Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Gafgyt, also known as BASHLITE, is a botnet affecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Linux-based systems. The malware aims to compromise and gain control of these devices, often by exploiting weak or default passwords, as well as known vulnerabilities. Gafgyt has been around since 2014 and has evolved into multiple variants, each with its own set of features and capabilities, including the ability to launch distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
|
Botnet
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2014
First seen
:
|
3 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2014
First seen
:
|
3 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 165
165
 0
0

 448
448
 0
0

 1911
1911
 0
0
Gafgyt, also known as BASHLITE, LizardStresser, and Torlus, is a malware family that targets Linux-based IoT devices such as routers and IP cameras. It is known for its botnet capabilities, which allow it to conduct DDoS attacks and perform other malicious activities.
Gafgyt has been active since at least 2014, when it was initially named Bashdoor. Over the years, it has been responsible for multiple high-profile DDoS attacks. For instance, in 2019, the botnet was used to disrupt the operations of Valve Source Engine and games like Fortnine by targeting their servers.
The prevalence of this malware can be attributed to the fact that its original code was exposed to the public in 2015. Since then, different threat actors have used it to build their own strains of the malware and employed them in numerous attacks.
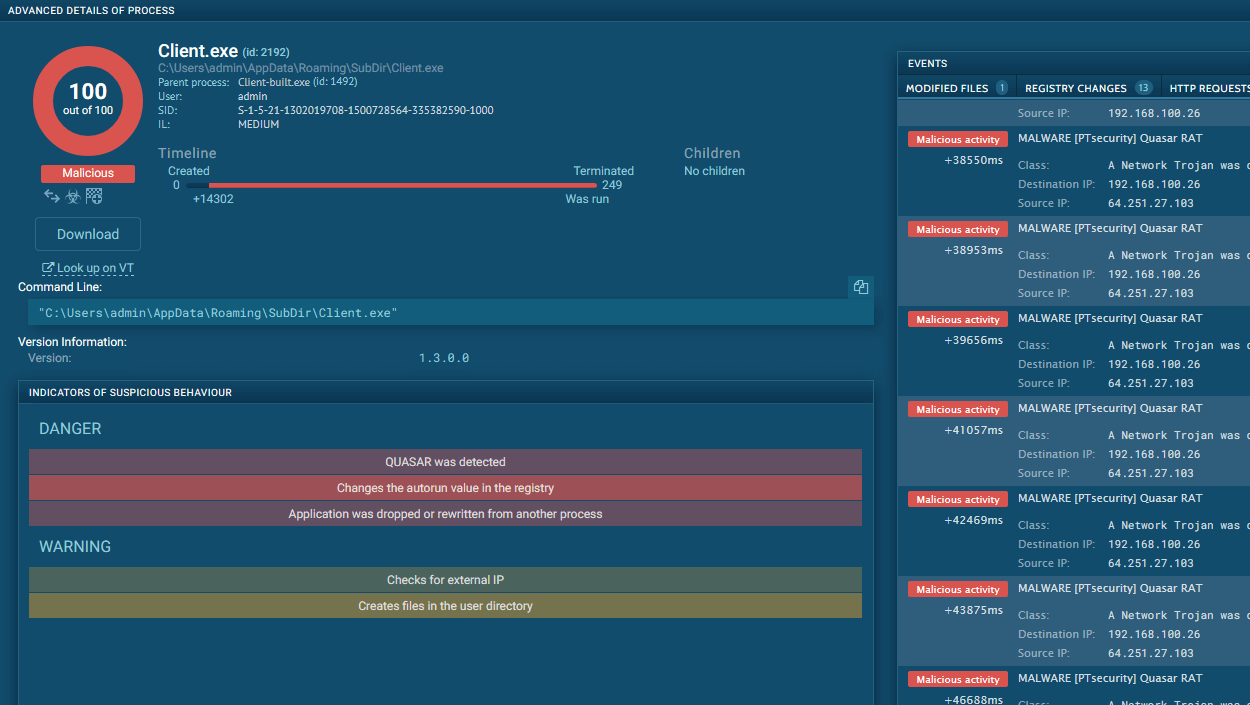
We can study the behavior of Gafgyt on an infected system by analyzing its sample in ANY.RUN’s cloud malware sandbox.
We are going to use an .elf file sample, which is an executable format on Linux systems commonly used by attackers to distribute Gafgyt. View the analysis session by following this link.
