Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

Adwind RAT, sometimes also called Unrecom, Sockrat, Frutas, jRat, and JSocket, is a Malware As A Service Remote Access Trojan that attackers can use to collect information from infected machines. It was one of the most popular RATs in the market in 2015.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Likely Mexico
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2012
First seen
:
|
19 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Likely Mexico
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2012
First seen
:
|
19 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Adwind RAT, sometimes also called Unrecom, Sockrat, Frutas, jRat, and JSocket, is a remote access trojan available as MaaS ( Malware-As-A-Service ). Adwind can collect user and system data, control the webcam of the infected machine, capture screenshots, install and run other malicious programs, log keystrokes, steal web browser passwords, and more.
First identified in January 2012, Adwind can’t be called a new malware, but it managed to become as popular as ransomware despite the age. In fact, in 2015, over 1,800 people purchased Adwind on its “official” website, making the site one of the most popular malware distribution platforms globally. It should be noted that Adwind poses a danger to users of all major operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and BSD.
Initially discovered for the first time in 2012, the malware was known as Frutas and presumably originated in Mexico. For the initial year of Adwind’s existence, the creator released multiple versions, all distributed on Spanish hacker forums for free.
The feature-set of the original version was somewhat limited as compared to the latest iteration of the virus. As such, in 2012, Adwind RAT could capture screenshots, steal passwords from selected online services, open specific web pages and take screenshots, as well as display pop-up messages.
In 2013, the creator of the malware released a new version, changing its name to Adwind. The new version added support for Android OS and started to gain traction outside of the Spanish hacker community, becoming a popular tool worldwide. Following the popularity of the malware, the author has set up a YouTube channel to post tutorials for other cybercriminals. During the same year, the first-ever case of Adwind malware used in a targeted attack was documented in Pacific Asia. In November 2013, the malware was rebranded as UNRECOM and sold to Unrecom Soft. The rebranded version of Adwind retained all functionality of the previous iteration.
In 2014, the source code of Adwind was leaked. As a result, it became available online free of charge, becoming a popular tool among cybercriminals who widely used the cracked versions in attacks during 2014 and 2015, further contributing to the overall popularity of Adwind. In response to the leak, the “official” version of Adwind Trojan was significantly upgraded and re-released as AlienSpy in October 2014. The Adwind RAT v3.0 learned to auto-detect sandboxes, gained cryptographically secured communication with the control server, and became capable of detecting and disabling antiviruses.
Finally, in 2015, the malware was renamed once again, becoming a JSocket RAT. As a malware-as-a-service, Adwind RAT is sold to users for a fixed fee charged monthly as a subscription and could be purchased at JSocket.org until the website became unavailable. The price depends on the package which the user chooses.
Based on the analysis, Adwind requires active actions from the potential victim to start the execution process. As such, being delivered in a malicious .JAR file, the malware won’t be able to execute itself until the victim double-clicks on the attachment.
