Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Loda is a remote access trojan (RAT) that has been in active use among multiple threat actors since 2016. The malware’s functionality includes stealing passwords and other sensitive information, keylogging, capturing screenshots, and delivering other malicious payloads. Loda is typically distributed as part of phishing email campaigns.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Morocco
Origin
:
|
|
Unknown
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Morocco
Origin
:
|
|
Unknown
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 1021
1021
 0
0

 598
598
 0
0

 2974
2974
 0
0
Loda is a remote access trojan that first appeared in 2016. It is written in AutoIT, a language designed for automating scripting on Windows systems, that is easy to learn and use. It is believed that the original creators behind Loda are the Kasablanka group, an advanced persistent threat (APT) from Morocco, which regularly published updated versions of the malware.
At the same time, the malware is also used by other threat actors, including YoroTrooper which has employed a variant of Loda malware to carry out assaults on various organizations around the world, with the most recent attacks occurring as early as 2023. TA558 is another APT that has implemented Loda in its malicious activities, primarily targeting hospitality businesses in Europe and North America.
To make it difficult for security researchers to analyze its code, Loda RAT uses string obfuscation on most variables. At run time, Loda RAT deobfuscates the strings and initializes the variables accordingly. Another technique used by Loda RAT is function name randomization, involving randomly assigning names to functions in the code.
In order to evade detection, Loda replicates itself within the temporary files folder of the targeted computer and then executes the copy. Additionally, Loda RAT generates a scheduled task, which is configured to initiate itself automatically during system boot-up. After running, the malware reports key information about the system to its C&C server, including the IP address, OS version, and architecture.
In terms of functionality, Loda possesses the standard set of RAT capabilities, which allow attackers to:
There is also an Android version of Loda RAT. It functions as a tracking application that can capture victims’ whereabouts and record any audio-based communication originating from the user. Additionally, it possesses the ability to monitor SMS messages and even make calls without users’ knowledge.
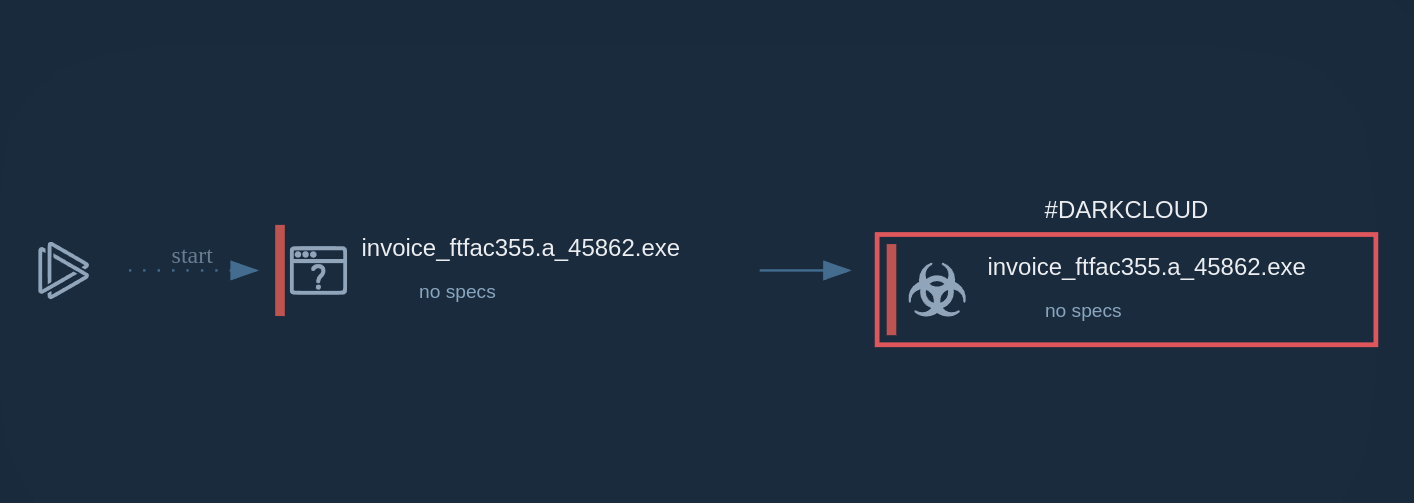
A sample of Loda RAT executed in the ANY.RUN interactive sandbox exposes the malware’s malicious activities and IOCs.
