Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


ValleyRAT is a classic remote access trojan first documented in 2023, targeting mainly Windows systems. It is used by threat actors to gain persistent access to infected devices, steal data, and control compromised machines. ValleyRAT is notable for its relatively advanced evasion techniques and its connections to a prominent Chinese APT group.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
ValleyRAT is a C++-based RAT first identified in early 2023. It is associated with the Silver Fox advanced persistent threat (APT) group, a suspected China-based threat actor.
It stands out of the plenty of RATs for its multi-stage infection chain, heavy reliance on shellcode for execution, and a focus on espionage and data theft. It is designed to infiltrate systems, maintain persistence, and provide attackers with extensive remote control. Including the ability to monitor activities, steal data, and deploy additional malicious plugins.
ValleyRAT employs a variety of distribution methods: phishing and spear-phishing emails, compromised websites, social engineering via instant messengers, fake downloads and DLL hijacking. For the initial infection, a loader disguised as a legitimate file is used, which triggers a multi-stage process to deploy the full payload discreetly.
The loader executes shellcode directly in memory thus minimizing its disk footprint and visibility to file-based detection tools.
Once rooted in the system, ValleyRAT provides attackers with its remote control (including keyboard, mouse, screen interaction via WinSta0), allows data exfiltration, file execution, and additional plugin deployment. Screenshot capture, keylogging, and activity monitoring are also performed.
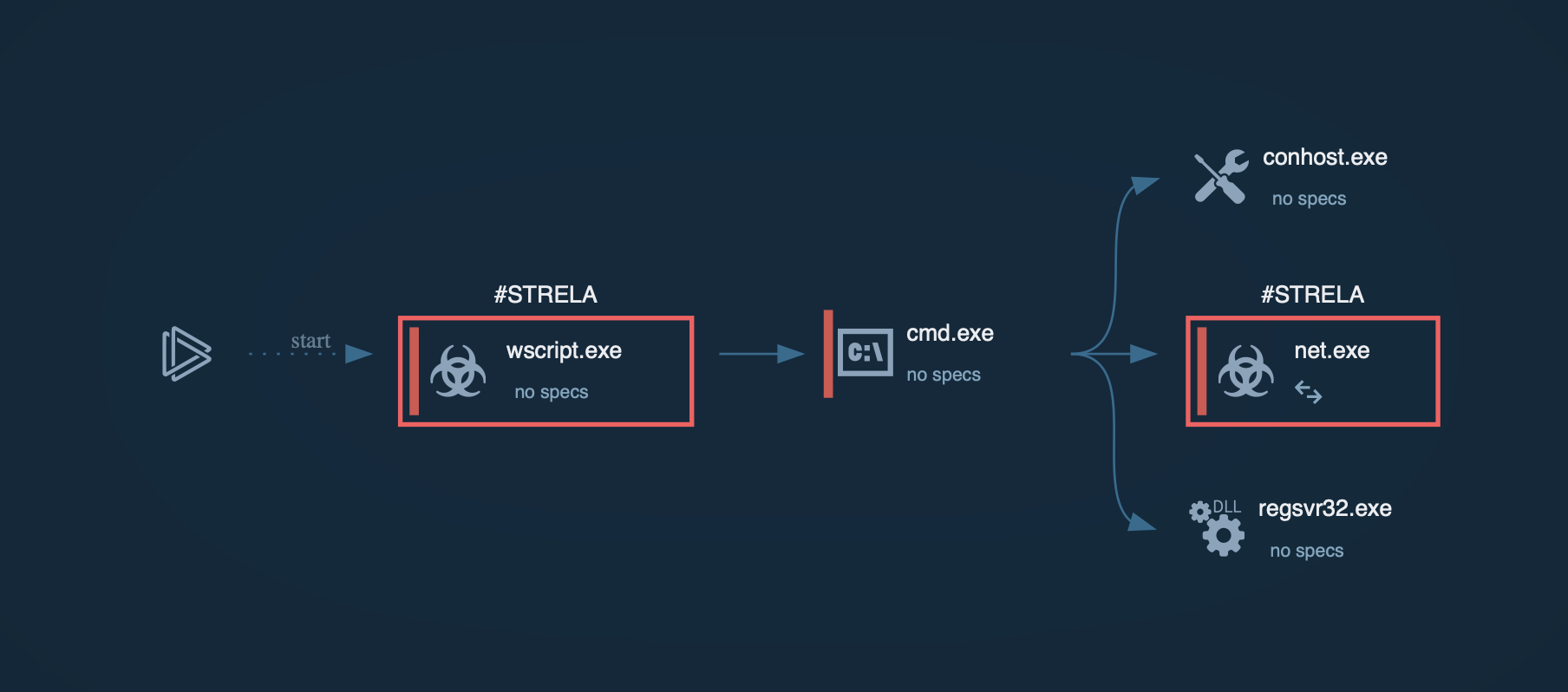
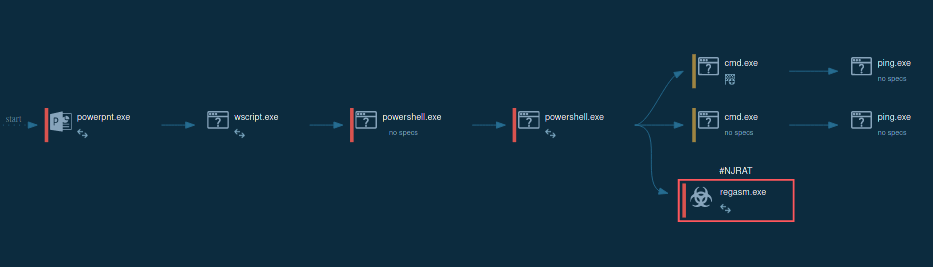
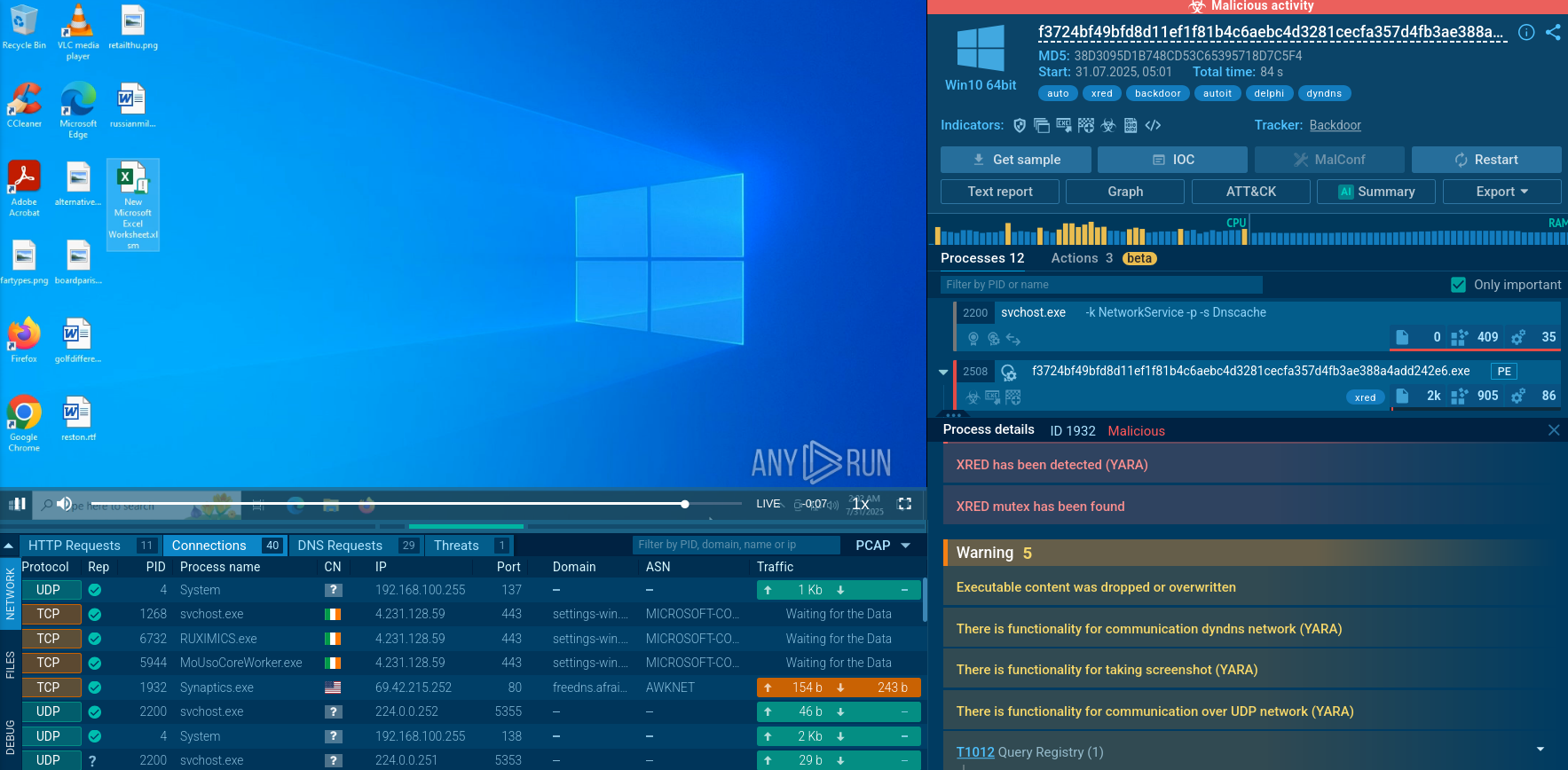
The complicated behavior of ValleyRAT is observable in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox. Let’s explore its processes, IOCs, connections, and other activities.
