Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Meduza Stealer is an information-stealing malware primarily targeting Windows systems, designed to harvest sensitive data such as login credentials, browsing histories, cookies, cryptocurrency wallets, and password manager data. It has advanced anti-detection mechanisms, allowing it to evade many antivirus programs. The malware is distributed through various means, including phishing emails and malicious links. It’s marketed on underground forums and Telegram channels.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2023
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2023
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
Meduza Stealer is a sophisticated piece of information-stealing malware designed to target a wide range of sensitive data on infected systems. Its execution process is systematic, involving several key stages that ensure efficient data collection while evading detection.
First discovered in 2023, it has quickly become notorious for its wide-reaching capabilities, targeting over 100 web browsers and 107 cryptocurrency wallets. Meduza can collect data such as login credentials, browser history, bookmarks, autocomplete fields, and even sensitive information stored in applications like Telegram, Discord, and Steam.
It has an advanced structure that allows it to operate stealthily, using several techniques to evade detection by antivirus programs and other security measures.
Meduza Stealer is distributed through a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model on underground forums and Telegram, making it accessible to cybercriminals with varying technical skill levels. For a subscription fee, attackers can customize Meduza Stealer to suit their needs.
Once it infects a system, the malware establishes communication with a Command and Control (C2) server to upload stolen data. A web panel allows attackers to view the exfiltrated information, which can include operating system details, IP addresses, and the nature of the stolen data.
Meduza Stealer collects a wide variety of sensitive data, including login credentials, browsing history, cookies, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Here are the main technical functionalities of this malware:
Meduza Stealer performs geolocation checks on the infected system using the victim's IP address. If the location matches a region in its exclusion list, the malware halts its operations, thus avoiding detection and action in certain regions.
This malware can be delivered via malicious files like .exe, .doc, and .zip attachments, typically spread through phishing emails and malicious links.
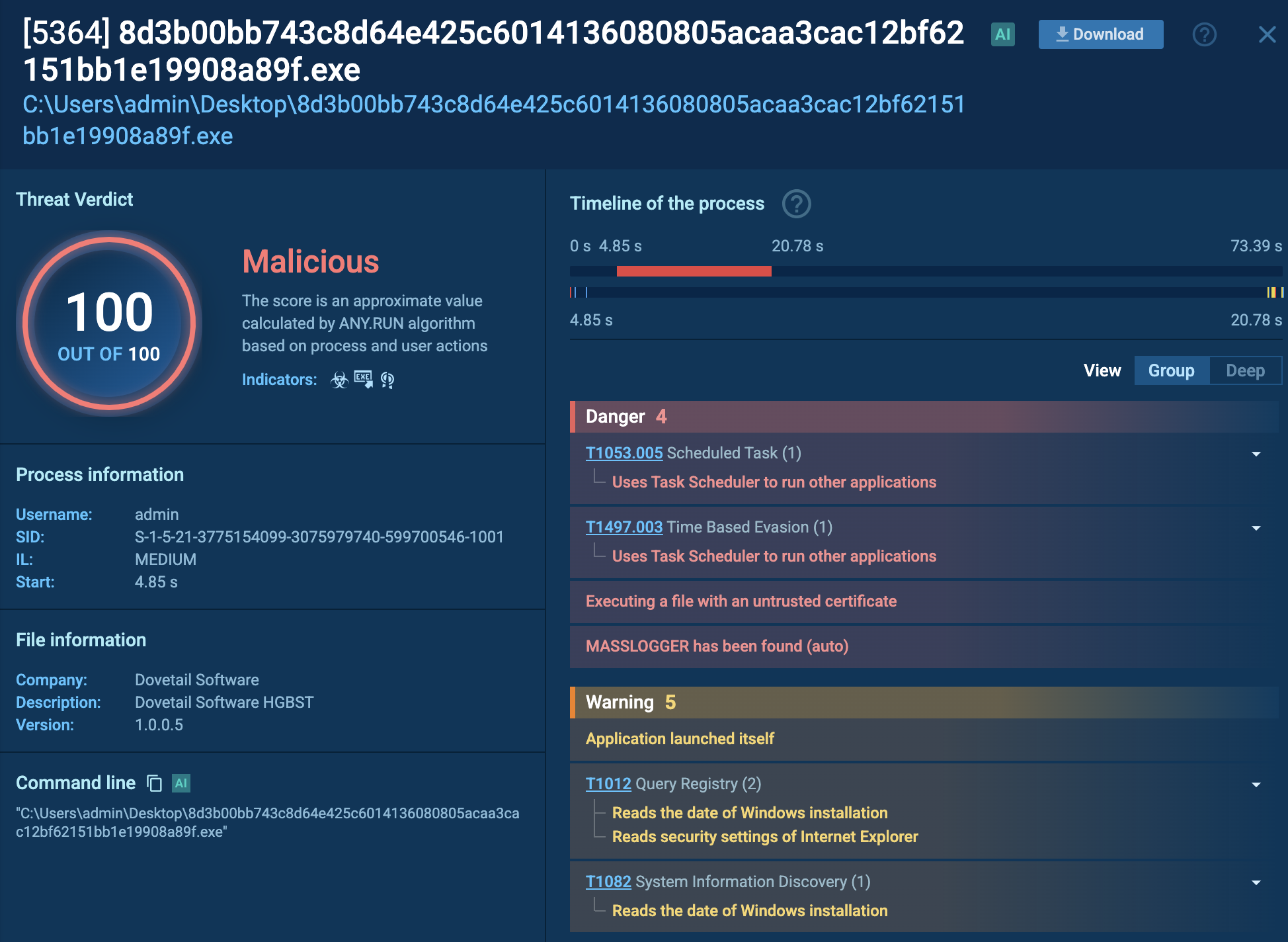
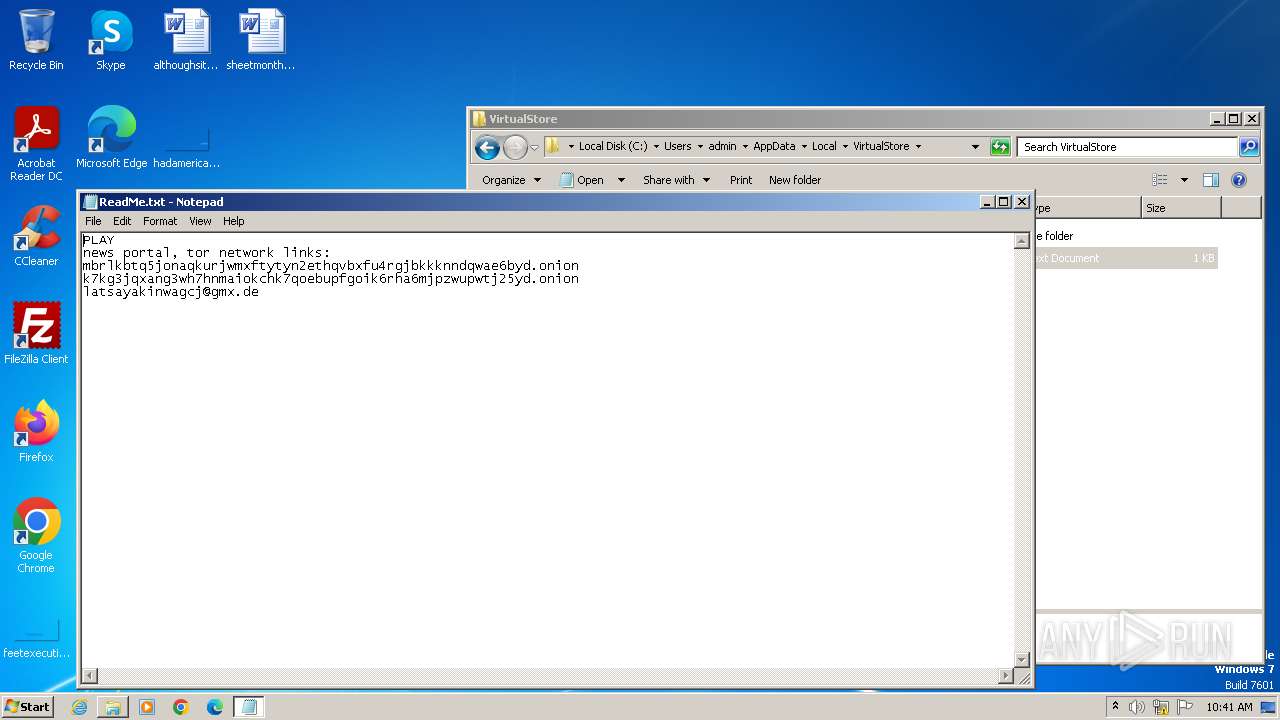
To see how Meduza stealer operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Upon infiltrating a system, Meduza first conducts a geolocation check using the victim's IP address. If the location matches an entry on its predefined exclusion list, the malware immediately halts its operations. If the check is passed, Meduza attempts to connect to its Command and Control (C2) server, which is one of the most crucial steps.