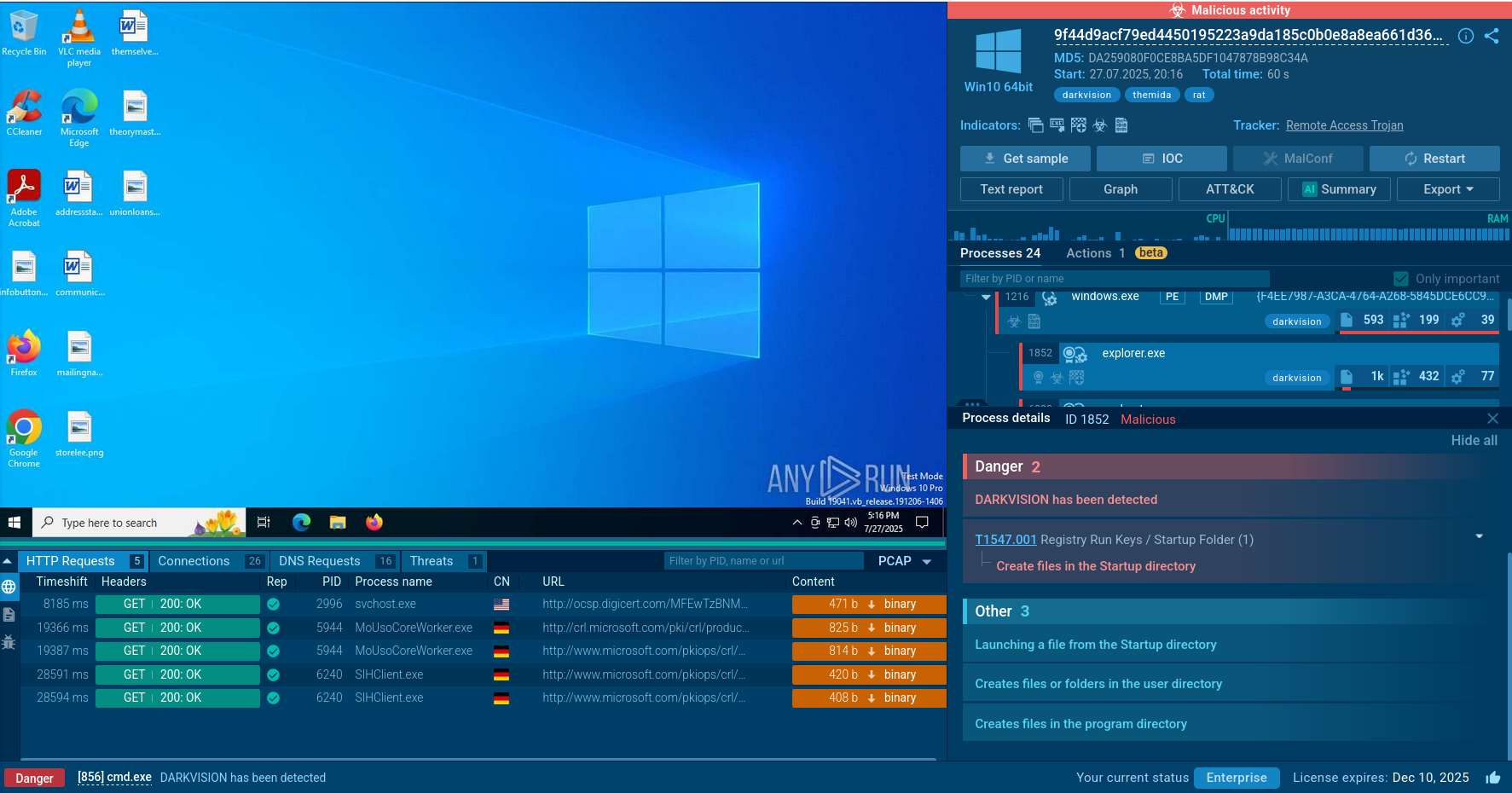
 Gafgyt analysis in ANY.RUN
Gafgyt analysis in ANY.RUN
After launching the analysis, the service instantly detects Gafgyt and starts to record all of its malicious activities.