During the first stages, ValleyRAT may employ techniques such as DLL sideloading and exploiting legitimate signed executables that are vulnerable to DLL search order hijacking. Additionally, process injection is used to inject malicious code into processes like svchost.exe. This allows ValleyRAT to execute its payload, which may include shellcode that decrypts an encrypted PE file in memory for execution without leaving traces on the disk. The payload also includes hooks to bypass security mechanisms like AMSI (Antimalware Scan Interface) and ETW (Event Tracing for Windows).
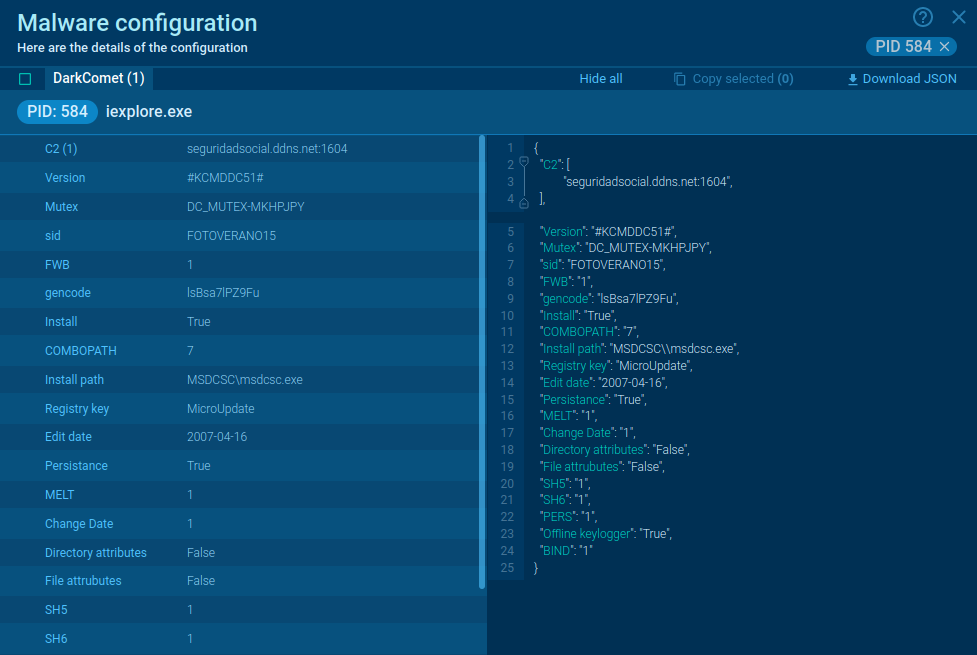
To ensure persistence, ValleyRAT modifies registry settings under Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run or, in our analysis, in the startup directory %AppData%\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\ by using the Windows Command Shell (CMD). It also stores files in directories such as C:\ProgramData. Once established, ValleyRAT communicates with its Command-and-Control (C2) server using UDP or TCP protocols. The commands supported by ValleyRAT include capturing screenshots, executing files or DLLs, setting startup configurations, filtering processes, and clearing event logs.
