Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

DCrat, also known as Dark Crystal RAT, is a remote access trojan (RAT), which was first introduced in 2018. It is a modular malware that can be customized to perform different tasks. For instance, it can steal passwords, crypto wallet information, hijack Telegram and Steam accounts, and more. Attackers may use a variety of methods to distribute DCrat, but phishing email campaigns are the most common.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2018
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2018
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
DCRat, also known as Dark Crystal RAT, is a remote access trojan (RAT) that lets threat actors take control over an infected machine and extract users’ data, such as the information copied to the clipboard and personal credentials from apps. The malware is known for its stealthiness and its ability to evade detection by security software. DCrat has been in operation since 2018, yet it regularly undergoes changes aimed at advancing and expanding its capabilities.
The malware consists of several components each responsible for a certain type of malicious activity, including stealing of cryptocurrency and keylogging. On top of that, the authors of DCrat have published a special software called DCRat Studio, which serves as a tool for developing new modules for the malware.
DCrat's popularity can be attributed in part to its low cost. Its one-month license goes for a mere $5, while a lifetime one is available for $40. This is a stark contrast to other malware-as-a-service options. For instance, a lifetime AgentTesla subscription will require forking out $120. According to researchers, such prices are due to the malware being simply a pet project of a single developer, who does not work on it full-time. The developer is likely based in the ex-USSR region.
