Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


GandCrab is probably one of the most famous Ransomware. A Ransomware is a malware that asks the victim to pay money in order to restore access to encrypted files. If the user does not cooperate the files are forever lost.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
26 January, 2018
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
26 January, 2018
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
GandCrab is a ransomware-type malware, which means that it encrypts files on infected machines and demands a ransom in cryptocurrency to restore the lost data. What’s more, this particular strain is distributed as a Ransomware-As-A-Service, allowing anybody to use this program by purchasing access to a control dashboard.
A unique business model and constant updates of the malware, in turn, helped GandCrab to become one of the most widely spread ransomware of 2018.
Since its discovery on January 26, 2018, at least 5 versions of GandCrab were created. The authors of the program are extremely active and respond to created countermeasures almost instantly, making GandCrab an elusive malware that continues to terrorize private and corporate victims today.
The last identified version of the malware is 5.1 and it targets users from all over the world with one exception – having originated in an ex-USSR country GandCrab is known to ignore users from X-USSR territories, identifying them by the keyboard or UI language settings. Only Windows operating systems are affected by ransomware.
It should be noted, that the virus is assigned a different name by various antivirus software:
Usually infecting users through mail spam or exploit kits, the ransomware redirects victims to a TOR website after the files on a victim’s PC are encrypted. For the newer versions of the malware, the only way of restoring the data is through paying the ransom, the amount of which usually fluctuates between 1000 and 3000 dollars. However, some victims, have reported that they were asked to pay as much as 700,000 USD.
Having a RaaS ( Ransomware-as-a-Service ) business model, GandCrab is distributed by the original creators to “clients”, who then deliver the malware to end victims, asking for a custom ransom amount through one of the unique features of the virus – customizable ransom notes. A percentage of the “revenue” is then shared with the malware authors, once a ransom is secured.
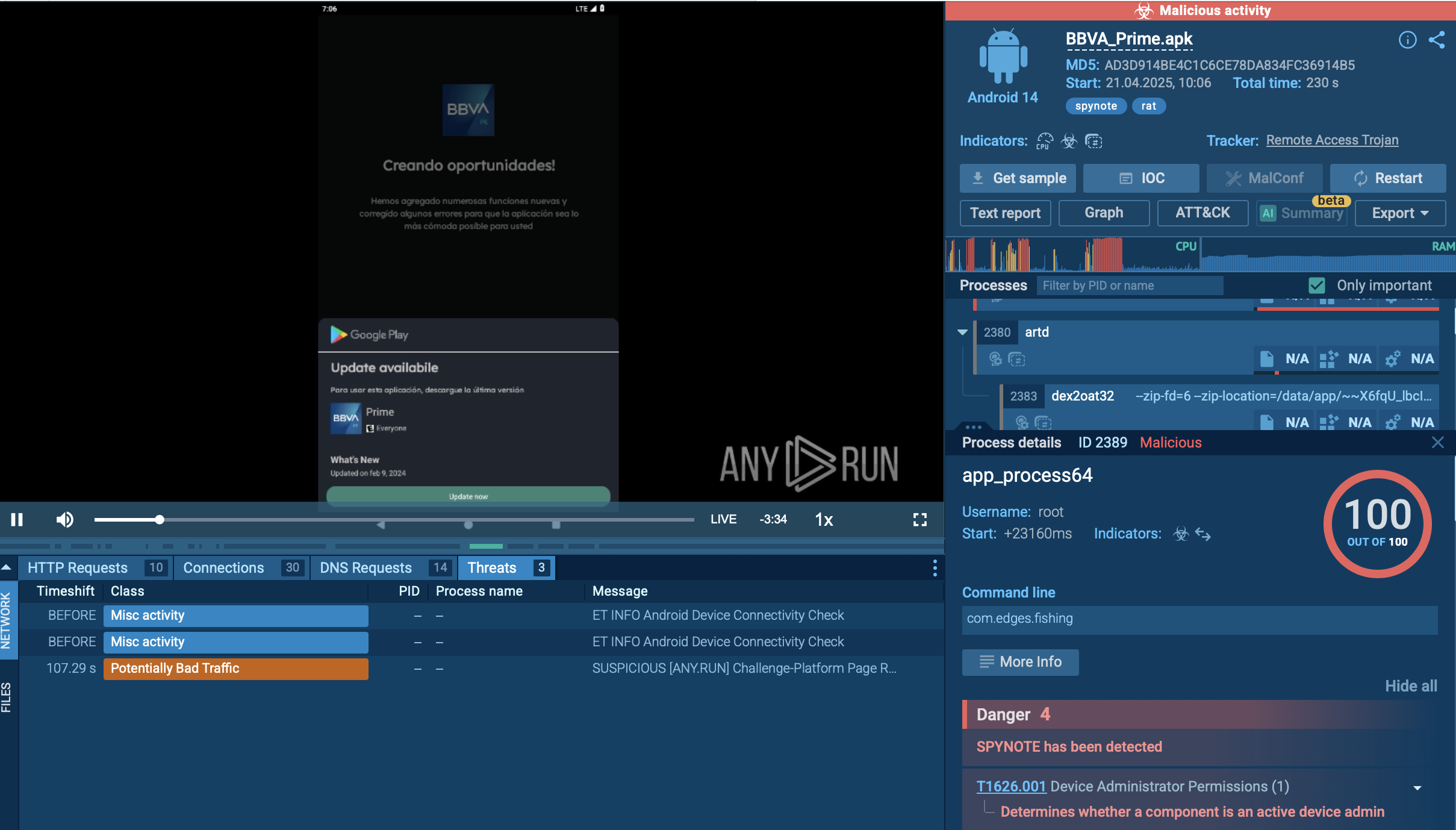
ANY.RUN provides the ability to watch the GandCrab program in action in interactive virtual machine simulation. Notably, ANY.RUN simulation can be used to perform the analysis of the stages of the virus life cycle:
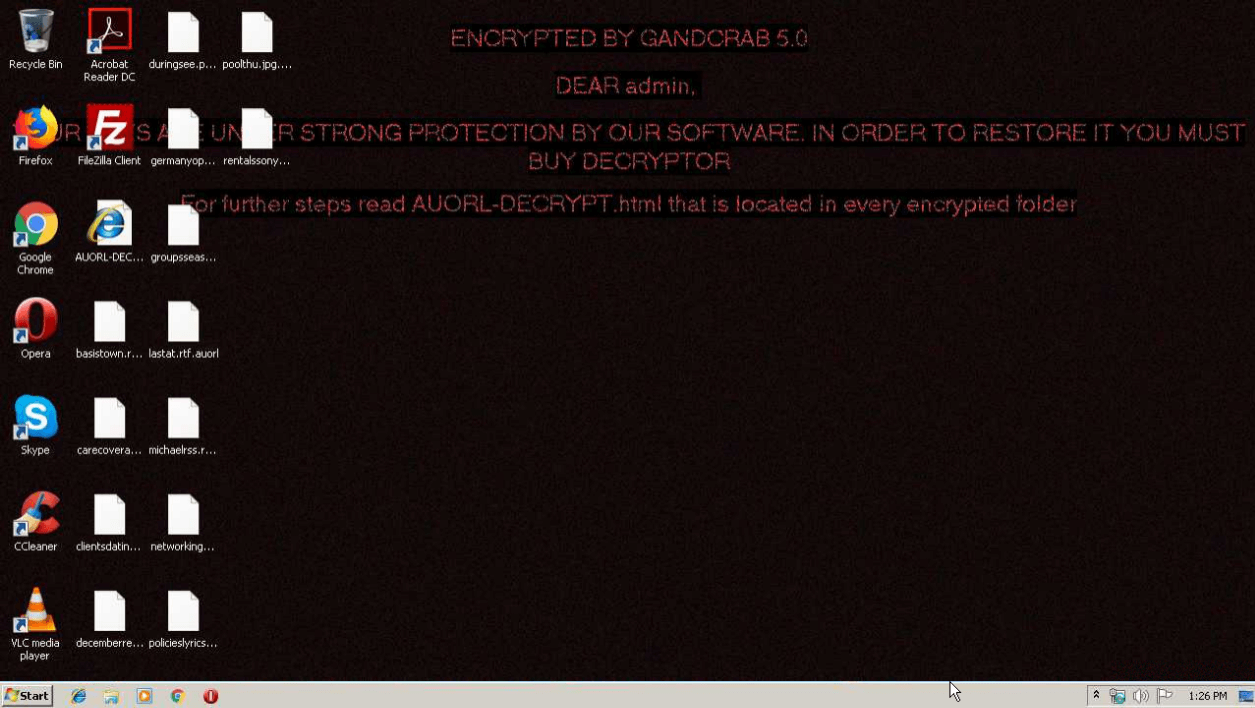
Figure 1: Some versions of GandCrab are known to change the desktop wallpaper. This function is omitted in version 5.0.
