Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Fabookie is an infostealer malware that was first observed as early as October 2021. The threat is known for targeting account credentials of Facebook users. The collected information is then sold by the attackers to other criminals. Fabookie is often distributed via loaders such as SmokeLoader.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2021
First seen
:
|
10 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2021
First seen
:
|
10 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Fabookie is a malicious software categorized as an information stealer. It primarily targets Facebook Business accounts, aiming to steal sensitive data like login credentials and account information.
This stolen data can then be exploited by attackers for various malicious purposes. Fabookie operates discreetly, running silently in the background without the user's knowledge, making it a significant threat to unsuspecting victims.
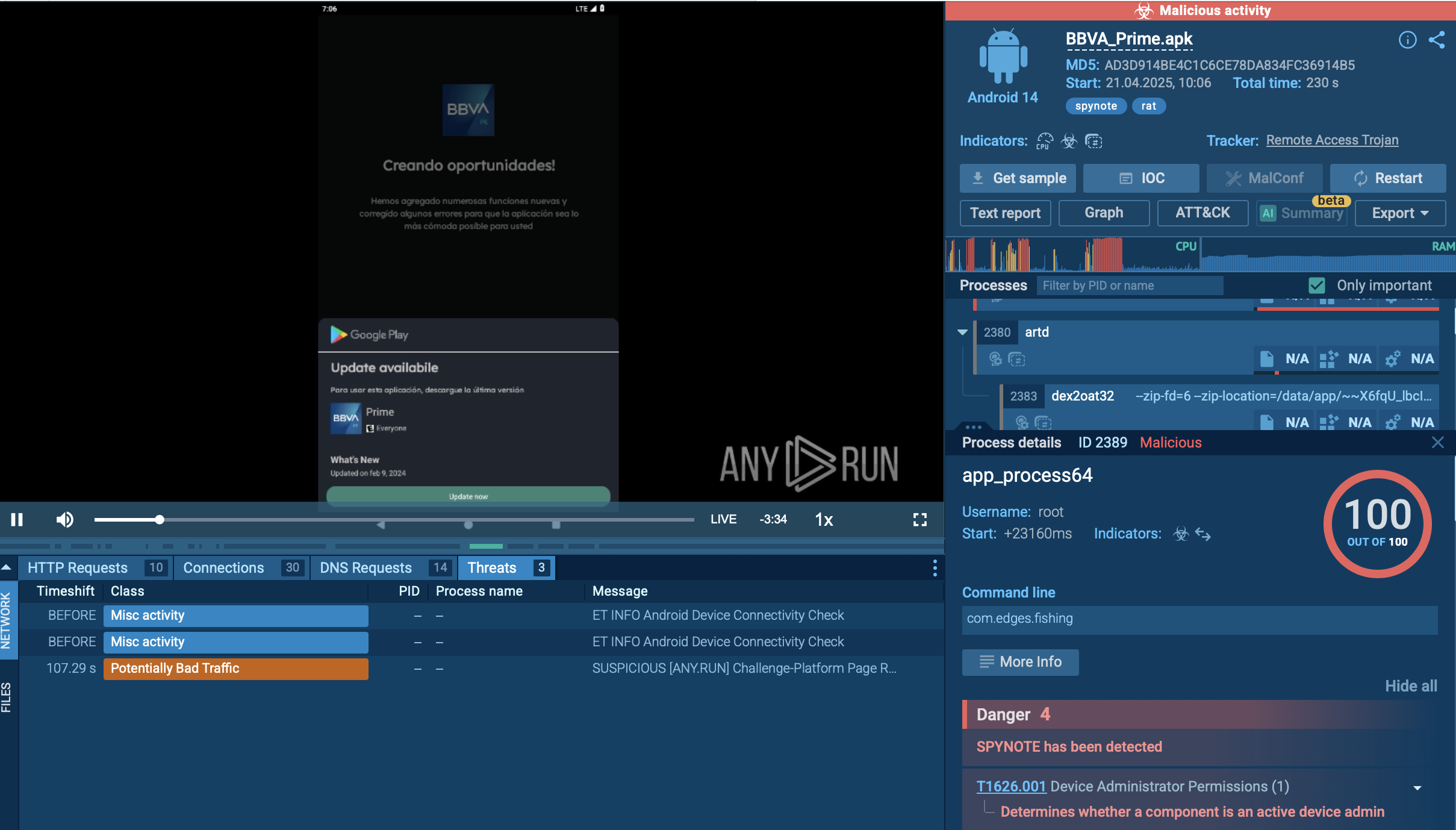
Fabookie primarily targets devices running 64-bit operating systems. Security researchers estimate over 100,000 infected machines worldwide, highlighting its widespread reach.
