What is Emotet Trojan?
Emotet is a highly sophisticated and destructive Trojan used to download and install other malware. First recorded in 2014, it was classified as a banking trojan, but Emotet has gained advanced capabilities throughout its lifetime and evolved into an entire malware distribution service.
So what makes the Emotet virus so dangerous? Based on the analysis, Emotet can act like a worm and spread using local networks, which makes it extremely hard to clean up. In addition to this, the trojan has advanced persistence and anti-evasion mechanics, such as detecting sandboxes and virtual machines with an option to generate false indicators to throw research off.
On top of that, the trojan has a polymorphic design – meaning that it can change its code to bypass signature-based detection, making this cyber defense strategy useless against its' attacks. Besides that, Emotet receives updates from the control server, performing this operation as if an operating system update is being installed. This allows the trojan to drop additional malware onto the infected machine stealthily.
It should also be noted that the Emotet trojan has a modular design which makes it possible to adapt this malware to various tasks and customize it for every particular campaign, giving the attackers maximum flexibility. Emotet's main targets are governments, corporations, small businesses, and individuals, focusing on Europe, America, and Canada.
General description of Emotet virus
The first version of Emotet malware which was spotted in the wild back in 2014, was designed to steal banking credentials by intercepting internet traffic and was much more basic than the beast of a Trojan which we know today. When Emotet was first spotted in the wild, the malware targeted mainly banks from Germany and Austria using only its native information stealing toolset.
Version two followed shortly after, this time carrying several additional modules such as a money transfer, mail spam, DDoS, and address book stealing modules. The third iteration of Emotet was released in 2015. This time attackers focused on upgrading the anti-evasion functionality of the malware and introducing banks from Switzerland into the list of potential victims.
The next overhaul of the Emotet malware followed in December 2016, changing the attack vector of the virus. At the beginning of its lifetime, Version 4 of the virus heavily relied on the RIG 4.0 exploit kit to make its way into the victims' computers, later switching primarily to mail spam. The same iteration of the malware also marked the moment when the primary use case of the malware started shifting from using its own banking module to dropping other Trojans onto infected machines.
Speaking of modules, Emotet malware can perform a large number of malicious activities that vary depending on the modules used in a particular campaign. Most versions of the virus included a spam module that can be used to continue the spread of the malware by sending out a series of malicious emails from the infected machine. Another typically included module is the one used for credential stealing, allowing Emotet to steal sensitive information from web browsers and mail clients.
In 2017, Emotet trojan was equipped with a spreader module, allowing the malware to infect all machines connected via a local network. The virus also gained the address book stealer module – this one is interesting. It analyzes the relationship between email senders and receivers and uses the collected information to enhance the effectiveness of subsequent campaigns originating from the users' PC, targeting friends, family members, and colleagues of the victim with personalized spam emails.
Not only does Emotet malware provide flexible functionality through the use of modules and has several anti-evasion functions, but it also puts a heavy emphasis on persistence. To ensure that the malware stays in the infected machine, it injects into running processes, downloads additional payloads, often targeting the Explorer.exe. In addition to that, the malware uses Scheduled Tasks and makes registry key changes.
In January 2021, the Emotet botnet was taken down by law enforcement. The global effort, known as Operation Ladybird, located the malware infrastructure around the globe. They arrested at least two of the cybercriminal gang members in Ukraine. Their attackers' names were not uncovered.
Security experts teamed up and simultaneously hijacked hundreds of Emotet command-and-control servers and disrupted its backups, too. Researchers placed their own machines at the IP addresses of crooks' computers and made the payload inactive to prevent connection with the botnet.
These actions led to the fact that Emotet's C2 servers didn't work for almost ten months.
On November 14, 2021, Emotet came back with a new version. The botnet started to spread numerous maldocs. Moreover, it changed its tactics. The Emotet virus used to drop Trickbot or Qbot. But right now, the malware is also dealing with Cobalt Strike. It means that the time between the initial infection and a ransomware attack shortens significantly.
Also, researchers noticed that Emotet brings up more and more C2 servers to life. The botnet's new version acquired ECC encryption, modified communication protocols - new initial check-in, etc.
It should be noted that the mentioned Trojan versions are extremely destructive, and their attacks can have several consequences. For example, malware can cause loss of private data, inability to operate the infected PC up to its total disability, and financial losses associated with restoring the damaged infrastructure. In fact, one company was forced to spend an excess of one million dollars in order to deal with the aftermath of an Emotet attack.
Emotet malware analysis
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service, displays the execution process of Emotet, allowing to perform the analysis of the malware behavior in a lot of detail. You can also investigate other malware like FlawedAmmyy or Agent Tesla.