To avoid running multiple instances of itself, the malware creates mutexes. In our case, the mutex " V‰°5i™þ«" contains non-standard characters.
It abuses Windows COM interfaces (e.g., CMSTPLUA, fodhelper.exe) to bypass User Account Control (UAC) and gain elevated privileges, often adjusting its security token to SeDebugPrivilege for deeper system access.
ValleyRAT employs multiple stealth mechanisms to evade detection. These include anti-VM checks to detect VMware environments and avoid analysis, as well as keylogging and screen monitoring capabilities to log keystrokes and collect screen data for remote control. Additionally, ValleyRAT injects DLLs into critical processes to prevent security applications from launching. This multi-layered execution chain highlights ValleyRAT’s ability to infiltrate systems stealthily while maintaining persistence and evading detection.
 ValleyRAT sample analysis inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
ValleyRAT sample analysis inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
Its famous arsenal of evasion tactics includes:
While specific attacks are not always publicly detailed with victim identities due to the sensitive nature of espionage-driven attacks, cybersecurity researchers have documented key campaigns that highlight ValleyRAT’s success in infiltrating systems, evading detection, and achieving its objectives.
The latter campaign’s reuse of URLs, gaming software exploitation, and focus on key organizational roles demonstrated Silver Fox’s strategic shift toward both wider and more precise targeting, cementing ValleyRAT’s reputation as a versatile RAT.
It would be a painful challenge to scrape ValleyRAT out of your system considering its persistence and evasion “talents”. And, of course, losses calculation and mitigation would be even more painful. So, it’s much better not to invite the digital culprit in.
Use threat intelligence to study and recognize ValleyRAT TTPs, and to gather IOCs, IOAs, and IOBs for tuning your monitoring and detection systems. You can also leverage ANY.RUN’s TI Feeds to be updated with the new ValleyRAT’s identificators automatically.
