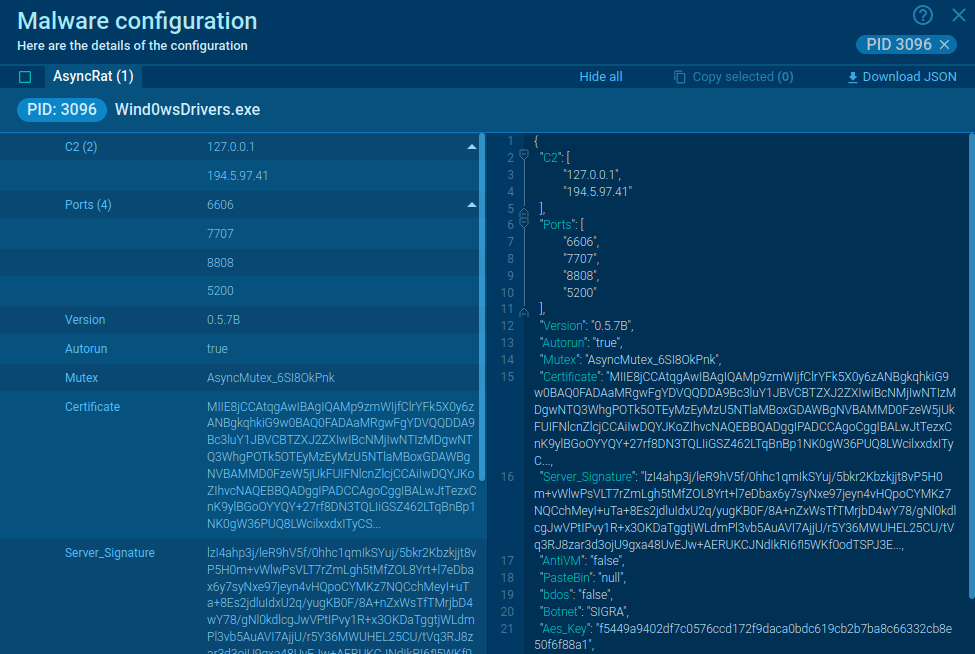
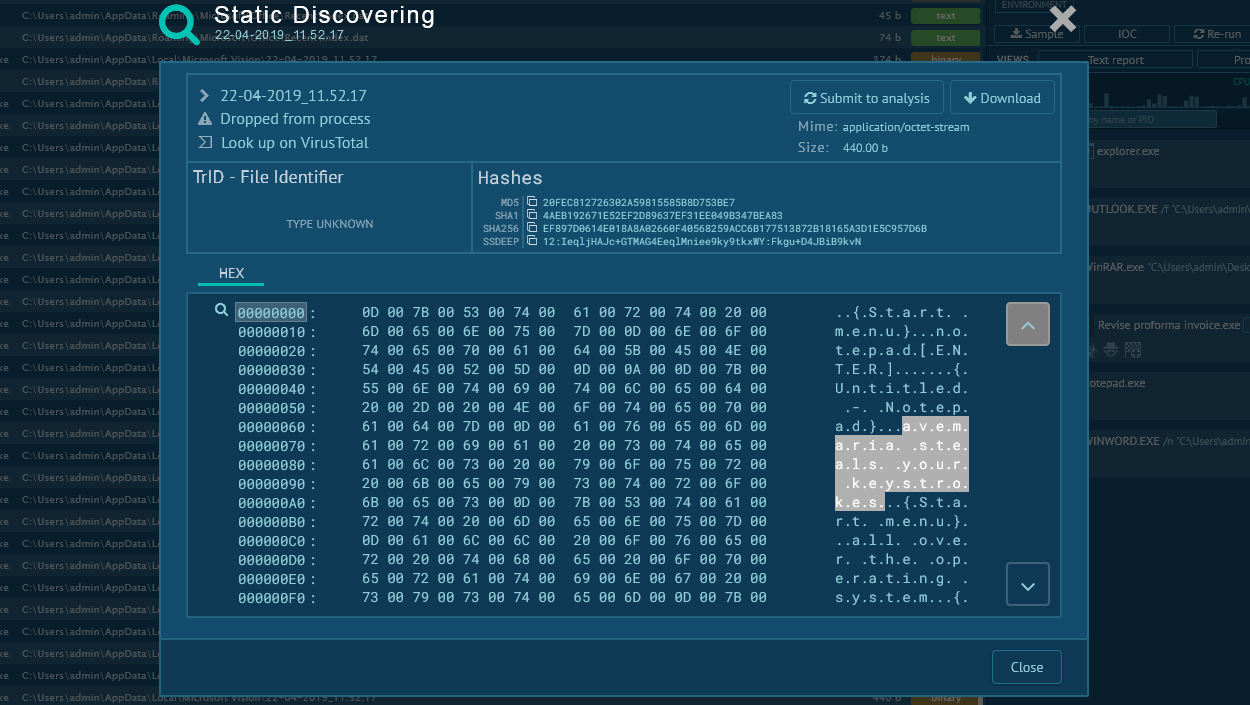
What is Ryuk Ransomware?
