Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases
AZORult can steal banking information, including passwords and credit card details, as well as cryptocurrency. This constantly updated information stealer malware should not be taken lightly, as it continues to be an active threat.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 440
440
 0
0

 2304
2304
 0
0

 4466
4466
 0
0
AZORult is an information stealer malware that is targeted at stealing credentials and accounts. Updated multiple times over the years, AZORult continues to be an active concern for the users, stealing information such as banking passwords, credit card details, browser histories, and even cryptocurrency.
AZORult stealer was discovered, analyzed, and documented for the first time on July 26, 2016, by Proofpoint researchers. At the time, the virus was distributed together with another trojan called Chthonic. However, subsequent spam email campaigns started distributing AZORult as the main payload while Hermes and Aurora ransomware were added as additional payloads. A new strain of the stealer Trojan was documented In July 2018. The analysis revealed that it brought several upgrades to the functions of both the stealer and the loader of the virus, additionally allowing to distribute AZORult with the RIG exploit kit. The latest recorded version of the malware is v3.3. This strain was first documented in October 2018. Most notably, this strain updated a way of encrypting the C&C domain string and improved crypto-stealing function.
A trojan type malware originated in one of the ex-USSR countries. AZORult spyware searches for useful information on the affected computer and sends it to the C2 server to potentially steal the victim’s bank account data. AZORult can steal cookies, browser autofill information, desktop files, chat history, and more.
Interestingly, to get into a machine, the virus, in some cases, requires secondary malware like HawkEye or Seamless. Notably, after every bit of useful data is obtained in campaigns with Hermes and Aurora, user files are encrypted, and a ransom is requested to restore the lost data.
One of the interesting features of AZORult is that after execution, the malware is removed from the system due to the lack of a persistence mechanism.
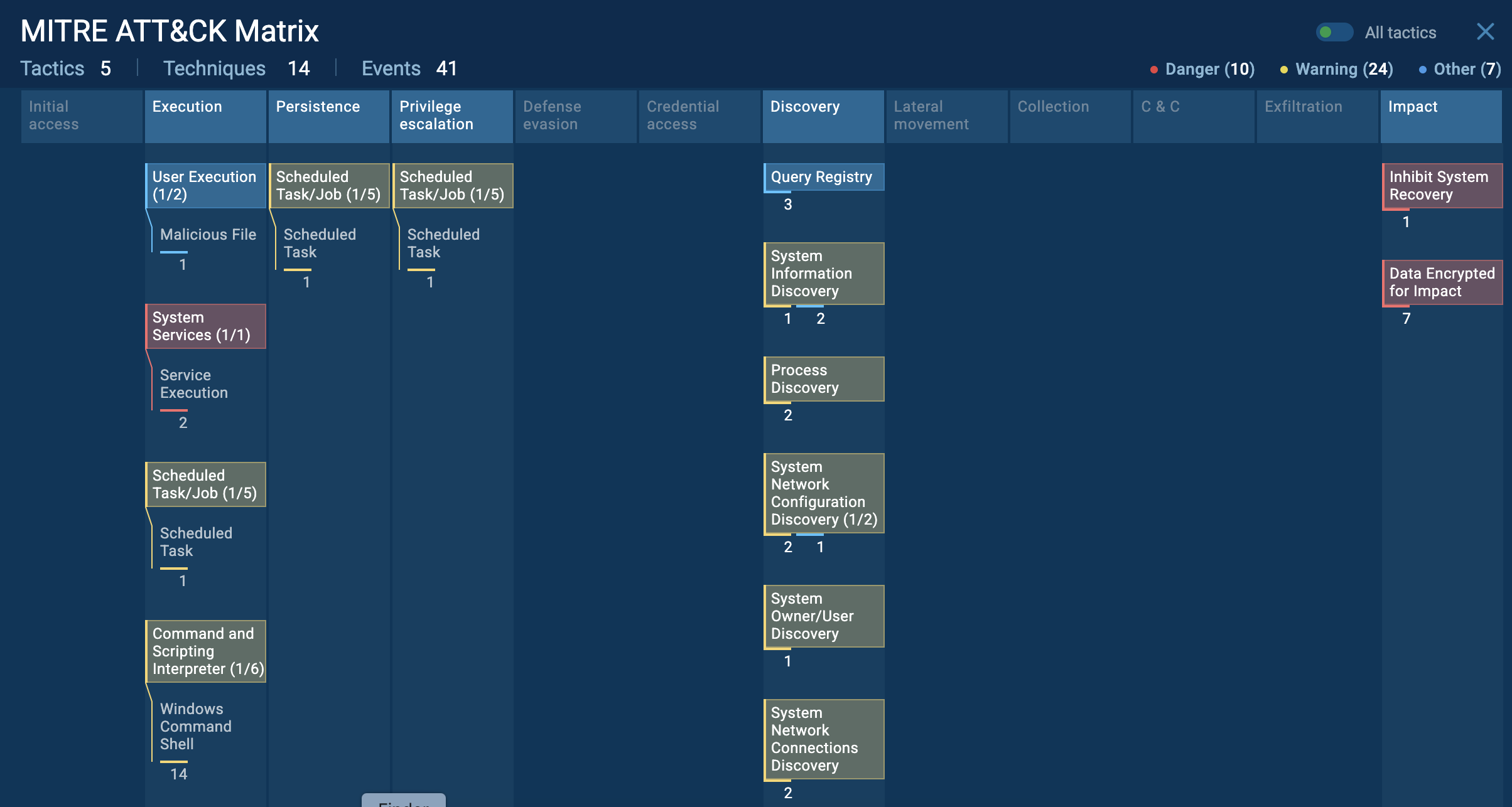
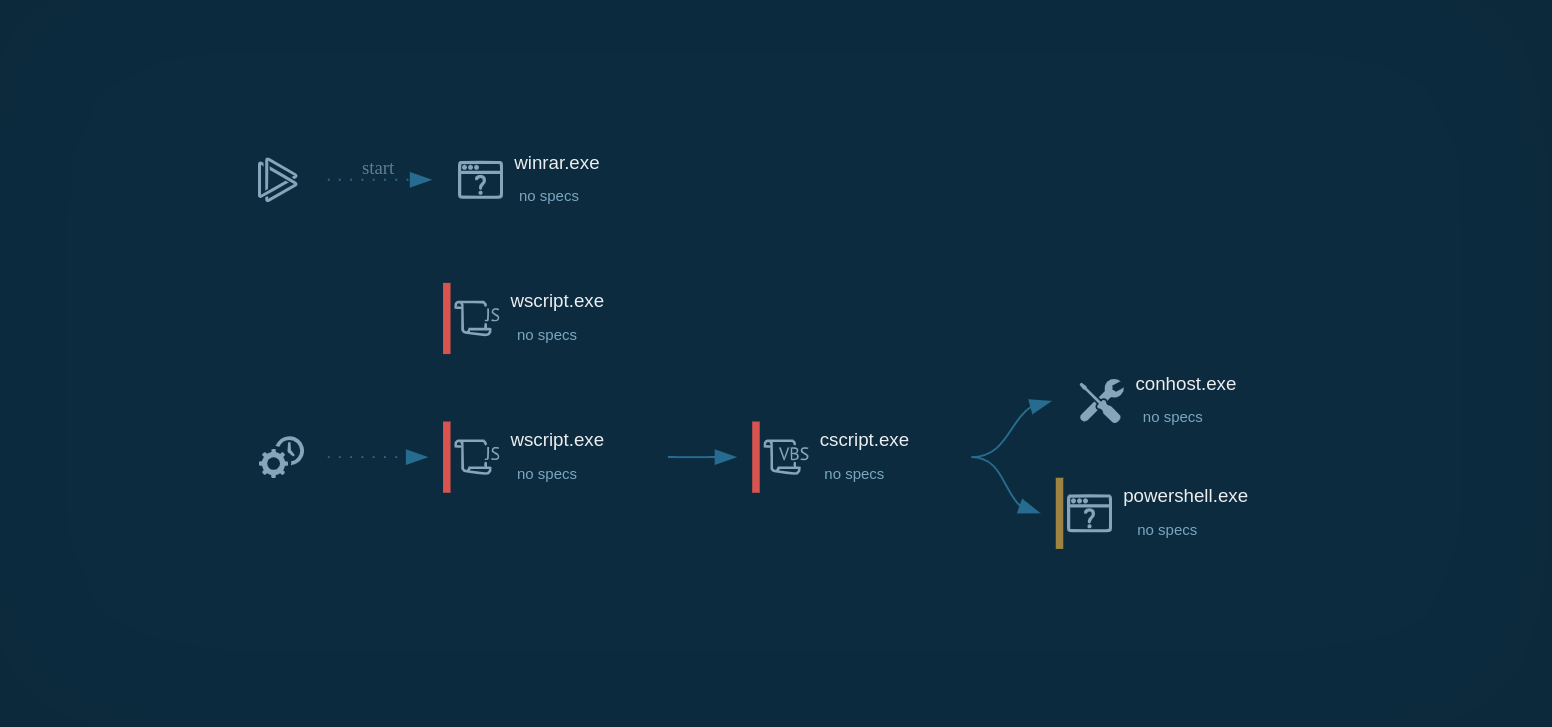
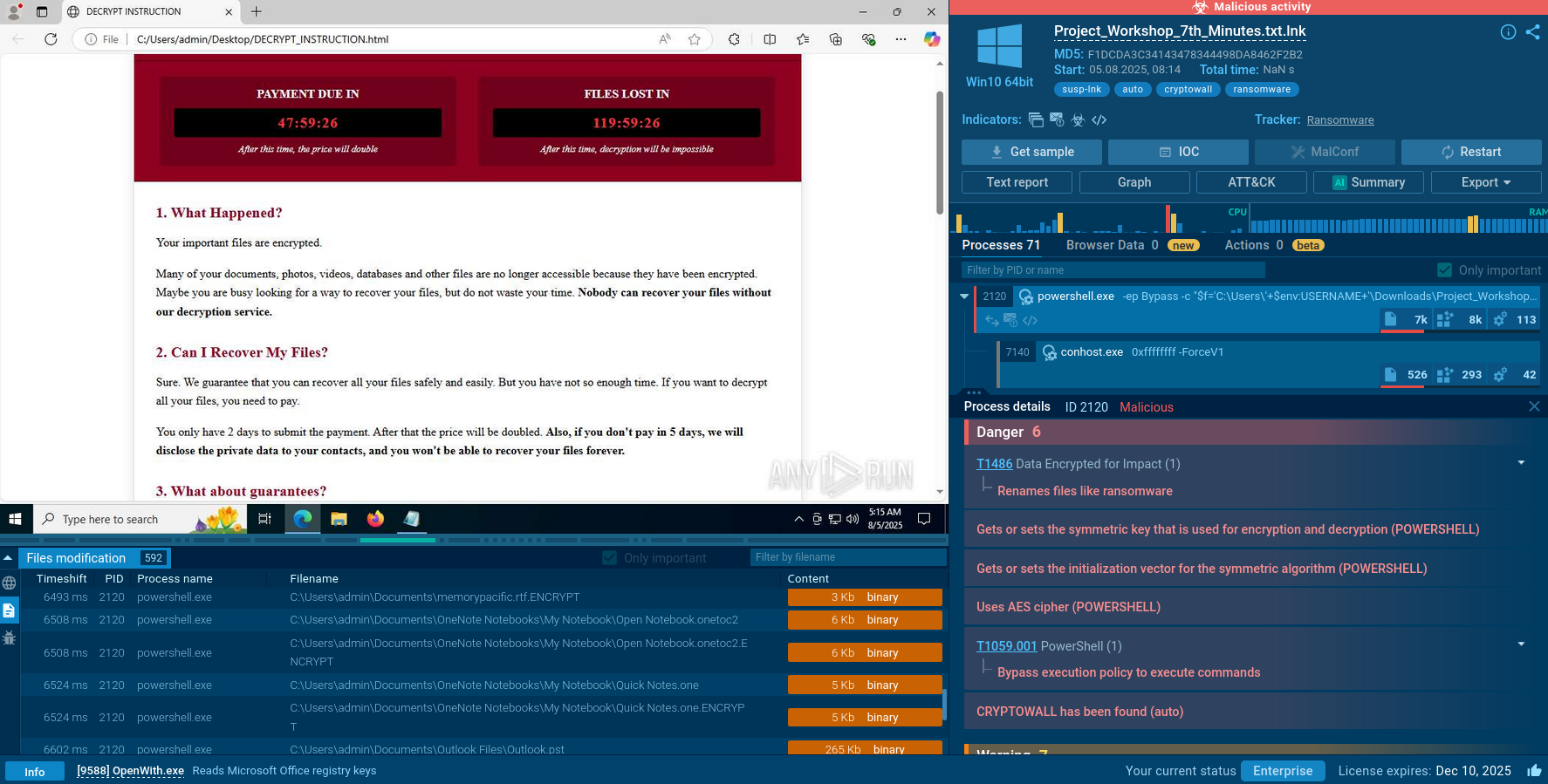
ANY.RUN displays the execution process of AZORult in an interactive virtual environment. As shown by the sandbox simulation, the virus launches the following process during its execution:
