Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


DBatLoader is a loader malware used for distributing payloads of different types, including WarzoneRAT and Formbook. It is employed in multi-stage attacks that usually start with a phishing email carrying a malicious attachment.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2020
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2020
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 165
165
 0
0

 448
448
 0
0

 1911
1911
 0
0
DBatLoader is a loader written in Delphi that has been in extensive use among attackers since 2020. One of the key features of the malware is its reliance on legitimate cloud-based platforms such as Discord for hosting its payloads. DBatLoader has been involved in numerous campaigns and leveraged to deploy stealers, trojans, and other threats.
In most cases, DBatLoader manages to infect machines via multi-stage attacks. For instance, victims may receive an email attachment in the form of a PDF file. Upon opening the attachment, users may be prompted to click on a seemingly genuine button embedded with a malicious link. Clicking this link will initiate the download of a Windows Cabinet file, which, in turn, will trigger the installation of DBatLoader on the unsuspecting user's computer.
DBatLoader’s sole purpose is to distribute other malware on the devices it manages to infect. To do this, the developers behind DBatLoader have equipped their malicious software with several advanced capabilities.
For example, DBatLoader can avoid User Account Control (UAC) to gain elevated privileges. It does this by exploiting the mock folder vulnerability. In Windows, executables launched from certain system directories can auto-elevate. DBatLoader exploits this by creating a mock folder with the same name as a trusted location, such as "C:\Windows\System32 ".
