Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Socks5systemz is a botnet that utilizes its infection capabilities to establish a network of compromised devices. These devices are then used to forward malicious traffic. The criminals behind this malware sell access to the infected endpoints to other threat actors. Socks5systemz maintains control over thousands of devices and communicates with them using specific commands.
|
Botnet
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2017
First seen
:
|
9 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2017
First seen
:
|
9 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 471
471
 0
0

 2431
2431
 0
0

 4670
4670
 0
0
Socks5Systemz is a botnet that has been observed by threat researchers since 2017, with a significant spike in activity in 2023. Notably, the first sample of the malware uploaded to ANY.RUN's public database dates back to 2020.
Unlike botnets such as Mirai, which primarily infect devices to use them in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, Socks5Systemz is mainly utilized for creating networks of compromised devices to rent out as proxies. Attackers sell subscriptions to their proxy services, enabling malicious actors to leverage bots to forward traffic through them. This allows them to hide the original source of the traffic and bypass security systems designed to detect malicious traffic.
Since its launch, Socks5Systemz has infected more than ten thousand systems worldwide. Often dropped by loaders like PrivateLoader and Amadey, the botnet mostly targets endpoints in India, the United States, Europe, and countries in Africa. At the same time, Socks5Systemz can enter devices through other means, including phishing emails and malvertising.
As mentioned, Socks5systemz botnet focuses on compromising devices to resell access to them as part of a proxy-for-rent scheme.
The malware employs two distinct types of Command and Control (C2) connections for its communication, distributing roles between two servers and creating a complex and efficient system for managing its operations.
