Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Snake is a modular keylogger written in .NET. Adversaries use this malware to exfiltrate confidential data, such as keystrokes, screen captures, and login credentials.
|
Keylogger
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
15 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
29 March, 2022
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
15 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
29 March, 2022
Last seen
:
|

 857
857
 0
0

 508
508
 0
0

 2788
2788
 0
0
Snake is a modular infostealer and keylogger that was initially discovered in November 2020. Developed using the .Net programming language, it exhibits similarities with the AgentTesla, Formbook, and Matiex malware families, particularly in its staging mechanism.
Snake poses a significant risk to privacy due to its ability to exfiltrate a broad range of data. Its capabilities include:
Snake is capable of stealing credentials from over 50 applications, including popular web browsers and file transfer clients, such as FileZilla. Notably, this malware is also able to steal wireless network profiles.
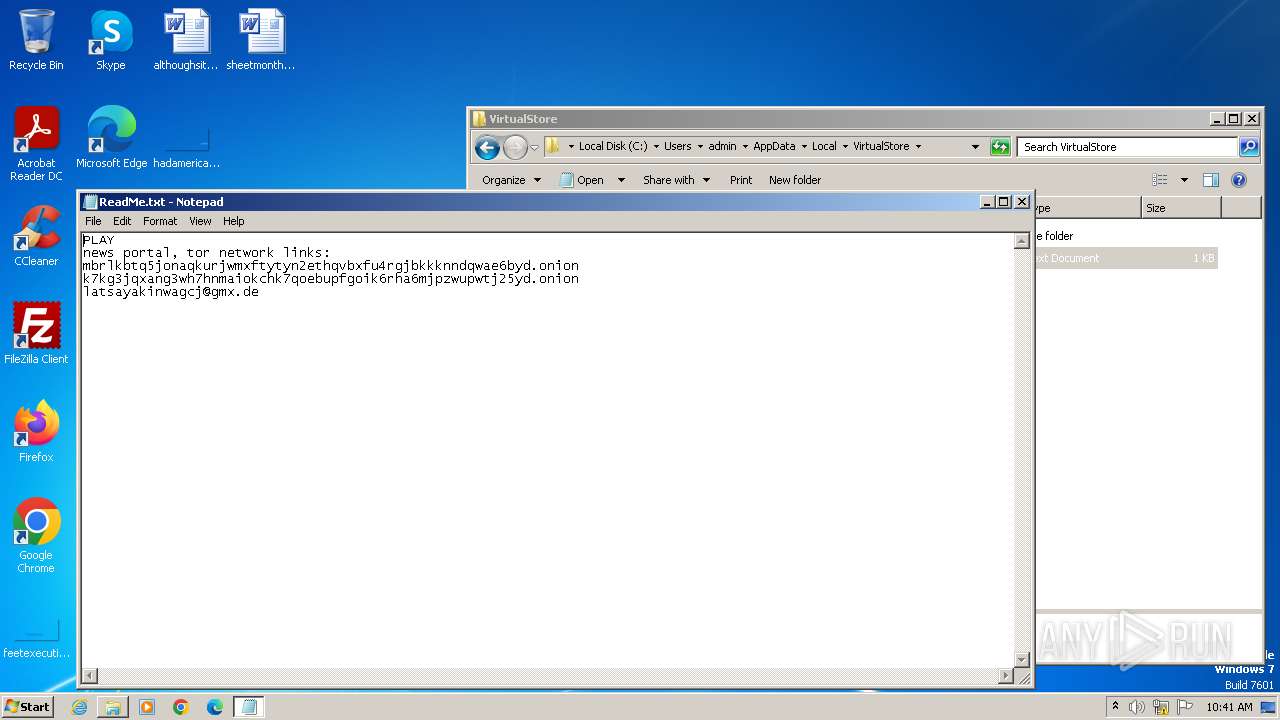
This keylogger is also notable due to its ability to exfiltrate that data through multiple protocols: FTP, SMTP, and Telegram.
Additionally, Snake collects system information including the hardware configuration, name, and operating system version of the infected machine.