Although back in 2018, the malicious program utilized Java, it switched to C# in 2019. As a result, nowadays, the majority of Dark Crystal RAT’s modules are written in the C# programming language. However, the administrative server for this malware is developed with JPHP, which is an implementation of PHP that relies on the Java Virtual Machine.
Different samples of the malware have been observed to be outfitted with evasion and obfuscation techniques. For instance, in order to create a layer of protection against malware analysts’ attempts to reverse engineer its code, DCrat’s payload can be obfuscated with Enigma Protector.
The standard set of tools available to threat actors using DCrat includes:
Additionally, DCrat can execute a persistence algorithm to retain control over the system. For instance, the malware can copy itself to a random running process and to the root directory (C:). It then can create shortcuts to these copies in the user's Startup folder. It can also add registry values that point to these shortcuts. This allows DCrat to start automatically when the computer boots up.
It is important to note that Dark Crystal RAT is polymorphic, meaning that attackers can use its builder functionality to add changes to the malware’s code to make it difficult to detect using traditional methods, such as file hash.
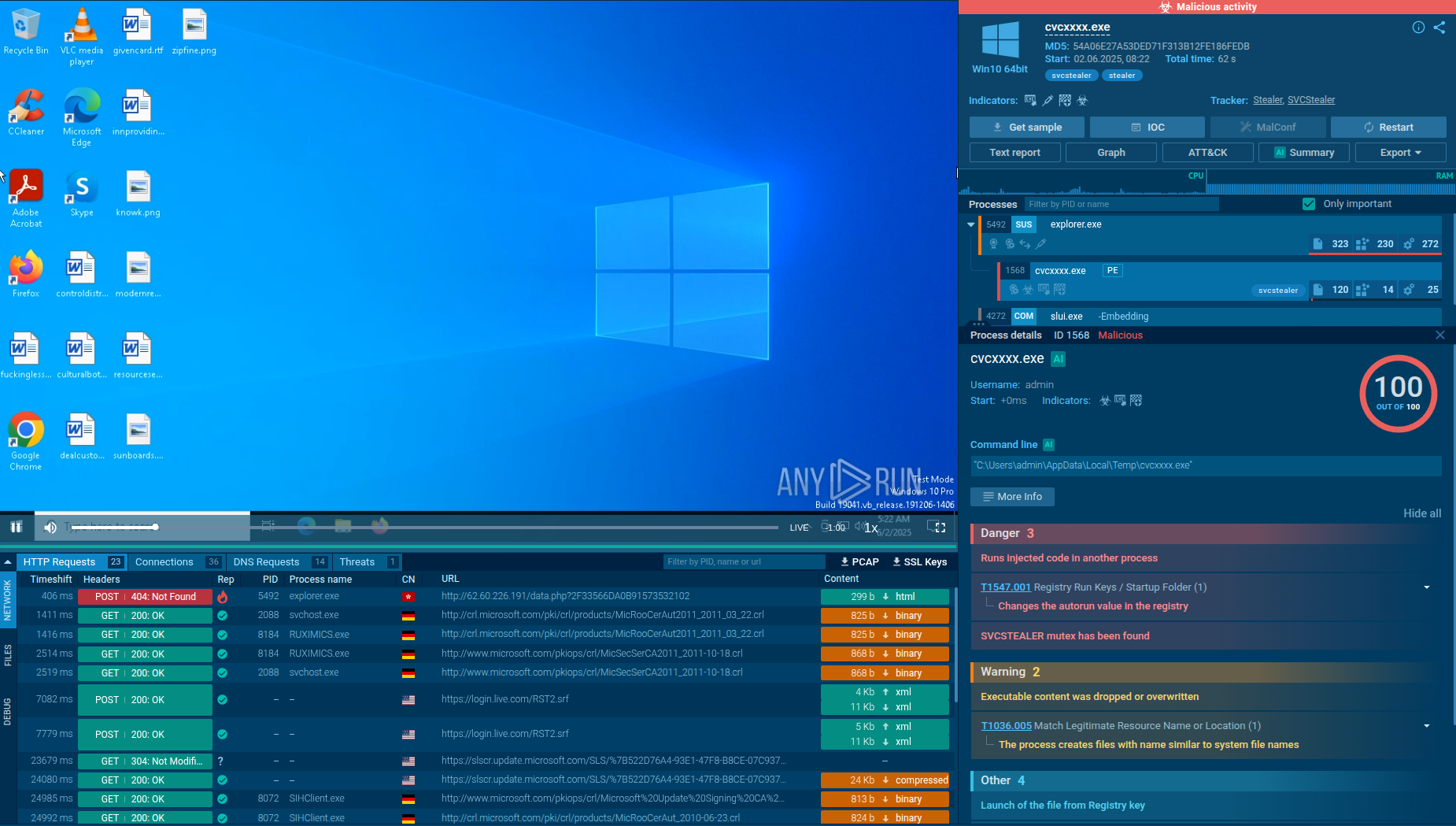
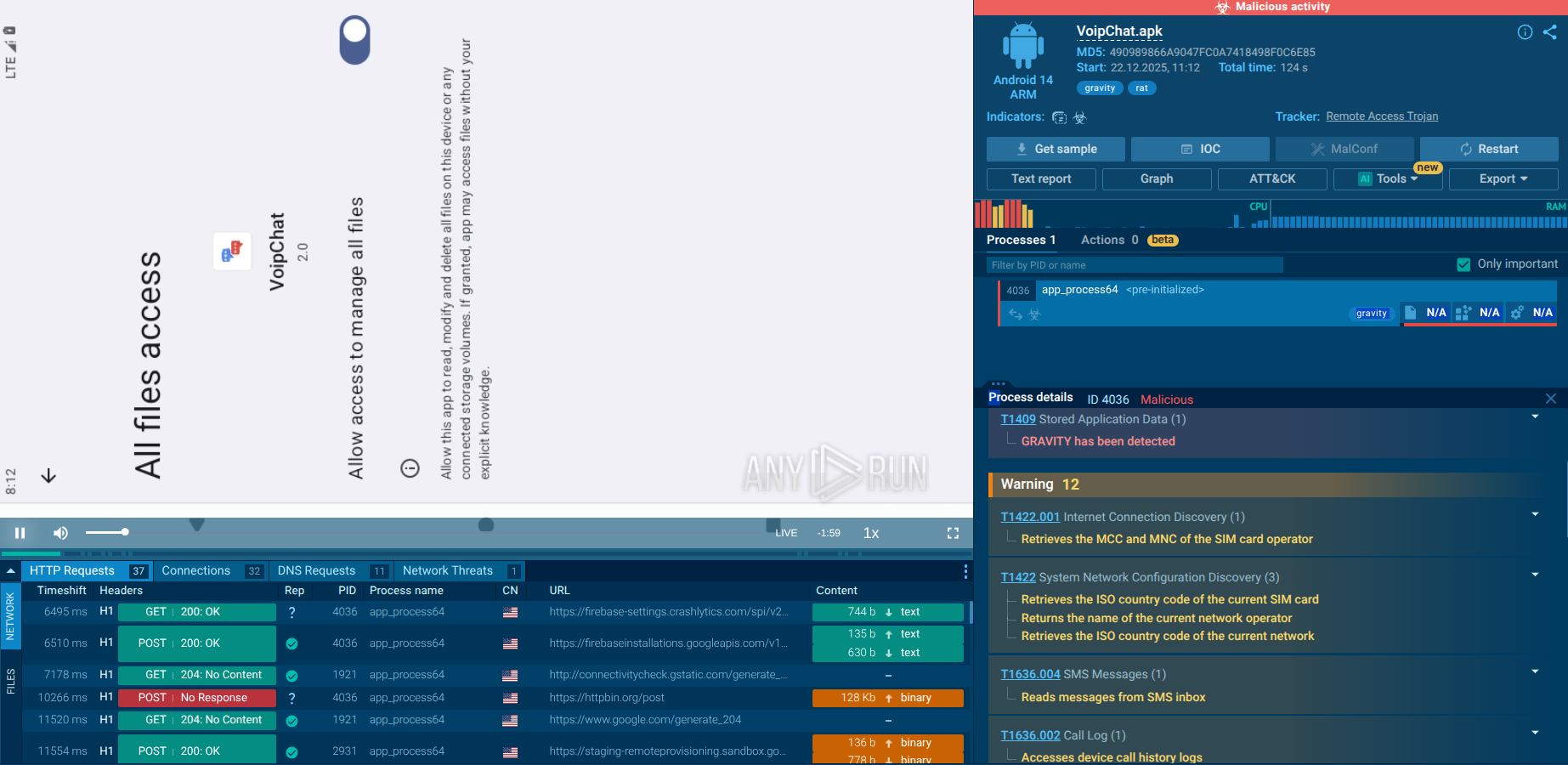
Uploading Dark Crystal RAT to the ANY.RUN sandbox lets you quickly see the malicious activities triggered by the malware. Here is a sample of DCrat executed in the interactive sandbox.