The execution process of AZORult can be viewed in more detail in the video provided by ANY.RUN sandbox.
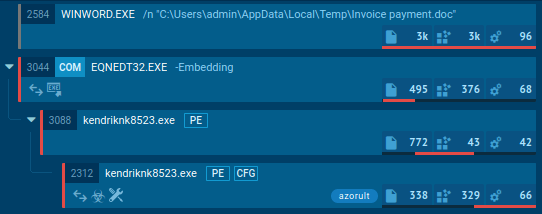
Figure 1: Illustrates the life cycle of malware. Process tree generated by ANY.RUN
AZORult is distributed mainly using spam email campaigns or via the RIG exploit kit. Notably, a major AZORult distribution campaign was observed on July 18, 2018, targeting North America.
Spam emails that the attackers sent carried largely employment-related subjects and included an infected and password-protected resume file that triggered the download of the virus.
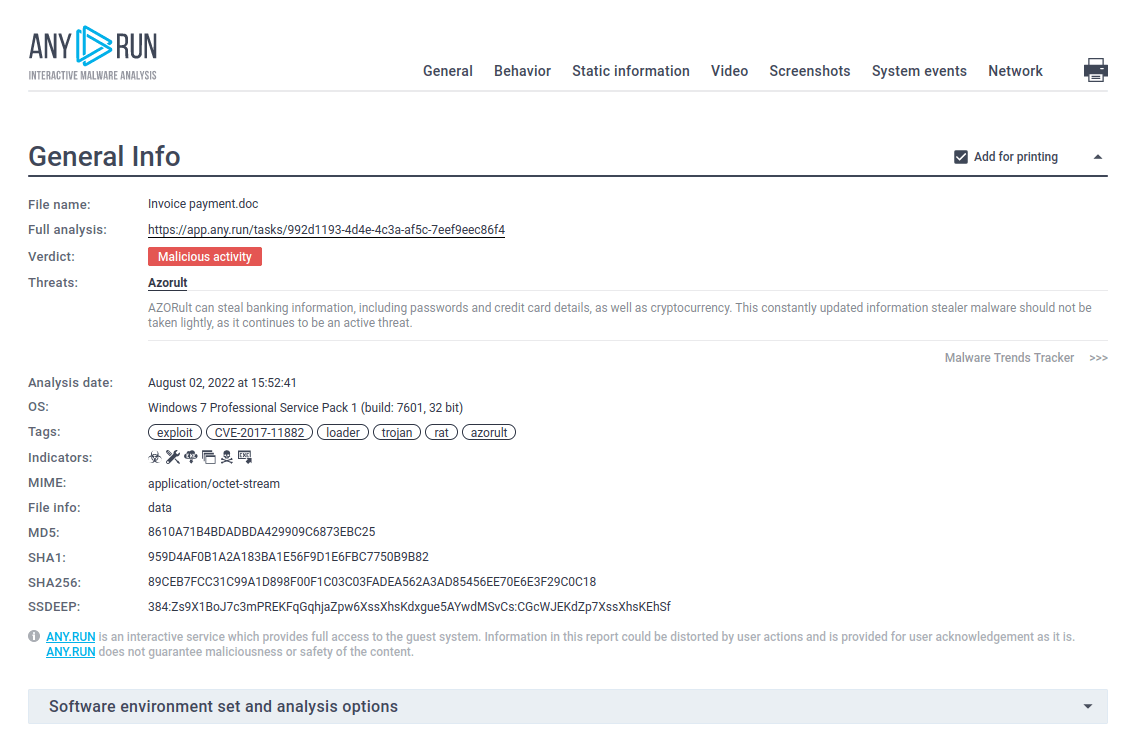
Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN
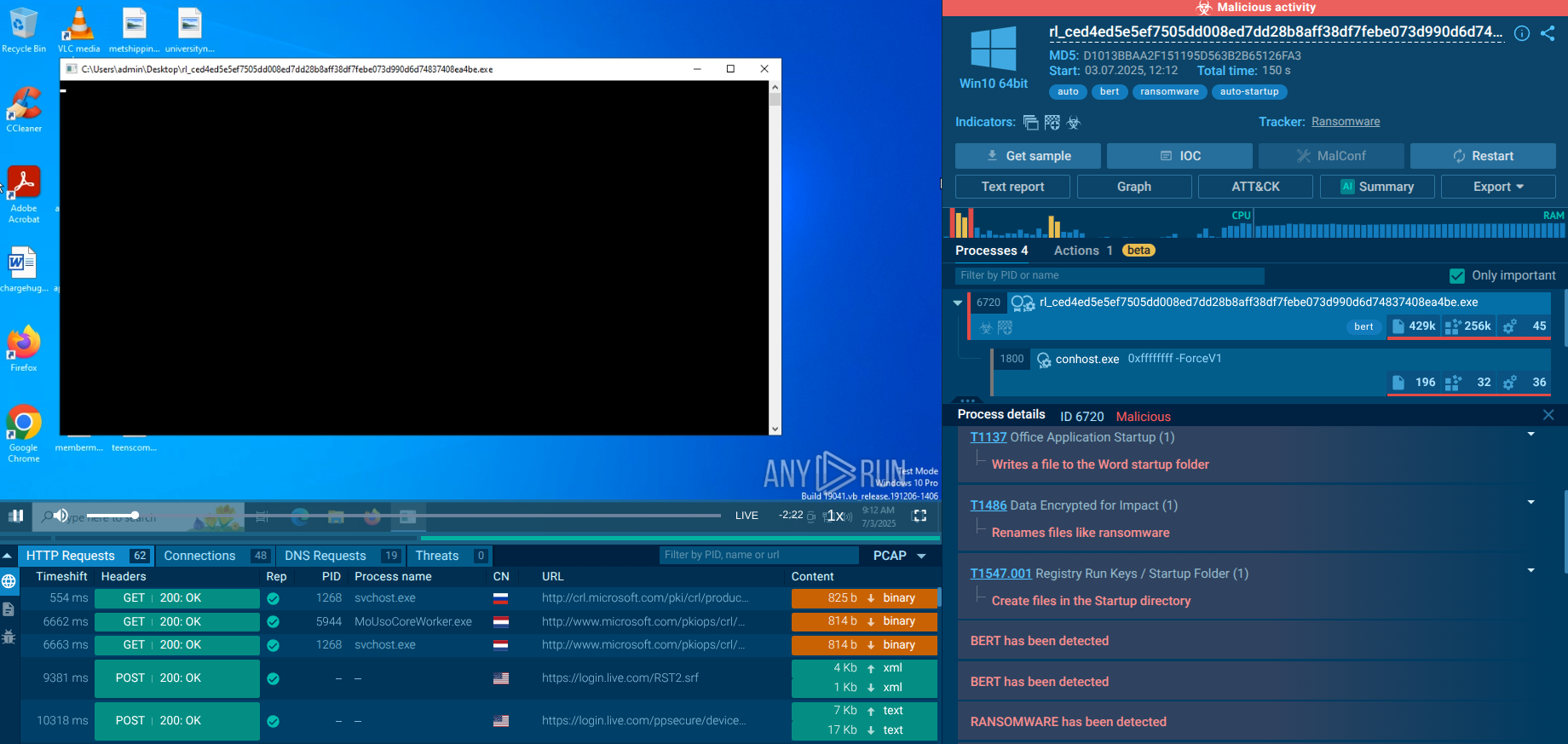