Utilizing the system's IP address and date-time information, it identifies the geolocation of the machine it operates on. Some Snake samples, though not all, use this data to activate a kill switch. Such behavior is common for malware originating from the ex-USSR region, typically avoiding targets within nearby countries.
The threat of Snake infection is not confined to specific industries or geographical areas. According to some reports, it has the potential to infect all major platforms, including Windows, Linux, and more recently, MacOS. In addition, Snake is a highly popular malware — it often competes with AgentTesla for the top spot of various charts.
Snake is readily available as a Malware-as-a-Service on underground forums, with pricing options that range from 25 to 500 USD.
This infostealer comes equipped with anti-evasion capabilities. In some samples, its downloader component was found to sleep for a period of time to evade automatic sandboxes. It can also terminate processes related to AV and network analysis tools, such as Avast and Wireshark.
Upon completing the initial process, Snake secures its persistence by duplicating itself into the AppData folder under a random name, generating a scheduled task configuration within a temporary directory, and initiating a scheduled task. What’s more, it possesses the ability to self-delete from the system post data exfiltration, employing a deletion command with a 3-second timer.
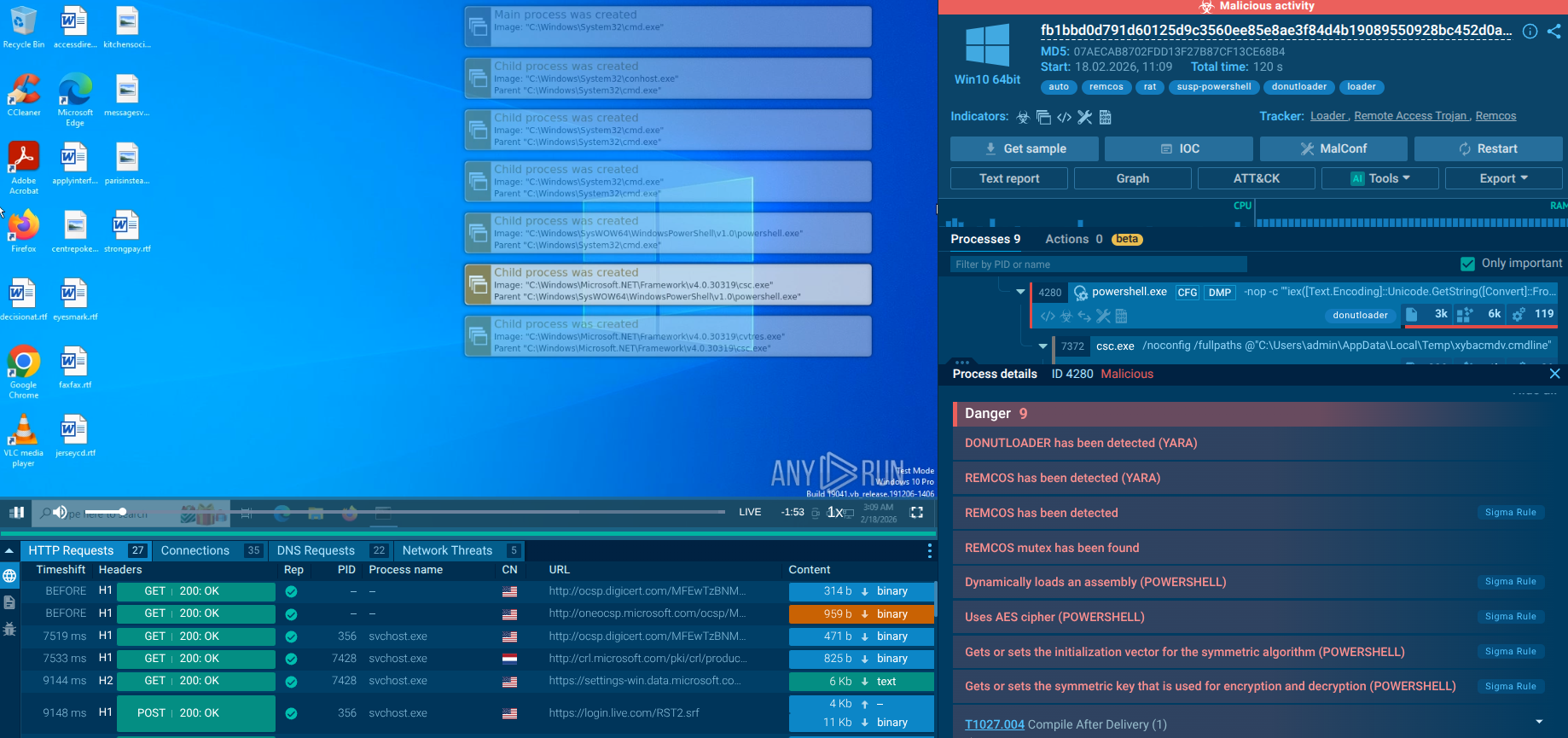
As a typical stealer, Snake keylogger doesn't produce a lot of noticeable activity, which makes its detection potentially tricky. However, once it's established on an infected machine, it may increase its activity — capturing more data and sending it to the command-and-control server.
