Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


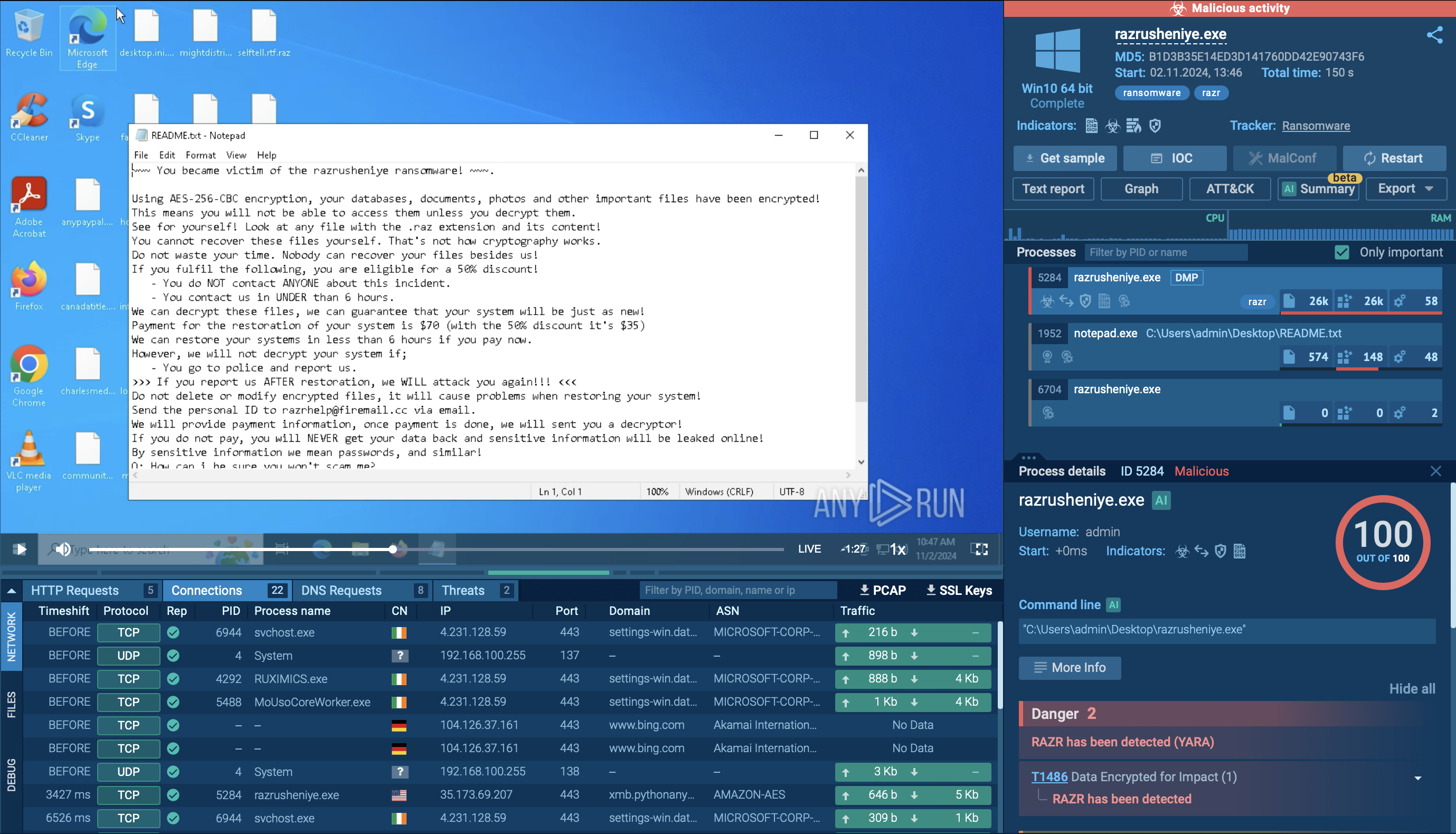
Amadey is a formidable Windows infostealer threat, characterized by its persistence mechanisms, modular design, and ability to execute various malicious tasks.
|
Infostealer
Type
:
|
Likely ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
13 October, 2018
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Infostealer
Type
:
|
Likely ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
13 October, 2018
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 450
450
 0
0

 2349
2349
 0
0

 4548
4548
 0
0
First seen about 5 years ago, Amadey is a modular bot that enables it to act as a loader or infostealer. It is designed to perform a range of malicious activities, including reconnaissance, data exfiltration, and loading additional payloads, which range from banking trojans to DDoS tools. It targets all versions of Microsoft Windows.
