Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


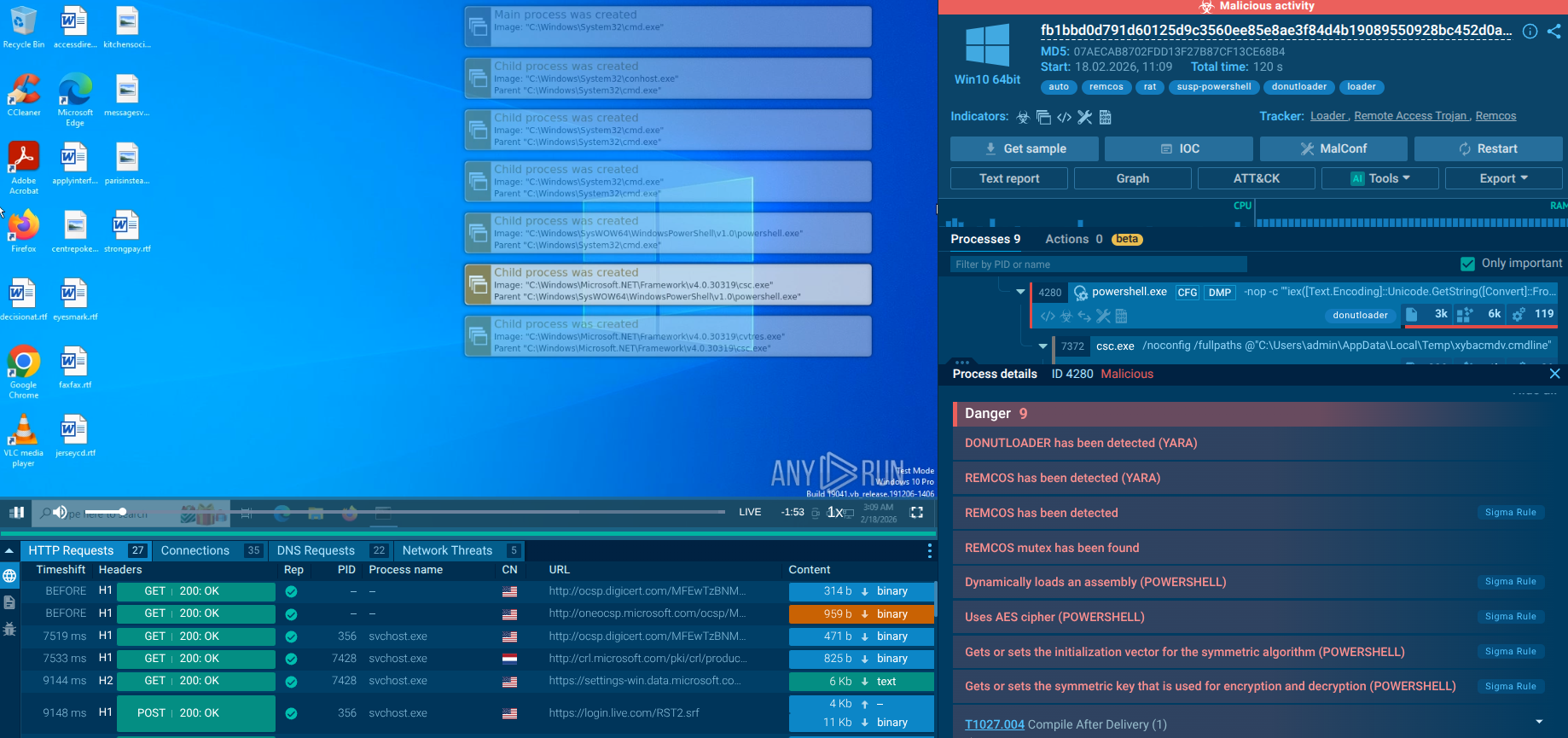
Pony is a malware with two main functions — stealing information and dropping other viruses with different tasks on infected machines. It has been around since 2011, and it still actively attacks users in Europe and America.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2011
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2011
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 890
890
 0
0

 530
530
 0
0

 2830
2830
 0
0
Pony, also known as Fareit or Siplog, is an information stealer and loader – a malware used to collect data from infected machines and install other malicious programs. This particular virus was First Spotted in the wild in 2011. It is known to attack users primarily in Europe and North America.
