Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


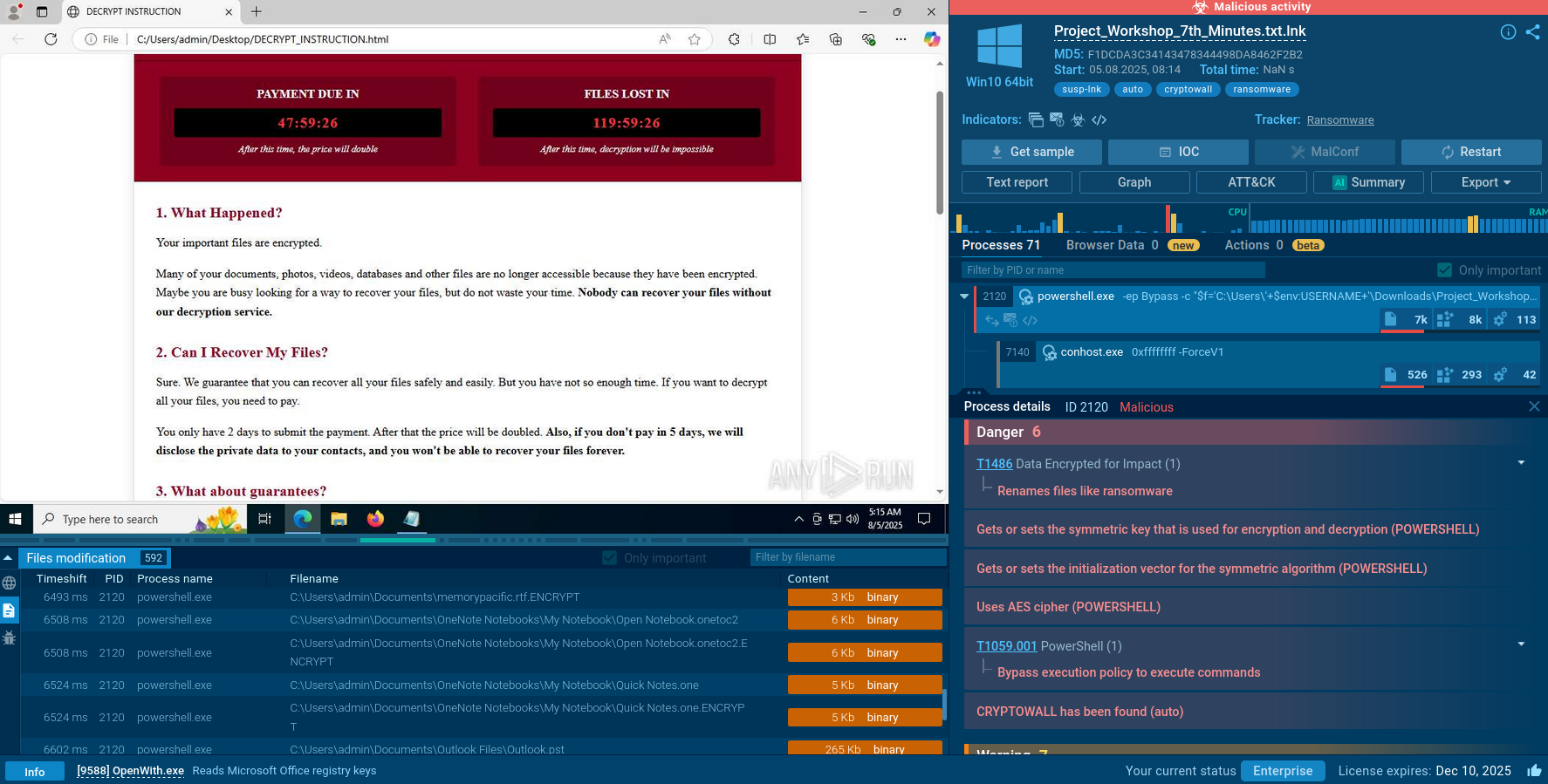
Lynx is a double extortion ransomware: attackers encrypt important and sensitive data and demand a ransom for decryption simultaneously threatening to publish or sell the data. Active since mid-2024. Among techniques are terminating processes and services, privilege escalation, deleting shadow copies. Distribution by phishing, malvertising, exploiting vulnerabilities.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
29 July, 2024
First seen
:
|
28 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
29 July, 2024
First seen
:
|
28 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Lynx is a ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) with both single and double extortion strategies. It can encrypt files and exfiltrate sensitive data with the threat of further publishing it unless a ransom is paid. Files are encrypted with a ‘.lynx’ extension, backup files like shadow copies get deleted to prevent recovery.