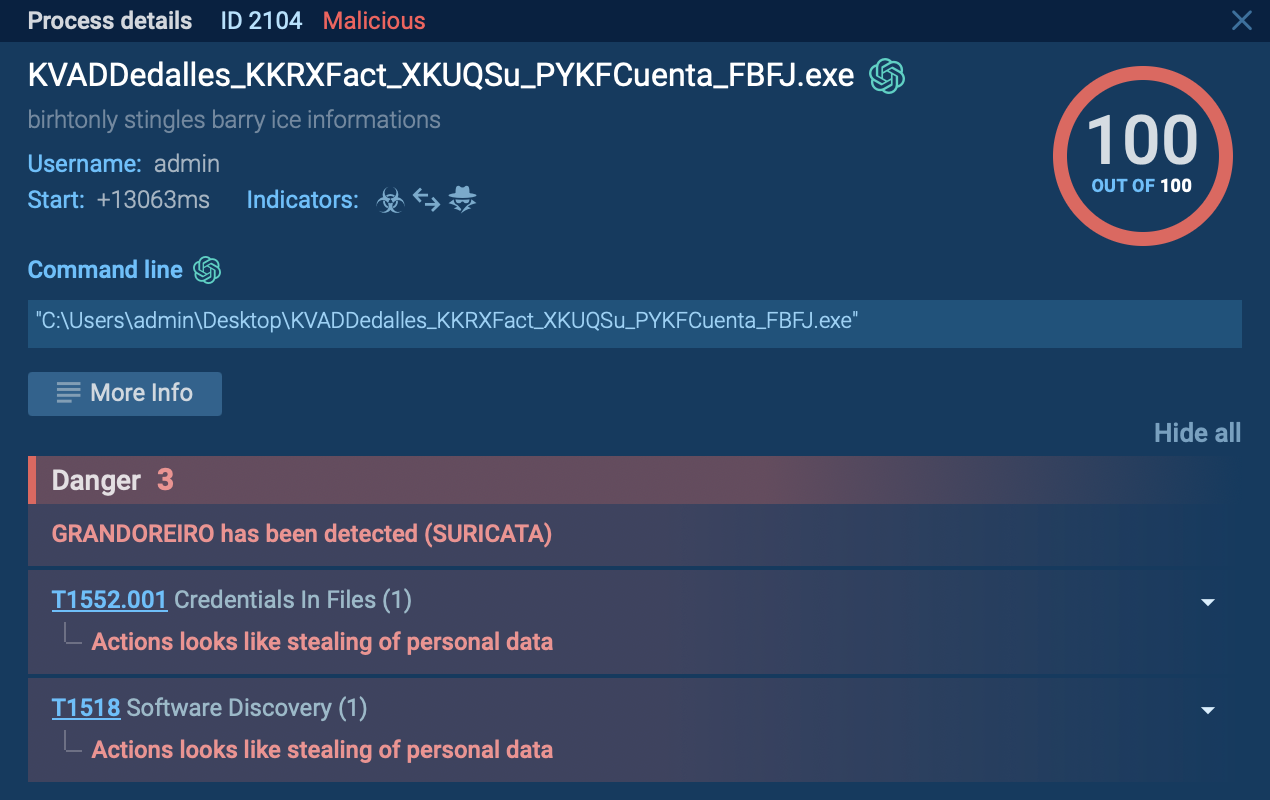
In the majority of Snake versions, a single process is responsible for all malicious activities, which include stealing data from the compromised system. In the specific sample of Snake we've analyzed, this process was identified as arinzehfkd685371.exe.