Ryuk is a highly targeted Ransomware — a malware that encrypts files of its victims and demands a payment to restore access to information. Ryuk was first identified in august 2018 and remains active to this day. It attacks newspapers, public institutions, banks, restaurants, and other businesses.
Although it is not considered to be the most high-tech malware in its class, Ryuk Ransomware is very successful. In fact, according to the FBI, it is the number one Ransomware in terms of completed ransom payments.
Thanks to a highly targeted approach to distribution, the malware has managed to infiltrate thousands of PCs and yielded attackers millions of US dollars. In fact, some of the ransoms paid by organizations reach 400,000 US dollars.
Despite not being the most cutting-edge, Ryuk is not be toyed with.
General description of Ryuk Ransomware
The success of Ryuk Ransomware likely can be tied to its selective attack approach. While a lot of malicious programs nowadays are starting to move away from widespread email spam campaigns, Ryuk malware goes another step forward. Its attacks not only use collected information about the victim for initial payload delivery but even the encryption process is being tailored to each victim, targeting the most valuable files.
This fact indicates that operators behind Ryuk malware carefully study each victim and perform expensive scouting and network mapping.
On top of that, Ryuk Ransomware operators are flexible with Ransom demands and adjust not only the ransom amount but also the ransom note context. At least two variants of the ransom note were observed since Ryuk Ransomware became active in 2018. One was well-written, almost polite, and quite long, used in an attack on a large organization with a high ransom demand. The use of a second variant was recorded in the majority of attacks on smaller victims. It is much shorter and uses more blunt and straightforward wording.
Some researchers expressed an opinion that this variation in ransom notes may indicate that the Ryuk Ransomware team uses two separate attack approaches with different complexity.
Preparing for attacks very carefully and learning about each victim allowed the Ryuk malware team to carry out successful campaigns with huge ransom demands. According to some data the average demanded ransom amount is around 674,039 US dollars, while the highest recorded ransom demand was over a million US dollars.
It is not exactly obvious who stands behind this Ransomware. Some evidence and code similarities to another Ransomware called Hermes point towards a North Korean APT, Lazarus Group. However, this is not hard evidence, considering that a sample of Hermes could have fallen into the hands of another criminal and serve as a base for Ryuk's development.
Other reports based on more recent data link Ryuk Ransomware to a Russian criminal group named WIZARD SPIDER, which is known for its work with TrickBot malware. For example, cybersecurity researchers found documents that contained Russian words in filenames while investigating a compromised network, that fell victim to Ryuk. This suggests that the WIZARD SPIDER hypothesis is more likely than the Korean connection.
Additionally, Ryuk checks the keyboard language and terminates execution if it detects Russian, Belarus, or Ukrainian languages, which can be used as a killswitch. This kind of behavior is typical for a malicious program that originated on an ex-USSR territory.
Ryuk malware analysis
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service allows us to watch the execution process of Ryuk malware in action.