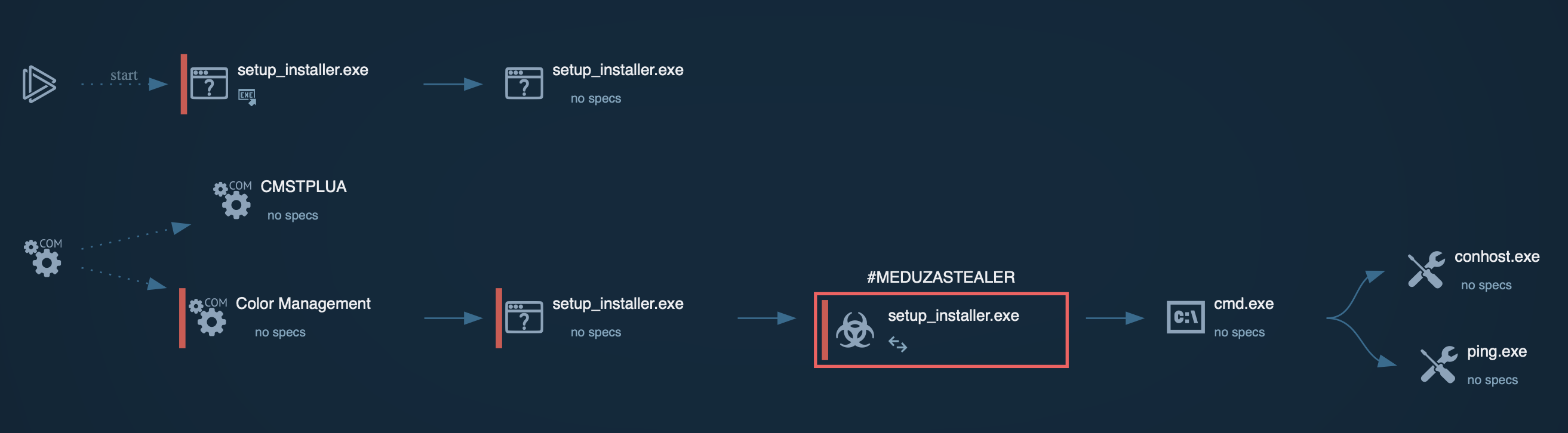 Process graph of Meduza Stealer inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Process graph of Meduza Stealer inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
If the server is unreachable, the malware terminates its process. Unlike many other stealers that delay contacting their C2 servers until after data collection, Meduza establishes this connection early in its execution.
