Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


FlawedAmmmyy is a RAT type malware that can be used to perform actions remotely on an infected PC. This malware is well known for being featured in especially large campaigns with wide target demographics.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
31 October, 2020
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
31 October, 2020
Last seen
:
|

 1287
1287
 0
0

 743
743
 0
0

 3203
3203
 0
0
FlawedAmmyy is a Remote Access Trojan – a malware that is utilized by attackers to take full control over the target machine. It is based on the source code of a completely legitimate program Ammyy Admin. Despite this RAT being recorded as a new malware in 2018, some researchers suggest that it has been in use since 2016.
FlawedAmmyy has been used by multiple attackers in massive email-spam campaigns as well as in highly targeted cyber attacks aimed at businesses in the automotive industry. Among others, a well-known hacker operating under the alias TA505 is known to have been using this malware in large-scale campaigns.
Being built using leaked source code of the third version of Ammyy Admin – which is legitimate remote access and administration program – Flawed Ammyy enables attackers to perform multiple actions on infected Windows PCs. With this malware, hackers can control the desktop remotely, manipulate files, steal credentials, and access audio on an infected machine to potentially collect information about their victims.
The popularity of FlawedAmmy started rising especially quickly in 2018, as the focus of malicious actors started shifting from operating ransomware to other types of malicious programs. In particular, in November of 2018, a threat actor known as TA505 started distributing various loader viruses in their spam email campaigns – using ServHelper at first and later switching to AndroMut – with the end goal of infecting victims with FlawedAmmyy.
In particular, researchers have detected two separate campaigns that distributed FlawedAmmyy using AndroMut loader – the first campaign targeted victims in South Korea with HTML attachments designed to download an Office file with malicious macros which installed a loader which would, in turn, drop the main payload – FlawedAmmyy RAT. The scope of other campaigns featuring AndroMut was more broad and included enterprises in the USA, UAE, and Singapore.
Other campaigns not necessarily by TA505 that took place in 2019 made use of an XLM document that contained a malicious macro that downloaded FlawedAmmyy directly, bypassing the loader stage.
