Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases
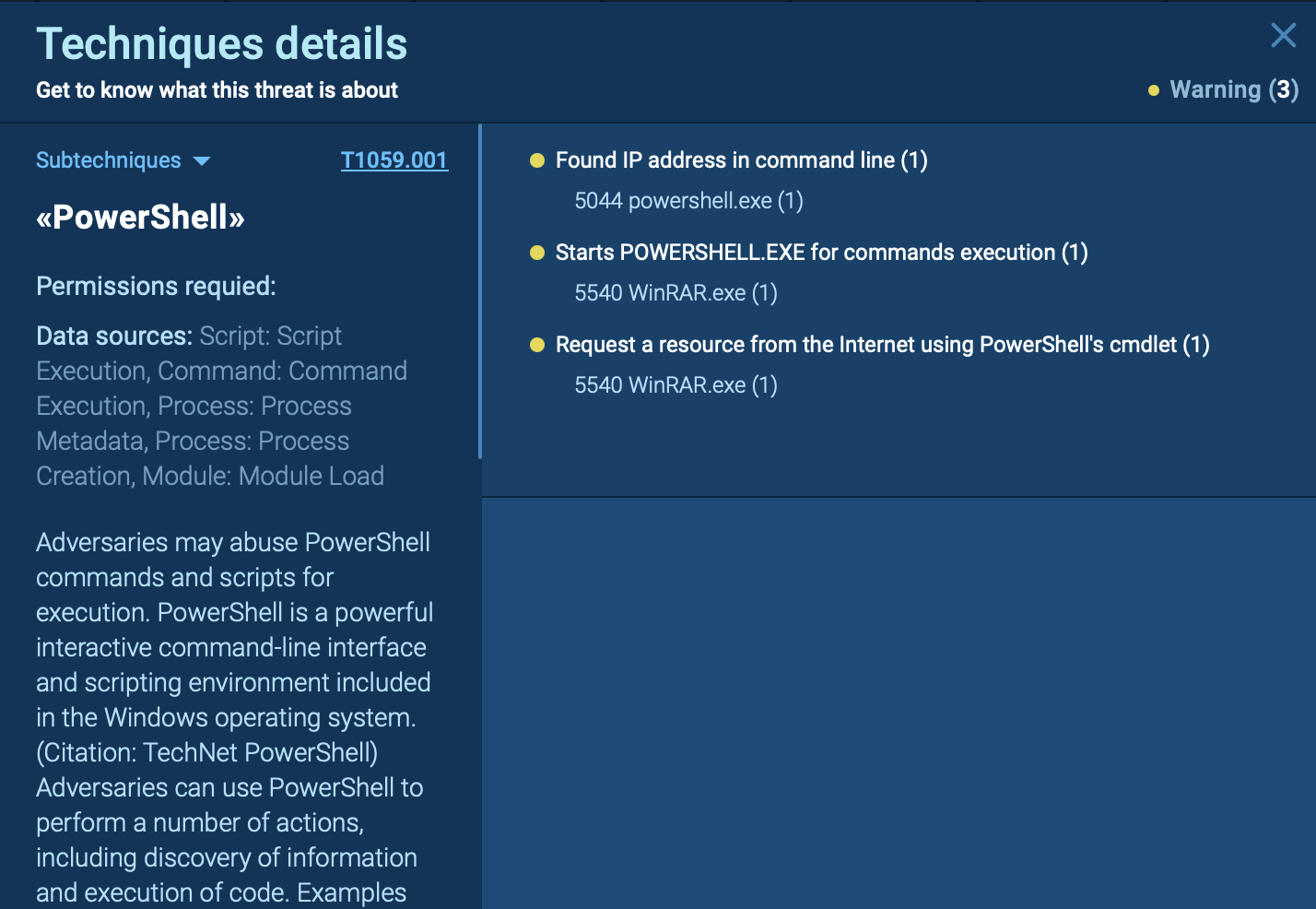
EvilProxy is a phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform that enables cybercriminals to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and hijack user sessions. It leverages reverse proxy techniques to harvest credentials and session cookies, posing a serious threat to both individuals and enterprises.
|
Phishingkit
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 820
820
 0
0

 491
491
 0
0

 2756
2756
 0
0
EvilProxy is a reverse-proxy phishing kit sold on dark-web marketplaces that has been active since mid-2022. The platform operates as a commercial service with subscription-based offerings for 10, 20, and 31 days. This advanced toolkit has fundamentally changed how cybercriminals conduct phishing attacks by providing even low-skilled threat actors with the capability to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) protections.