ValleyRAT has a habit of reusing the same URLs or IP addresses across campaigns, and besides, it often employs unique mutexes. Address ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup and start your research with malware’s name:
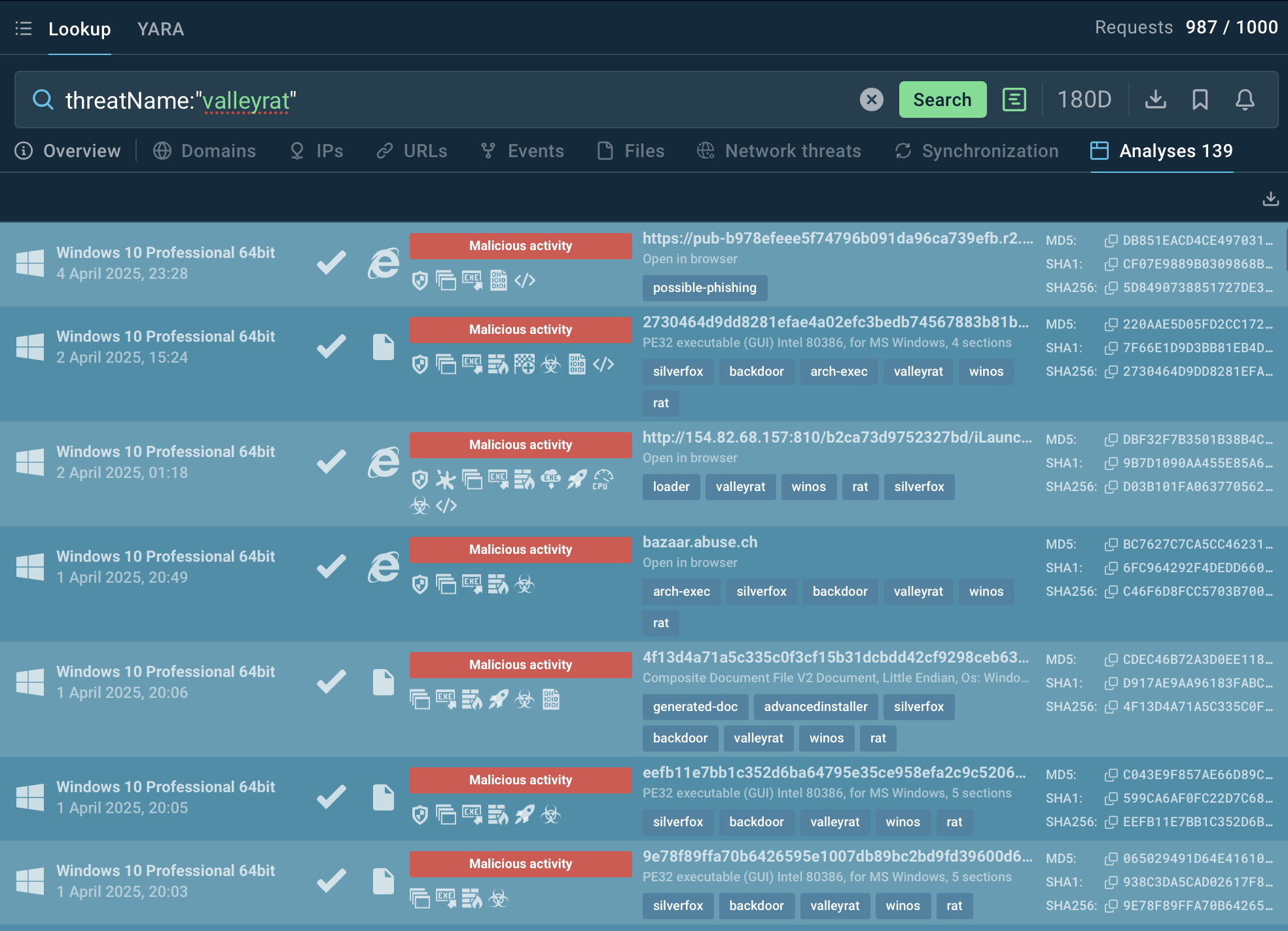 _ ValleyRAT samples in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox_
_ ValleyRAT samples in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox_