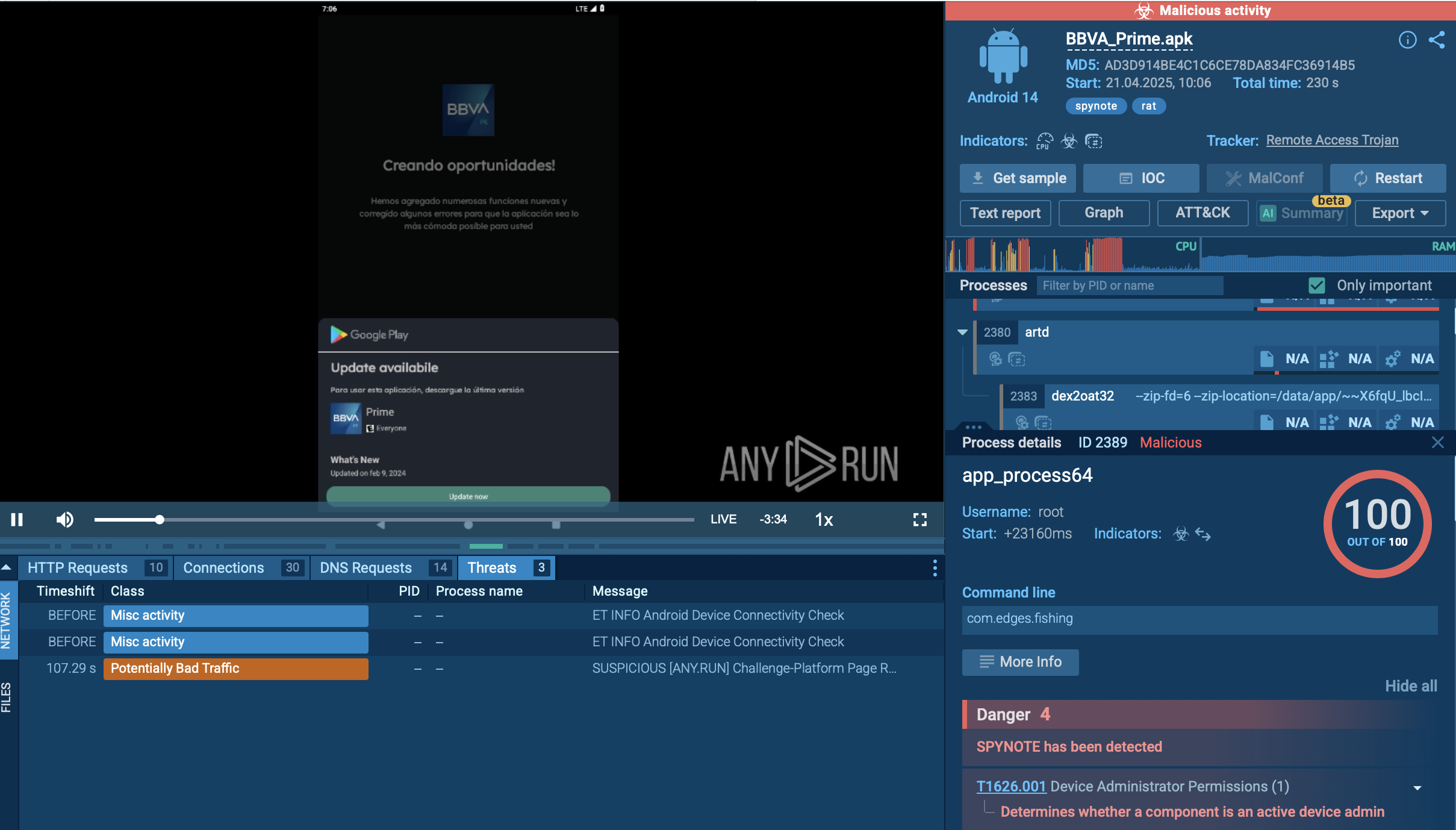
ANY.RUN interactive service enables researchers to perform the analysis of the execution process of Adwind Trojan in a secure environment in multiple formats, including video.