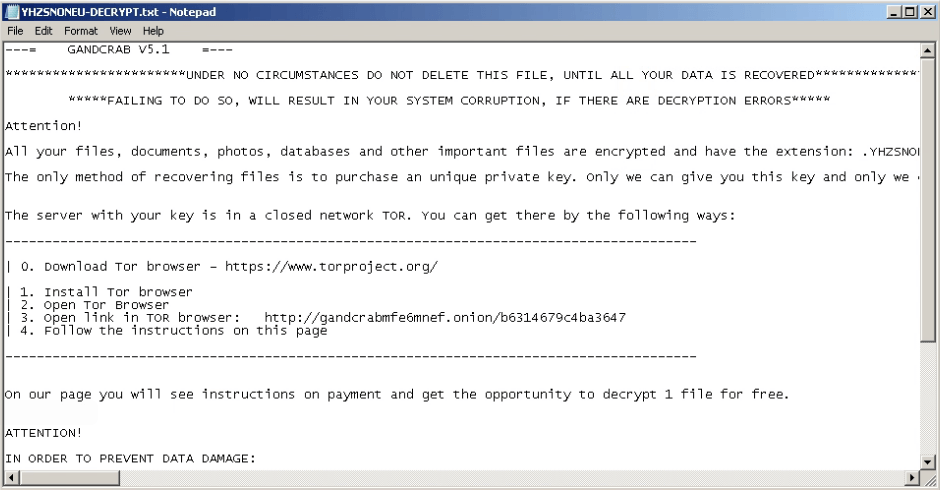
Figure 2: A ransomware note displayed by GandCrab v5.1
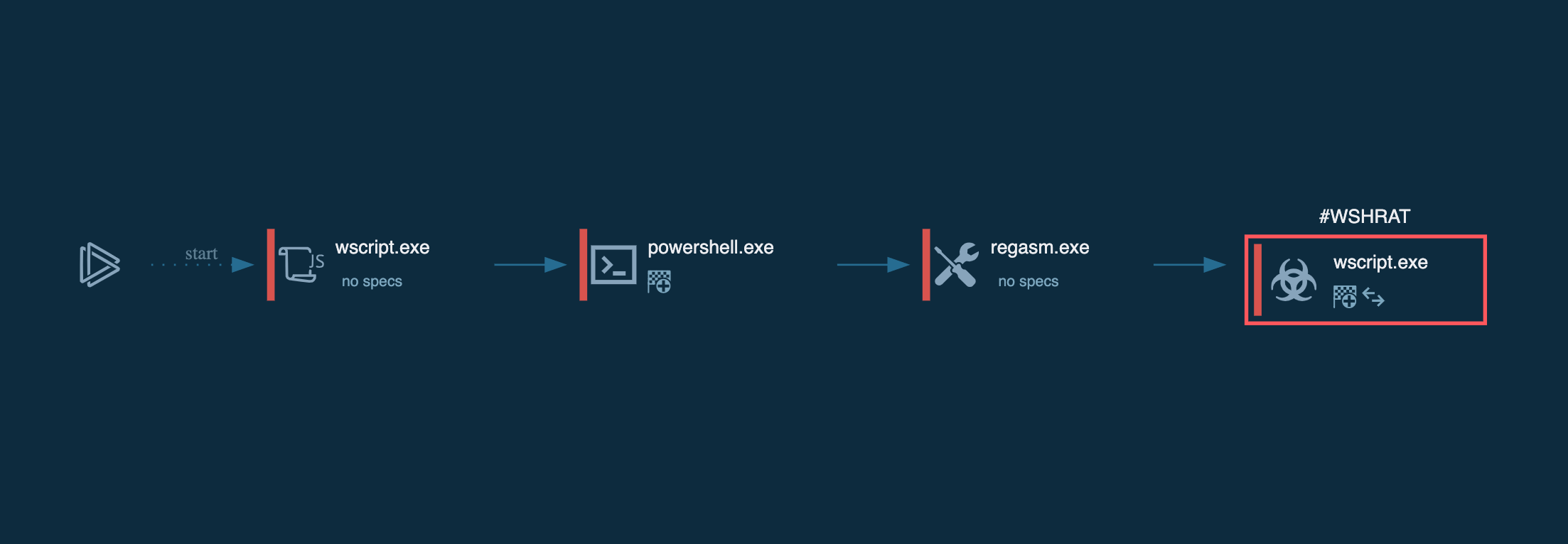
The following contamination processes are launched by the ransomware:
The whole contamination process can be seen in a video, displaying the ANY.RUN simulation.
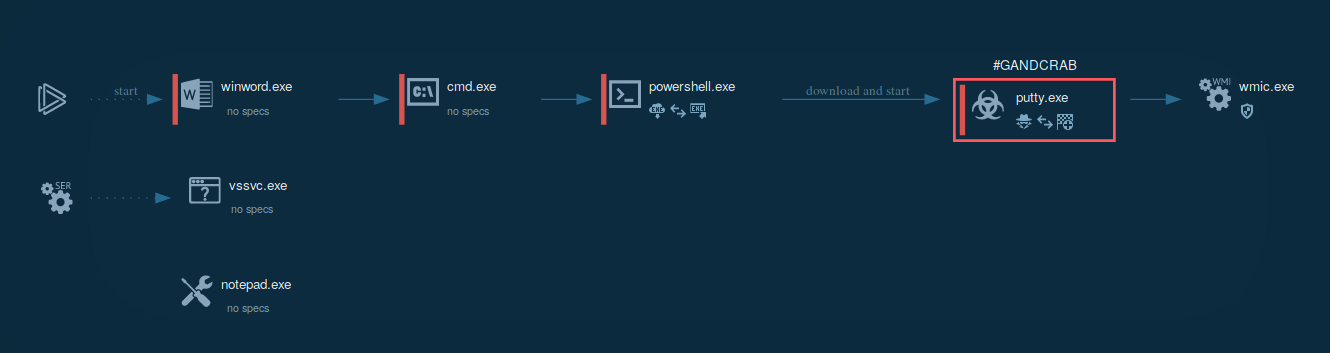
Figure 3: Illustrates the processes launched by GandCrab during its life cycle.
To build itself into the system, GandCrab starts with decrypting an extension name record that is held in the binary. By going through logical drives from “a” to “z” the malware separates all drives that are equal to 0x2 and not equal to 0x5, creating and separating thread to enumerate and encrypt all data that is prepared for encryption. After the encryption is complete, the malware uses wmic to erase all shadow copies. As a result, all data remains affected by the program even after a reboot.
The ransomware leaves behind artifacts that can help to recognize the version. Those exist in the form of extensions of encrypted files.