The earliest discovered version of Pony stealer is 1.7, and the latest updated known version is 2.2. Though being regularly updated, the malware did not gain groundbreakingly new features since the time of its first discovery by Microsoft. In addition to the core functionality, Pony can also steal cryptocurrency wallet credentials, FTP clients, and autofill values from the browsers.
In contrast to the majority of botnets, Pony stealer does not require a centralized C&C server or a group of C&C servers to carry out its attacks. Instead, each attacker can set up their own custom control server or purchase a server that was previously set up by another criminal, instantly gaining access to infrastructure that provides reports about the stolen data. In addition, the malware itself can be divided into two modules, the builder, which is used to construct clients that are then have to be downloaded on the victim’s machine to collect data, and the bot itself – the final payload.
The robust functionality of Pony trojan helped this malware to keep its position as the most popular password stealer through 5 years. Apart from being able to steal credentials the same as RedLine, malware can disable certain antivirus and windows security features and run in the background completely hidden from the user, who may not have a clue that his or her PC is, in fact, infected. When activated, Pony stealer can use the infected PC to take part in botnet attacks, for example, using a hijacked machine to send spam emails. Pony can also download other malware to the victim’s machine and send harvested personal data to a destination specified by the attacker.
What’s more, Pony has been mentioned by multiple “hacker celebrities” as the backbone of many attack campaigns. For instance, the author of the infamous Andromeda botnet has referred to Pony as the “titanic work of the author of miracle (Fareit Bot),” further stating that the loader was incorporated in the Andromeda botnet attacks as a plug-in.
Part of the malware’s popularity is because the source code of multiple Pony loader versions has been leaked and is available for download on the darknet. Particularly, the source code of Pony builder and loader versions 1.9 and 2.0 are available for download on several underground forums.
The Pony stealer builder is a program that attackers can use to construct custom Pony bots with pre-programmed C&C addresses, where stolen data can be sent. The Pony Bot is the actual program that is used for information stealing. According to the analysis, the Bot is written primarily in assembly language. A peculiar feature of this malware that separates it from the rest of the pack is its unique decoding technique. The Bot itself does not come equipped with a decoding algorithm, instead of using just simple functions that are programmed to send encrypted information to the control server, where stolen passwords and other data are decrypted.
Even though the core feature-set of Pony trojan has not changed drastically over the course of its lifespan, newer versions of the malware gained several anti-detection features designed to prevent research and disassembly of the malware. As such, in addition to standard anti-evasion and debugging techniques, each attacker has the ability to implement various packers, including custom ones, to avoid detection by antivirus software.
With the use of Packers, the malware gains a Russian “matryoshka” nesting-doll like-design. While the payload is inactive when the package containing Pony stealer is analyzed, the final payload cannot be detected by antivirus signatures since it is hidden in the innermost and smallest package. However, once activated, the Pony loader has to unpack itself, thus revealing its presence.