AZORult stealer uses a clever technique to trick various antivirus engines. Particularly, the version of the stealer Trojan distributed in the July 2018 spam campaign was activated after unlocking a password-protected document. Since a password protected the document that was attached to the email, antiviruses had not been able to scan it and determine whether it was malicious or not. For the virus to become active, the victim had to unlock and enable macros for the document. In this particular campaign, the malware was distributed with two payloads embedded in the main binary. Both payloads were dropped to the disk and executed, with the first executable payload being the information gatherer – AZORult itself and then the secondary ransomware.
It should be noted that in aforecited ANY.RUN simulation AZORult uses an exploit when a Microsoft Office file is opened, allowing to embed several malicious OLE objects into a document and executes arbitrary code on a machine, and even download any file from a remote server and execute it.
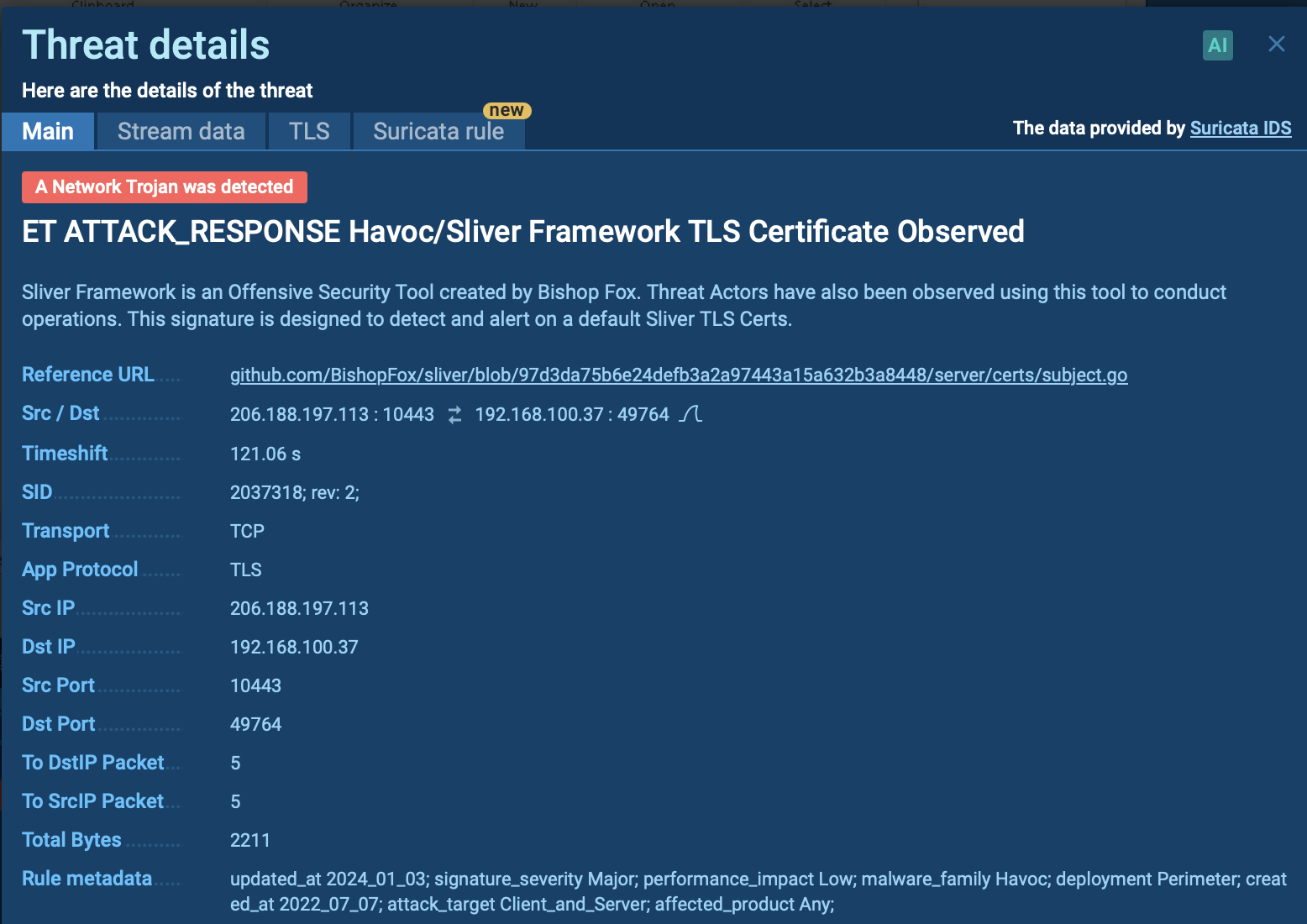
If you want to share your virus analysis with others, you can create a text report and send it to anyone you want. Just click the "Text report" button. You can save it by using a printer icon in the upper-right corner of the report, or using your browser function by clicking the "Save page as..." or "Print..." buttons. You can also download or share other malware investigations, for example Adwind or Remcos. Note that you can choose that information section in your report you want to print or save into a file using the "Print..." button by clicking in the checkbox "Add for printing" on the right side of the sections. On the illustration below, the second section won't be included in the report.