This malware’s capabilities include:
While many adversaries primarily use this malware as a keylogger to steal credentials, it can also transform infected devices into spam email senders or add them to a botnet that adversaries use to launch DDoS attacks.
However, that’s not everything this threat is capable of. Owing to its modular design, Amadey can significantly expand its range of attack targets, enabling the extraction of a broader variety of information, such as files, login credentials, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Furthermore, current Amadey variants can recognize more than 14 antivirus solutions. This ability allows the malware to intelligently deploy a payload designed to evade the specific antivirus product installed on the compromised device.
In addition, this malware can move laterally, propagating to devices within the same network by pushing EternalBlue exploit onto victims. Although outdated, EternalBlue remains relevant, especially in public sectors like government and education, where end-of-life software usage is widespread.
As for the origin of this threat, little is known at this point. Older activity associated it with GandCrab campaigns, which might connect Amadey to the REvil gang or one of their affiliates. Additionally, Amadey is distributed on Slavic-speaking underground forums, which possibly places its origin in one of the ex-USSR territories.
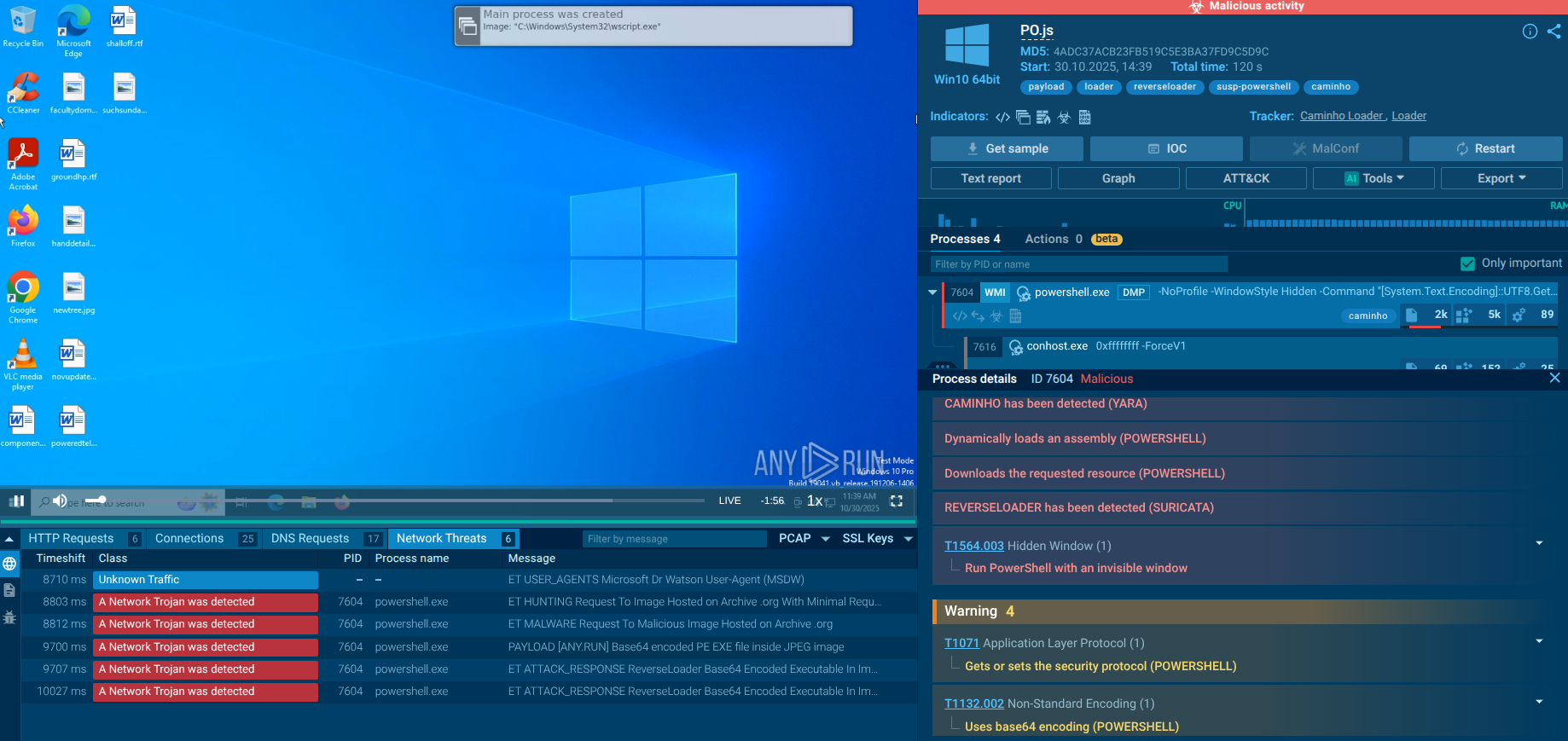
In ANY.RUN, users can safely detonate Amadey samples and analyze it dynamically in a fully interactive cloud sandbox. Our service automatically collects and displays the execution data in user-friendly formats, such as this process graph.