Presumably descendant of INC ransomware (is based on its sold source code), it emerged in July, 2024.
Lynx encrypts files using AES-128 in CTR mode and Curve25519 Donna encryption algorithms. It uses the Restart Manager API “RstrtMgr” to encrypt files that are currently in use or locked by other applications.
It prints a ransom note on any printer connected to the compromised system.
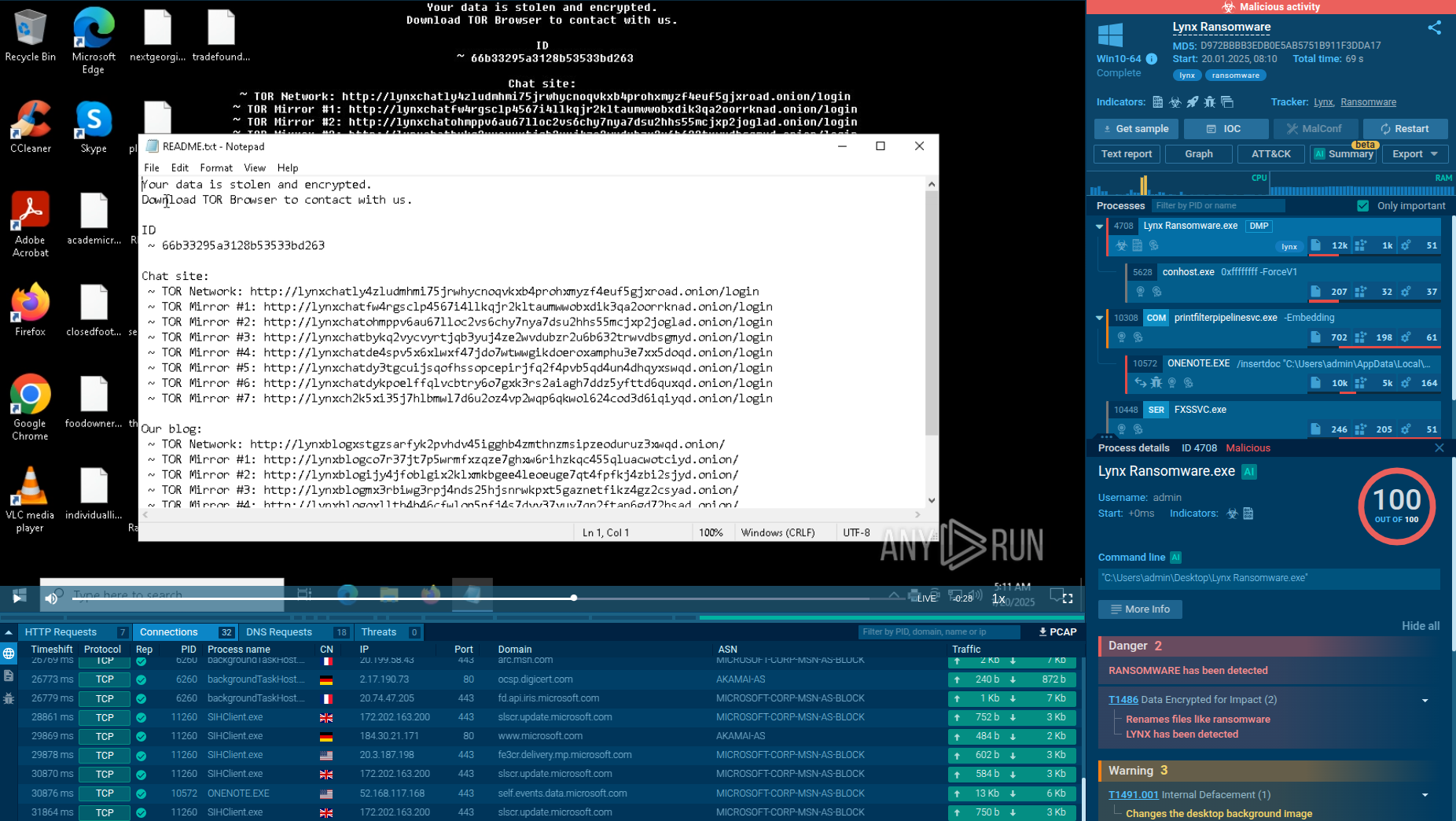 Lynx ransom note opened inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
Lynx ransom note opened inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
Distributed via targeted pishing email campaigns, software vulnerabilities, infected ads and websites, it evades detection and analysis by a number of techniques. Lynx is customizable and can deliver additional payload.