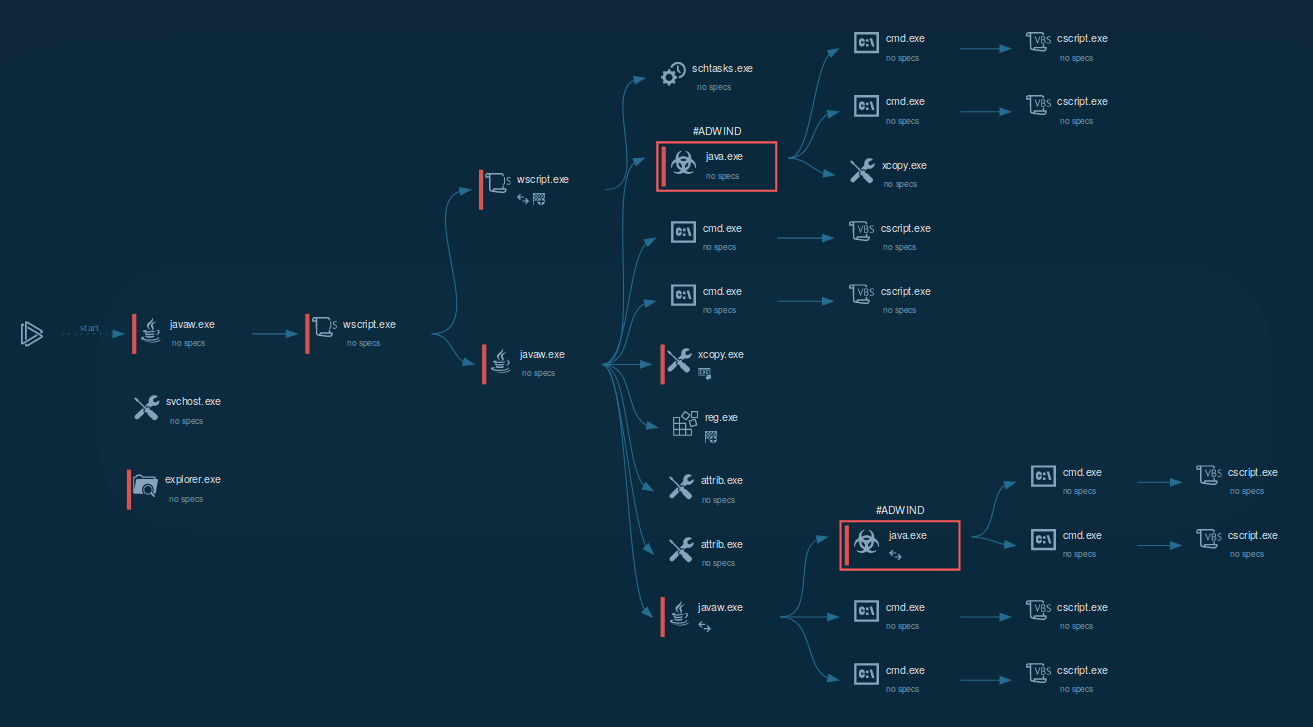
Figure 1: Visual process graphs generated by ANY.RUN help to simplify and speed up research work
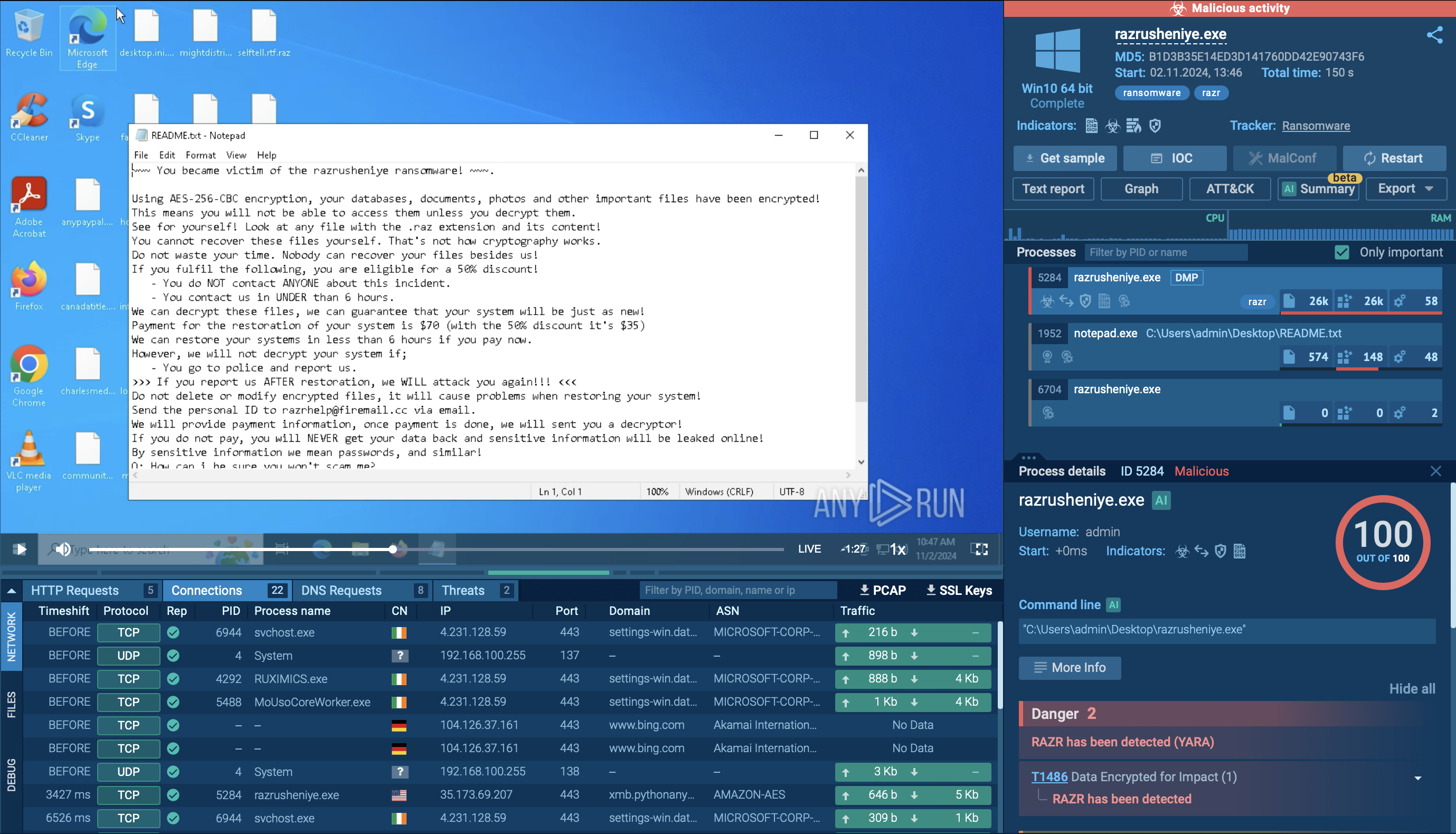
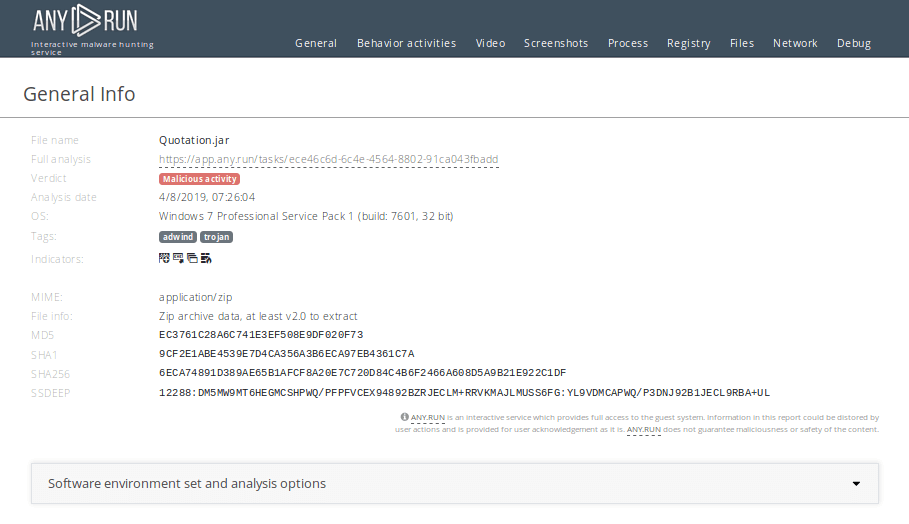 Figure 2: ANY.RUN creates customizable text reports allowing researchers to share the results of the simulation easily
Figure 2: ANY.RUN creates customizable text reports allowing researchers to share the results of the simulation easily
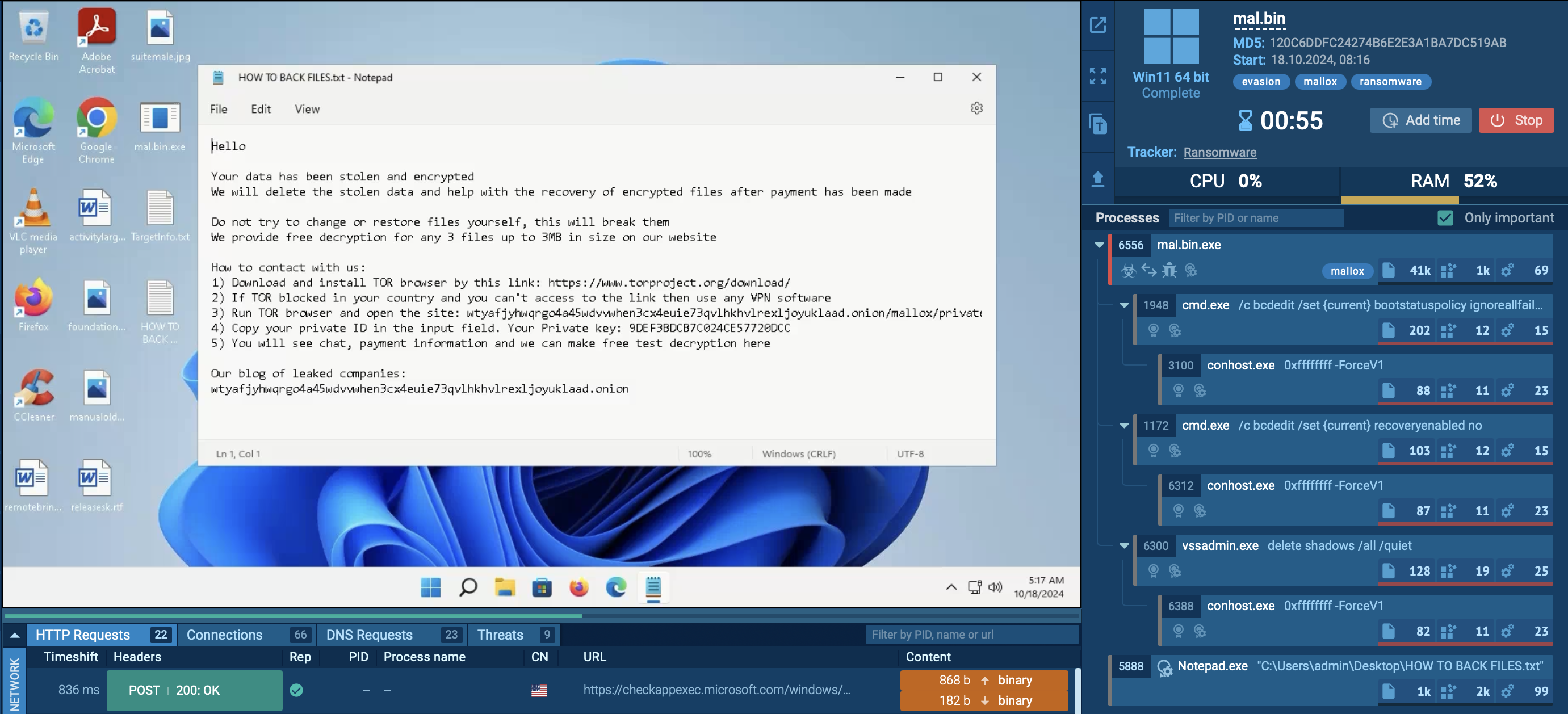
In the case of our simulation, after a user opened the malicious .jar file, the malware started execution through Java virtual machine. This initial process executed the js script, which ran one more js script and another .jar file.
JS script also used Task Scheduler to run itself later. Jar file started a series of malicious activities such as using attrib.exe to mark files or folders as hidden, running VBS script files, changing the autorun value in the registry, and more. It has been noted that sometimes Jar file runs a series of taskkill commands to shutdown processes by their names based on a list containing names of system processes, names of common Anti-virus programs, and analyzing programs wireshark.exe, procexp.exe, processhacker.exe, and so on. It should be noted that this malware doesn't work without installed Java.
Exhibiting caution when handling emails from unknown senders is a reliable way to prevent contamination since Adwind trojan requires a victim to interact with the malicious file to enter an active phase. Therefore, never downloading attachments in suspicious emails is a sure way to stay safe when you are dealing with any malicious objects such as ransomware, RAT, or others. In addition, preventing .JAR files from running in %AppData%[random folder name], and prohibiting the creation of .JAR in the same folder can be considered a good security measure.