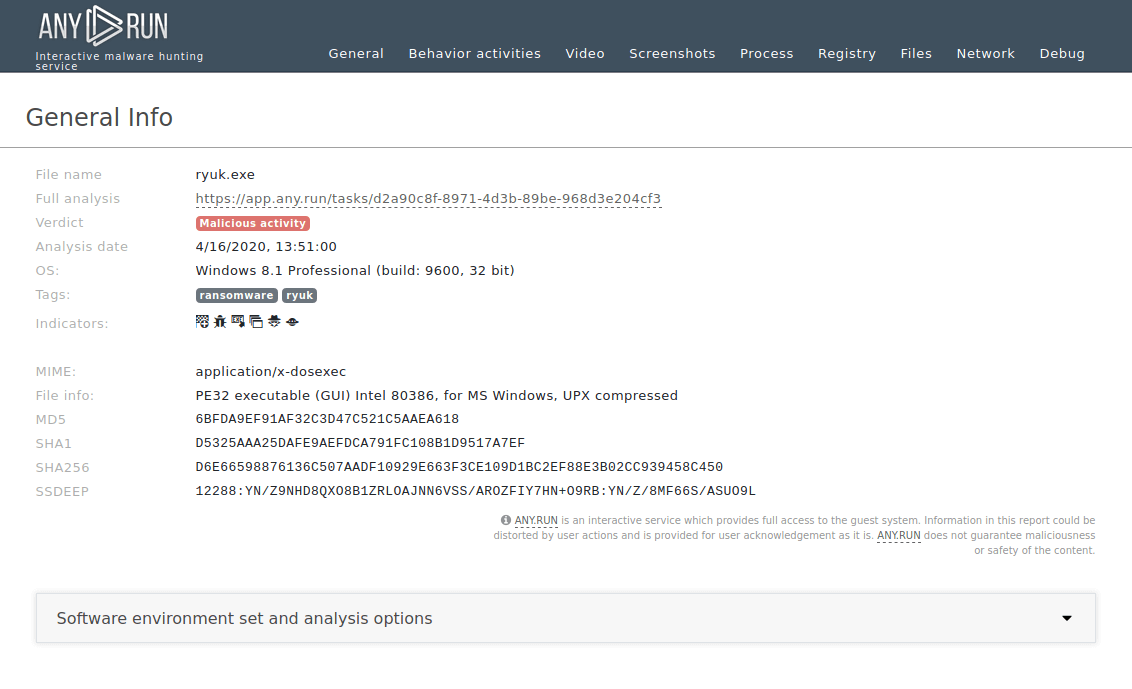
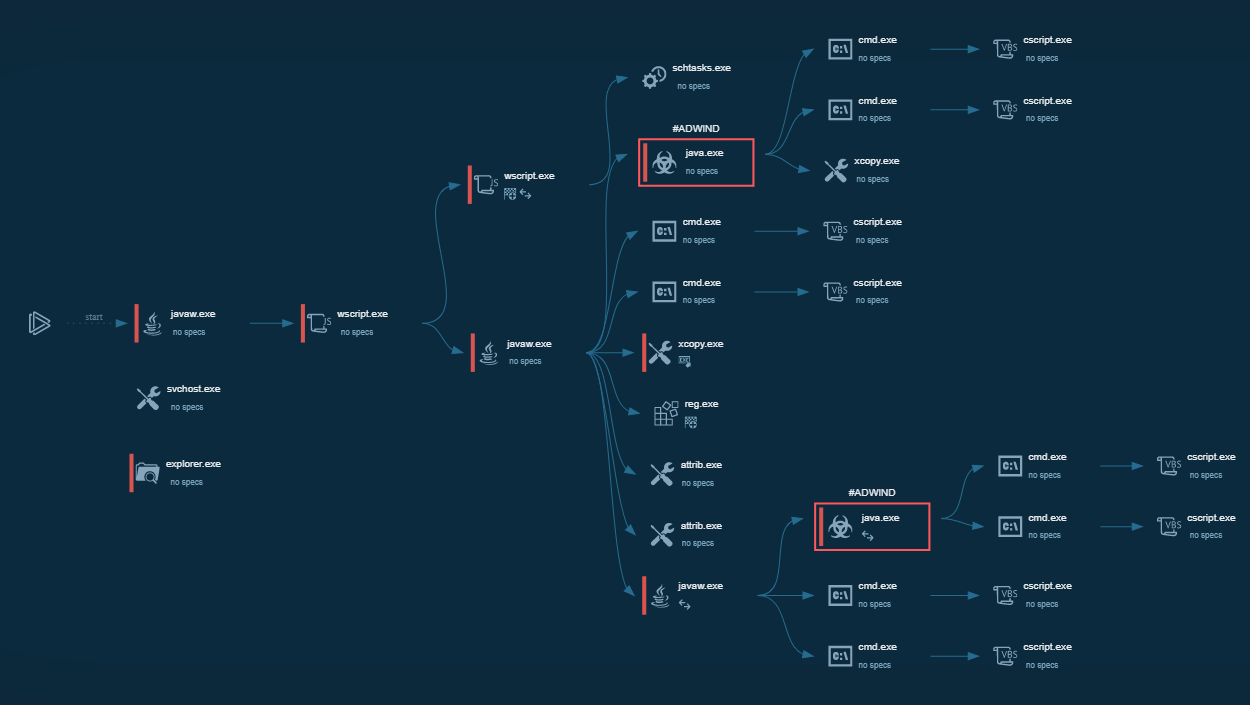
Figure 1: Displays the text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service

Figure 2: One of the variants of the Ryuk ransom note
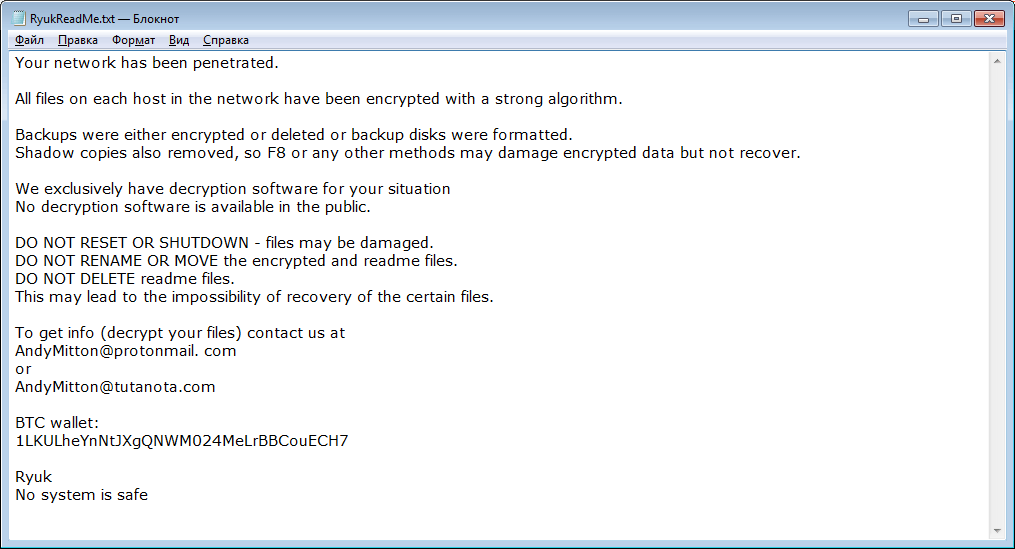
