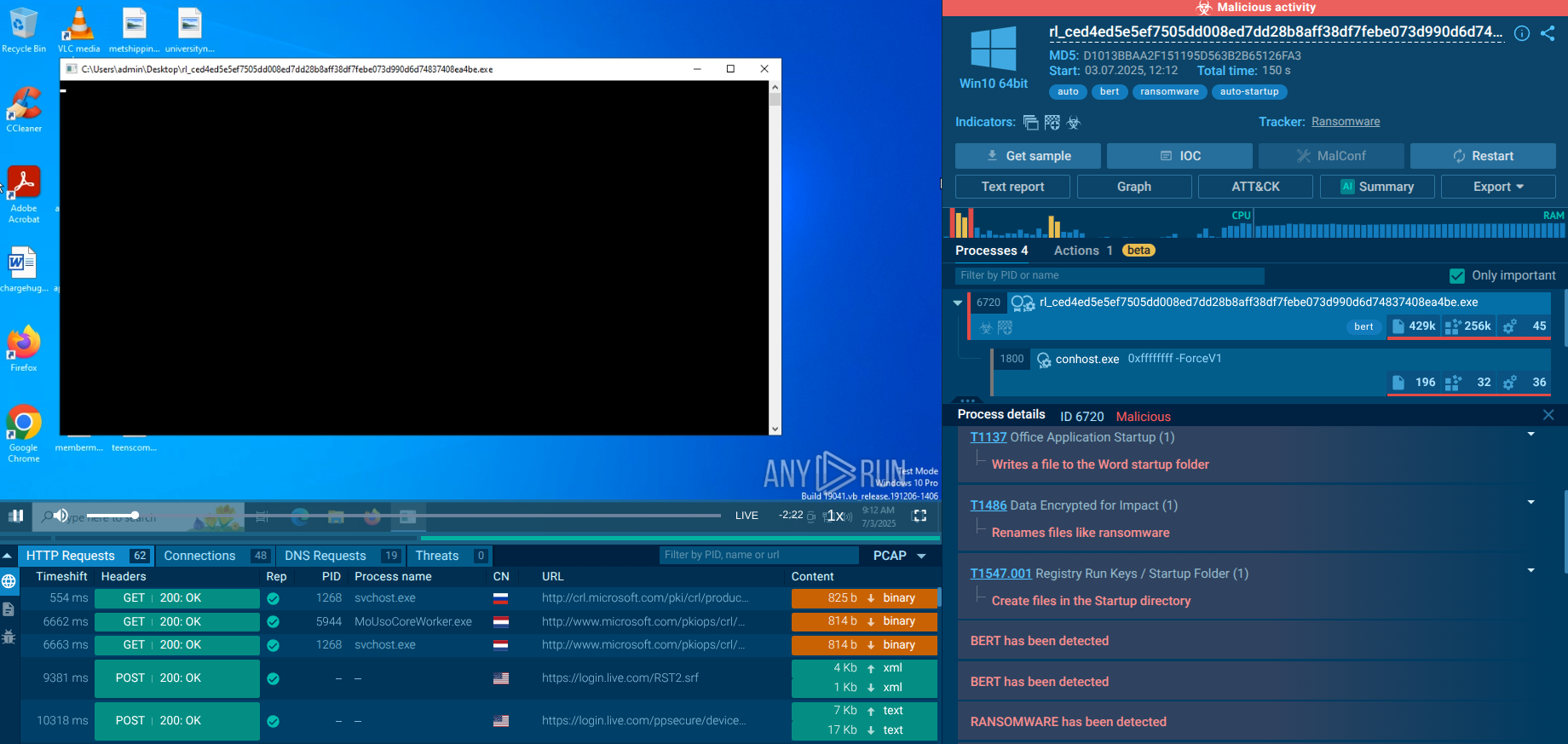
Analysts can take a look at what modules malware uses. Choose the process by clicking on it in the process tree of the task then click on the "More info" button. In the "Advanced details of process" window switch to the "Modules" tab and take a closer look.
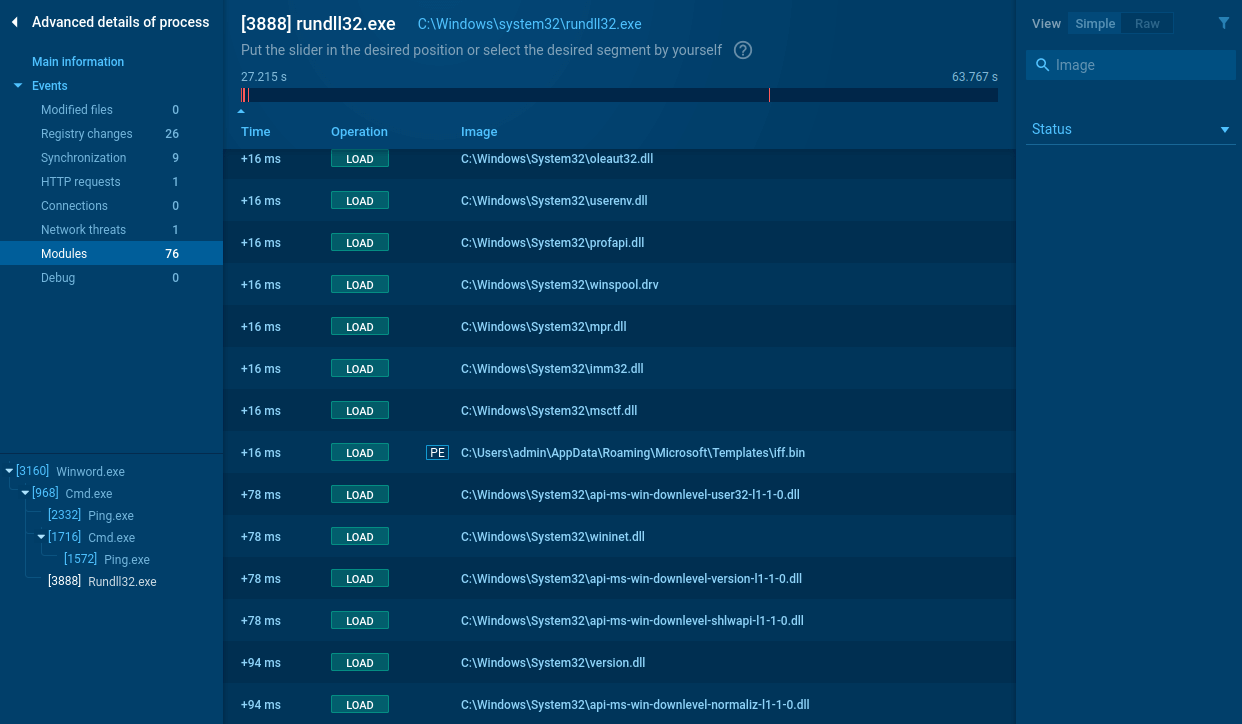 Figure 3: Modules loaded by Hancitor
Figure 3: Modules loaded by Hancitor
Despite its simplicity and vulnerability to even simple countermeasures, Hancitor Trojan somehow remains to be an active malware that continues to target it is limited demographic, evidently with a good success rate the same as Zloader. The authors of Hancitor are extremely active and regularly come up with new iterations of this loader.
Researchers can take advantage of malware hunting services such as ANY.RUN to take malware samples apart and perform the in-depthHancitor analysis.