Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


RisePro, an information-stealing malware, targets a wide range of sensitive data, including credit cards, passwords, and cryptocurrency wallets. By compromising infected devices, RisePro can steal valuable information and potentially cause significant financial and personal losses for victims.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 424
424
 0
0

 2248
2248
 0
0

 4369
4369
 0
0
RisePro is a malware program primarily designed to exfiltrate sensitive information from compromised devices. It is often distributed through deceptive methods, such as fake cracks sites or malicious email attachments. Once installed, RisePro infiltrates the target system and silently collects a variety of personal and financial data.
First detected in late 2022, the malware continues to be actively updated and developed by its creators. It is sold openly online, including via a Telegram bot, where users can choose a preferred subscription plan and control the malware.
RisePro's underlying architecture is similar to Vidar’s, another well-known password-stealing malware. It employs a system of embedded DLL dependencies to achieve its malicious goals.
The malware's typically focuses on stealing the following types of information:
Additionally, RisePro gathers information about the compromised system, including operating system, installed software, and hardware specifications. It can also capture screenshots of the victim's desktop, providing attackers with visual insights into their activities.
Once collected, the stolen data is bundled and sent to the attacker's command and control (C2) server. As mentioned, RisePro is constantly evolving, as its creators continue to enhance its capabilities. In a recent development, the malware has transitioned from HTTP-based C2 communication to a custom TCP protocol.
Check out a comprehensive analysis of RisePro’s C2 communication.
RisePro employs various obfuscation techniques to evade detection by security software, making it more challenging for antivirus and anti-malware solutions to identify and neutralize the threat.
To see how RisePro behaves on an actual system, let’s upload its sample to ANY.RUN sandbox for detailed analysis.
Like most malware, RisePro's execution chain can vary significantly even within one version. It can be either a single process performing all malicious activities or multiple processes involving the operating system's system utilities.
In our case, using the Static discovering function, we can see that a macro launches a process named crome.exe, which was downloaded from a remote server with the address 89.23.98.22.
Subsequently, we can use Script Tracer to verify this information and ensure that this process was also launched after the download. The WINWORD process, through macros, downloaded and initiated the crome process, which was the RisePro stealer, and carried out the main malicious activity. Additionally, the malware added itself to the Task Scheduler to ensure persistence on the infected system.
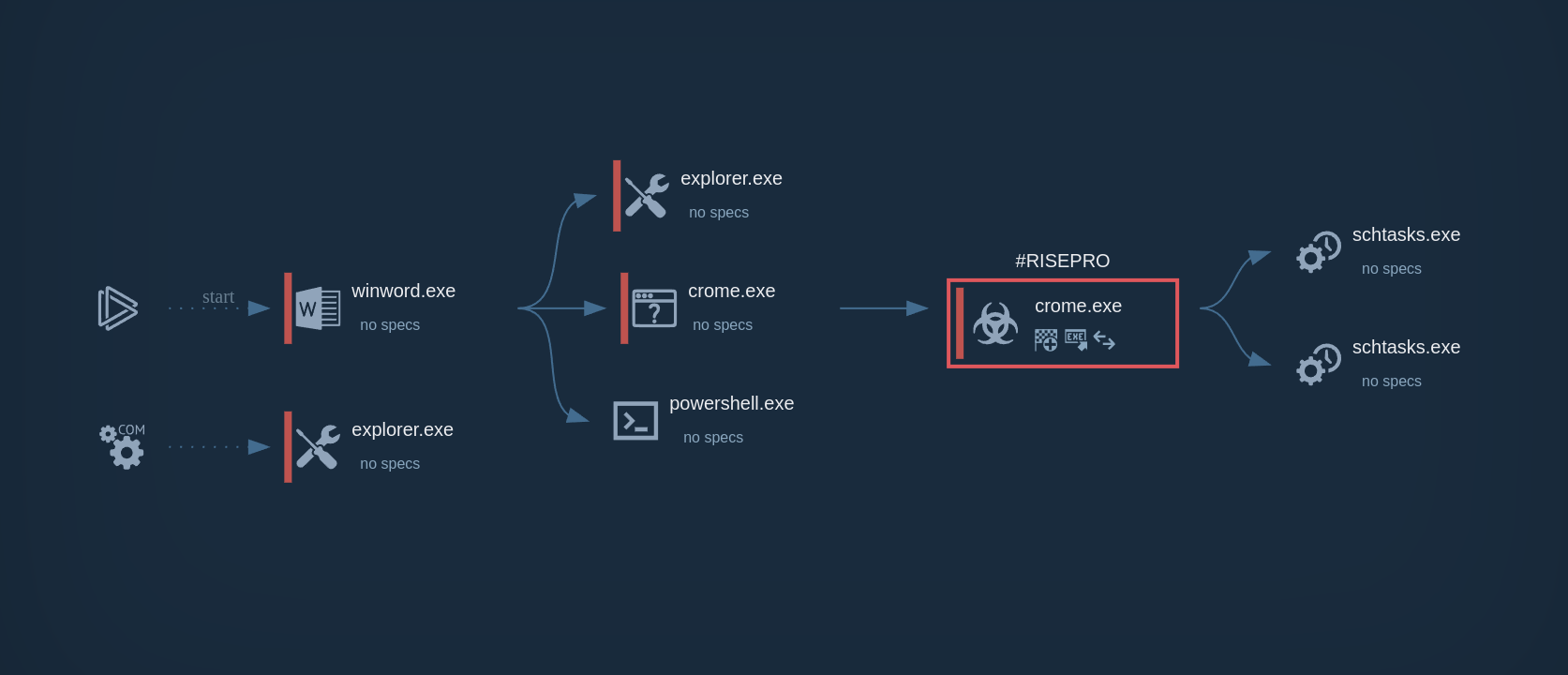 RisePro`s process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
RisePro`s process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
RisePro is often spread by a loader called PrivateLoader. PrivateLoader is a pay-per-install service that charges malware distributors for each installation of their harmful software.
PrivateLoader's most common tactic is to disguise itself as pirated software. This means that they create websites that look like they are offering free downloads of popular programs.
One way that PrivateLoader makes its websites look legitimate is by using SEO poisoning. This is a technique that involves manipulating search engines to rank websites higher in search results.
As RisePro is constantly changing, it's important for individuals and organizations to take steps to protect themselves from its attacks. To make sure you avoid downloading any suspicious files or clicking links, it’s crucial you check them in a malware analysis sandbox.
ANY.RUN helps you identify if a suspicious file or link is safe by analyzing it in seconds. It provides detailed threat reports with all the necessary information, such as indicators of compromise (IOCs), for effective prevention and incident response.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!