The toolkit got notorious for letting attackers create convincing replicas of legitimate websites while maintaining real-time communication with the authentic service. This reverse-proxy architecture allows EvilProxy to intercept and manipulate communications between victims and legitimate services without detection. The service targets major platforms including Apple, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter, GitHub, GoDaddy, and even niche platforms like PyPI.
What sets EvilProxy apart from traditional phishing kits is its sophisticated evasion capabilities. The platform incorporates advanced detection mechanisms to identify security researchers, automated analysis systems, and virtual machines. When suspicious activity is detected, EvilProxy can redirect connections to legitimate websites or completely drop connections to avoid analysis.
Similar to other phishkits like Tycoon 2FA and Sneaky2FA, EvilProxy primarily relies on phishing as its initial infection vector. Phishing emails impersonating legitimate organizations or services are the most common method. These emails often contain urgent requests, security alerts, or enticing offers to trick recipients into clicking malicious links.
The links can be disguised through URL shorteners, legitimate-looking domain names, or by embedding them within seemingly harmless attachments (e.g., HTML files). Attackers heavily leverage social engineering tactics to manipulate victims.
Once an account is compromised via EvilProxy, the attackers can use it to send out more phishing emails to the victim's contacts, leading to a chain reaction of compromises within an organization or its network.
When a user visits an EvilProxy-hosted phishing page, the malicious service:
The endpoint device itself may not show traditional signs of infection, making EvilProxy attacks particularly insidious. Users may notice unusual login notifications or unexpected account activity, but the device's security software typically cannot detect the attack since no malicious code is installed locally.
EvilProxy poses severe threats to businesses and organizations across multiple dimensions:
EvilProxy operates through a reverse-proxy architecture that works as an intermediary between victims and legitimate services. The operation involves several key components:
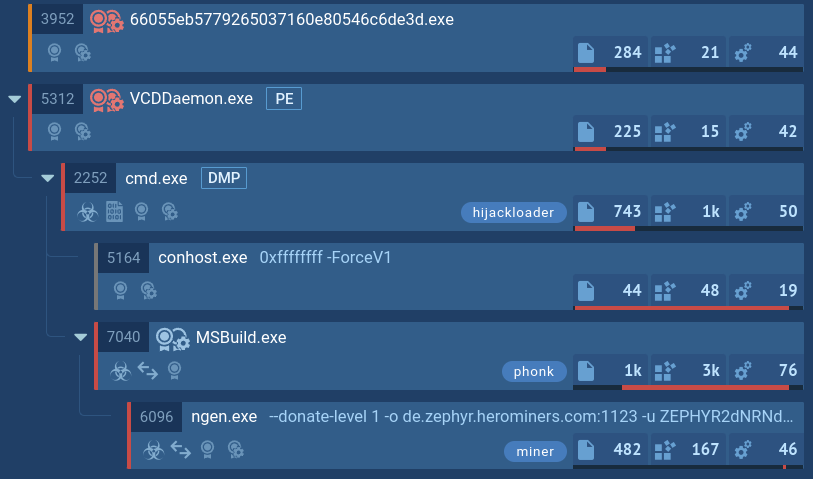
ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox contains thousands of EvilProxy samples that can be found with the aid of ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup:
 EvilProxy malware samples found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
EvilProxy malware samples found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
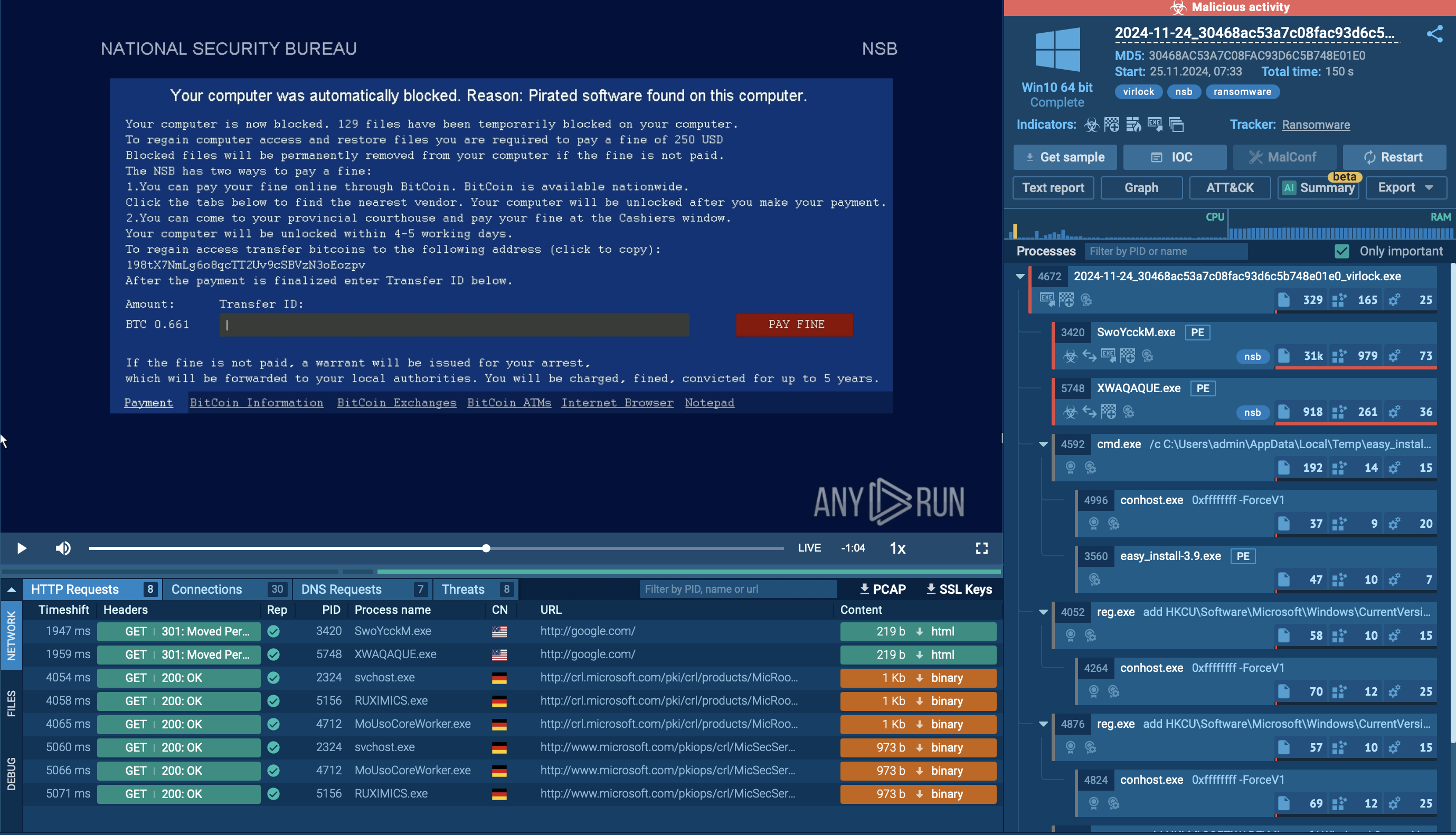
You can choose a freshly submitted analysis session and view EvilProxy in action along with its network connections, process details, attackers’ TTPs, and IOCs extracted from the malware’s configuration.
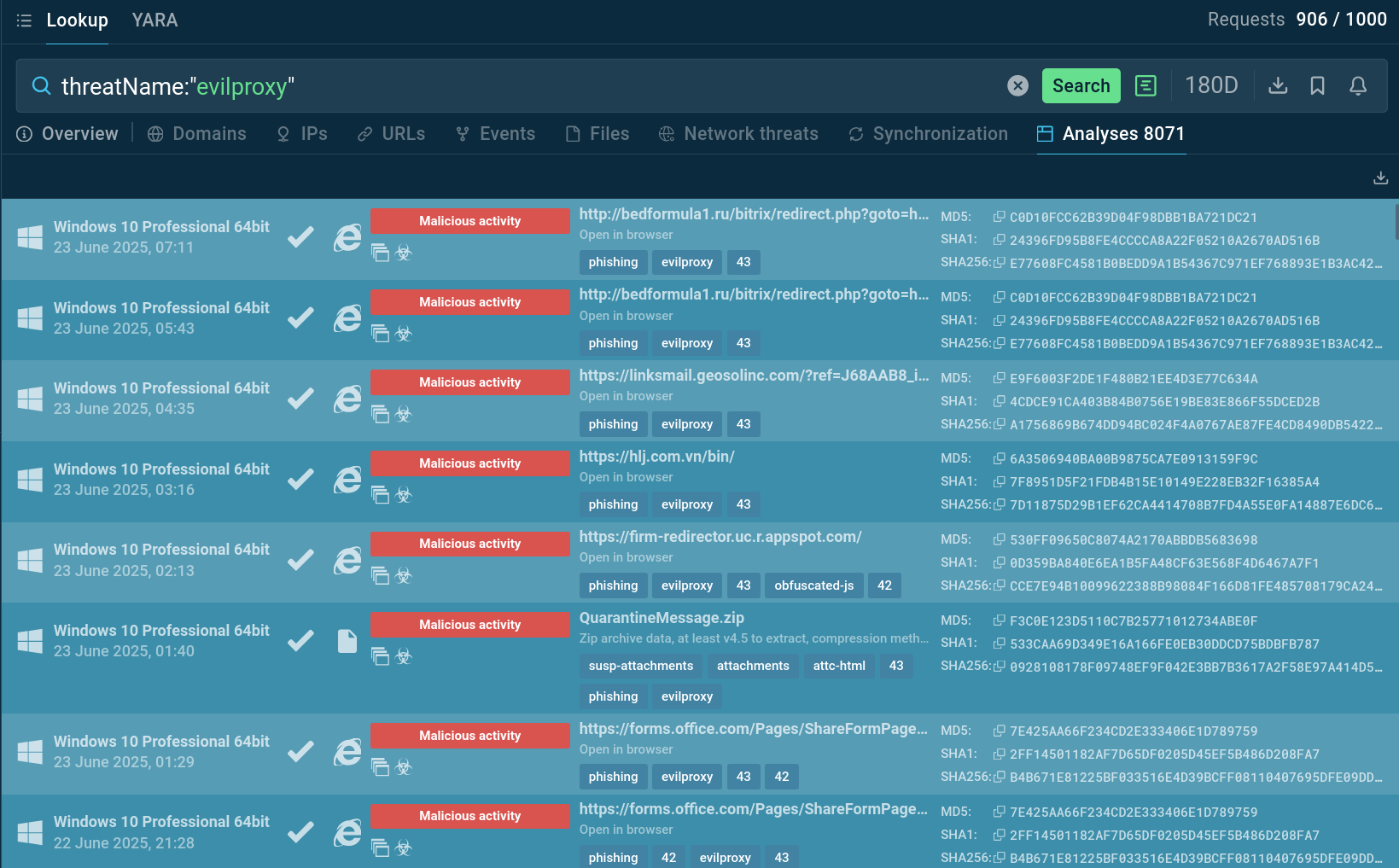
Watch an analysis session of EvilProxy fresh sample
 EvilProxy attack analysis in ANY.RUN Interactive Sandbox
EvilProxy attack analysis in ANY.RUN Interactive Sandbox
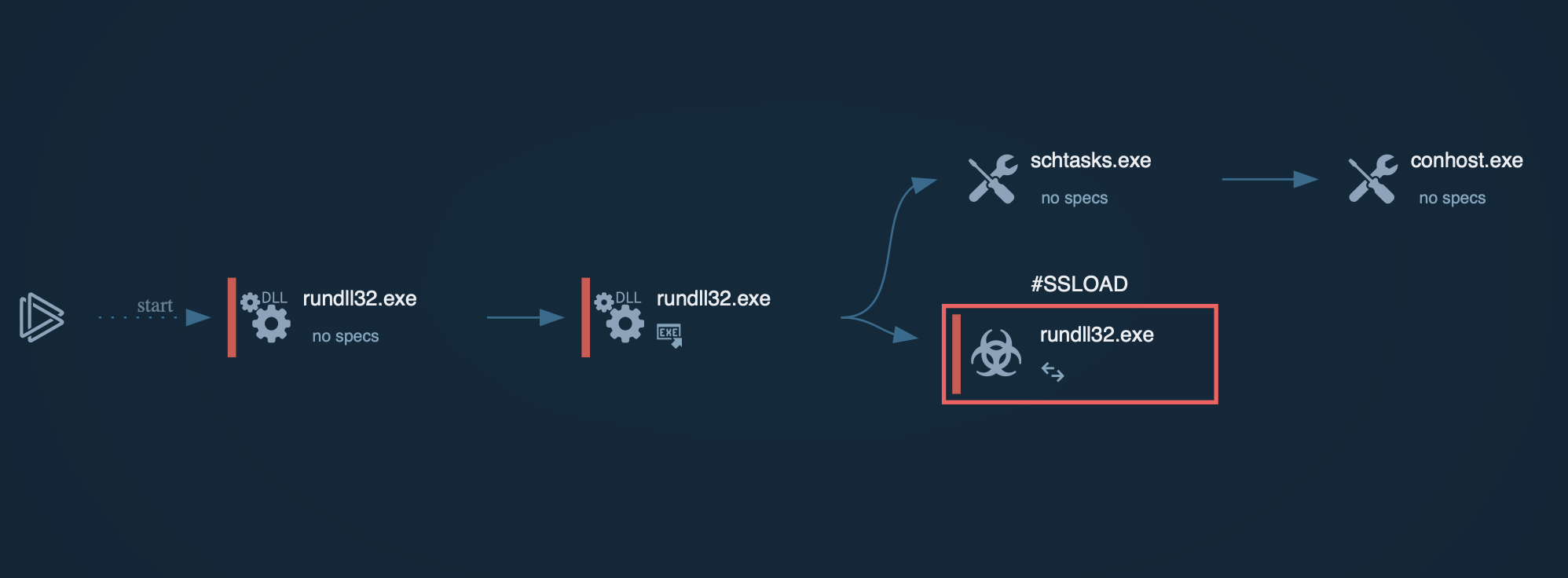
The execution chain of the EvilProxy phishing kit begins when a victim receives a phishing email that appears to originate from a trusted service or brand, such as DocuSign, Adobe, Concur, or another legitimate-looking website. These emails often contain a malicious link that exploits an open redirect vulnerability on a legitimate domain, allowing attackers to bypass email security filters and avoid detection.