Lynx ransomware is a sophisticated malware variant renowned for its aggressive tactics and operational efficiency. Thanks to ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox, we can observe the malware's entire execution chain in a safe virtual environment.
Upon launching, Lynx parses any command-line arguments that dictate its behavior; if no arguments are provided, it defaults to encrypting all files on the system.
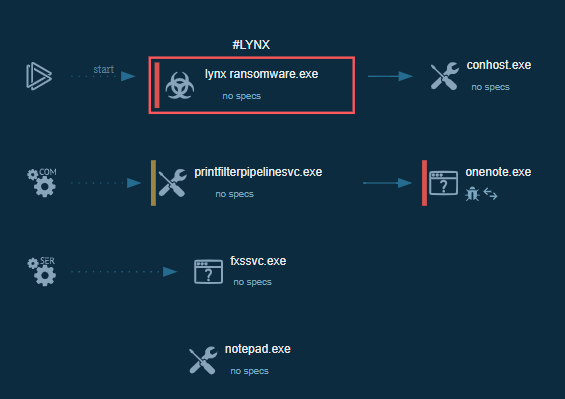 Lynx process graph displayed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Lynx process graph displayed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
One of Lynx’s first actions is to terminate processes that could interfere with the encryption. It specifically targets backup and database-related applications — such as SQL, Veeam, Backup, Exchange, Java, and even Notepad — and iterates through these on its target list to stop them.
With potential obstacles removed, Lynx enumerates directories to identify files for encryption. To broaden its reach, it can mount hidden drives and network shares. It also hinders recovery efforts by deleting shadow copies and backup partitions, making it significantly more difficult for victims to restore data without paying the ransom.
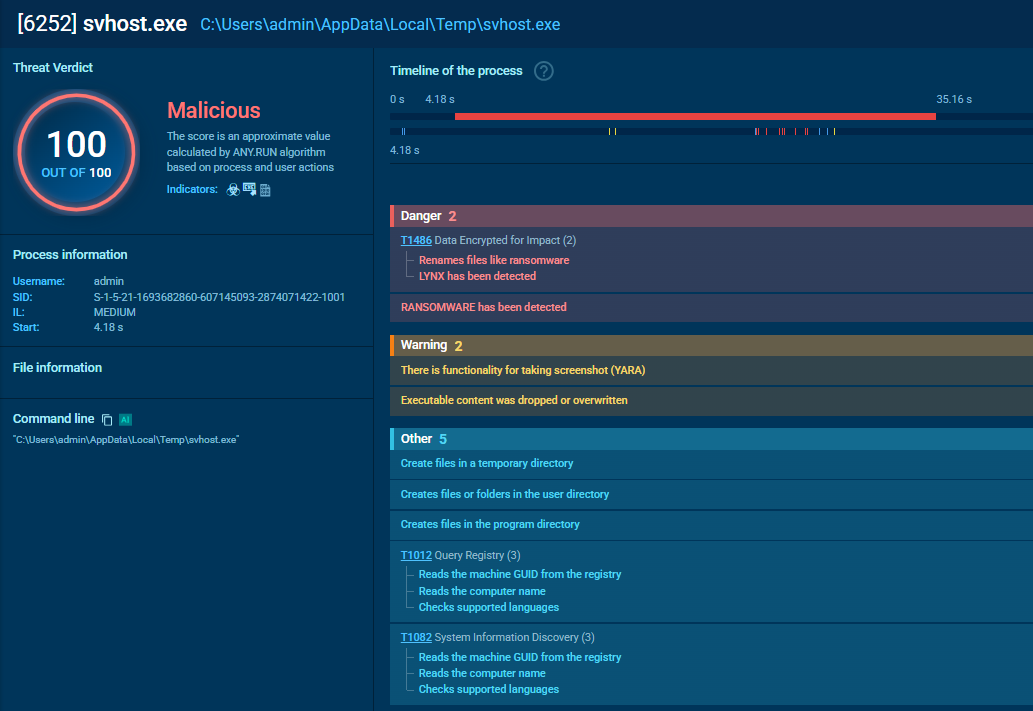 Lynx malicious process analysis in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Lynx malicious process analysis in the ANY.RUN sandbox
The malware uses robust encryption techniques, generating unique keys for each file, and appends the .lynx extension to all encrypted files. It can encrypt mounted drives, shared folders, and specified network resources.