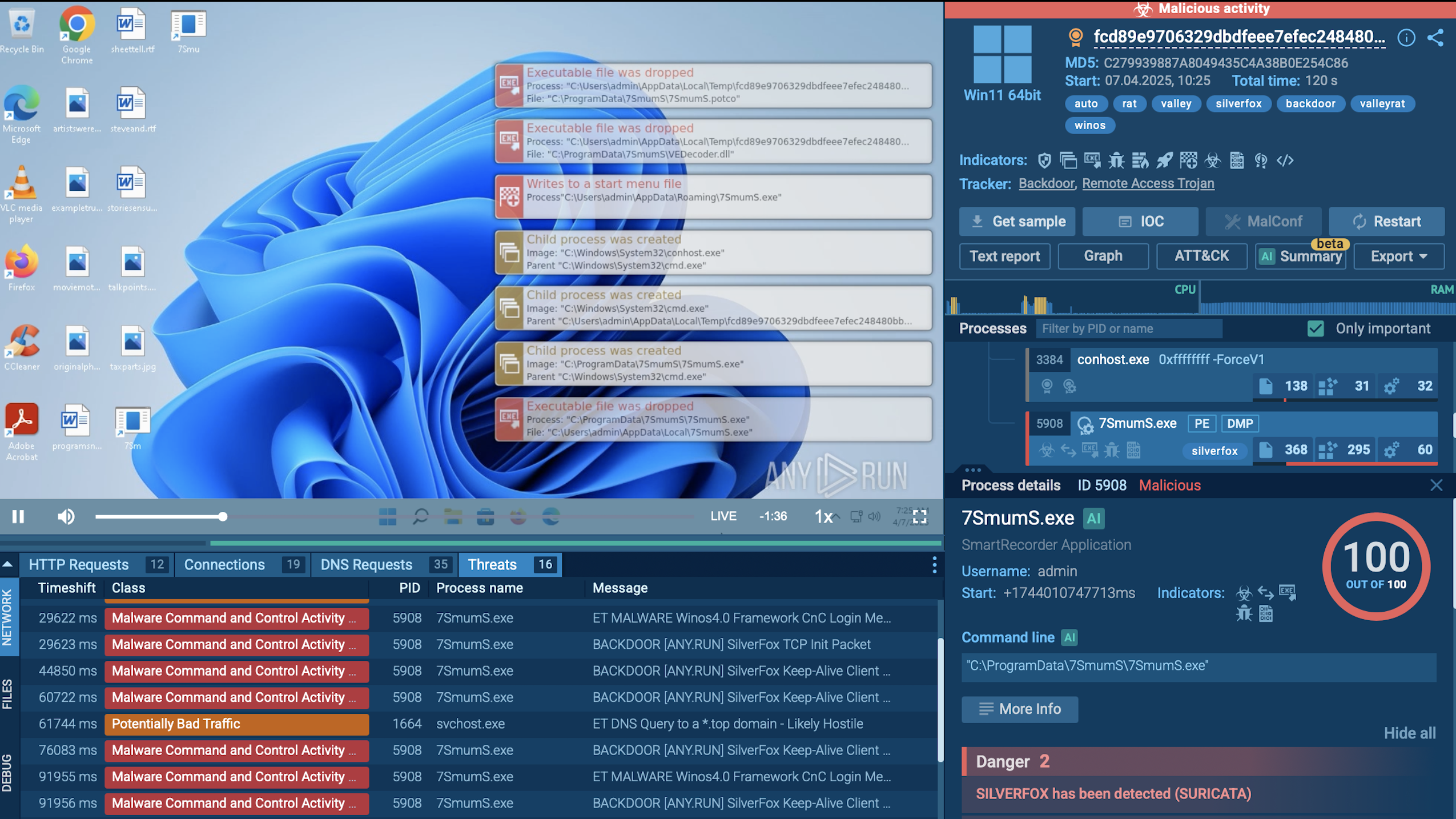
A video of a simulation recorded in ANY.RUN malware hunting service helps us to perform the analysis of the behavior of Pony in-depth.