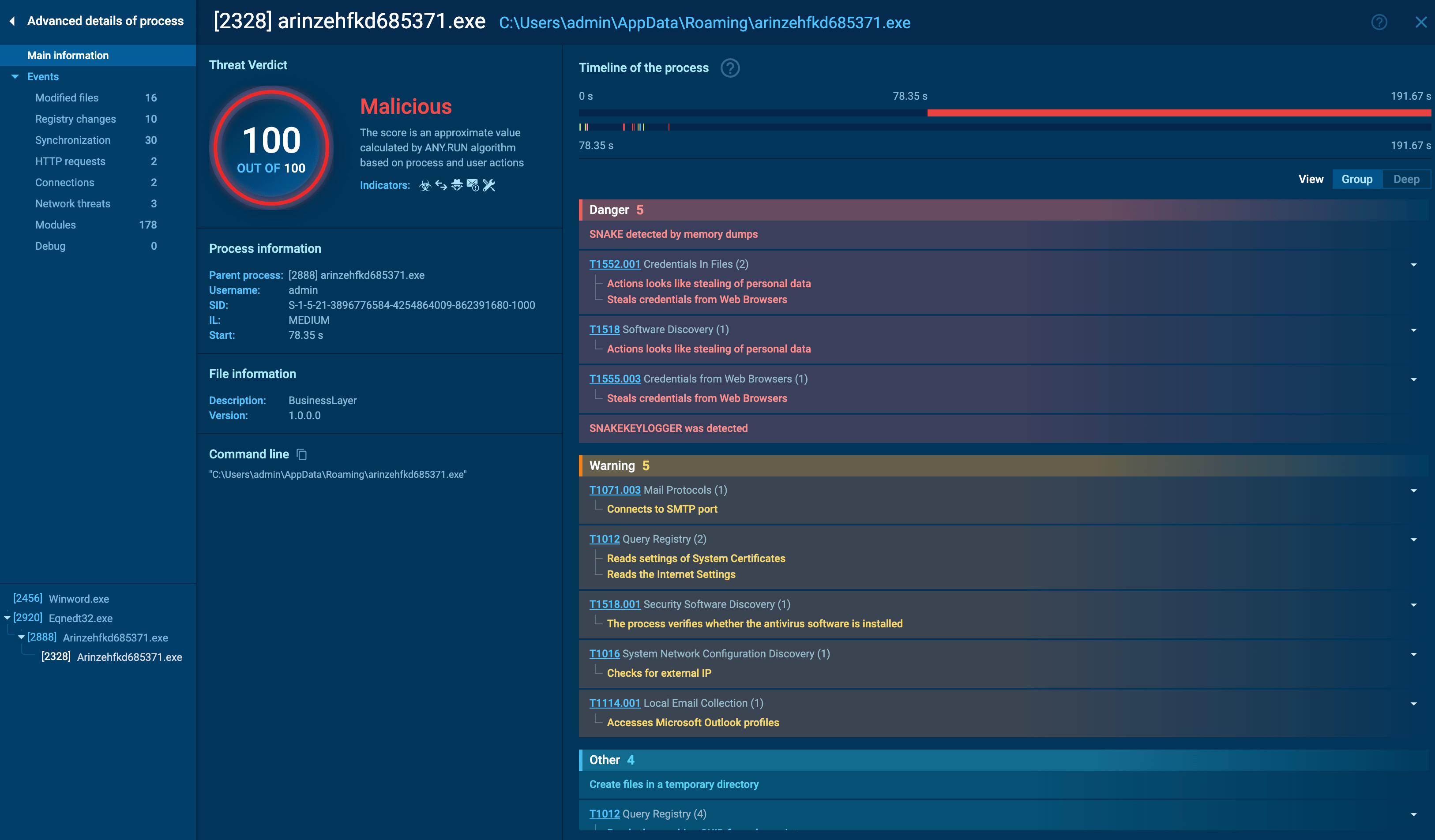
arinzehfkd685371.exe process details
The Snake malware uses a variety of tactics and techniques, as illustrated in the Mitre ATT&CK Matrix. Key strategies include:
It also uses tool transfers and mail protocols for command, control, and exfiltration purposes. Notably, a significant proportion of events (270) involved stealing credentials from files.