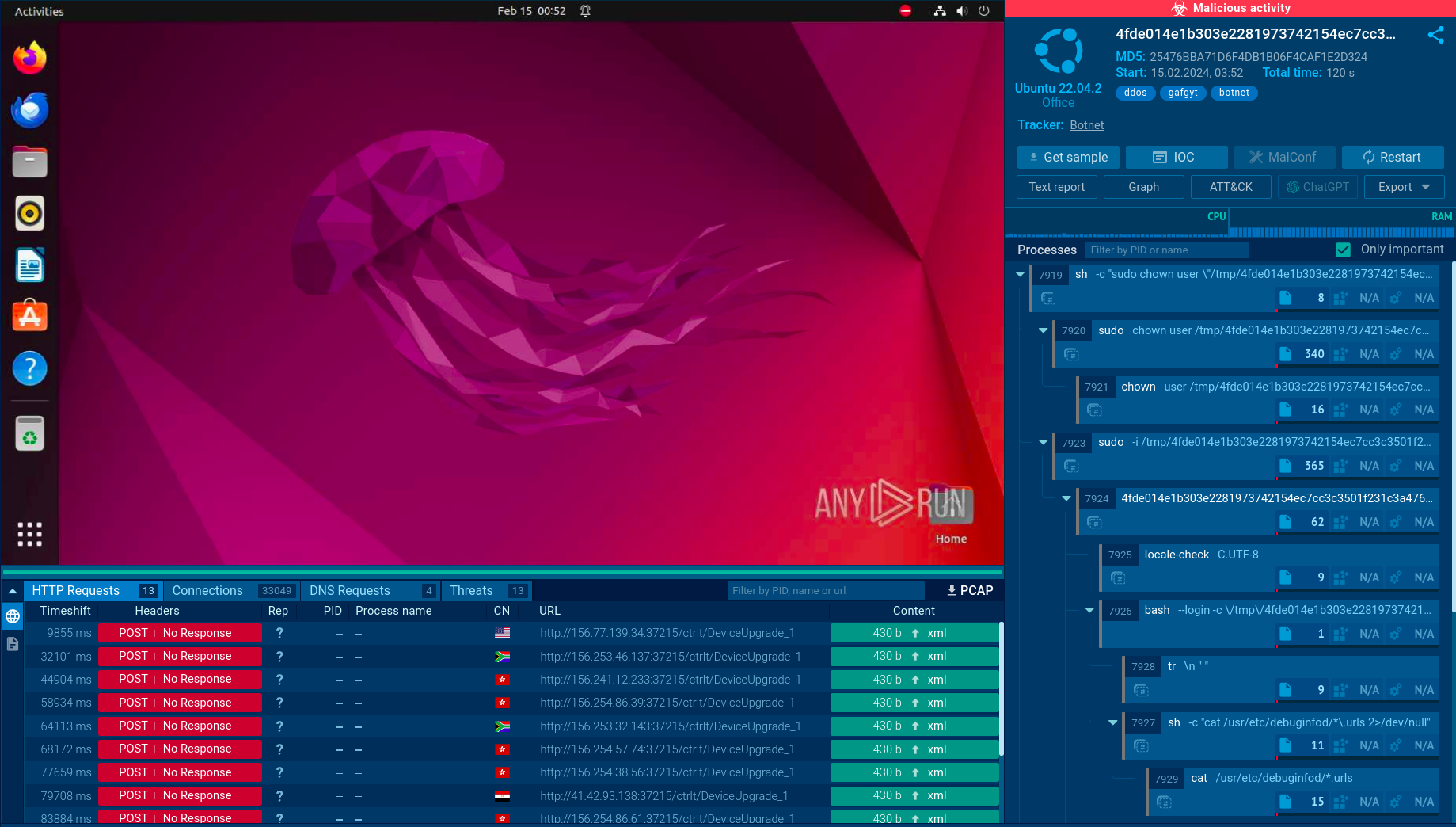
When looking at the Connections tab, we can see how the infected machine joins a botnet and participates in a DDoS attack. Specifically, the sandbox shows how the machine begins making thousands of connections.
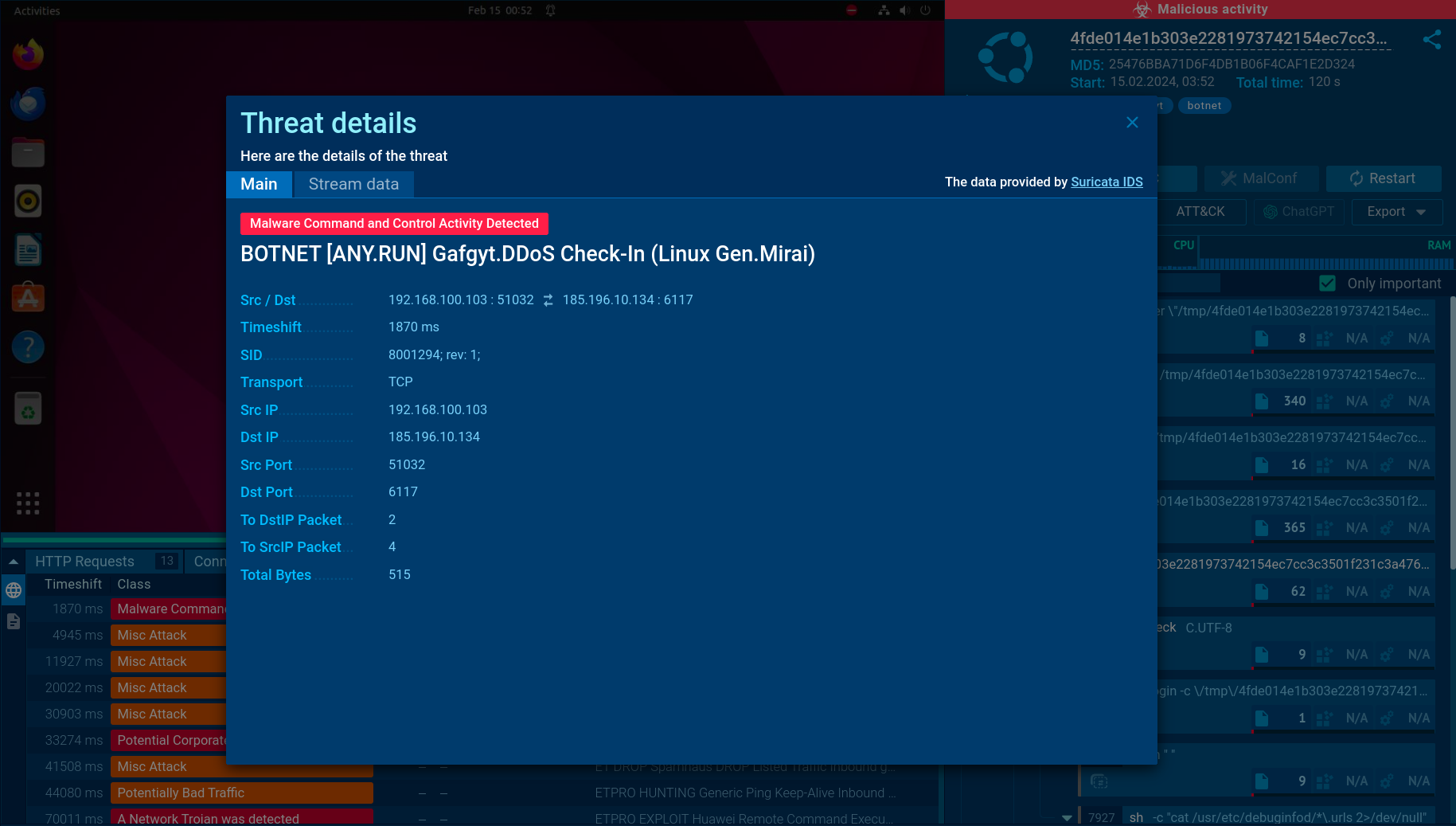 ANY.RUN also provides the Suricata rule which was used to detect Gafgyt
ANY.RUN also provides the Suricata rule which was used to detect Gafgyt
When exploring the Threats tab, we can observe the Suirata rules which were triggered during the analysis process. We can click on each one to access more details.
Gafgyt is written in C programming language. It uses a modular structure, which allows it to dynamically load and execute plugins. Interestingly, some of the versions of Gafgyt utilize code originally found in the Mirai malware, including TCP and HTTP flooding modules.
The primary way used by Gafgyt to hijack IoT devices is through brute forcing. The malware has a hard-coded list of default Telnet and SSH credentials which it employs in its attempts to penetrate devices.
Another method of infecting devices utilized by Gafgyt is through vulnerabilities. For instance, CVE-2017-18368 is one of the flaws exploited by the malware to target Zyxel routers. It is possible because of a lack of proper input validation in the Remote System Log forwarding function.
CVE-2023-1389 is another vulnerability abused by the most recent variants of Gafgyt. It is present on TP-Link Archer devices and once again involves the execution of an unauthorized malicious command that can be added to the country form in the web management interface.
After infecting the device, Gafgyt usually downloads a script from a pre-configured address and launches it. After collecting the device’s IP address and system information, it connects to its command-and-control server (C2).