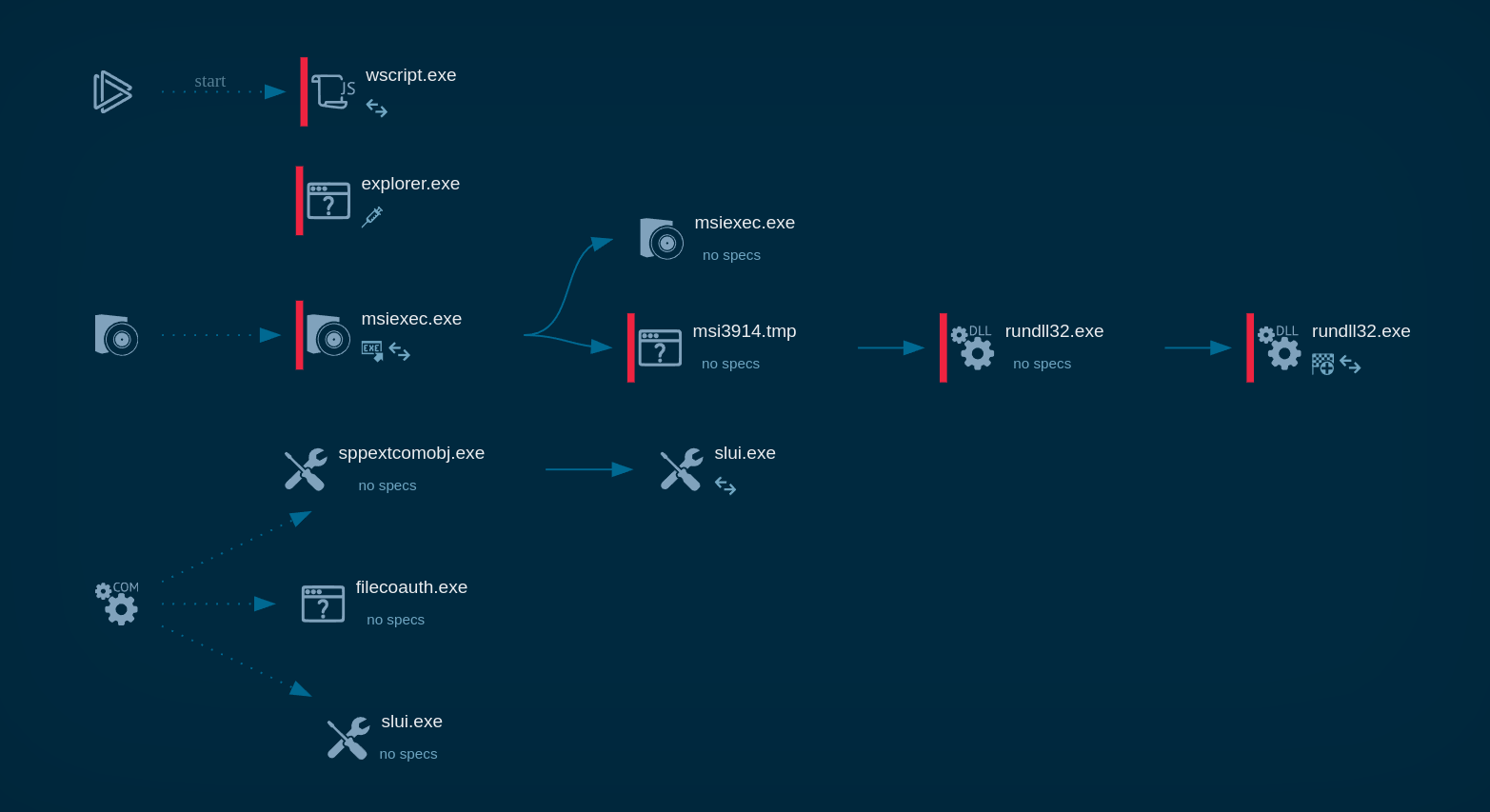
It follows a straightforward execution process. Loda first drops executables into the %appdata%, Startup, and Temp directories, then creates a service via schtasks to gain persistence, executes a Visual Basic script, and finally connects to the C&C server.
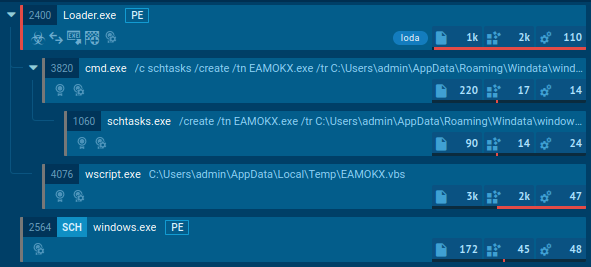
Loda RAT process tree
Phishing email campaigns are the most common attack vector used by threat actors to infect victims’ systems with Loda. Typically, such emails contain attachments of different formats, including PDFs, executables, and Microsoft Office documents, embedded with malicious code. Some of the early instances of Loda RAT infections were carried out by exploiting the CVE-2017-11882 and CVE-2017-0199 vulnerabilities.
As mentioned above, Loda RAT is popular among various criminal groups. For instance, in 2019, TA558 utilized PowerPoint attachments injected with macros to distribute both Loda and Revenge RAT, while in 2022, the group switched to container formats (e.g., RAR) and expanded their payload selection to include AsyncRAT. Similarly, in 2022, the Kasablanka APT devised a multi-stage attack targeting government agencies, which employed .iso email attachments to spread Loda and WarZone RAT.
Loda remains a top cyber security threat, with no signs of slowing down. A large number of criminal actors take advantage of this malware’s configurable design and accessibility to conduct attacks against businesses and government organizations in different parts of the world. The best way to avoid compromising your system by accidentally downloading Loda is to steer clear of any unsolicited emails and take precautions before opening suspicious links and files. You can do it by analyzing them in an online sandbox like ANY.RUN. By uploading your sample to the platform, you quickly and safely gain the knowledge needed to prevent infection.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!