The primary capabilities of Fabookie include:
Similar to other malware families, such as Amadey and RisePro, Fabookie is capable of ensuring persistence on the system by remaining active even after a reboot.
One notable feature of Fabookie is that it exploits .jpeg images to deliver malicious code.
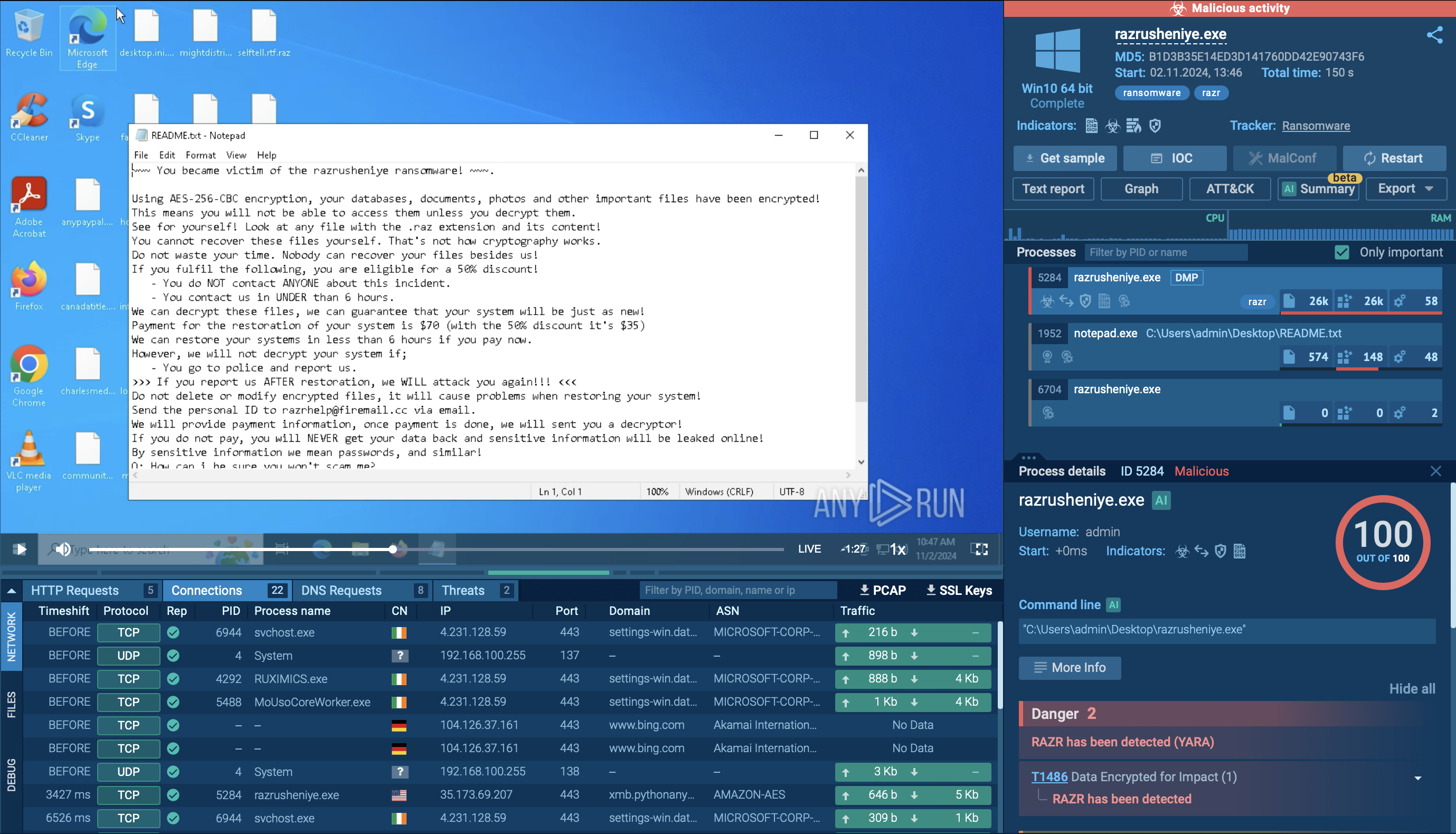
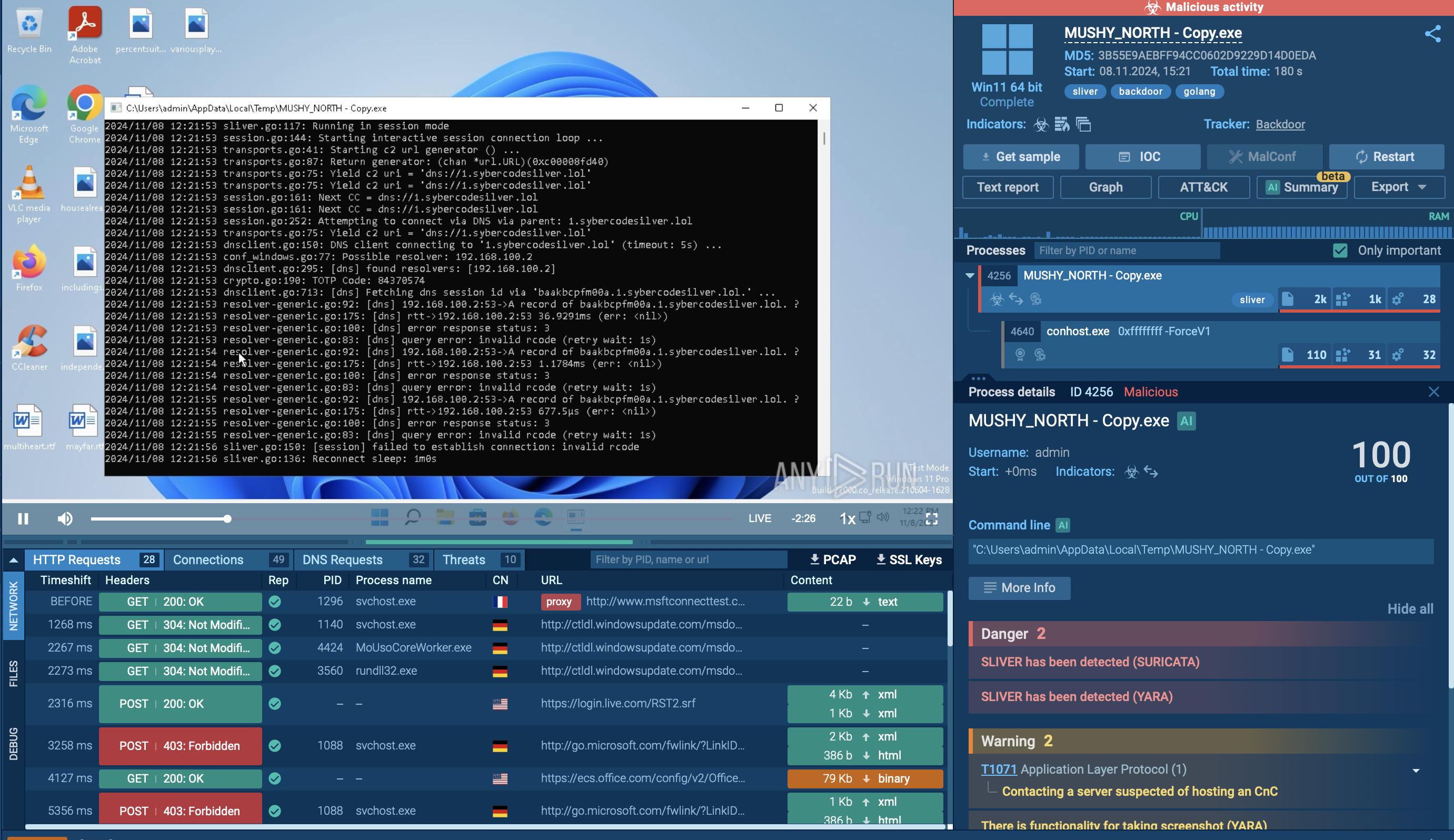
Let’s observe the execution process of the Fabookie malware by uploading its sample to ANY.RUN for analysis.
The Fabookie stealer infiltrates systems through various means such as malicious websites or phishing emails. Once installed, it silently collects sensitive information like login credentials and credit card details from the infected device. This data is then transmitted to remote servers controlled by the attackers. To remain undetected, Fabookie employs persistence techniques and may allow remote access for further malicious activities.
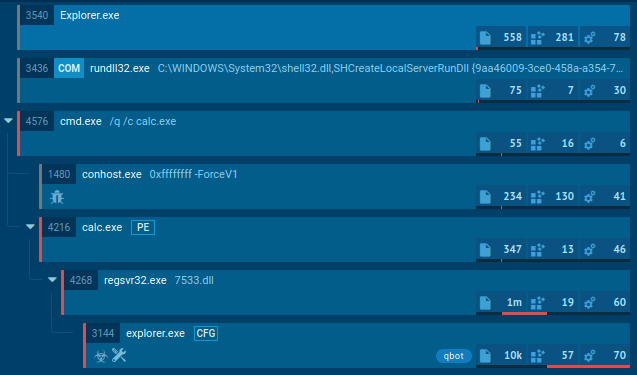
In our example, the execution chain of this stealer is straightforward. Once Fabookie initiates its own child process, it proceeds with its malicious activities centered around stealing credentials, cookies, and other valuable information from web browsers. The stealer collects this data and sends it to the C2 (Command and Control) server for remote access and further exploitation.