The first type of connection is the HTTP/80 C2 connection. This connection is primarily used for communication between the bot and the server. The second type of connection is the TCP/1074 Client connection streams and proxy server commands. This connection is responsible for managing client streams and executing proxy server commands.
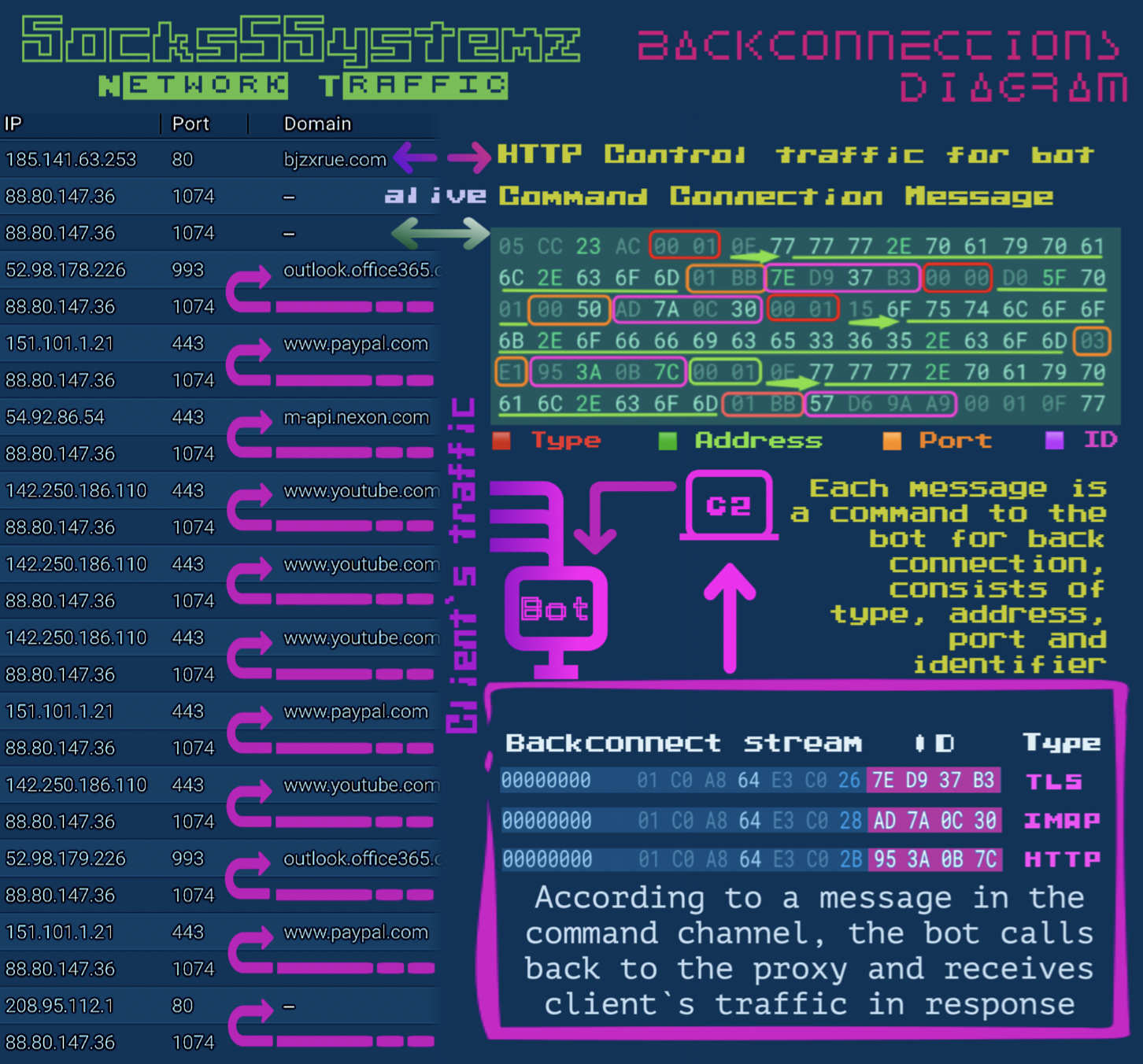 Socks5Systemz network traffic
Socks5Systemz network traffic
The Socks5Systemz proxy bot binds TCP/1074 sockets to facilitate communication with the proxy server. The first packet, which is one byte long, determines the type of command being sent. These commands can be one of three types: 0x00, 0x01, or 0x02.
An alive command connection on TCP/1074 is used to convey messages from the server. These messages describe client streams and are structured as follows:
When server commands are received, the proxy bot executes a series of steps in response. It transmits a 0x01 command packet type to the TCP/1074. Subsequently, it dispatches a 10-byte packet containing the client connection ID. Lastly, it forwards data from the proxy-server clients to the internet.
This particular method of interaction with a pair of servers enables the proxy bot to maintain its online status with the C2 server, facilitating updates to proxy addresses, and with the proxy server, allowing it to accept new client streams.
Some versions of the malware have been observed to connect to domains that were automatically generated with the help of algorithms (DGA).
To study the behavior of Socks5Systemz closely, we can upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Threat actors often employ malware loaders to deliver the Socks5Systemz payload, setting up persistence and injecting the proxy bot into the system. The malware uses a custom command and control protocol to communicate with threat actor-controlled servers, mimicking well-known protocols or developing custom ones.
The malware may maintain persistence by creating a Windows service to run the loader. It evades detection using a domain generation algorithm and supports commands like connecting to backconnect servers to serve as proxies.
The malware's execution chain involves initial delivery, command and control communication, persistence setup, proxy injection, and malicious activity execution, all aimed at facilitating cybercriminal operations and evading detection.