Once connected to the C2 server, Meduza begins collecting extensive information from the infected machine, including:
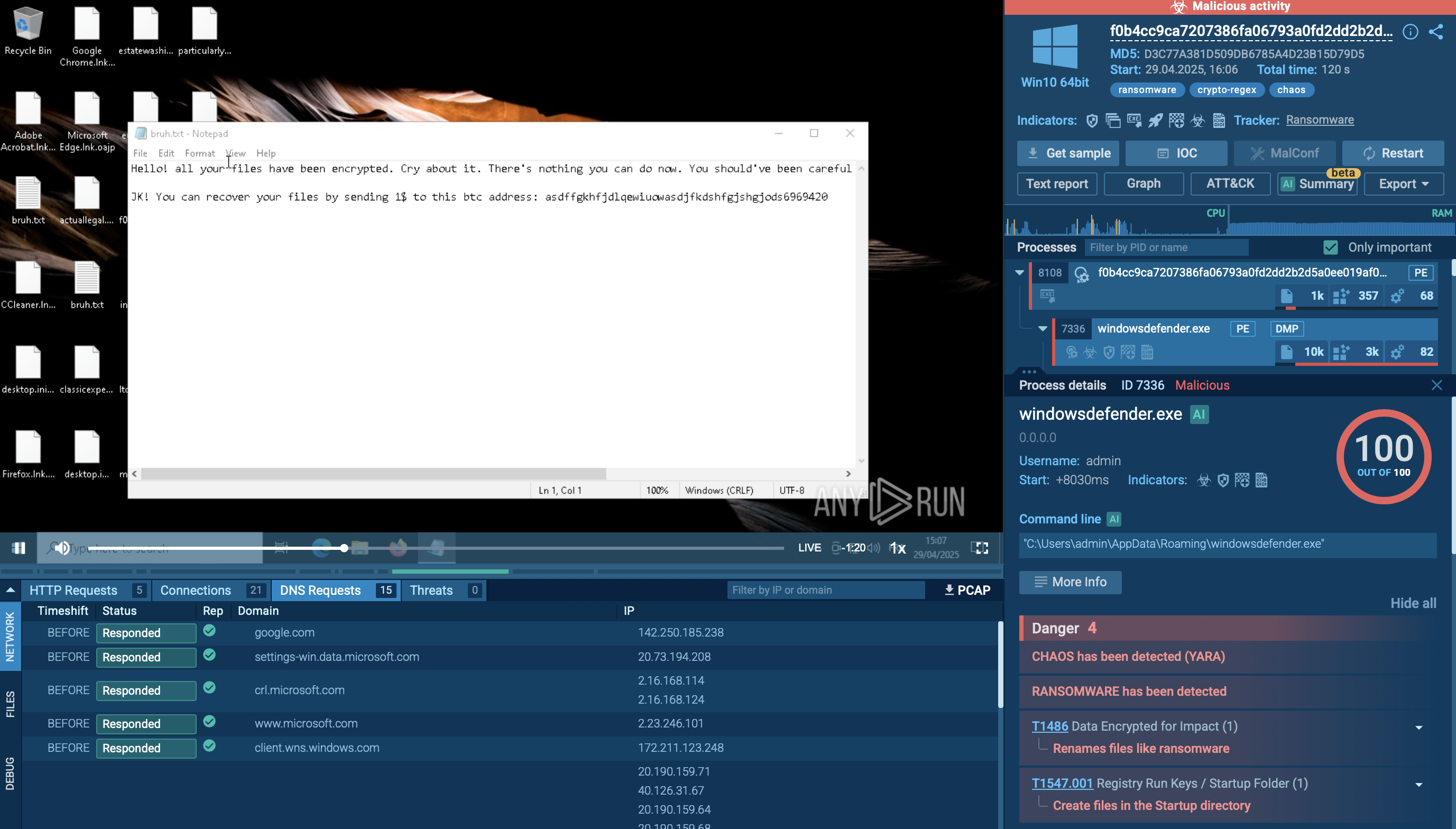
In our analysis session, we can see that the sandbox detected a connection that triggered a Suricata rule. This suggests that the Meduza Stealer managed to capture and possibly exfiltrate sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or other authentication data.