Analyze malware for free in a fully interactive cloud sandbox – sign up now!
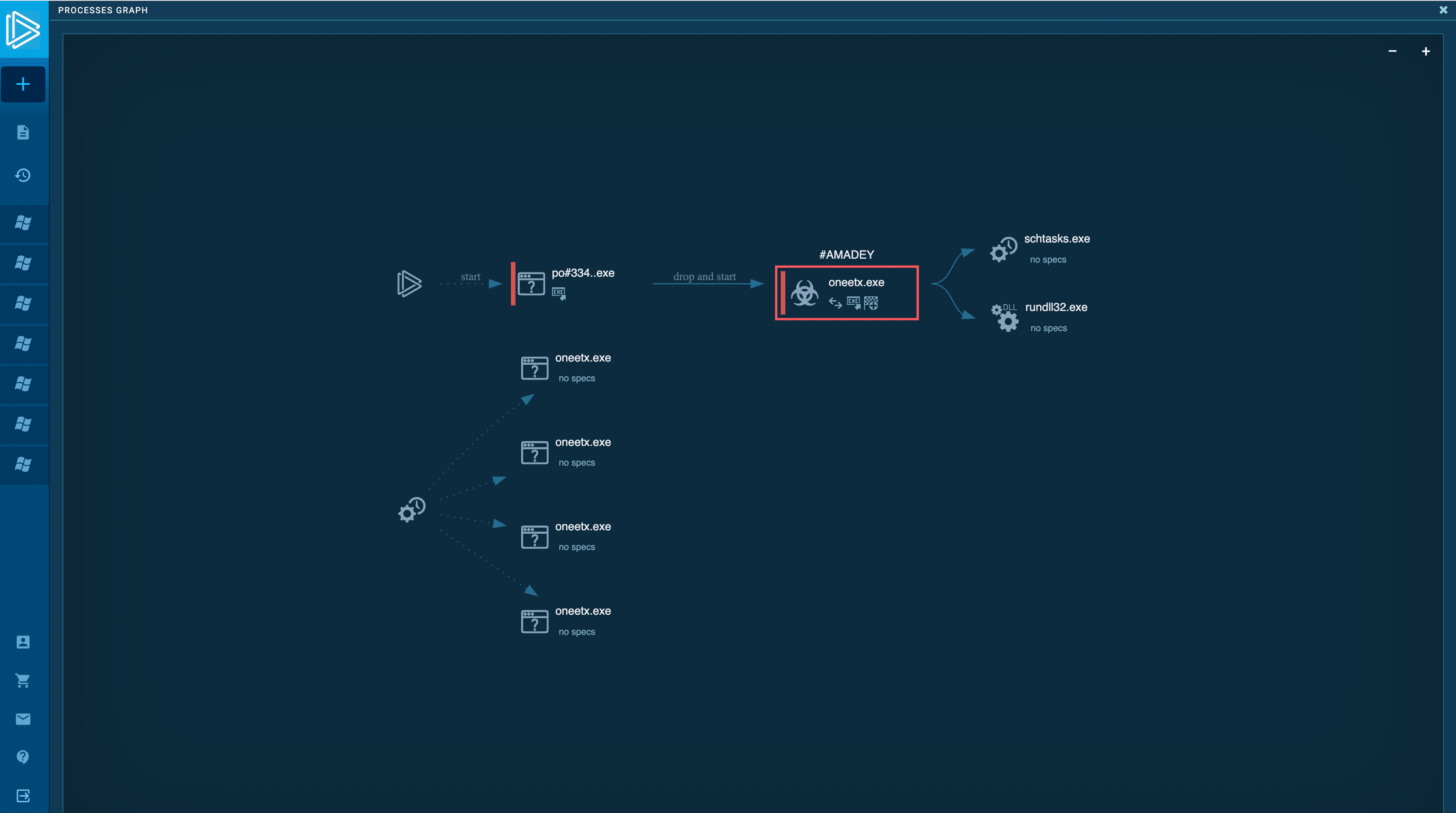 Figure 1: A graph showing Amadey’s execution process
Figure 1: A graph showing Amadey’s execution process
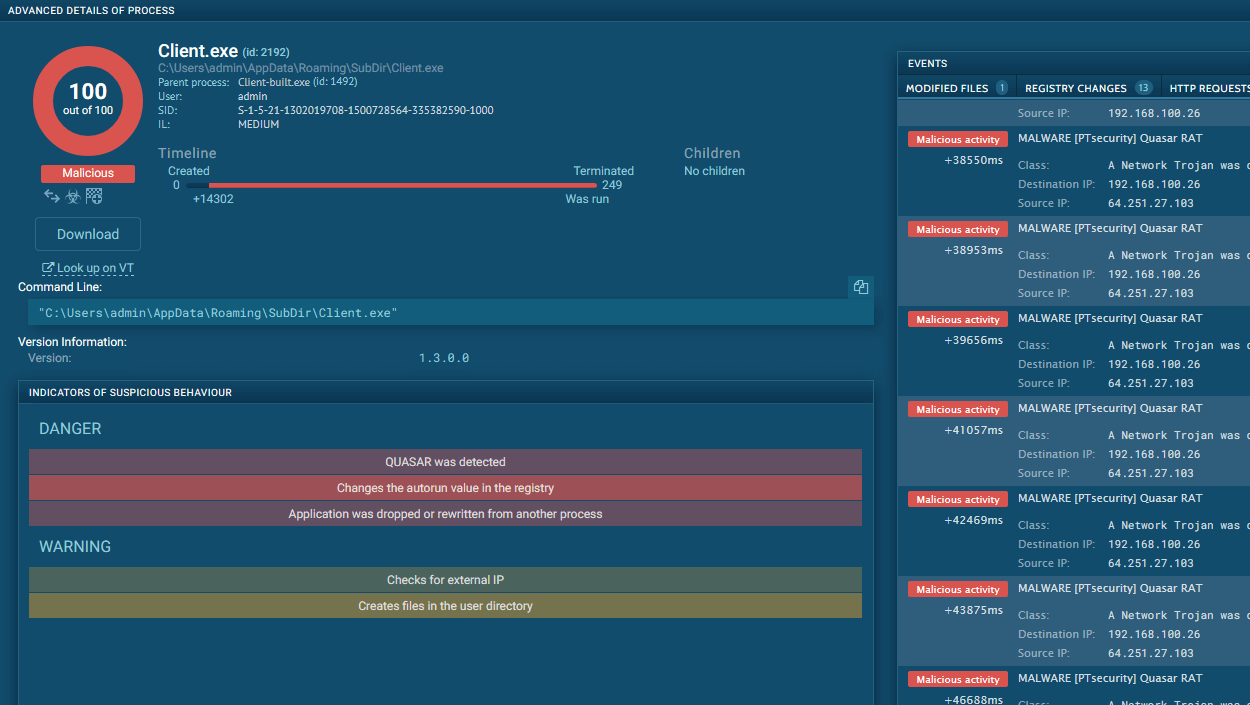
ANY.RUN detects Amadey using Suricata rules, allowing analysts to identify both new and old samples from this family. We also provide configuration details. This way, analysts can access important sample information like its version, options, and C2 addresses. The configuration is typically extracted within the first 10 seconds of launching a task. This ensures quick access to information.