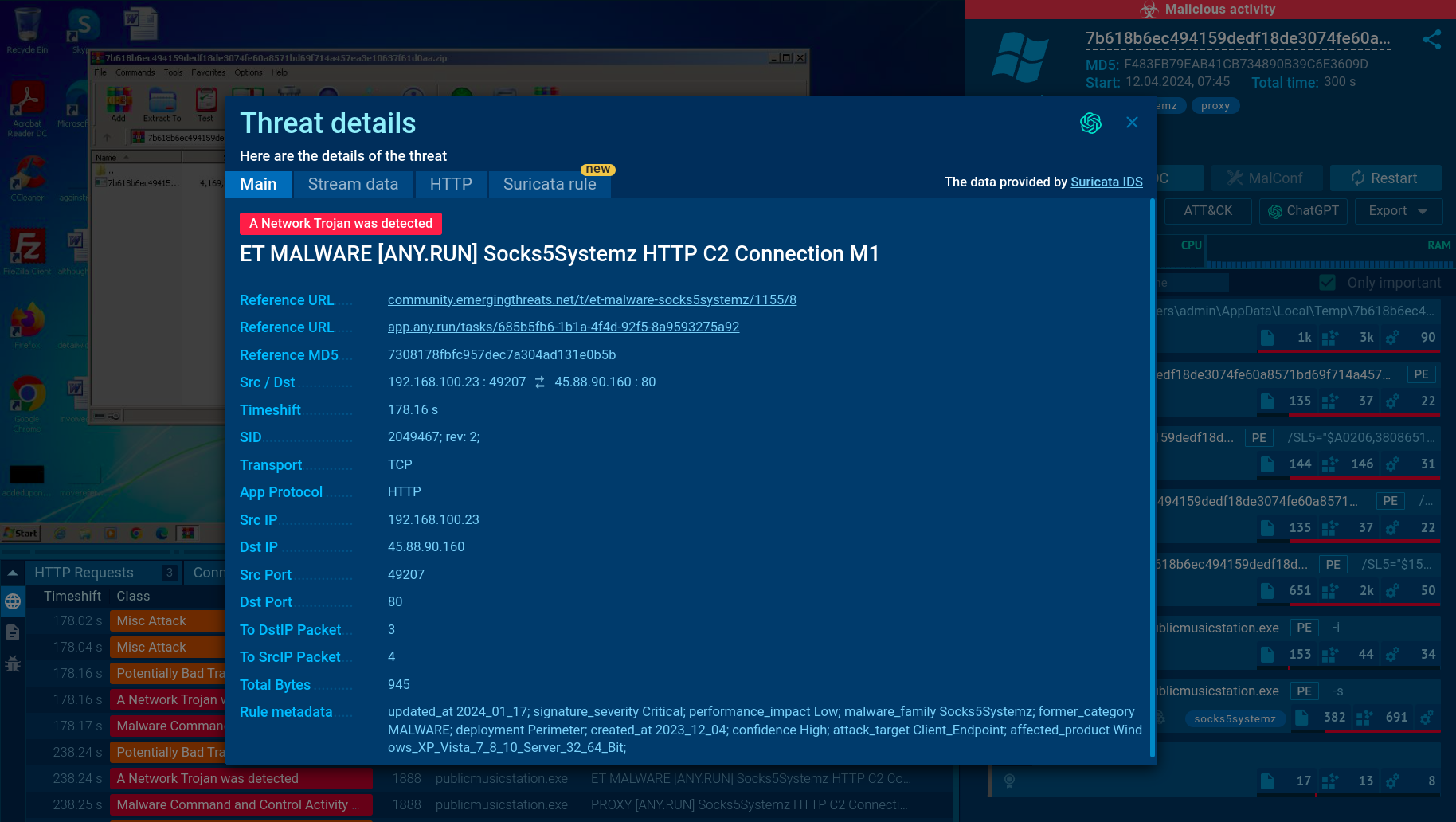 Socks5systemz Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
Socks5systemz Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
Socks5Systemz is commonly delivered via loaders, such as PrivateLoader and CrackedCantil. These drop the malware on compromised systems and allow it to begin the infection process.
Some attacks involving Socks5Systemz are also performed via phishing emails. Criminals can employ various social engineering tactics to trick victims into downloading and executing the malware on their devices.
Socks5systemz continues to be used in attacks on both individuals and organizations. To prevent it from taking over your system, it is crucial to undertake proactive measures. One of them is using a sandbox to analyze suspicious files and URLs.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based sandbox service that helps users detect malware families like Socks5systemz. It provides a detailed view of the behavior of any malware in a secure environment. ANY.RUN supplies reports on the analyzed threats, containing crucial information such as indicators of compromise and TTPs. These reports are useful for making informed security decisions.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!