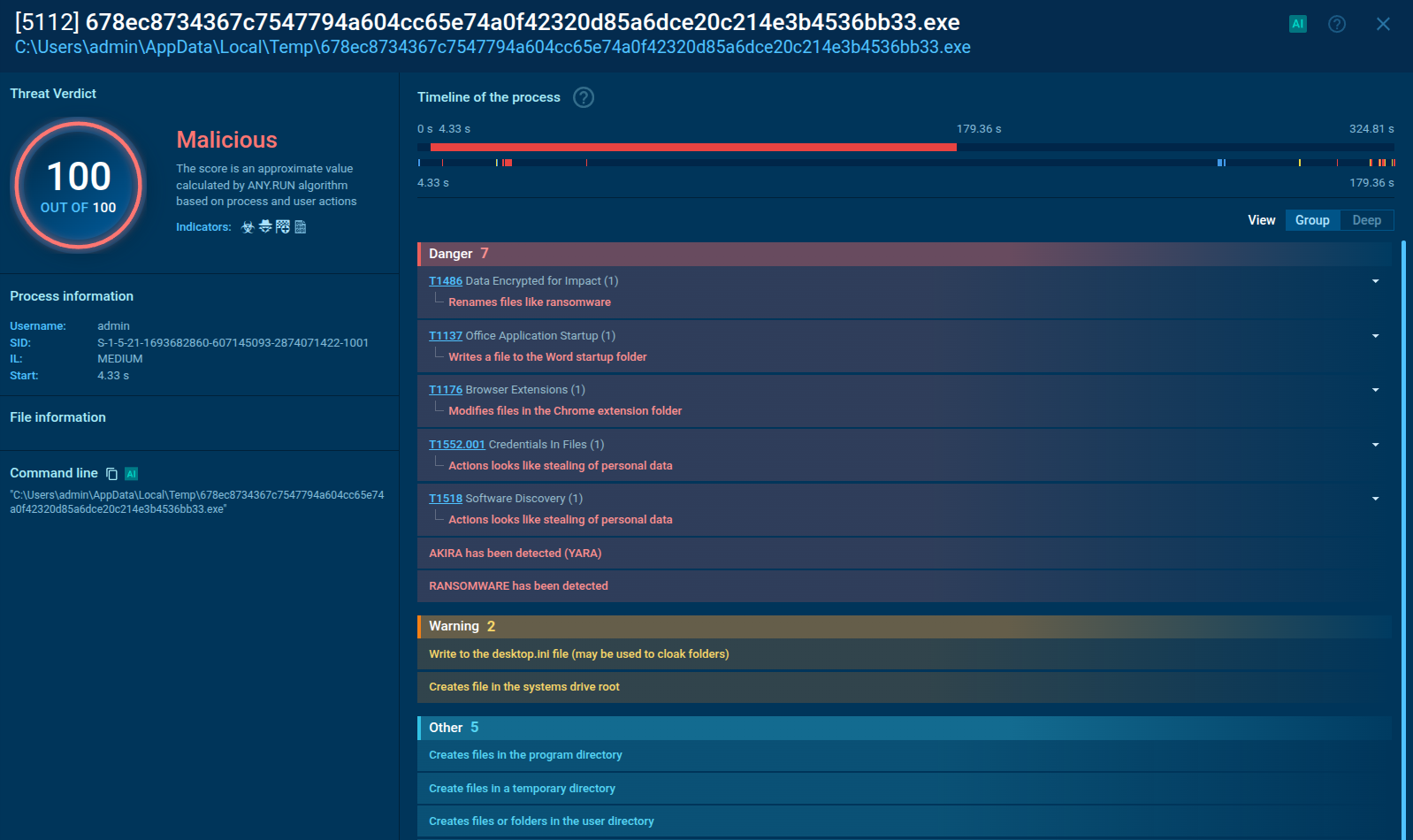
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service displays the execution process of FlawedAmmyy, allowing one to examine it in a convenient and safe environment.
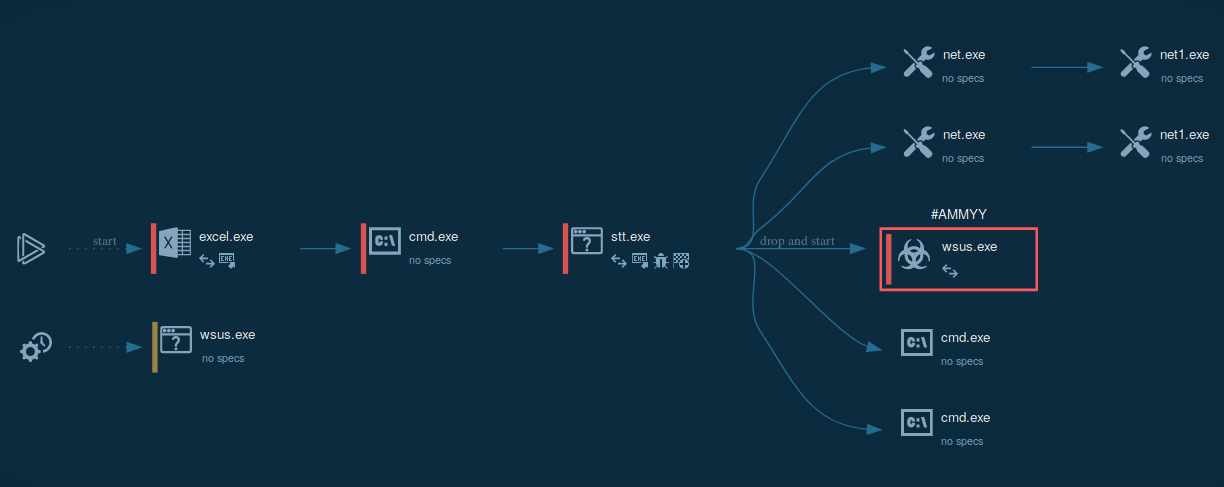
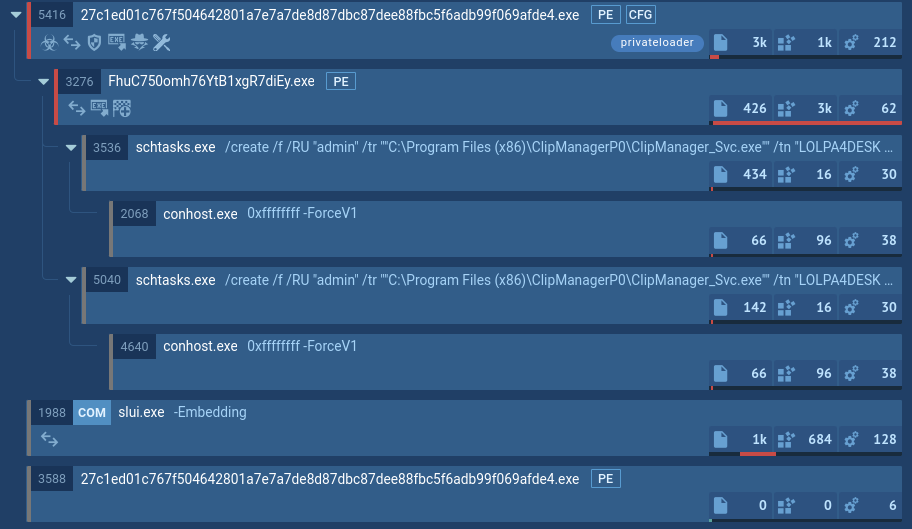
Figure 1: Displays the graph of processes generated by the ANY.RUN malware analyzing service
Figure 2: Even more information about the execution of malware can be found in customizable text reports generated by ANY.RUN
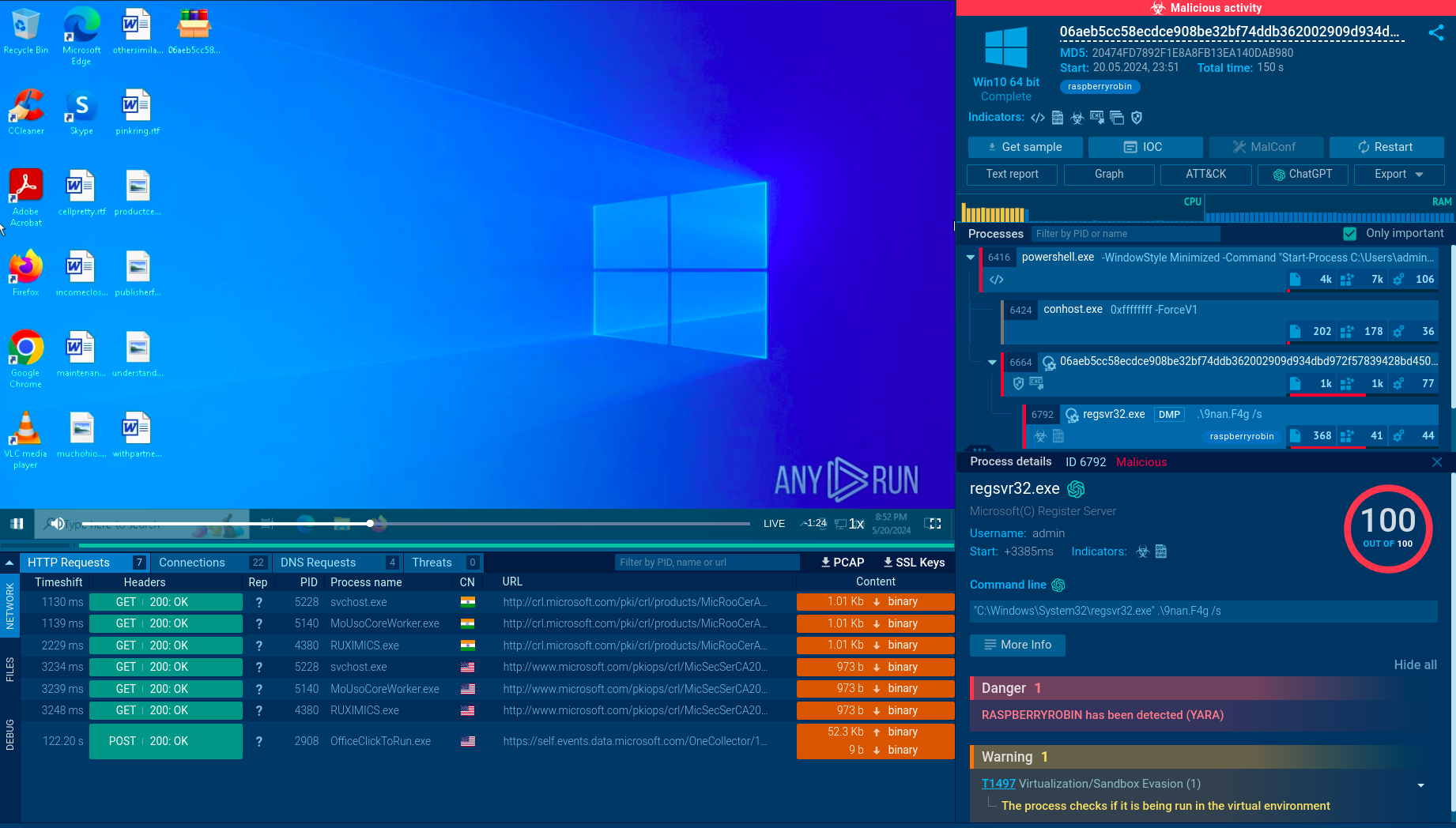
Usually, Flawed Ammyy makes its way into the machine through mail spam in a form of a MS Word or MS Excel document with a malicious macro. Examples of such malicious docs you can find on ANY.RUN's public submissions browsing by tag maldoc-21. After the malicious .xls file is opened, it automatically runs a macro function that runs either msiexec.exe or cmd.exe to download and execute the first stage payload. This first stage executable file then downloads and decrypts another file, which usually has a filename "wsus.exe" and it is the FlawedAmmyy malware itself. Wsus.exe creates persistence in the system and communicates with C2 servers.