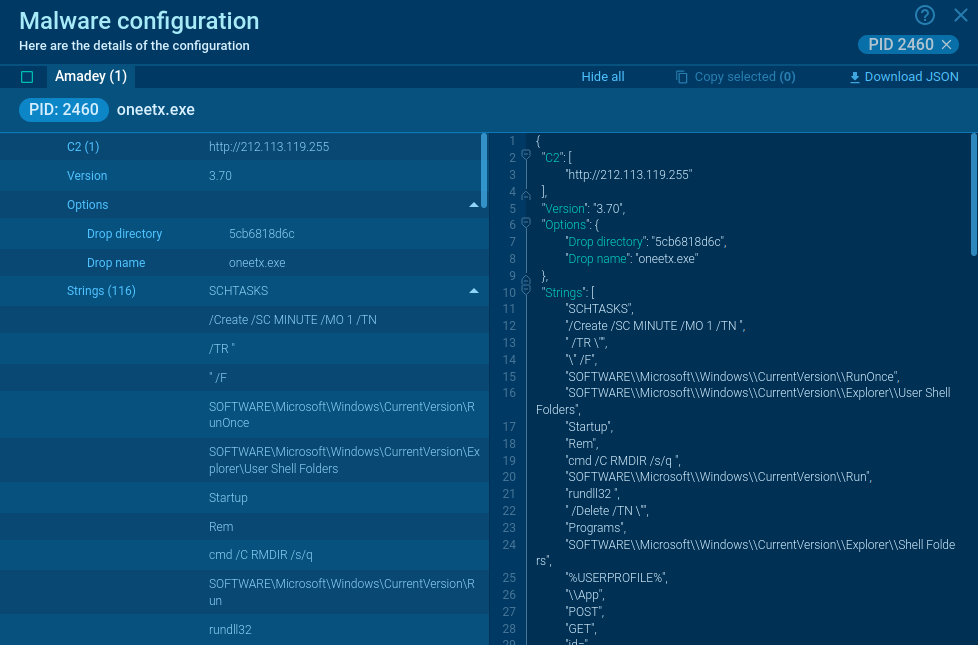 Figure 2: Amadey’s malware configuration
Figure 2: Amadey’s malware configuration
Once, when Amadey initiates its execution, the malware duplicates itself into a TEMP folder (sometimes naming itself bguuwe.exe). Following that, it modifies the Registry and creates a scheduled task to achieve persistence. Subsequently, Amadey sets up C2 communication and transmits a system profile to the adversary's server. While active, Amadey takes screenshots at regular intervals and stores them in the TEMP directory, ready to be transmitted to the C2 server with subsequent POST requests.
Amadey often serves as a loader for other malicious programs, such as in this task.
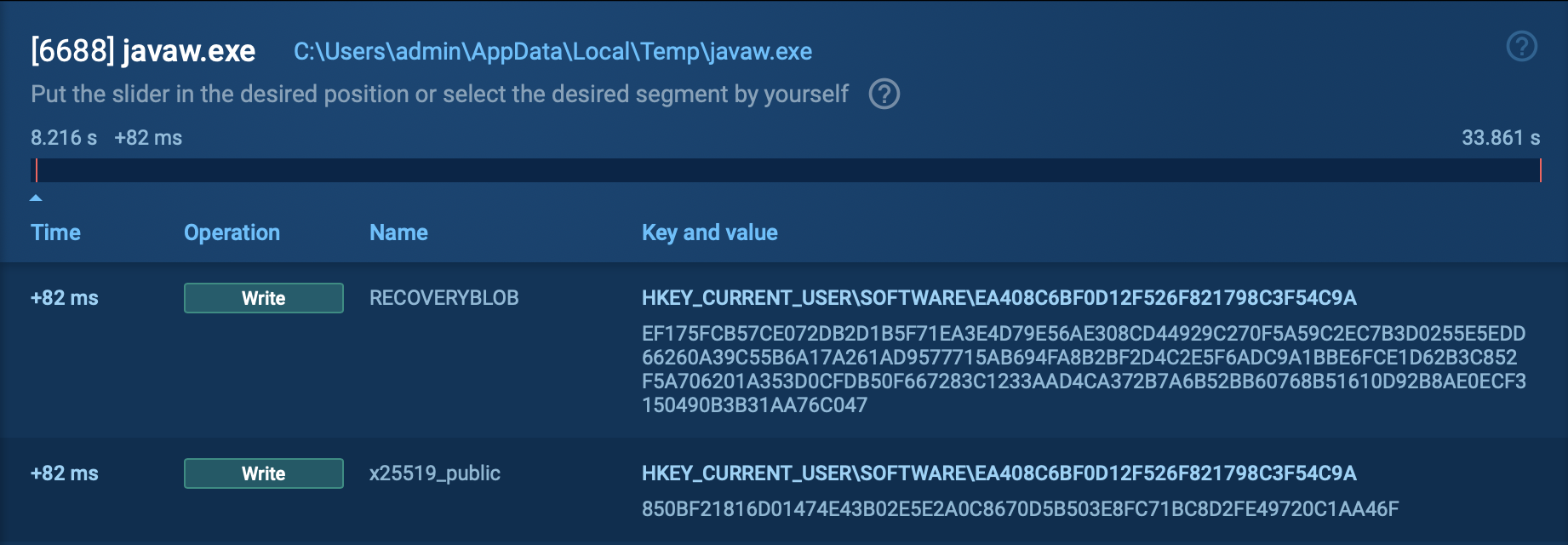
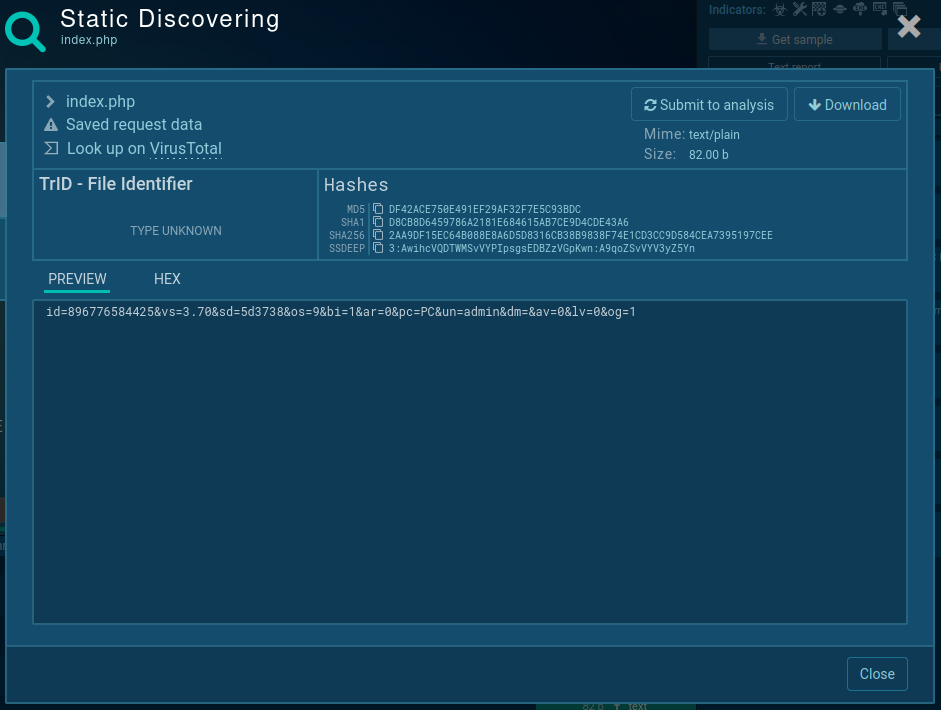
Also, Amadey has a very specific structure of POST requests, that can be used to identify it with a high degree of probability:
Figure 3: Information about infected machine, exfiltrated by Amadey and sent to C2
Amadey primarily relies on spear-phishing emails containing malicious attachments, such as Microsoft Office documents, to target specific organizations or individuals. The email content is carefully crafted to appear legitimate, enticing the victim to open the attachment.
Alternatively, Amadey can employ exploit kits (Fallout and Rig), drive-by downloads, or be dropped as a payload by other malware (in recent cases it was distributed by SmokeLoader).
Amadey malware presents a notable challenge for cybersecurity researchers. Its persistence and evasion techniques, coupled with a highly customizable modular architecture, make it a high-level threat. Understanding its various infection vectors, exploitation methods, and malicious activities is essential to develop effective countermeasures and improve our overall cybersecurity posture.
You can efficiently detect and examine threats such as Amadey, with the help of ANY.RUN interactive sandbox, which provides analysis results in minutes.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!