Figure 3: One of the variants of the Ryuk ransom note
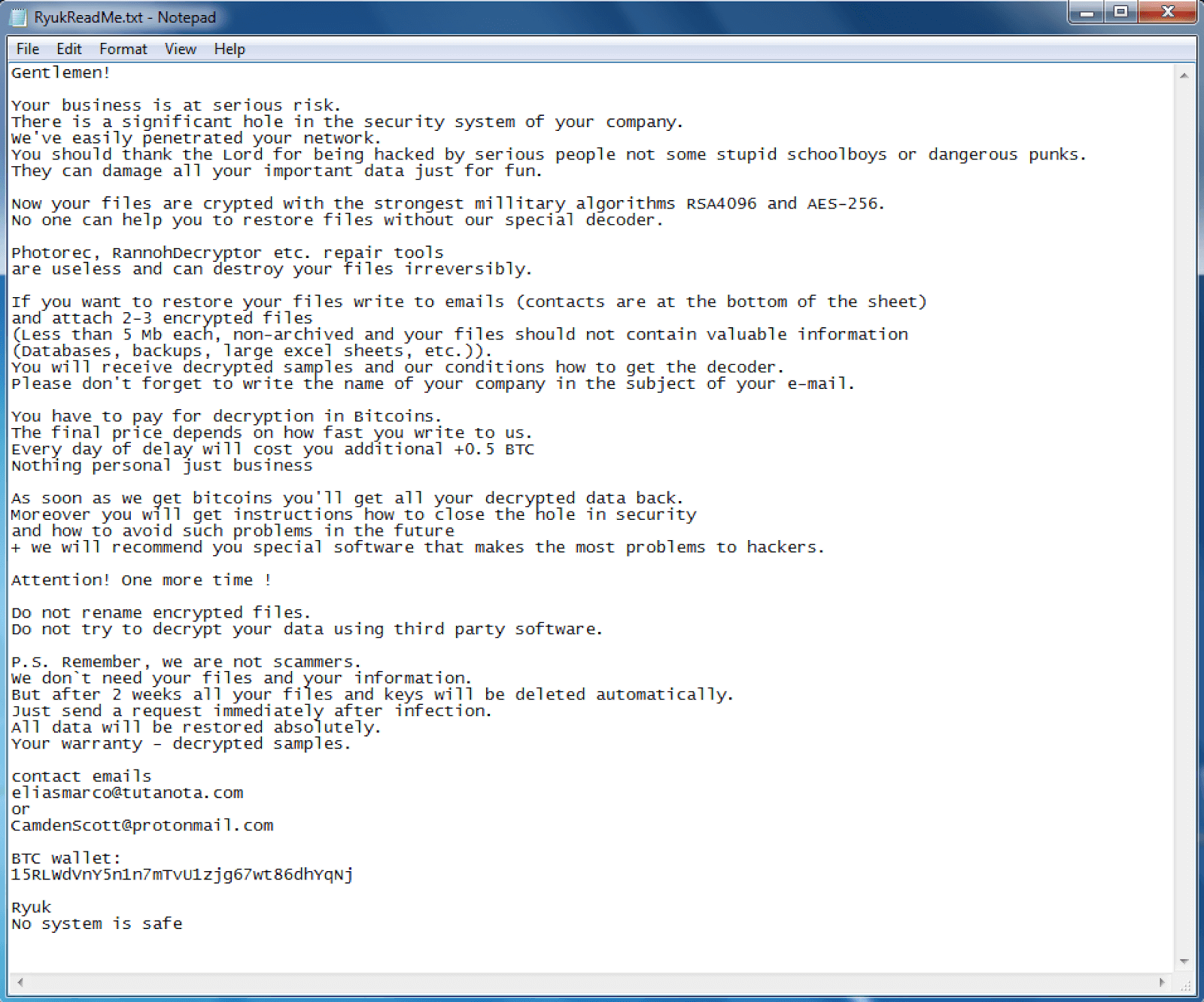
Figure 4: One of the variants of the Ryuk ransom note
Ryuk Ransomware execution process
The execution process of Ryuk is not much different from other ransomware such as WannaCry or Netwalker. After the executable file makes its way into an infected system and runs, the main malicious activity begins. Like many other ransomware families, Ryuk deletes shadow copy files. It also stops processes from the hardcoded list. Like other malware of this type, it creates a text or HTML file with a ransom note.