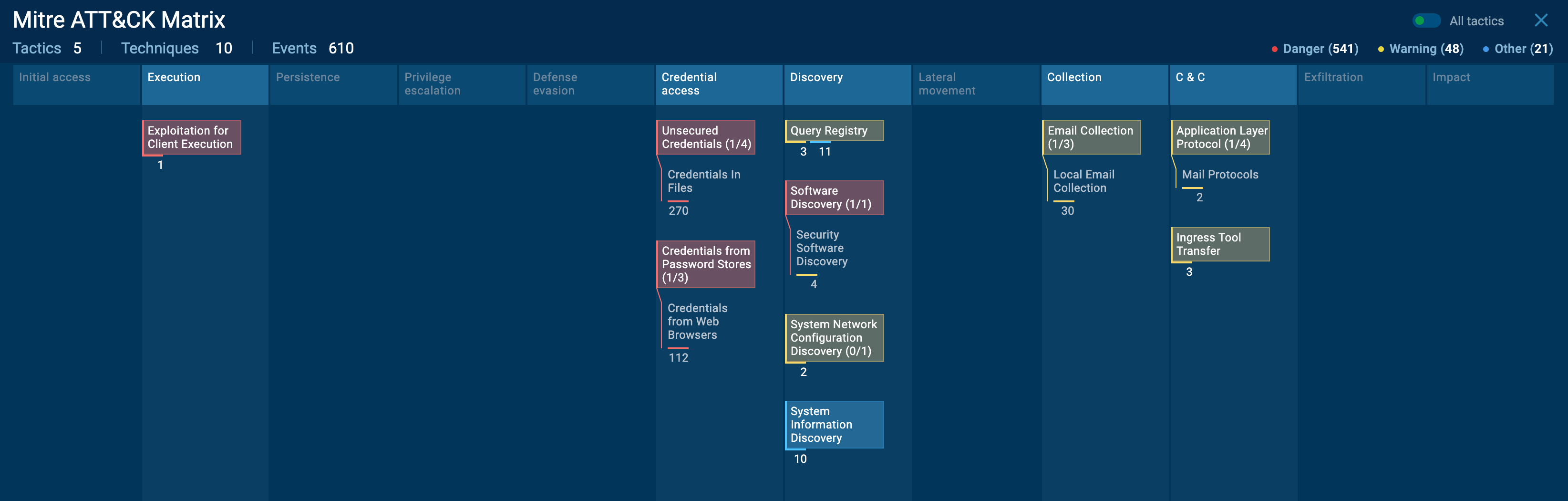
The Mitre ATT&CK Matrix for Snake malware
During the analysis, ANY.RUN cloud interactive sandbox was able to retrieve Snake’s config automatically. The displayed configuration reveals the DES encryption key and the SMTP credentials used for data exfiltration.