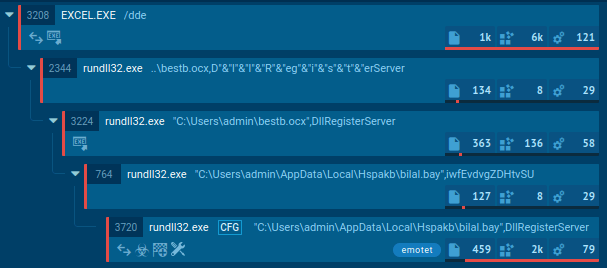
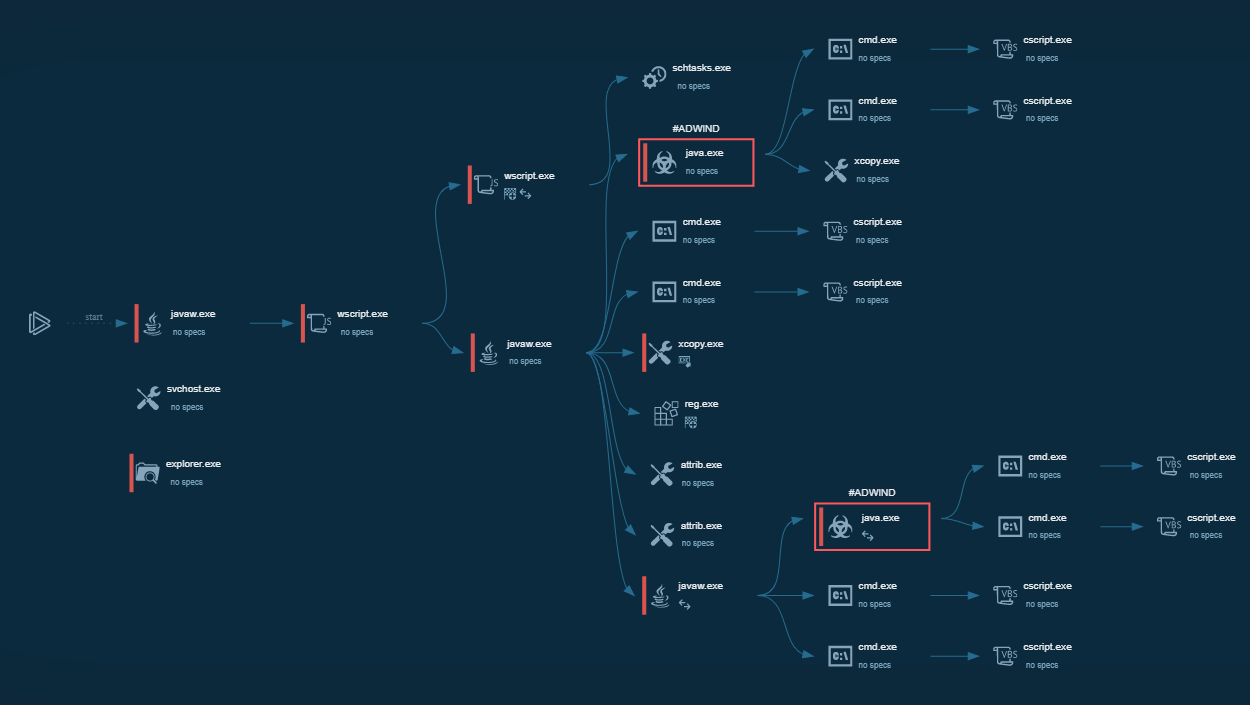
Figure 1: Displays the processes list generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service
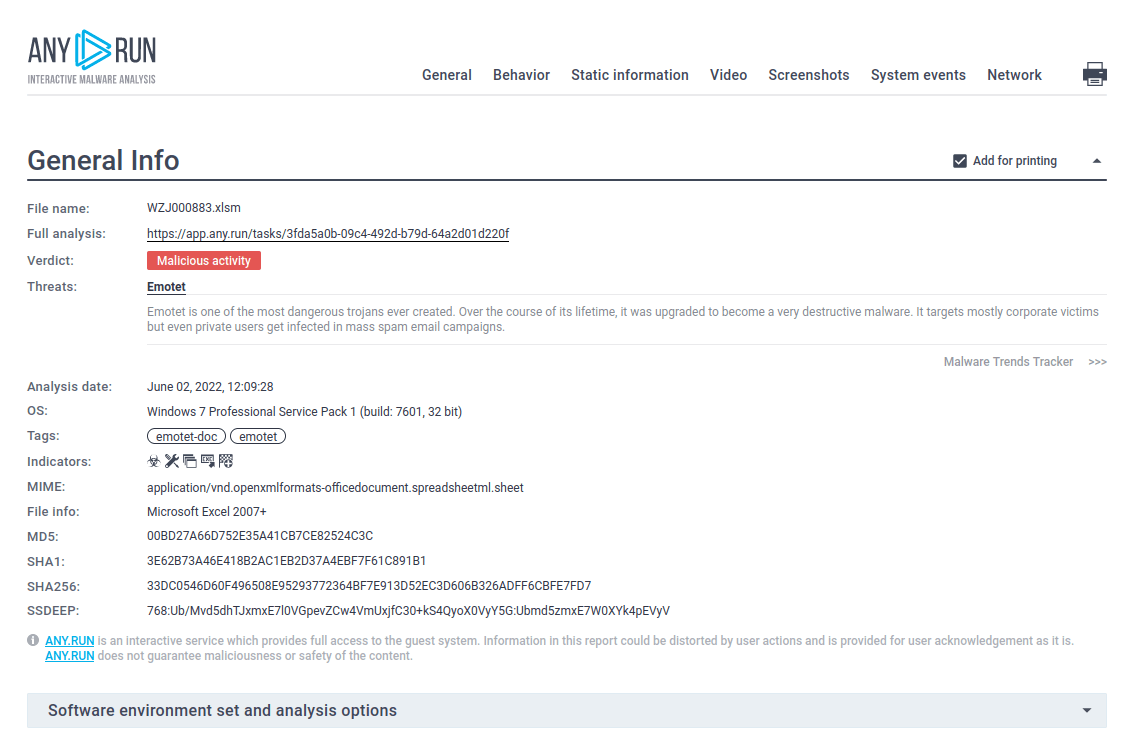
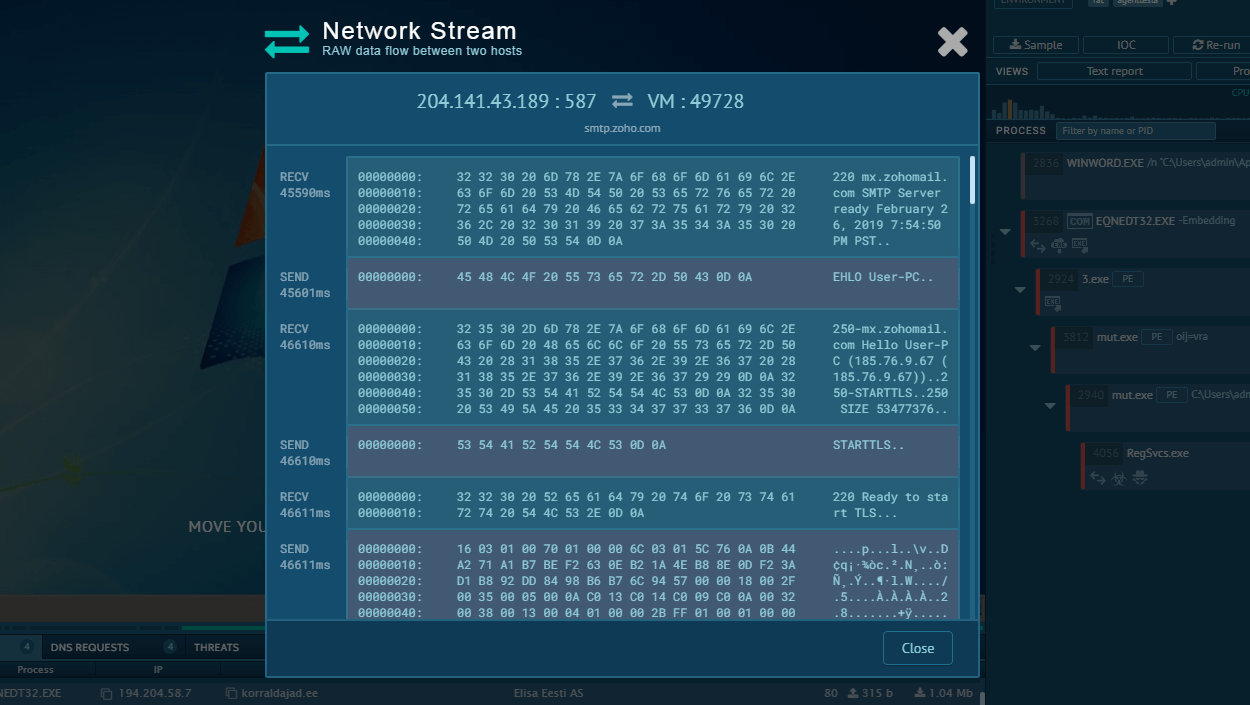
Figure 2: Even more information about the execution of Emotet can be found in customizable text reports generated by ANY.RUN
Emotet execution process
The Emotet trojan's primary distribution is through malicious email spam campaigns. The first step in the chain of infection involves tricking the potential victim into opening an attached Microsoft Office file using social engineering. After the file has been opened and macros enabled, there is no need for additional user actions.
Downloaded files contain malicious VBA code that runs after a document has been opened. One of the possible options of the infection process is when the VBA code utilizes WMI to launch a Powershell code which downloads the payload – a malicious executable file from the webserver. Notably, the Powershell script is encoded.