Adwind RAT is distributed in mail spam campaigns the same as AZORult or Remcos and has two general attack vectors. It can be delivered to the victim's machine as an email attachment in the form of a malicious file such as a PDF or a Microsoft Office file.
The other attack vector is a malicious URL that redirects the victim to a website from where Adwind is downloaded.
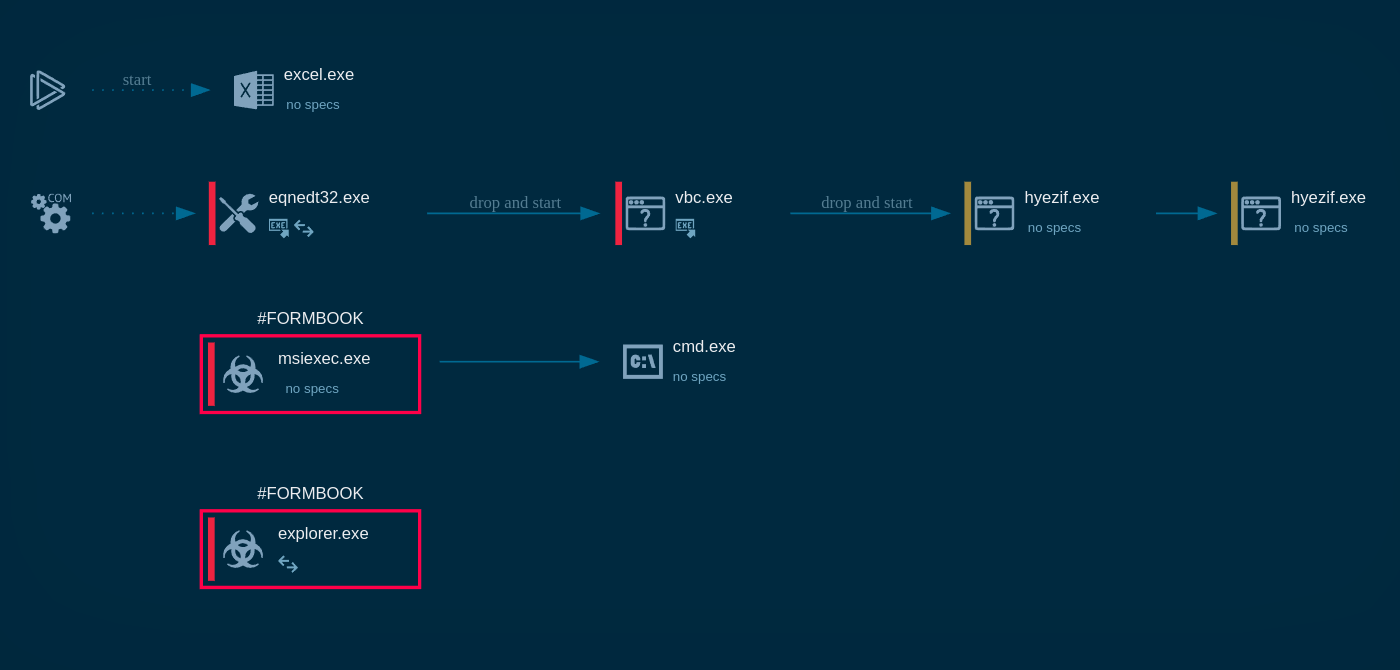
Analysts can export the process graph from a task to SVG format if they want it to share. Just click on the "Export" button and choose "Export Process Graph (SVG)" in the drop-down menu.