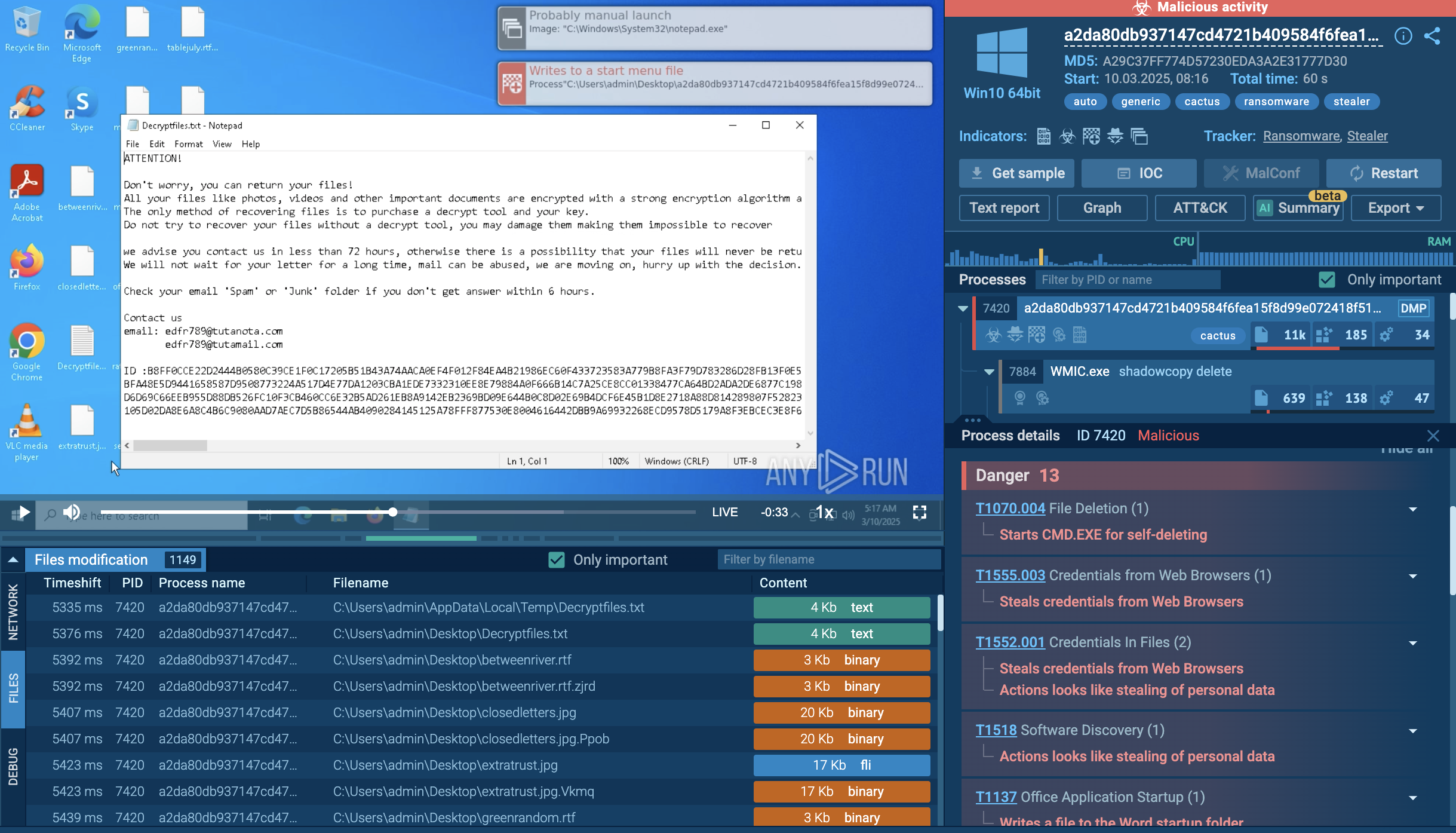
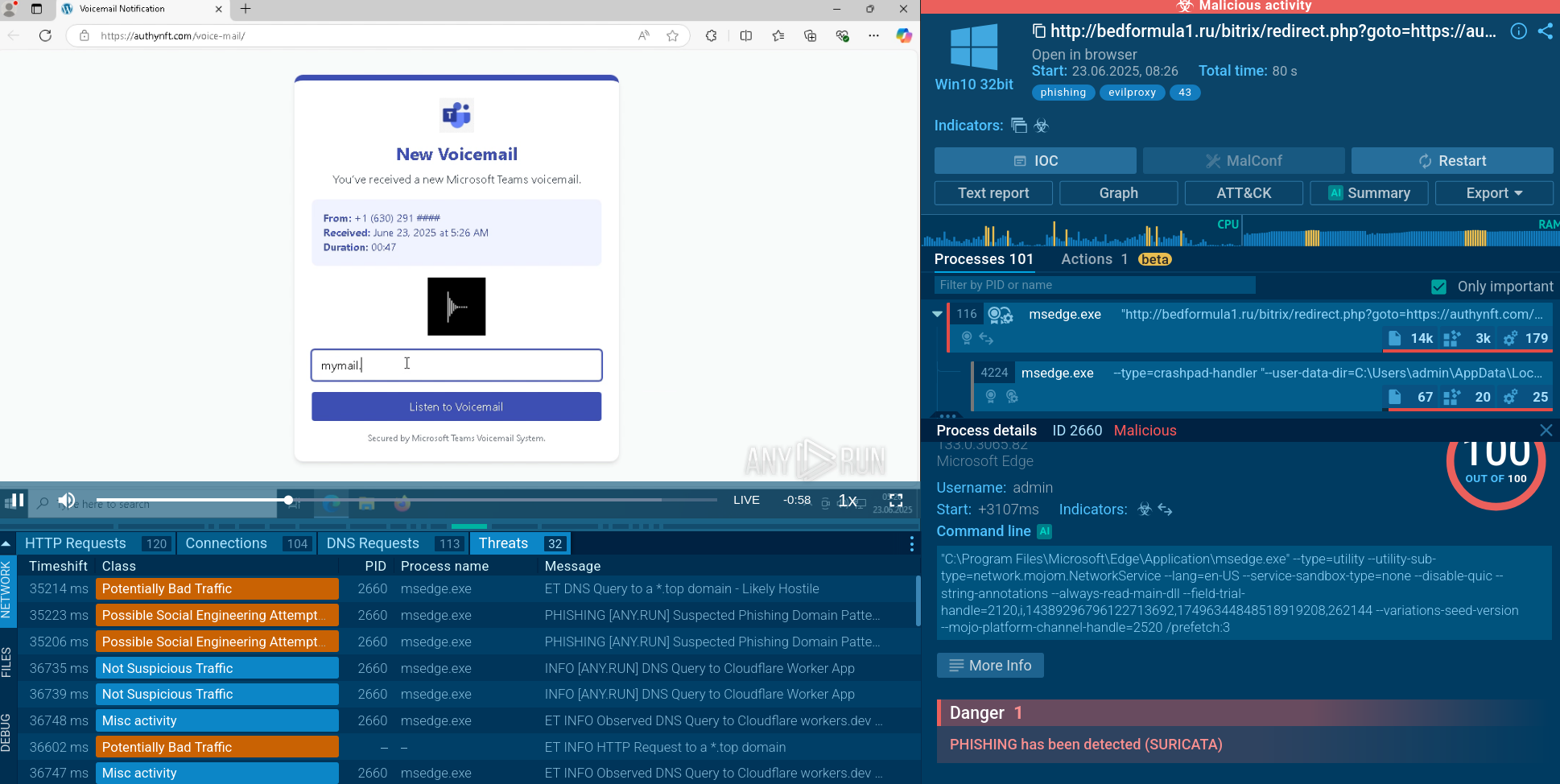
When the victim clicks the link, they are redirected through several legitimate websites before landing on a phishing page that impersonates a genuine login portal—typically Microsoft 365 or a similar service. In one observed task, the lure involved a fake voicemail message that prompted the user to enter their email address, after which they were redirected to a counterfeit Microsoft login page. Another case involved a fake "Secure Vault" prompt.