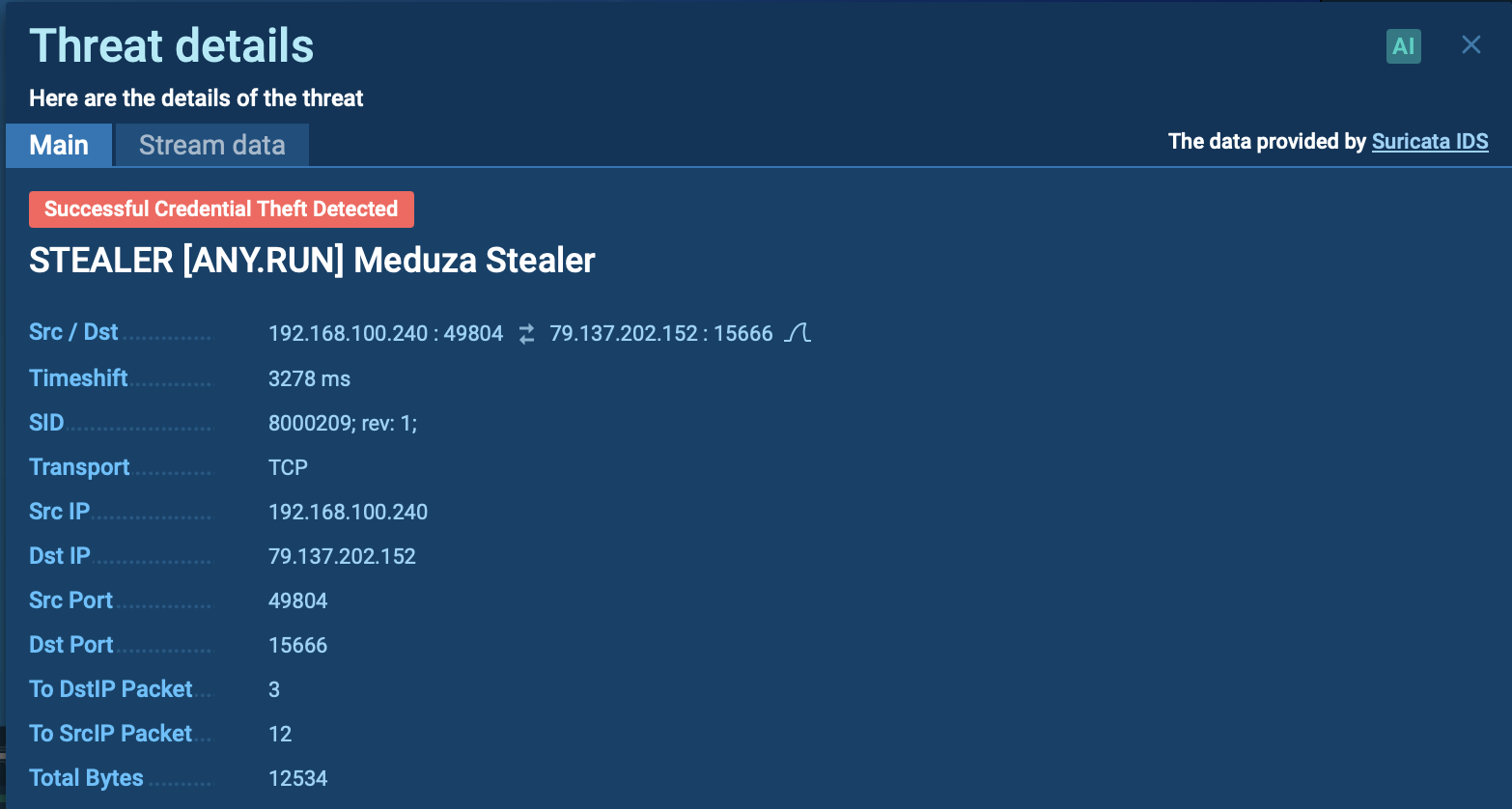 Meduza detected by Suricata IDS in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Meduza detected by Suricata IDS in the ANY.RUN sandbox
After gathering the necessary data, Meduza compiles this information and uploads it to the attacker’s remote server. Its architecture enables it to evade detection by many antivirus solutions, making it particularly difficult for cybersecurity measures to recognize its presence.
Meduza Stealer is distributed through several methods, making it a versatile threat for attackers. Below are the primary ways in which Meduza Stealer spreads:
To collect up-to-date intelligence on Meduza Stealer, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can efficiently gather relevant data on threats like Meduza Stealer.