Sometimes malicious executable files are digitally signed with a certificate from trusted vendors. Also, it's interesting that trojan checks the user privileges and presence of Anti-Virus programs on the infected machine and changes behavior based on the results of this check. You can also find out how this execution method differs from Trickbot and Zloader.
FlawedAmmyy is distributed with spam email campaigns with subjects usually concerning invoices or receipts. Emails can contain a .zip attachment disguised to contain information related to the email subject, a Microsoft Office file, or an XML attachment. Attached files, in reality, can hold a URL that automatically opens a browser window and redirects victims to a website from where malware samples would be downloaded.
In some campaigns, another virus designed to install the final payload is downloaded first and it then drops FlawedAmmyy onto the machine. Other campaigns made use of something called the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol to download malware directly, bypassing the browser download which is quite a rare trick for malware.
Once FlawedAmmyy infects a PC, it can operate discreetly without letting users know that their machine is in fact infected. This allows attackers to collect various information about their victims over time and makes this malware potentially very destructive.
However, adhering to simple online safety tips can make avoiding the infection fairly easy – as long as a user never clicks on suspicious links or downloads emails from unknown senders they will be safe. However, things get a little bit more complicated with FlawedAmmy since some of the attacks are very targeted and feature believable emails.
Therefore users are advised to conduct their own checks about email authenticity and pay attention to small details before downloading files or following URLs in their correspondence.
Analysts can export all significant events from a task to MISP for further analysis and export to IDS/SIEM systems or simply for share. Just click on the "Export" button and choose "MIST JSON format" in the drop-down menu.
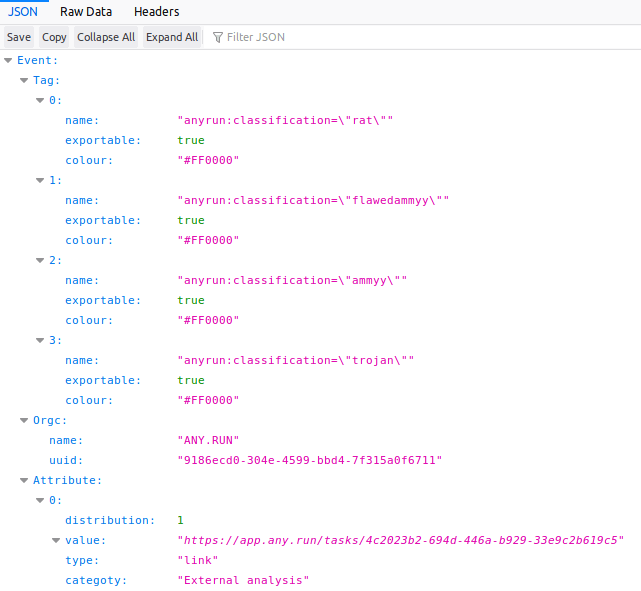 Figure 3: Export events from the task with flawedammyy into MISP JSON
Figure 3: Export events from the task with flawedammyy into MISP JSON
FlawedAmmyy RAT is an interesting malware that is capable of operating stealthily on infected machines and causing potentially serious damage with its remote access capabilities. It was featured both in massive, large-scale email spam campaigns as well as in targeted attacks against businesses operating in particular industries which indicates the diversity that operators behind this malware can show in regard to choosing their victims.
Security researchers only documented this malware in 2018 despite its being around since 2016, which means that it managed to operate in the dark for two whole years, evading researchers or maybe even tricking them. Thankfully, modern malware analysis services like ANY.RUN provides multiple specially designed tools to simplify and greatly streamline the research process to help us identify current and future threats.