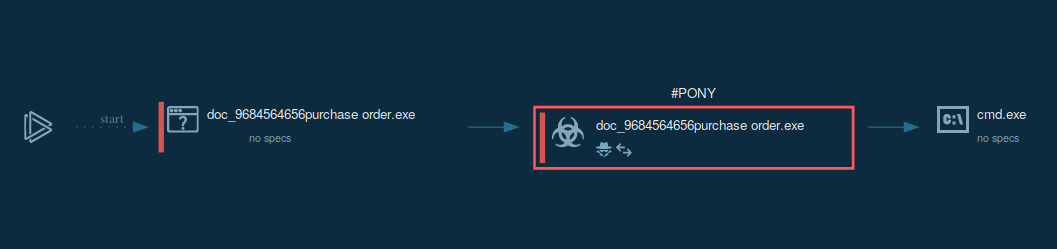 Figure 1: A process graph generated by ANY.RUN enables to examine the lifecycle of Pony in a visual form
Figure 1: A process graph generated by ANY.RUN enables to examine the lifecycle of Pony in a visual form
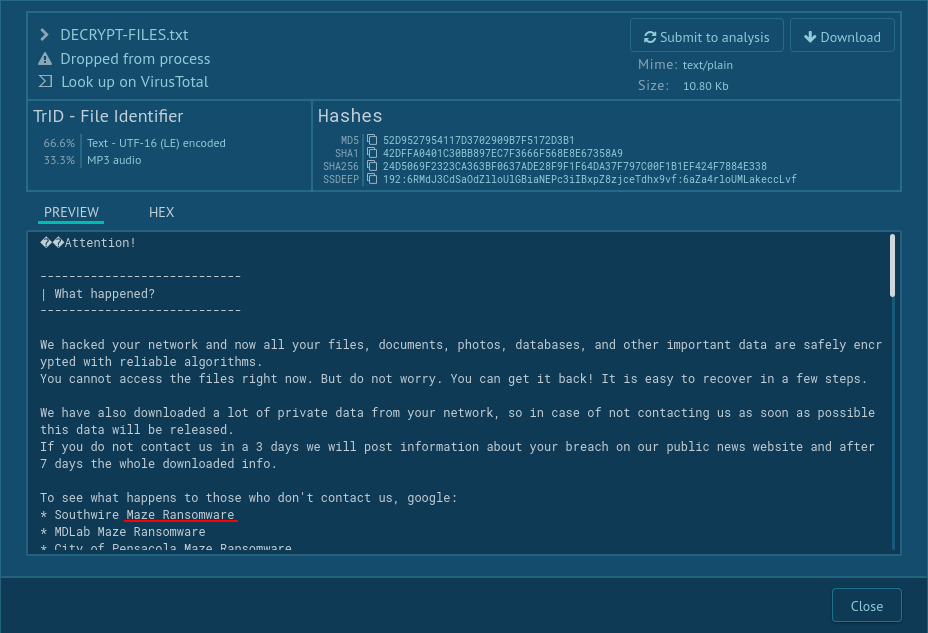
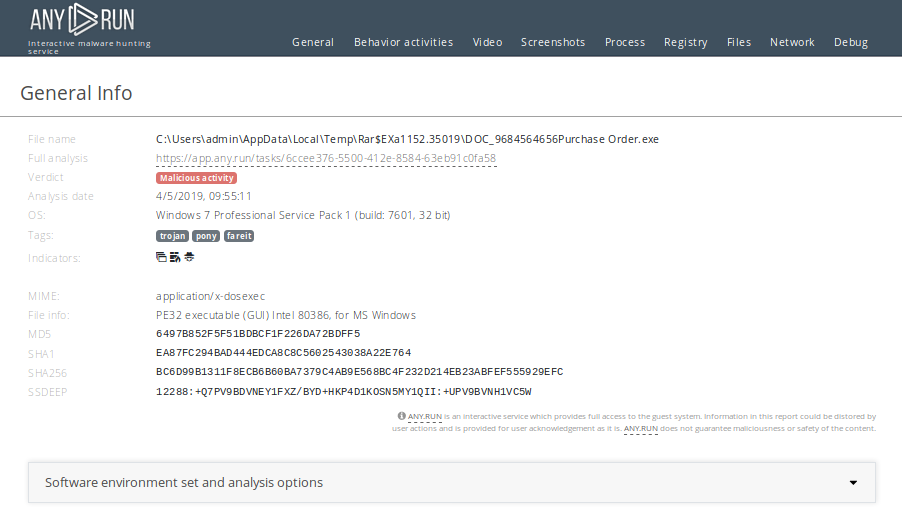 Figure 2: Customizable text reports provided by ANY.RUN gives more opportunities for research or sharing of study results
Figure 2: Customizable text reports provided by ANY.RUN gives more opportunities for research or sharing of study results
In the case of our simulation, after the user ran the malicious file, the malware launched itself. Next, the malicious executable file connected to the C2 server and started stealing information from the infected system. It should be noted that in some cases, Pony is known to download other malware to the victim’s machine.
Based on the analysis, Pony is distributed in multiple ways, including email spam campaigns, exploit kits and DNS poisoning. Also, Pony can be hidden within free downloadable online programs and can mimic legitimate software. For example, malicious emails usually include either a Microsoft Word archive or a JavaScript file. As soon as the document is downloaded and opened, Pony injects the victim’s PC and starts execution.