Overall, the execution chain of the Fabookie stealer is designed to silently compromise systems, steal valuable data, and maintain control for as long as possible without raising suspicion.
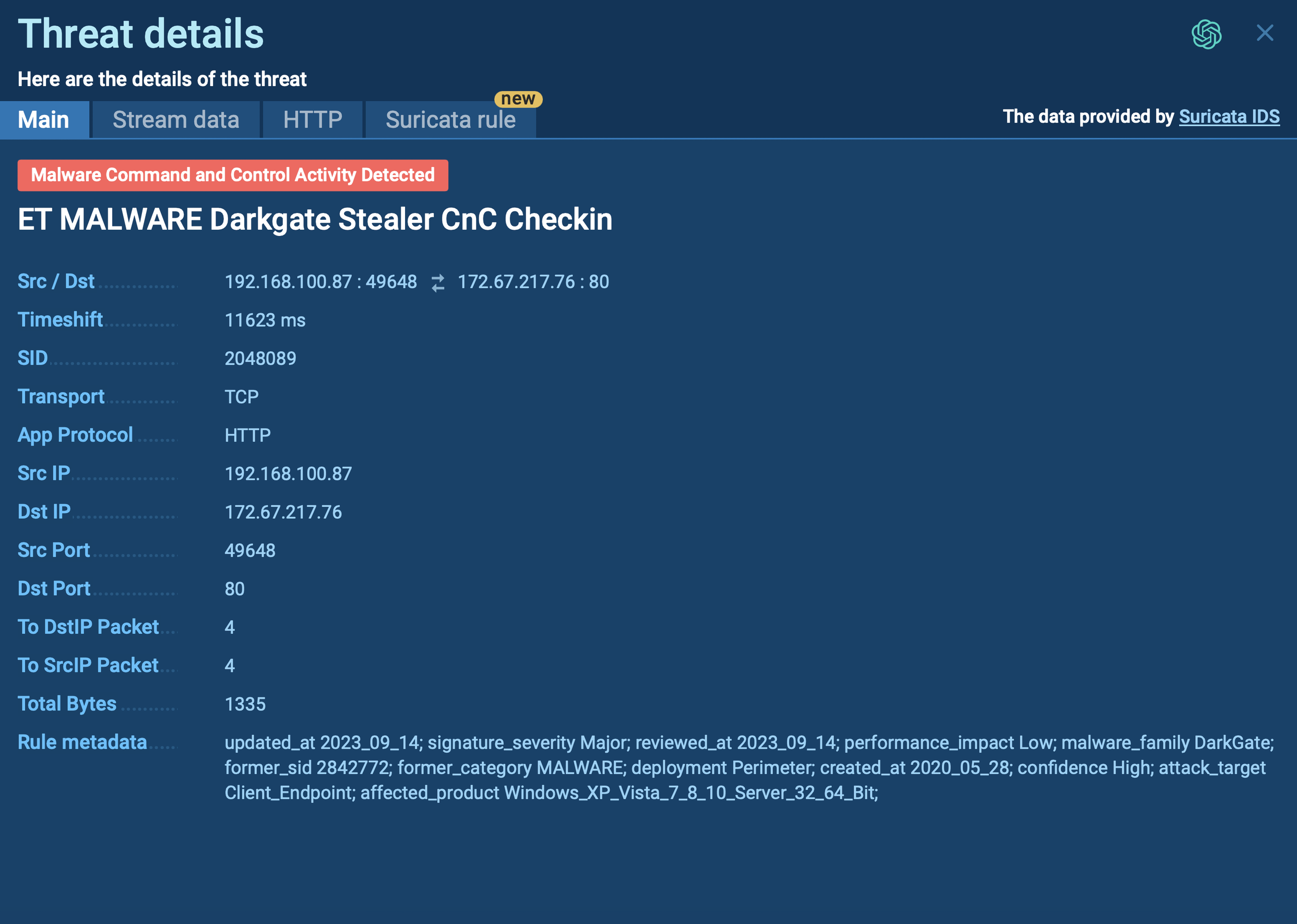
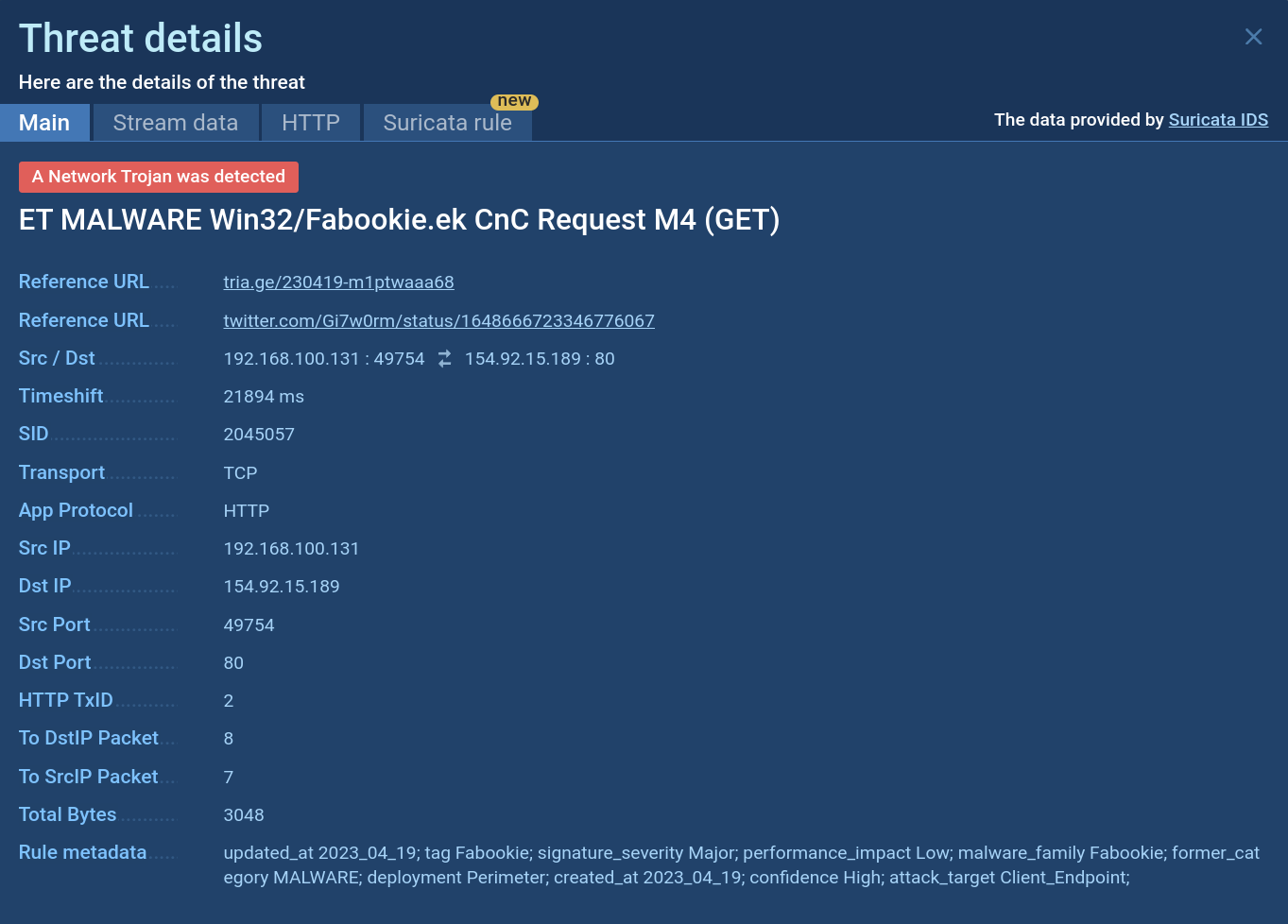 Fabookie Suricata rule demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Fabookie Suricata rule demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Attackers employ various ways of distributing Fabookie. One of the most common ones is via special loader malware that first penetrates defense systems of endpoints and delivers Fabookie to them. NullMixer and SmokeLoader are two examples of such loader malware.
Alternatively, Fabookie can be spread through spam emails that are crafted in a way to appear legitimate to users. These emails usually contain phishing links and files which eventually lead to the infection with Fabookie.
Fabookie is just one example of the ever-evolving threat landscape. By understanding its capabilities and implementing these protective measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to such attacks and safeguard your sensitive information.
The ANY.RUN sandbox provides a cloud-based environment for analyzing files and links suspected of being malicious. It effectively identifies threats like Fabookie and generates reports summarizing the detected malware's technical characteristics, including TTPs and IOCs.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!