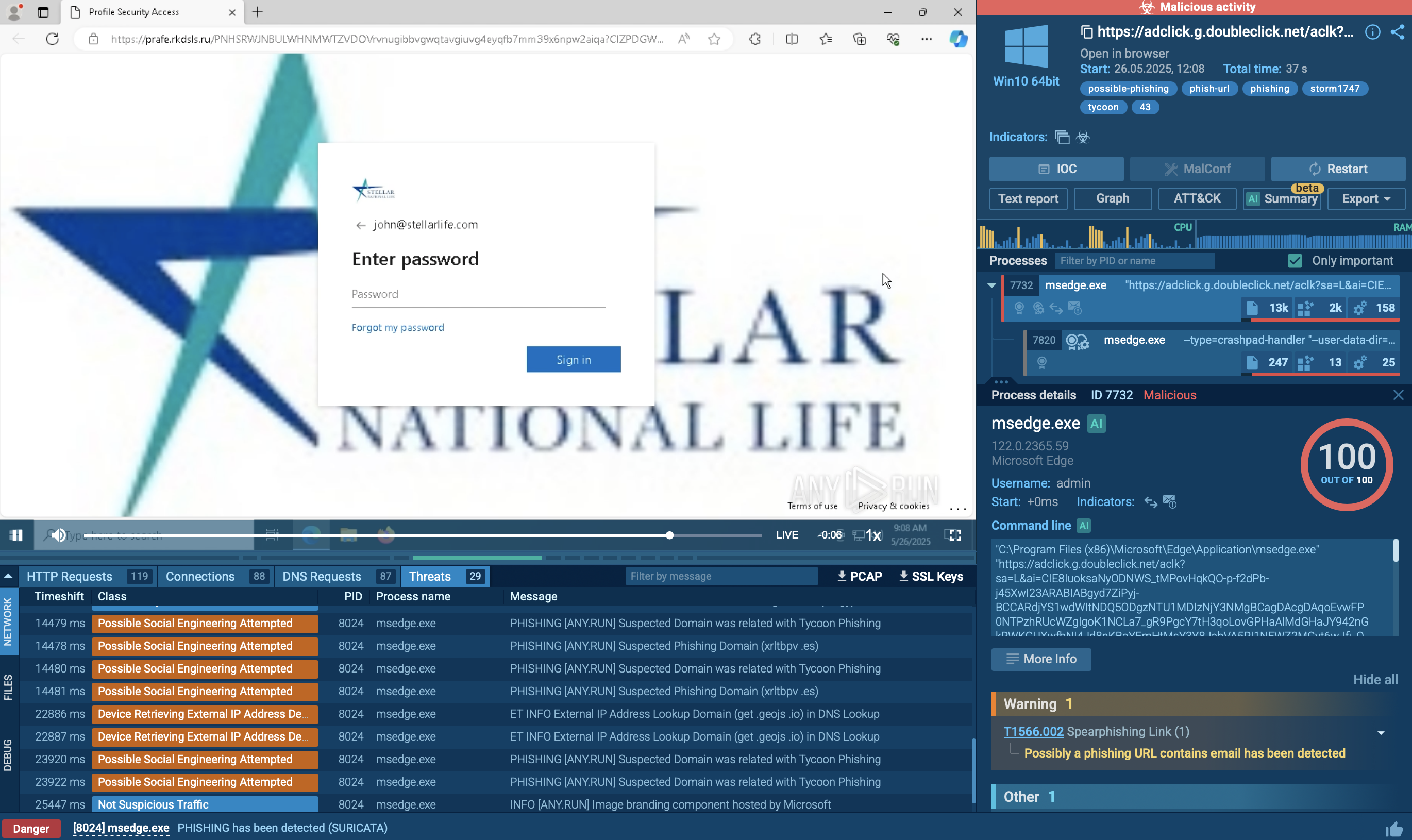
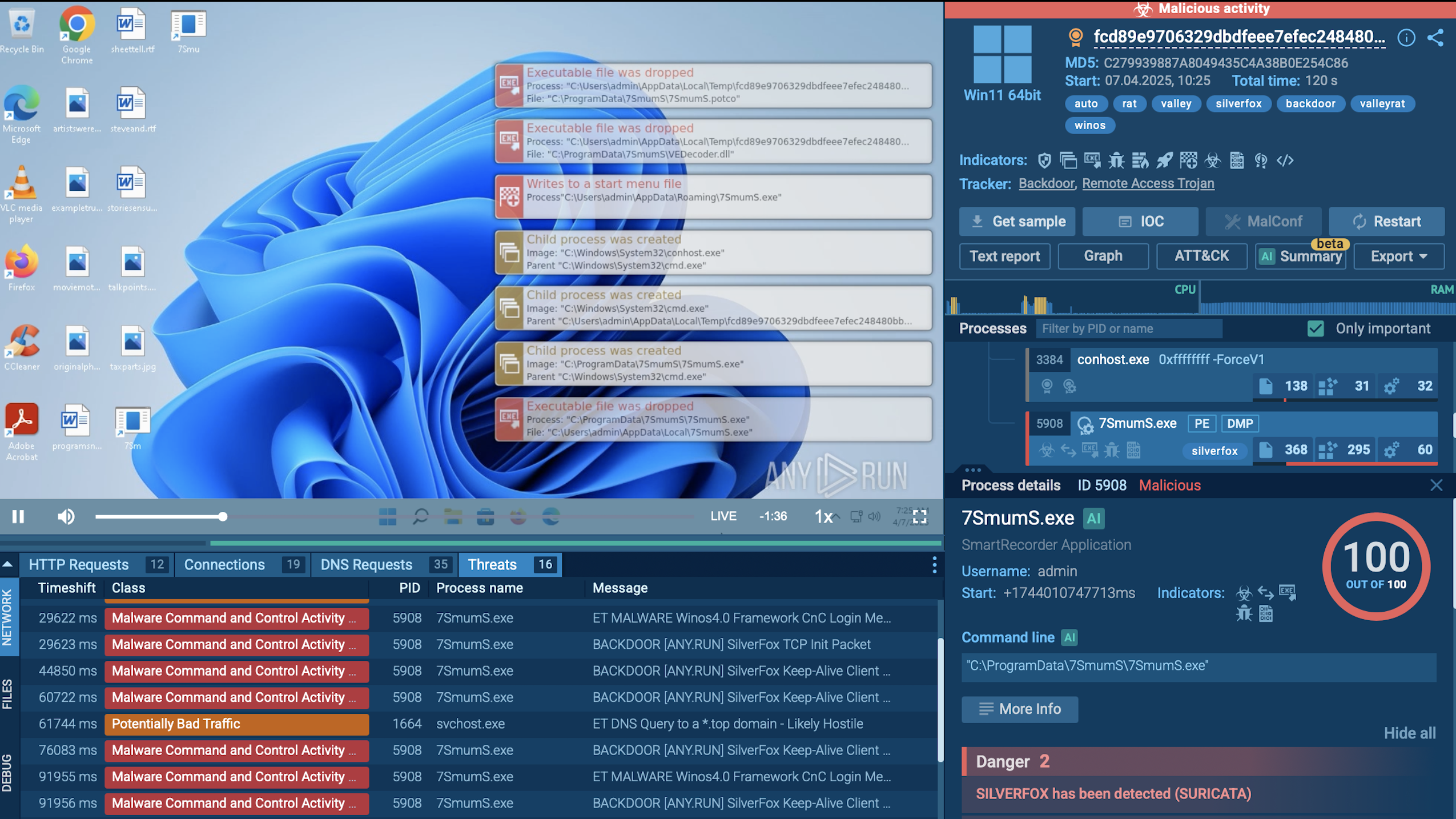
ValleyRAT often leaves byte patterns that can be matched by custom or shared YARA rules. Suricata rules are also of much help in detecting the trojan’s malicious processes. This is what the detalization of such process looks like in TI Lookup:
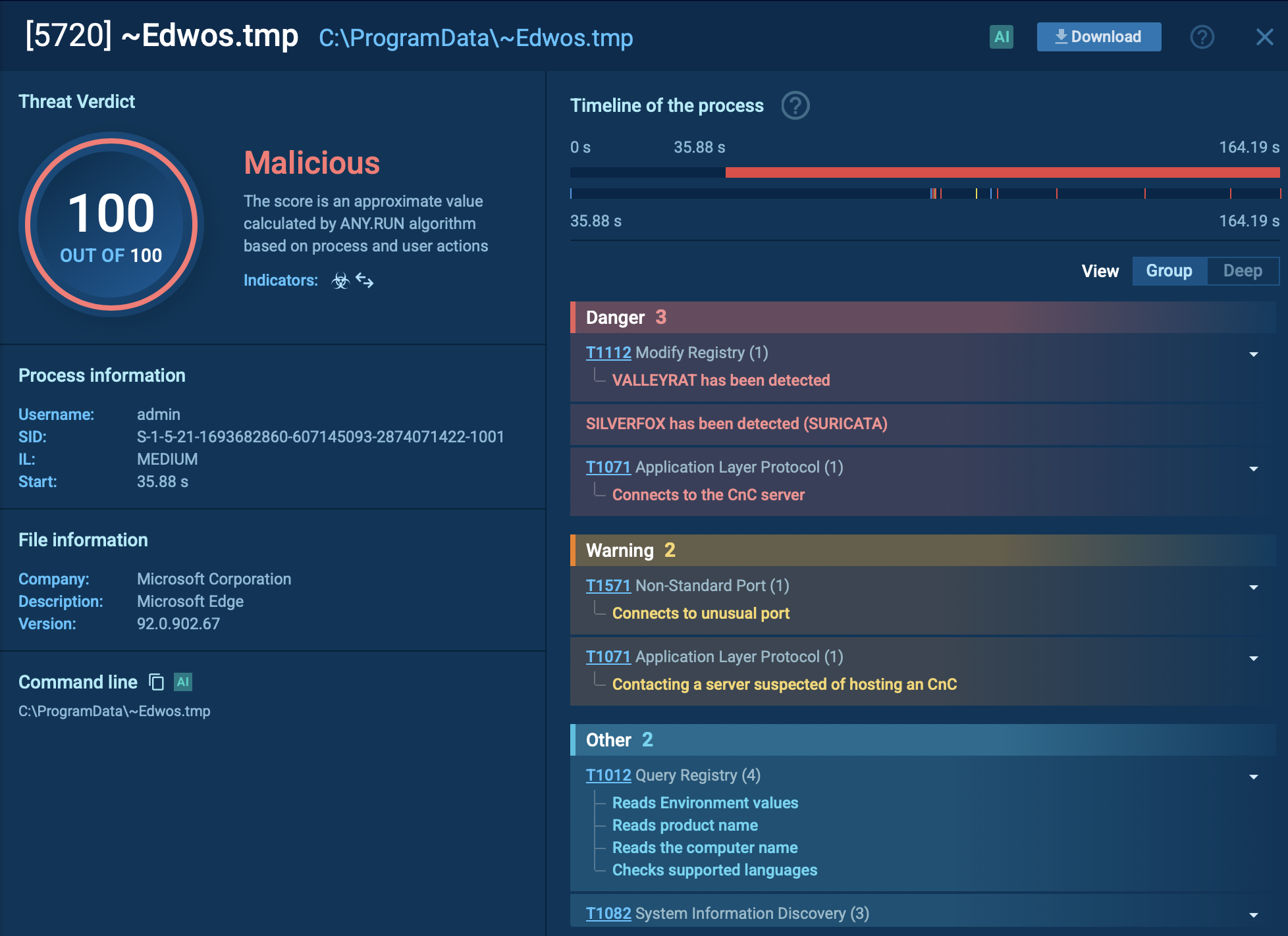 Details on ValleyRAT actions in the system
Details on ValleyRAT actions in the system
ValleyRAT is an example of modern malware evolution, blending traditional RAT functionality with advanced evasion and persistence tactics. Its danger lies in its ability to quietly infiltrate networks, target valuable data, and maintain long-term access. Countering it demands a blend of cutting-edge detection tools, robust threat intelligence, and proactive security measures to stay ahead of its cunning Silver Fox operators.
Though it did start as a threat for Chinese enterprise and users, now, if you are on the opposite side of the world from China, you are not safe. APTs’ appetites always grow, so be ready and proactive against ValleyRAT.
Gather IOCs on ValleyRAT with 50 trial requests in TI Lookup