Next, the C2 may send instructions to the malware which usually include engaging in different types of flooding attacks on specified targets.
The malware uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption for its communication.The malware's C2 servers are typically hosted on compromised devices.
Some versions of Gafgyt also have a persistence mechanism that allows it to survive device reboots.
Unlike botnet malware such as Socks5Systemz that spreads via loaders, Gafgyt is usually distributed through exploitation of security flaws in IoT devices. This can include devices with open Telnet or SSH ports, devices with default or weak credentials, and devices that have not been patched for known vulnerabilities.
It also has a self-propagation mechanism, which allows it to spread to other devices without any user interaction. This is typically done by scanning the internet for devices with open ports and attempting to gain access using default credentials.
The malware can also be distributed through malicious downloads. This can occur when a user downloads and executes a file from an untrusted source, such as a malicious website or email attachment.
Despite being decade-old, Gafgyt continues to be a considerable threat. It is particularly serious for organizations with Linux-based infrastructure. Protecting against a Gafgyt infection requires a combination of security measures, including strong unique passwords and timely patching.
To understand how Gafgyt and other malware operate, as well as to collect indicators of compromise, use ANY.RUN’s interactive sandbox.
The service is invaluable for malware analysts and SOC professionals, as it:
With ANY.RUN, you can strengthen your security posture.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!