According to the analysis, creators of GandGrab patch all exploits in the malware code fairly quickly, which makes the development of countermeasures tricky. Upon contamination with on of the latest versions, the only way to restore the lost data is to pay the ransom. Thus, the best way to stay safe is to prevent contamination.
That said, effective countermeasures do exist for older versions of the ransomware like Troldesh or Nemty, including free decrypters and Killswitches. Most notably, a Killswitch for GandCrab v4.1.2 was developed by a cyber threat analysis and response company Ahnlab. The defensive application exploits the mechanics of GandCrab ransomware by creating a file with the .lock extension, which simulates the files that GandCrab itself generates and uses to check whether the victim's computer is included in the record of previously affected machines to avoid double decryption.
The execution of the ransomware stops upon discovery of .lock file if it is placed in %Application Data% for Windows versions before Windows 7 and in %ProgramData% directory for newer OS versions. Even in cases when the malware has already activated, the killswitch will prevent some of the damage.
Interestingly, in response to the killswitch, the GandCrab authors released an exploit, targeting the Ahnlab antivirus software. The exploit was introduced in version v4.2.1 and v4.3 of the malware but did not cause sufficient harm to the antivirus users.
For versions 1, 4 and up through 5.1 there are free decryption tool from Bitdefender.
Based on the analysis, ransomware is known to utilize multiple attack vectors, however, compromised list and spam email campaigns are the most commonly used delivery channels. Being delivered to users in spam emails, GandCrab tricks users into downloading a ZIP archive that contains a script file that triggers the download and execution.
An illustration of an execution process can be found below.
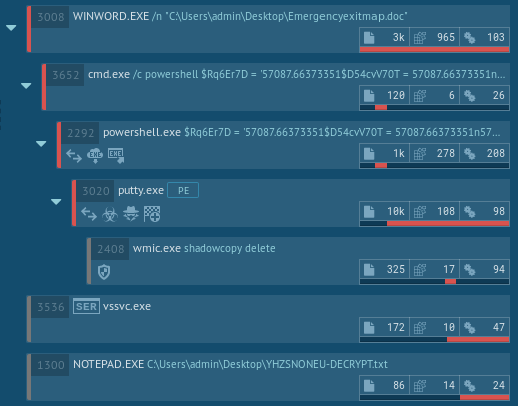
Figure 4. Malware analysis of the GandCrab execution process in ANY.RUN
The following behavioural activities are shown in ANY.RUN’s malware analysis report.
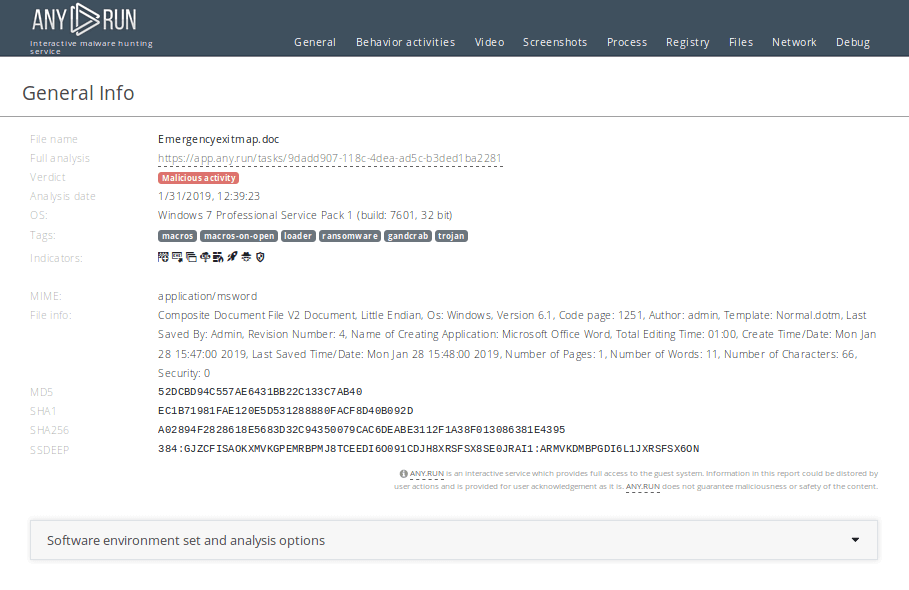
Figure 5: A text report created in ANY.RUN
During the execution the malware creates several artifacts that can be viewed in detail in the ANY.RUN simulation.