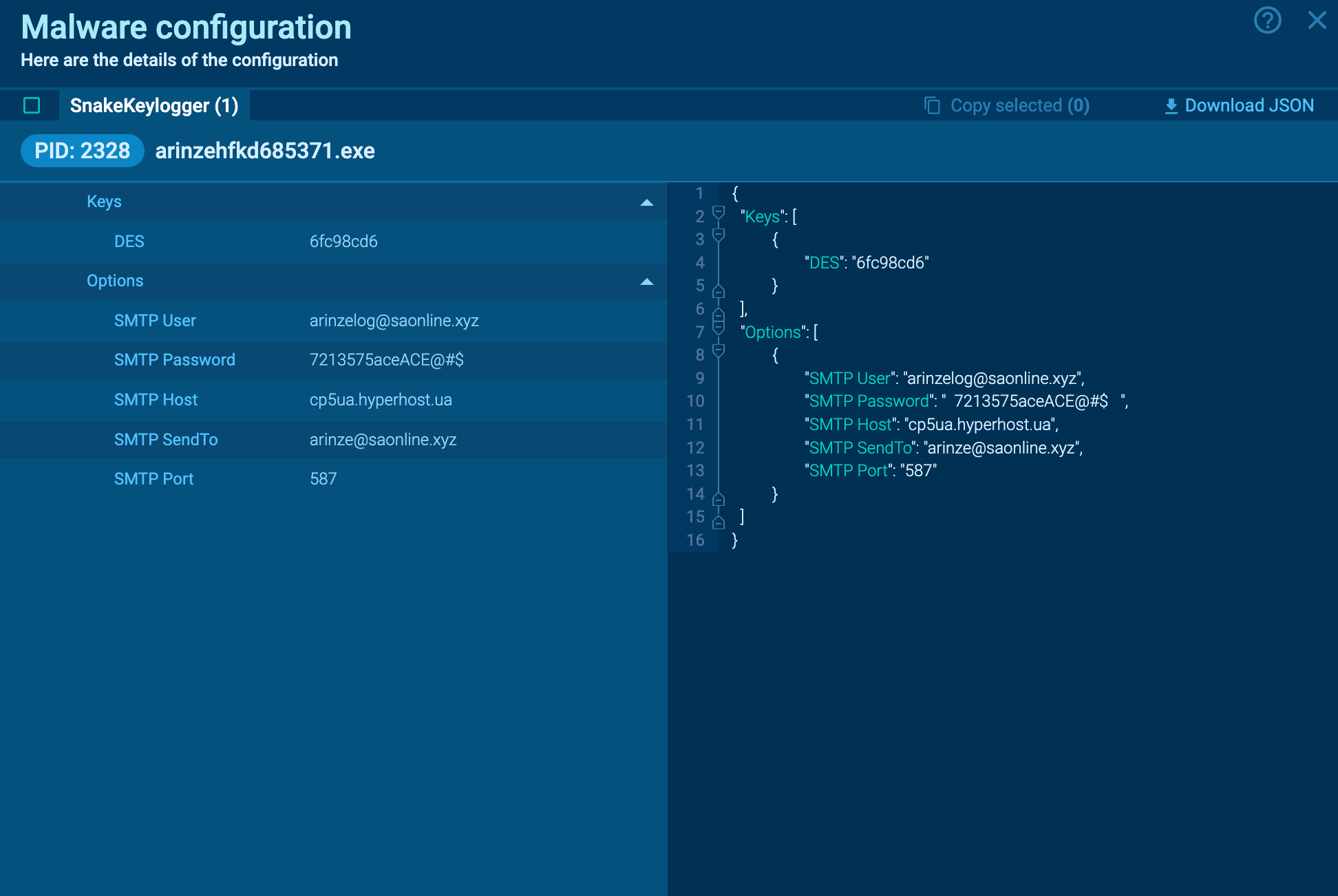
Snake keylogger malware configuration
Network monitoring tools can use this SMTP information for detection, potentially flagging or blocking traffic associated with the host or email addresses.
Read a detailed analysis of Snake Keylogger in our blog.
As is common with Malware-as-a-Service families, Snake is distributed through mass email phishing campaigns and targeted spearphishing. It is known to arrive via infected Microsoft Office documents or PDFs, typically embedded in payment-related messages.
Upon the user extracting the executable, it proceeds to decode and decrypt the base-64 payload, which is contained within a string variable.
Users are recommended to remain vigilant when downloading payment receipts or any documents from unfamiliar senders. Key signs of phishing attempts to look out for include poor grammar, manipulative messaging, and an unusually high number of typos for a professional email.
In closing, Snake is a powerful infostealer and keylogger that targets various industries and platforms, capable of extracting a wide range of data. Its sandbox evasion capabilities only add to the challenge of detection and analysis.
Try analyzing Snake in ANY.RUN. Create a free account using your business email to try out our interactive cloud malware sandbox.