After the encryption phase, Lynx delivers a ransom note on the victim’s desktop by changing the wallpaper, dropping a text file containing the ransom note, and placing an XPS file with the same message. This note typically provides a link to a dark web portal for paying the ransom and communicating with the attackers. Furthermore, Lynx employs “double extortion,” threatening to leak sensitive data if the ransom is not paid. This tactic amplifies pressure on victims, making Lynx a particularly formidable threat.
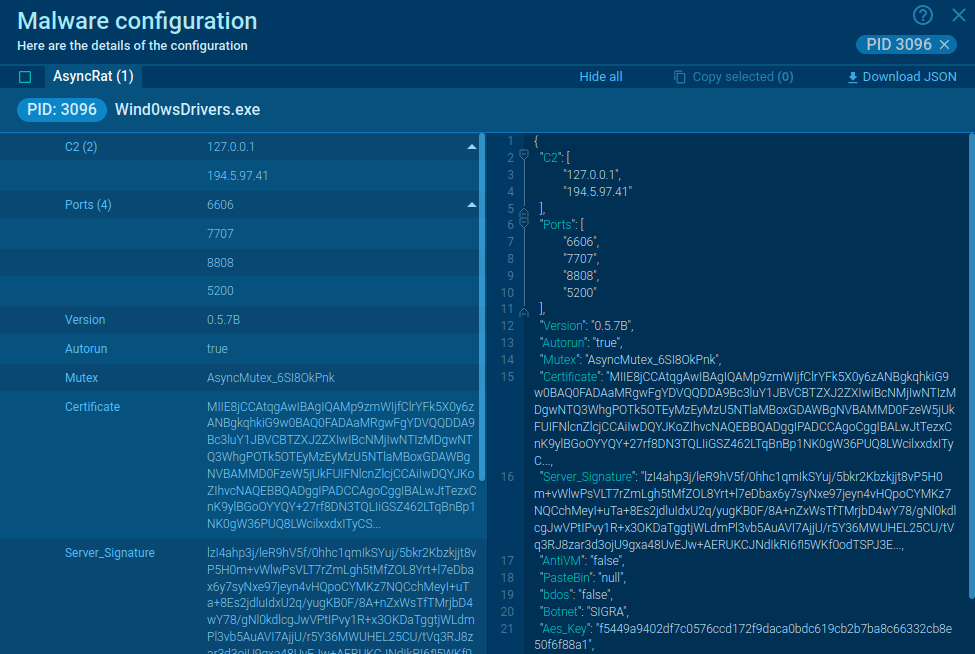
Use Threat Intelligence Lookup from ANY.RUN to study IOCs and TTPs associated with Lynx and enforce your security framework against it. Search within a database of millions of malware analyses done in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can gather relevant data for further proactive measures.