Another attack vector of Pony is through a compromised DNS server which is infected by another malware. In this case, the victim is redirected to a malicious website from where Pony downloads itself onto the users’ PC.
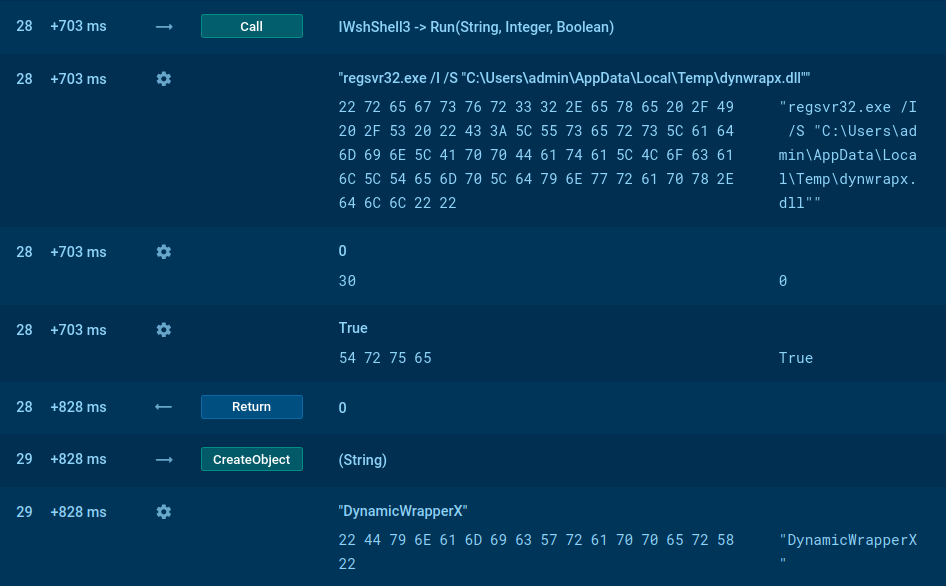
Analysts can perform an analysis of what changes the malware made in the registry. Just click on the process and then on the button "More Info" in the appeared window. Then, in the "Advanced details of process" window, switch to the "Registry changes" tab. Note that you can switch between the friendly and raw display of changes. You can also try this method while analyzing GootKit or Danabot.
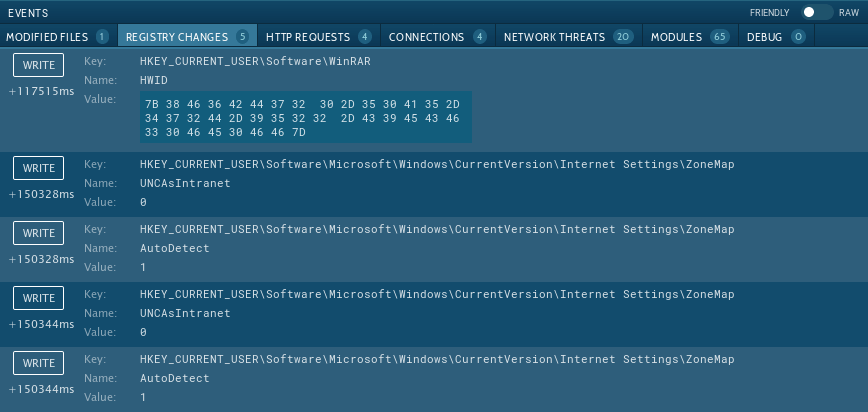 Figure 3: Registry changes made by Pony
Figure 3: Registry changes made by Pony
Availability and robust feature set helped make Pony stealer one of the most widely used information stealers. In fact, this malware is regularly being used in attacks targeting Europe and North America. The danger of Pony attacks is further enhanced by its nesting-doll-like design, where the final payload hides within a layered package, allowing to avoid easy detection. Interactive malware hunting service ANY.RUN gives researchers the ability to take a look at how this dangerous malware functions and examine its behavior in action in a safe environment.