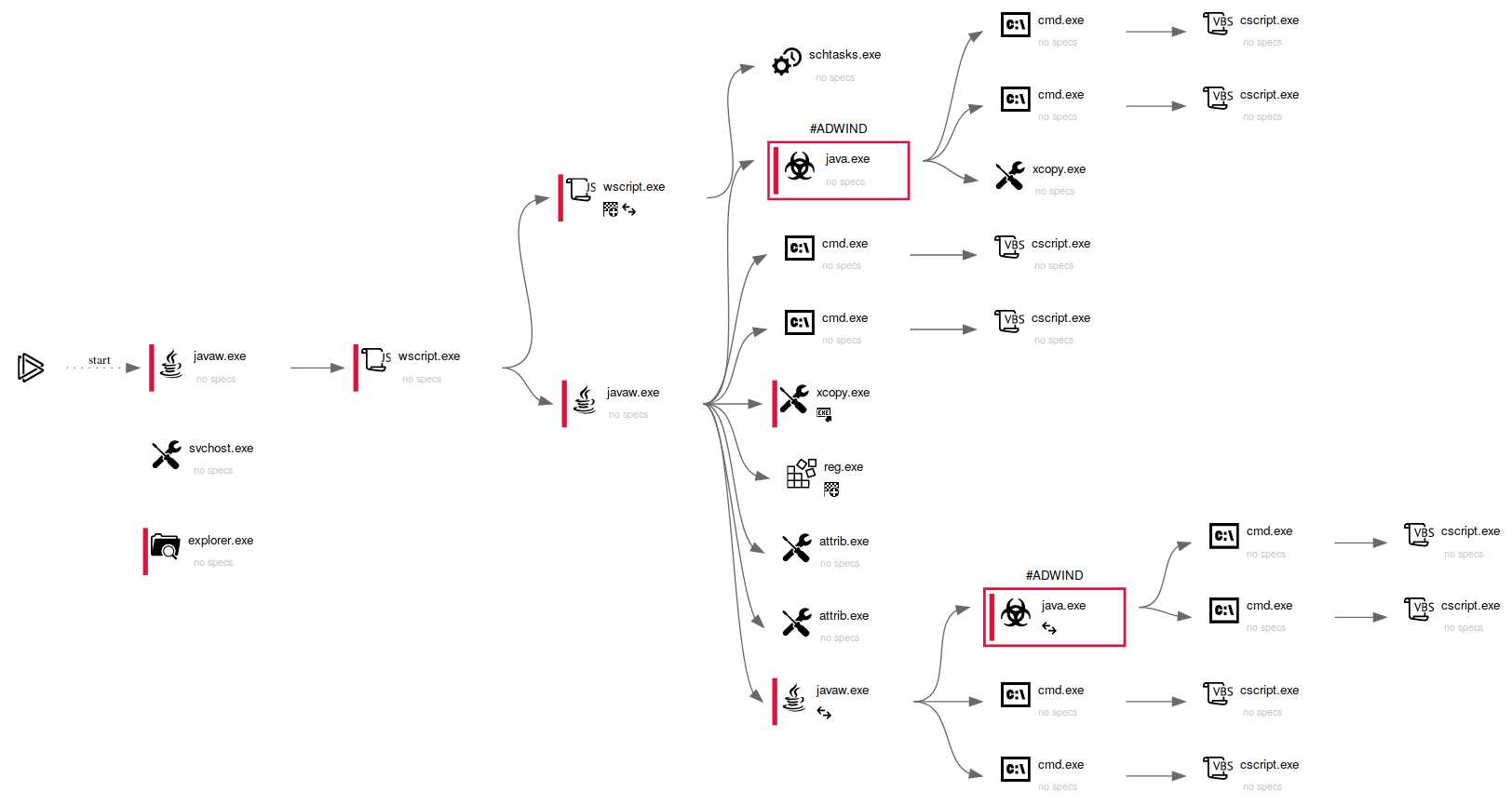 Figure 3: Adwind's process graph exported in SVG format
Figure 3: Adwind's process graph exported in SVG format
Distributed as a malware-as-a-service, the Adwind RAT v3.0 has become one of the most popular RATs and targets users of all major operating systems worldwide.
Not only is the “official” paid version of the malware is known to have created a massive following, but several slightly outdated but still very powerful cracked, free-to-use versions are readily available online on the underground hacking forums together with ransomware. As a result, today, Adwind remains a serious, active, and, perhaps, even growing threat.