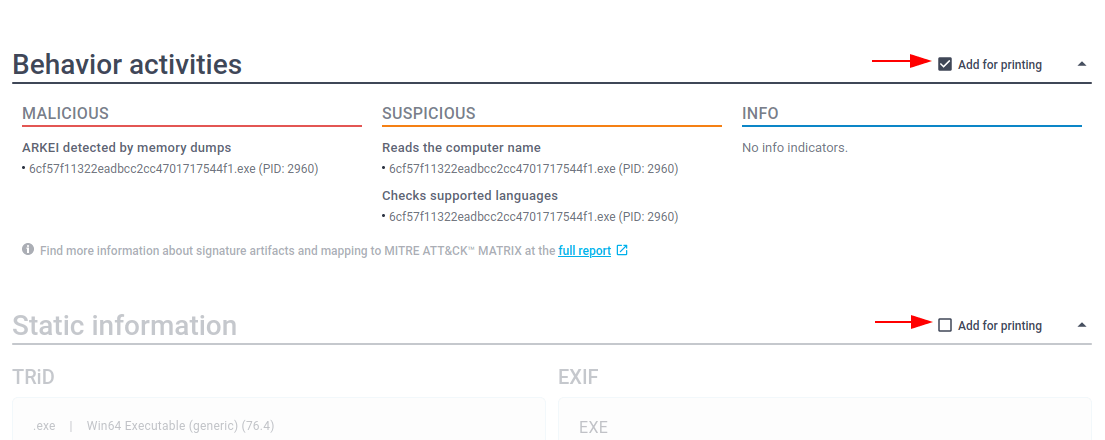 Figure 3: Text report
Figure 3: Text report
AZORult remains to be a hazardous trojan. The stealer Trojan has been upgraded throughout its lifespan and currently poses even more dangers than during the first days of its lifespan. Particularly, most recent versions of AZORult are distributed in bundles with ransomware and can steal cryptocurrency from the victims.
AZORult's distribution in clever email campaigns makes becoming a victim of the stealer Trojan by accident relatively easy. The interactive sandbox analysis provided by services like ANY.RUN is a great way to learn more about the threat and greatly increase cybersecurity.

From May 15 to May 31
Celebrate with us and grab your gift