View another analysis session of EvilProxy
 EvilProxy attack abusing Secure Vault
EvilProxy attack abusing Secure Vault
The phishing pages are powered by the EvilProxy framework, which acts as a reverse proxy. It fetches live content from the real login page and displays it to the victim, making the phishing site look legitimate. As the victim enters their username, password, and two-factor authentication (2FA) code, EvilProxy intercepts these credentials in real time. The stolen credentials and 2FA tokens are immediately used on the attacker’s side to generate a valid session cookie, effectively bypassing MFA protections.
The attacker hijacks the session by proxying the victim’s traffic, allowing them to impersonate the victim and access the legitimate service without needing to re-enter credentials or 2FA tokens. This enables persistent access to the account. To evade detection, EvilProxy employs techniques such as browser fingerprinting, IP reputation checks, and filtering out connections from security researchers, bots, VPNs, proxies, Tor nodes, and virtual machines.
ANY.RUN’s Residential Proxy feature in the Sandbox helps users mask their traffic to appear as if it originates from real consumer devices rather than hosting environments, enabling full observation of the phishing attack chain without being blocked.
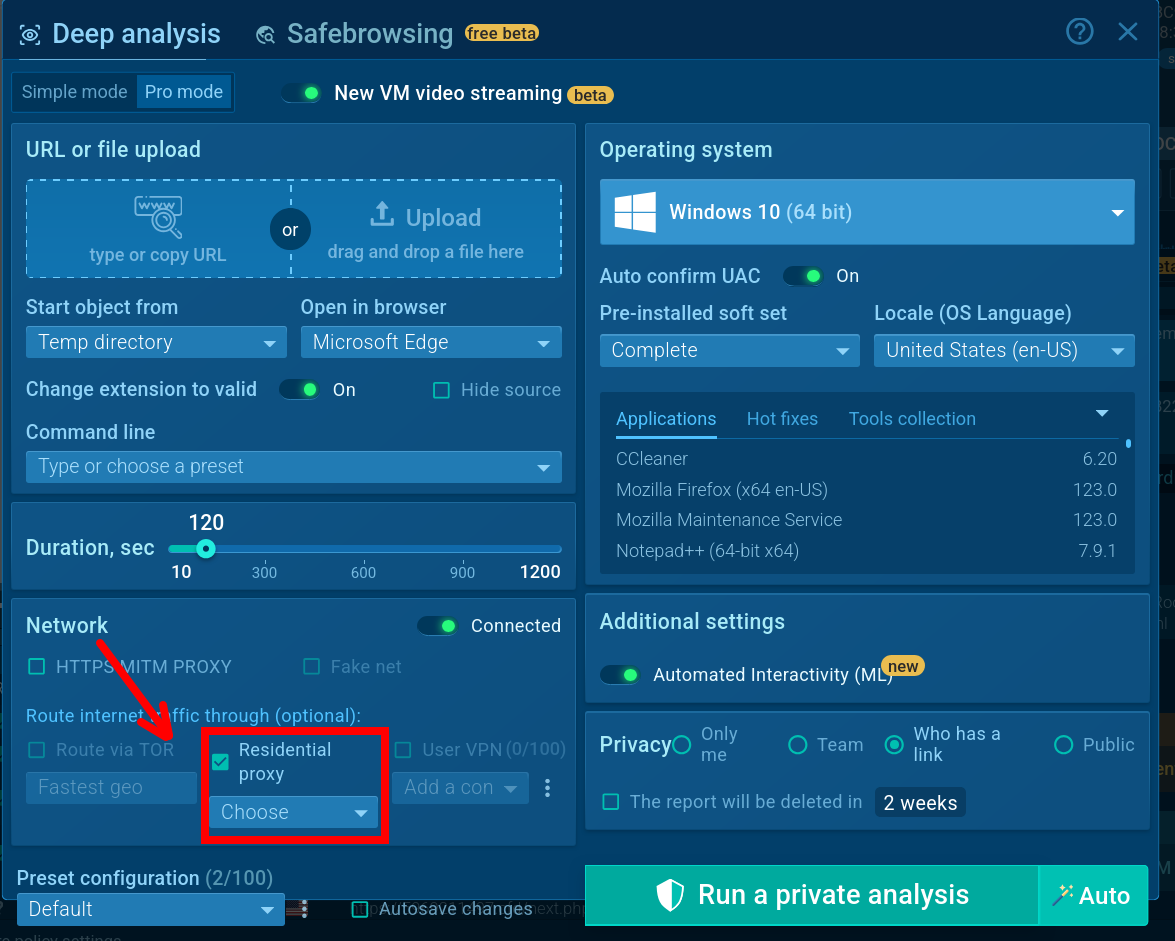 Set up Residential Proxy when starting a new analysis in Interactive Sandbox
Set up Residential Proxy when starting a new analysis in Interactive Sandbox
Threat intelligence provides actionable data for proactively defending against EvilProxy and the like.
ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup supports quick IOC checks for immediate verdicts but also allows deep research that brings understanding of malware’s behaviors, architecture, and tactics.
Extract IOCs from Sandbox analyses and explore them further via Threat Intelligence Lookup:
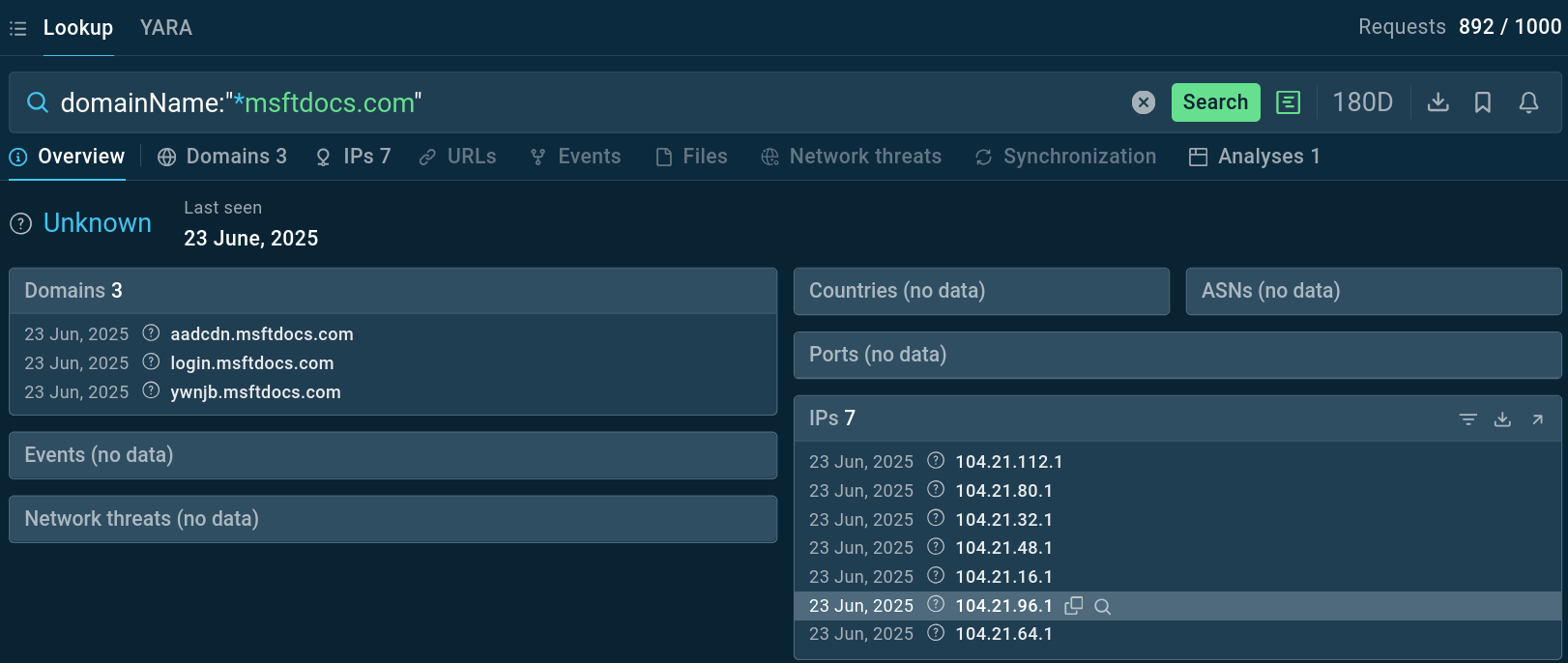 Search for EvilProxy-associated domain IOCs by pattern
Search for EvilProxy-associated domain IOCs by pattern
Threat intelligence empowers defenders to:
EvilProxy is a powerful weapon in the phishing landscape, offering a turnkey solution for bypassing MFA and hijacking sessions. It demonstrates the growing professionalization of cybercrime and underscores the urgent need for organizations to upgrade their defenses. Traditional security measures are no longer enough—organizations must adopt phishing-resistant MFA, leverage threat intelligence, and continually train users to recognize the signs of these highly convincing attacks.
Gather actionable intelligence via ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup: start with 50 trial requests.