Ryuk Ransomware distribution
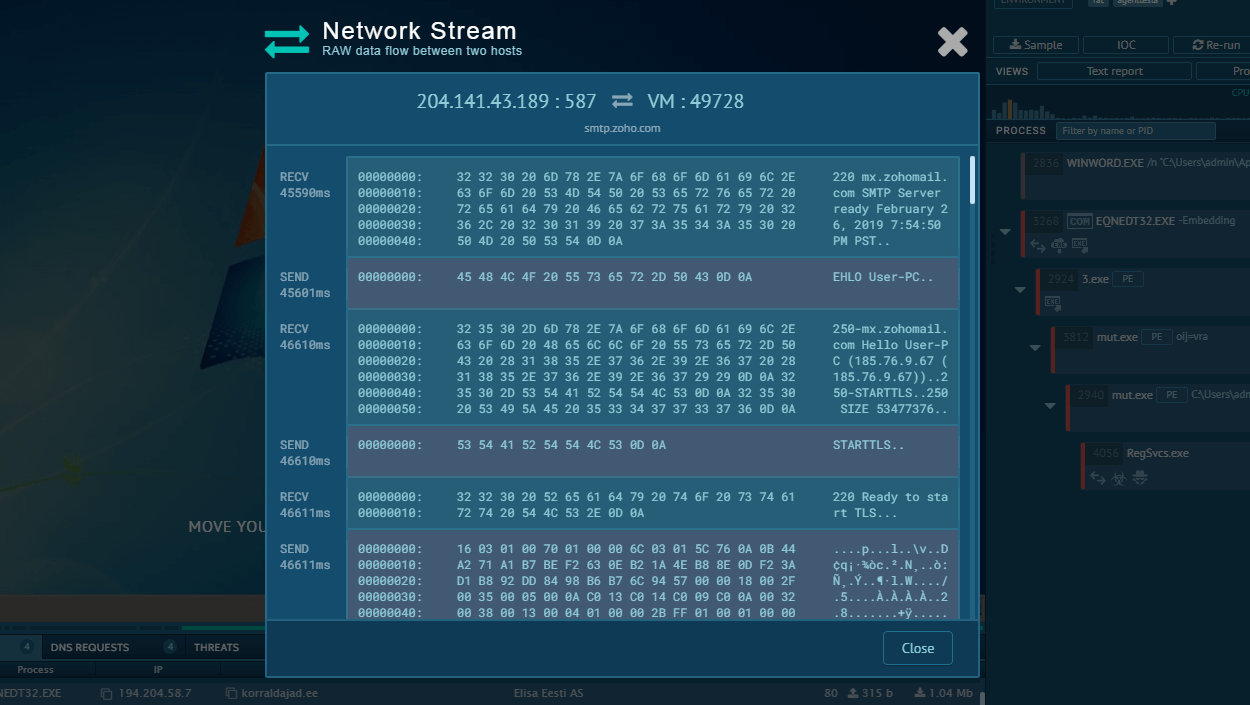
In many instances of confirmed Ryuk malware infections, the victim’s machine was also infiltrated by TrickBot. This led researchers to believe that Ryuk Ransomware makes its way into computers with TrickBot, which in turn is usually delivered through mail spam or with a Trojan Emotet.
This distribution method further supports the theory that Ryuk is operated by WIZARD SPIDER.
It is a known fact that the organization associated with Emotet is MUMMY SPIDER, which has been connected with the WIZARD gang in the past.
Conclusion
A high degree of personalization and a careful approach to victim selection made Ryuk Ransomware exceptionally successful. To date, malware operators behind the Ransomware have already collected over 64 million US dollars in payments, according to the FBI reports. The recipe for success is simple but solid — attackers choose successful businesses, that are definitely capable of paying the ransom and quite often will lose more money if they withhold the payment since their operation becomes completely frozen by the inability to access the most vital information.
Unfortunately, this means that a lot of the victims gave in to the demands of the criminals and unwillingly supported future attacks. It is a known fact, that besides capturing Ransomware operators, arguably the most important thing to do — is not paying the ransom.
Sadly, with the success that Ryuk malware has, it is unrealistic to hope that the attacks will stop in the near future. Therefore, the best thing to do now is to study this malware and prepare defense measures against it. Thankfully, ANY.RUN malware hunting service gives cyber teams all the tools they need to analyze Ryuk Ransomware in a secure online interactive sandbox.



 0
0