With file encryption being the main goal of the payload, the malware launches a command line with pre-specified parameters after opening a Microsoft Word file. Startup powershell is then sent as command line parameters, followed by downloading and launching the executable file from the Internet.
You can perform malware analysis of files using ANY.RUN's "Static Discovering". Open either "Files" tab in the lower part of the task's window or click on the process and then on the button "More Info" in the appeared window. After that, all you need to do is just click on the file.
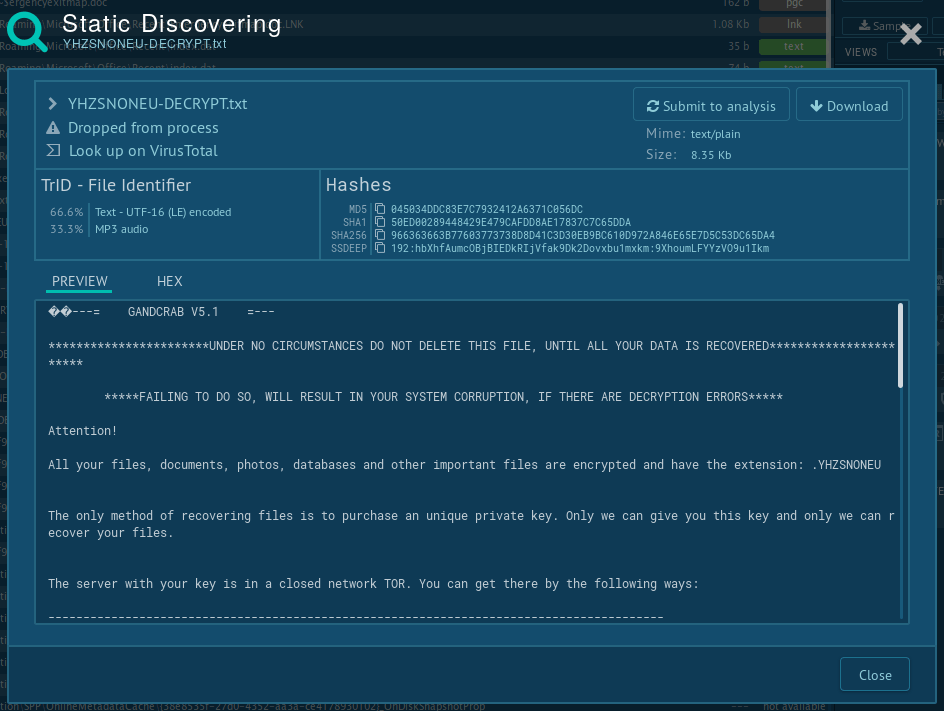
Figure 6: Gandcrab ransom note
Thanks a unique business model which involves selling the program as a service and defining characteristics like customizable ransom notes, GandCrab’s popularity quickly escalated in 2018, making the virus the most widely spread ransomware of the year.
Unfortunately, the creators proved to be very active and continued to respond quickly to all attempts to create effective countermeasures. While adhering to common practices of staying safe on the internet decreases the probability of getting attacked greatly, running interactive sandbox malware analysis in a service such as ANY.RUN is the best way to ensure personal or corporate safety.
On the 1st June 2019 creators of the GandCrab ransomware made a post in which they stating that they have generated more than $2 billion in ransom payments, with average weekly payments of $2.5 million dollars. They also said that they have personally earned $150 million, which they have cashed out and invested in legal business entities. In the same post, they announced about ending of distributing the program within 20 days and that keys will be deleted.