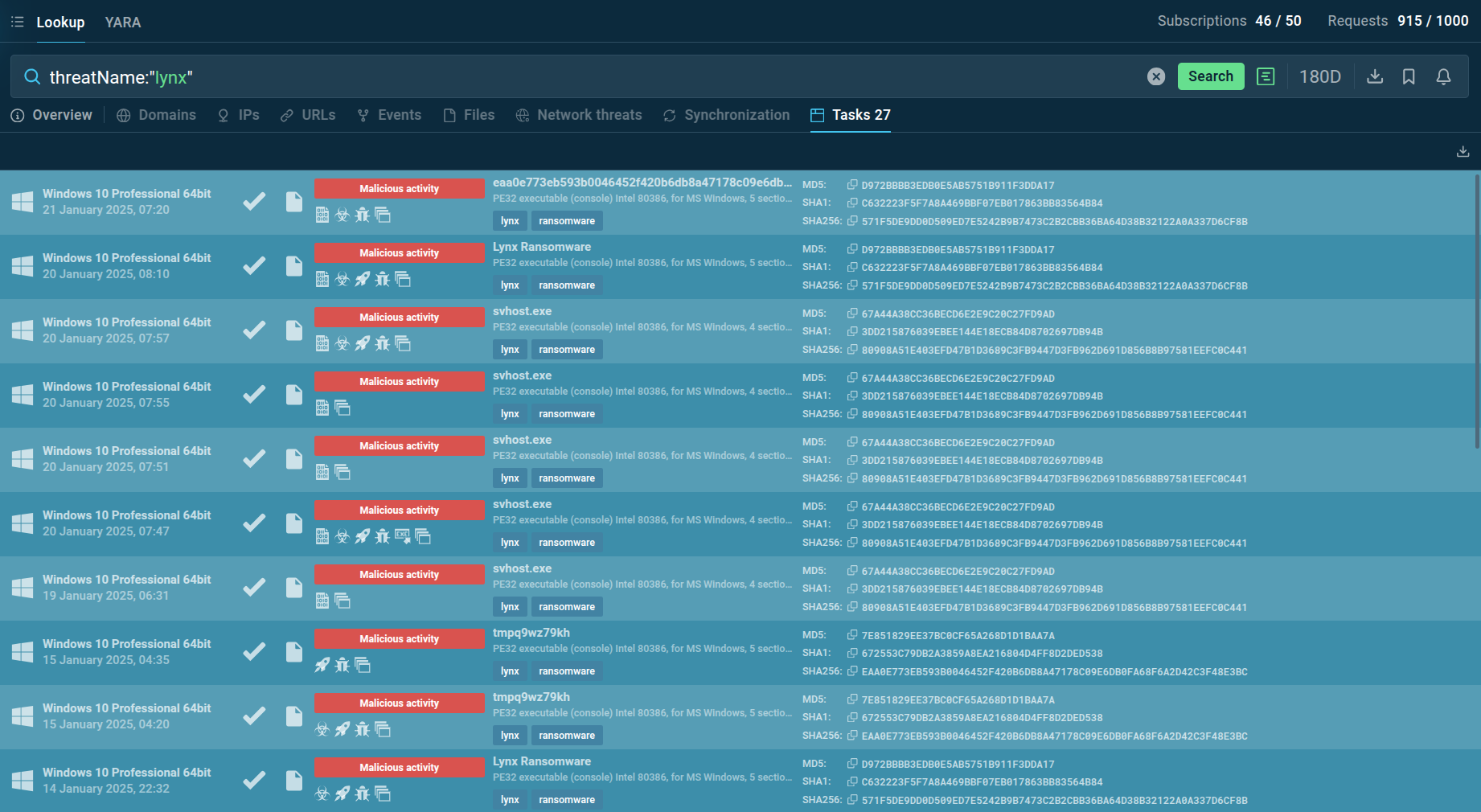 ANY.RUN’s sandbox sessions with Lynx found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
ANY.RUN’s sandbox sessions with Lynx found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
You can search directly by the threat name or use related clues like hash values or network connections. By entering a query like threatName:"lynx", you'll get a list of sandbox reports featuring the most recent analyses of Lynx samples. You can navigate to each report and explore it in detail to understand the malware's behavior and collect crucial threat intelligence.
Lynx is a highly dangerous piece of ransomware aimed both at encrypting data and stealing it to do the most damage to the victim’s operations and reputation.
By default, Lynx is set to encrypt every file on the system. But as a RaaS, it is customizable via command-line arguments to precisely select files and directories to target.
It exploits various entry points into targeted networks and uses a number of anti-malware evasion techniques. Nevertheless, sophisticated tools like ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox and Threat Intelligence Lookup successfully withstand Lynx’s defenses and allow security teams to study its behavior, get ready to detect it and protect against it.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to strengthen your security posture!