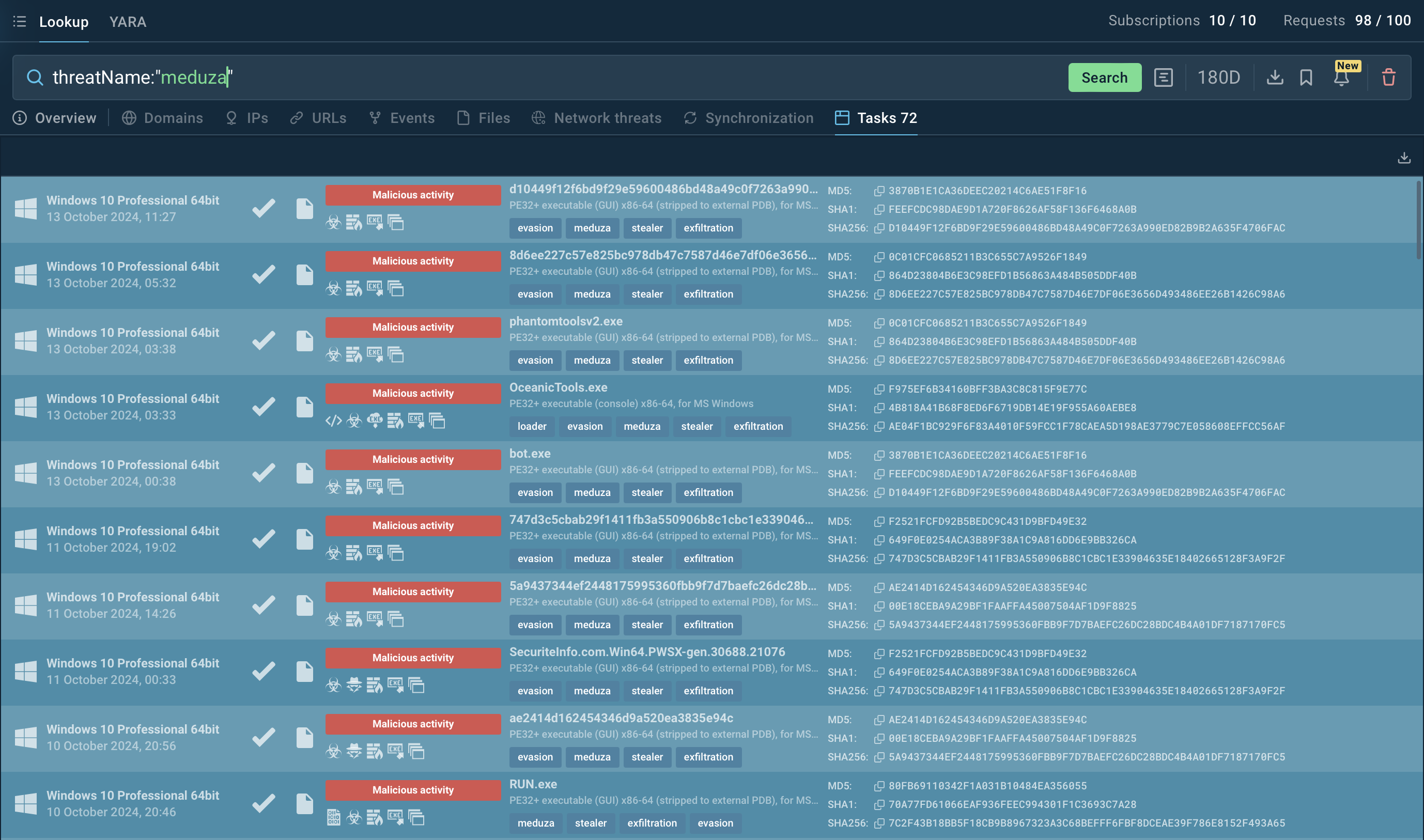 Search results for Meduza Stealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Meduza Stealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"Meduza" will generate a list of associated samples and sandbox results, giving you comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Request a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with ANY.RUN’s sandbox for detailed malware analysis.
Meduza Stealer is a dangerous piece of malware due to its extensive data-harvesting capabilities, including the ability to steal sensitive information from browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and password managers. The malware’s stealth techniques make it difficult to detect, posing a serious threat to both individuals and businesses.
ANY.RUN offers a powerful solution for analyzing suspicious files and URLs in real time, enabling users to identify threats like Meduza Stealer before they can cause damage.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today to analyze malware and find solutions to prevent potential breaches!