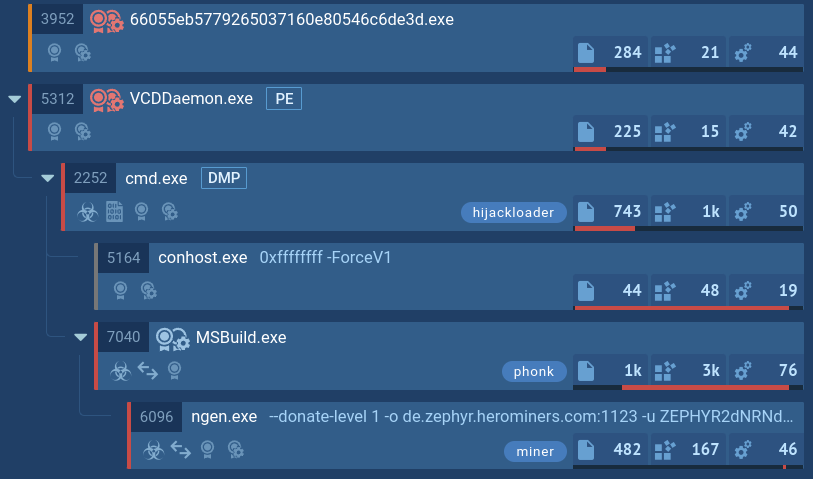
DCrat's flexibility makes it challenging to handle, but there are things that can help us pinpoint it. For example, DCrat rarely produces malicious activity in its current process. Like most malware, it prefers to create large process trees and then infiltrate a harmless process at some point to detonate later. By using ANY.RUN, we can easily identify the process targeted by the malware.
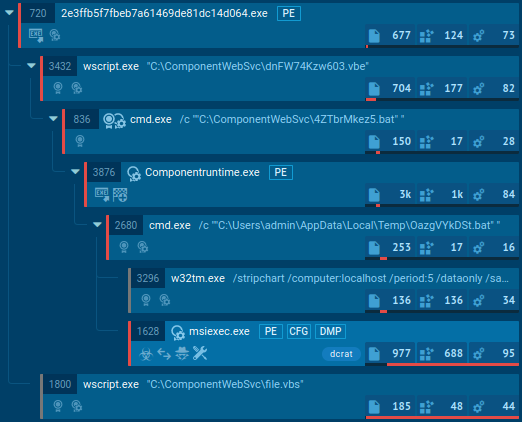 DCRat's process tree
DCRat's process tree
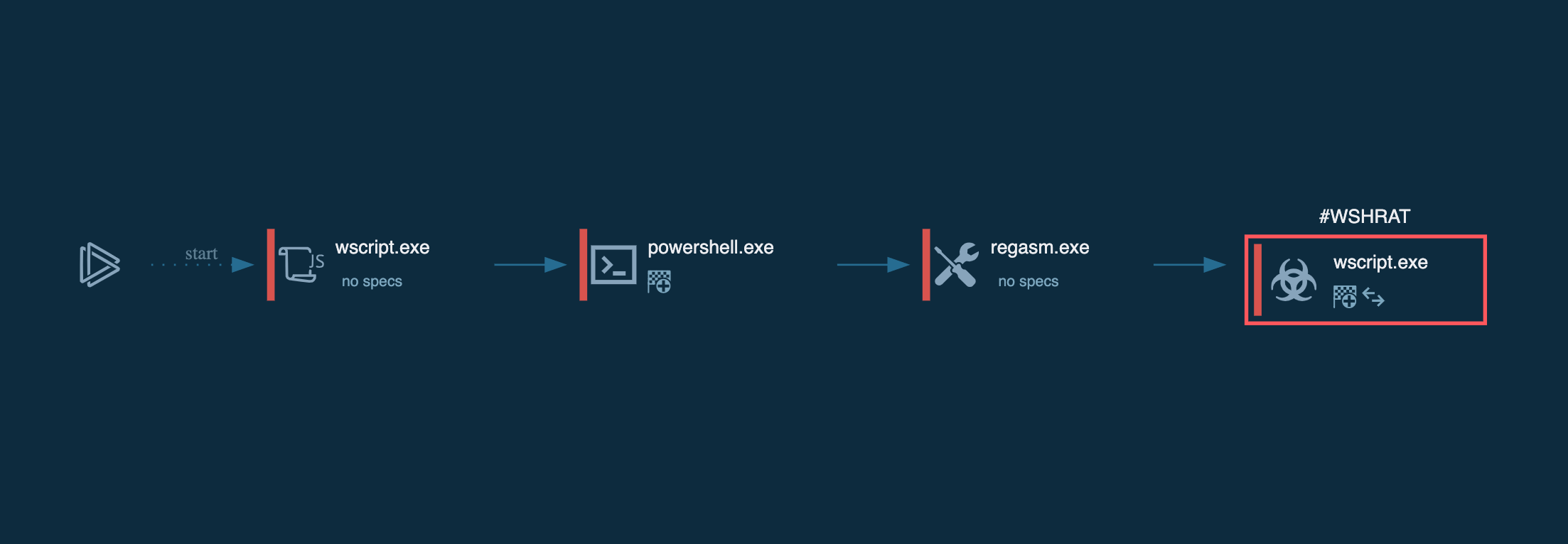
On top of that, it can delay execution for a period of time after the infection, drop executables, run embedded payloads, and use WMI queries to detect a virtualized environment or or to gain persistence in the system.
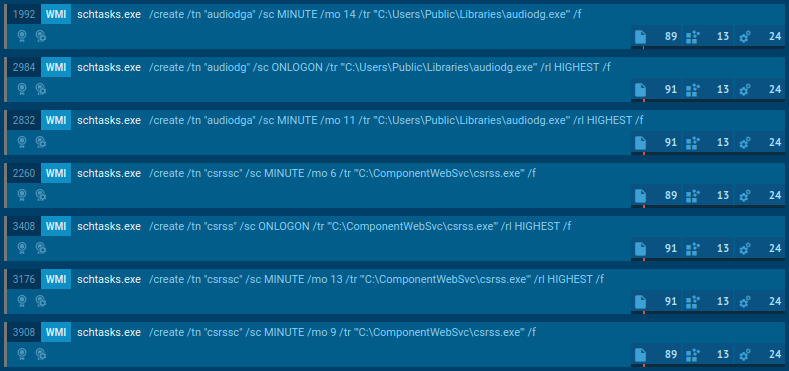 DCRat's WMI queries
DCRat's WMI queries
Since Dark Crystal RAT is sold openly on the Internet, cyber criminals of all skill levels have access to it. Subsequently, there are many different methods they implement to drop the payload on victims’ computers. Yet, as is the case with most remote access trojans, including Vidar, njRAT, and QuasarRAT, DCrat’s main way of infecting a system is via phishing emails.
Threat actors devise sophisticated multi-staged attacks intended to manipulate the victim into believing that the fake email is actually legitimate and the attachment file it contains is safe to open. These downloadable files are usually in an office suite format, such as .docx or .xls, and have built-in macros or other mechanisms that can trigger the chain reaction which will result in DCRat being dropped onto the system.
There are also accounts of users unsuspectingly downloading a DCrat executable from websites distributing torrent files. In such cases, the malware can be disguised as a legitimate program. Once executed, the program installs the malicious program and runs it, stealing the user’s data often without them being aware of it.
Dark Crystal RAT is a remote access trojan that constitutes a significant concern for organizations and individuals worldwide. The malware’s low price tag and modular design make it an in-demand tool among cyber criminals. To protect your system from DCrat, you should be very careful about opening links or attachments from unknown senders.
Instead of taking the risk of downloading and opening potentially harmful files or clicking on malicious links, you can first analyze them in a sandbox environment like ANY.RUN. This will allow you to quickly and safely determine whether the file is malicious or not. ANY.RUN will also provide you with a detailed report about the malware, including its indicators of compromise (IOCs) and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This information can be used to protect your organization from future attacks.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!