Emotet makes steps to maintain a presence in the infected system - it copies itself into %AppData% subfolders and changes the autorun value in the registry. Besides that, the malware allows its attackers to download additional payloads. The malware sends information to and from a server through all infection processes. As the last execution step, Emotet waits for commands from command-and-control servers.
Prevention of Emotet attacks
To minimize the risk of Emotet virus infection and potential destruction if such infection does occur, users are advised to follow a set of standard best practices, such as not downloading files from suspicious emails and keeping an updated version of antivirus on the machine at all times.
For organizations, it is advised to restrict inbound SMB communication between client systems to prevent Emotet from spreading from one machine to another within the local network, provide security training for personnel and instruct employees about the danger of mail spam as well as take all possible precautions to filter out potentially malicious emails at the firewall.
How does Emotet spread?
According to the analysis, the main distribution method of Emotet malware is malicious email campaigns. The trojan uses its address book stealer module in order to pull the contacts from the email account of its victim and send its payloads to the contacts found from the hijacked account.
Bearing in mind that potential victims are receiving an email from somebody they know and trust, Emotet has a very high chance of a successful attack. The received email usually contains a link to a malicious URL that downloads the malware and launches the payload when clicked.
However, email spam is not the only distribution Method that this malware utilizes. It may also take advantage of certain Windows vulnerabilities, thus the malware can make its way into a machine completely "silently," without the user ever knowing about it.
How to collect Emotet's IOCs using ANY.RUN?
For your detailed Emotet malware analysis ANY. RUN's "Fake Net" feature will be very useful. It intercepts HTTP requests and returns a 404 error, forcing malware to reveal its command-and-control server links.
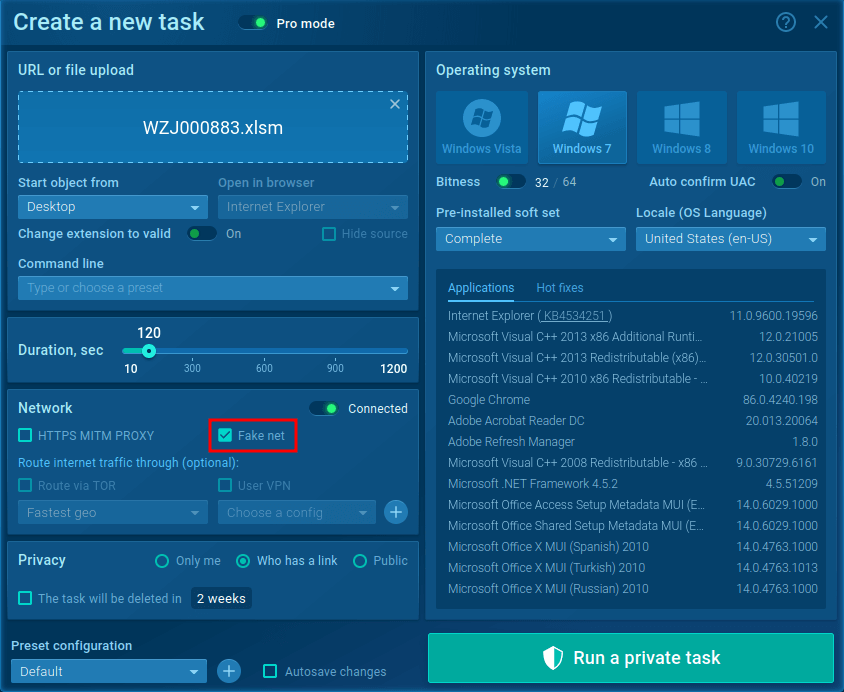 Figure 3: Run Emotet sample with turn on "Fake net" feature
Figure 3: Run Emotet sample with turn on "Fake net" feature
To turn it on in the "Advanced mode" of the "New task" window, check the box next to the "Fake net" in the "Network" section.
Conclusion
Emotet malware is one of the most sophisticated and destructive trojans. Since its first introduction back in 2014, the malware has underground a substantial evolution gaining a lot of anti-evasion features, obtaining worm-like functionality, and even changing the main focus from information-stealing to installing other trojans onto infected machines. With the ability to spread to adjacent systems, Emotet can easily infect all machines in a single network, making dealing with the consequences of an attack a true nightmare.
The situation is further worsened by the fact that the malware is equipped with a series of anti-evasion tricks that make analyzing it quite tricky. As a result, the process of developing countermeasures is much more complicated in comparison to more straightforward trojans.
Thankfully, modern online hunting services like ANY.RUN are equipped with equally advanced research functions and allow professionals to study cyber threats with maximum efficiency, helping researchers battle evasive malware like Emotet.
Create your free ANY.RUN account to analyze malware and phishing without limits!


 0
0