On top of that, DBatLoader copies a legitimate process to this fake folder and then injects it with its malicious DLL that allows the payload downloaded by DBatLoader to execute freely without any security notifications, achieving sustained persistence.
Another common vulnerability abused by DBatLoader in previous attacks was CVE-2018-0798, an exploit targeting Equation Editor in Microsoft Office. The malware has also been observed to utilize steganography.
As mentioned, DBatLoader is usually configured to pull malicious payloads from servers of popular cloud storage services, including Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive. Some of the notable examples of malware dropped by DBatLoader are Formbook, Warzone, and Remcos.
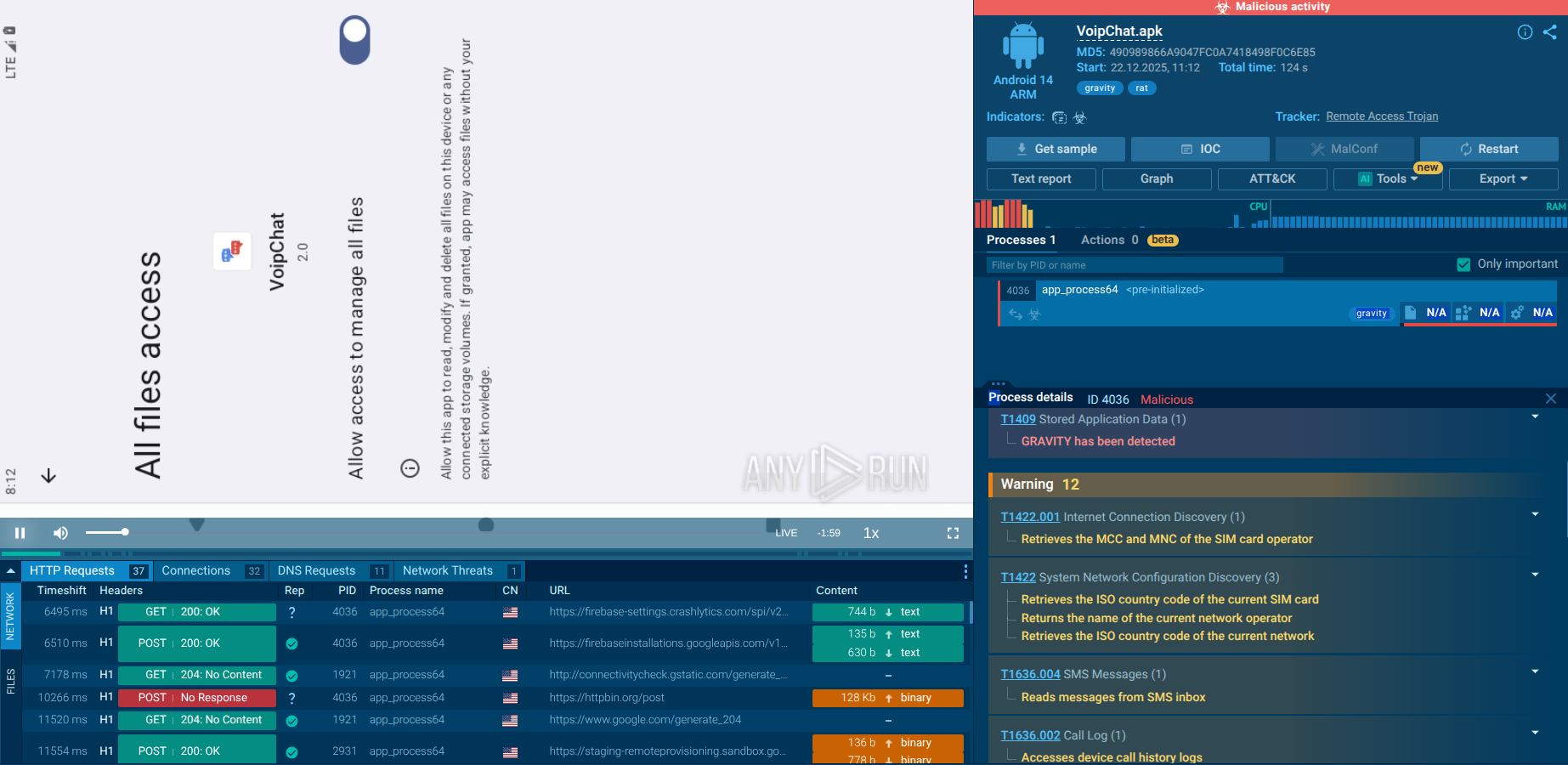
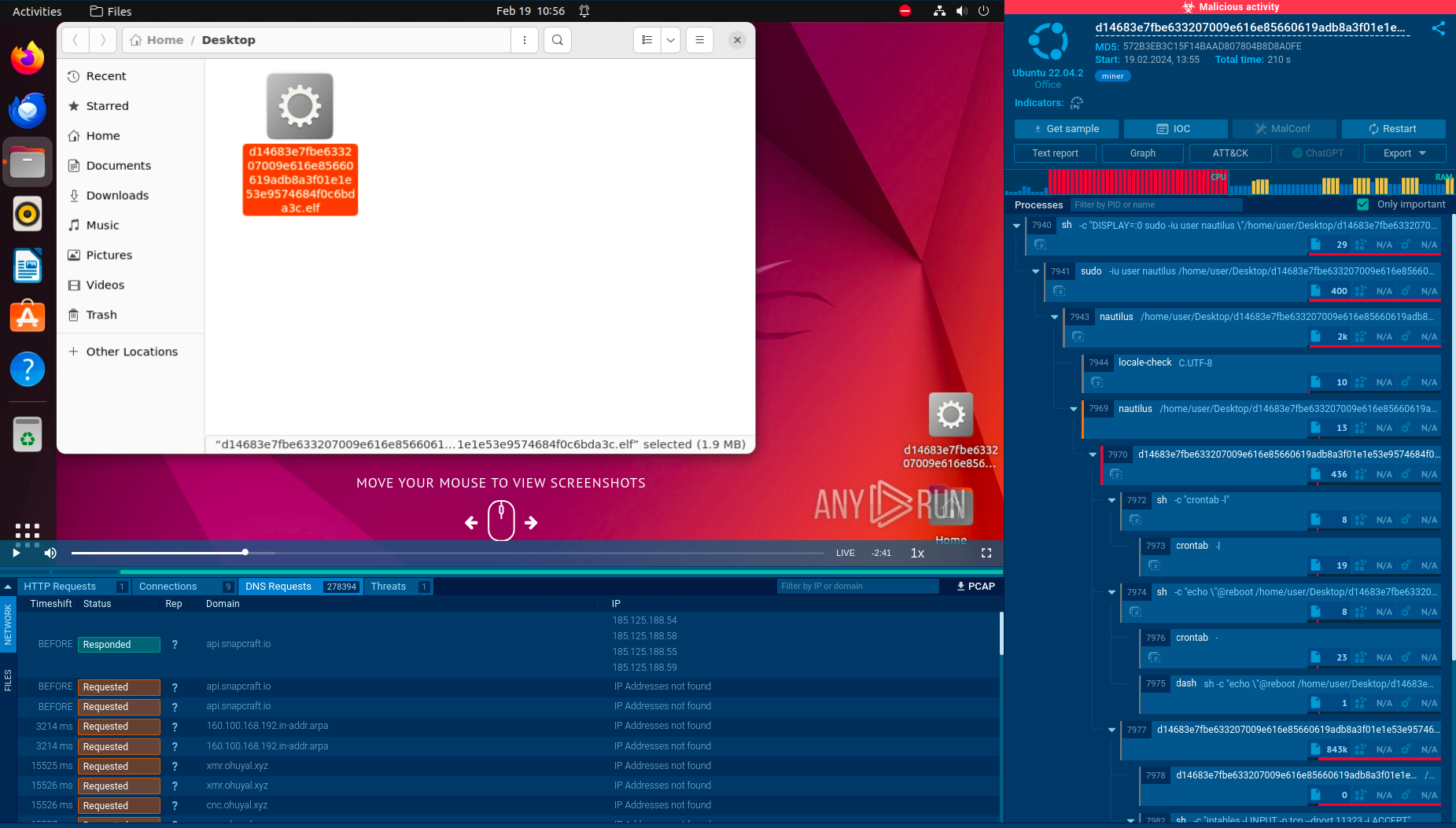
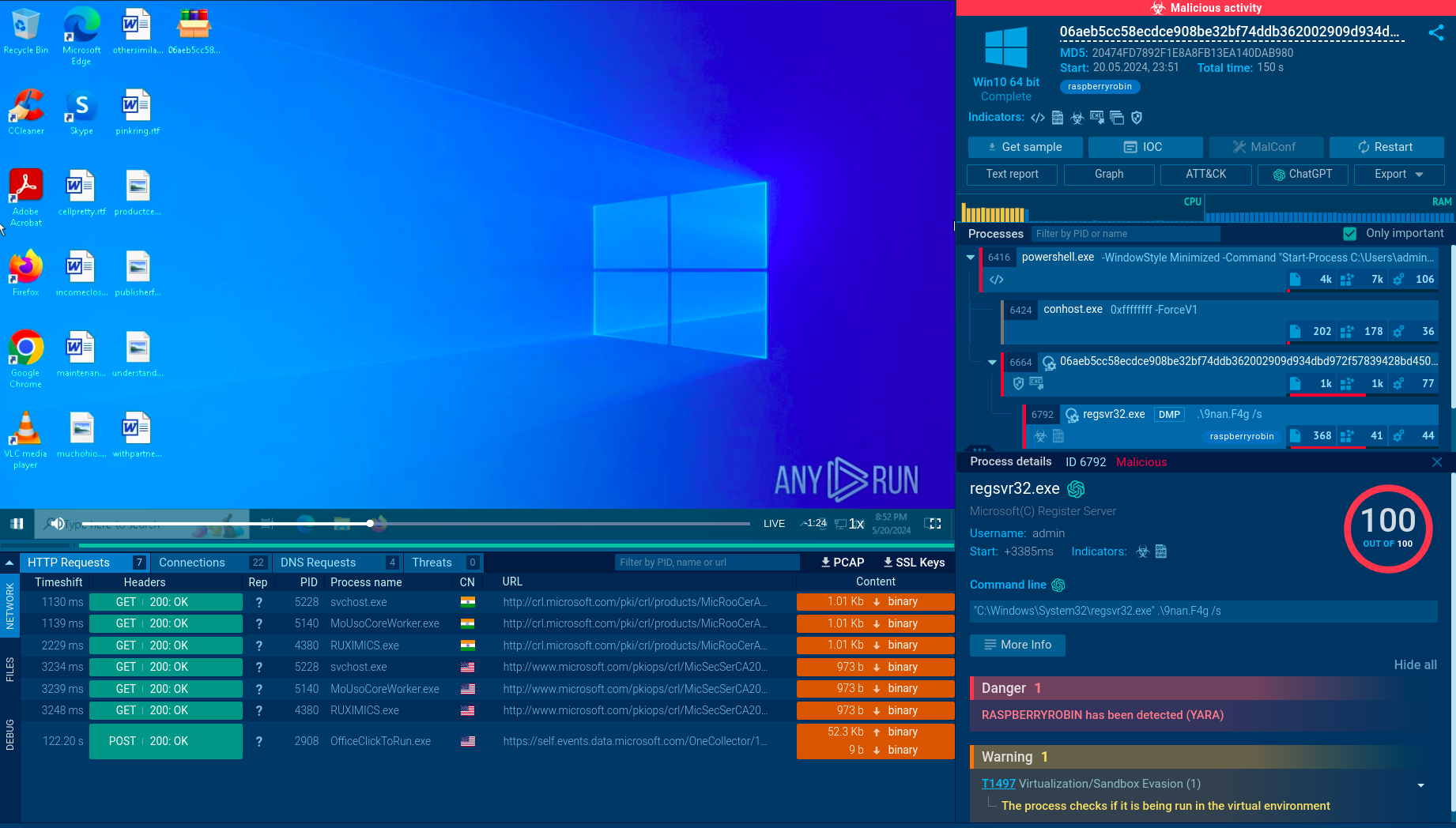
In order to detect DBatLoader, it is vital to analyze the latest samples of this malware and collect up-to-date information on it. To this end, we can use ANY.RUN, a malware analysis sandbox that lets us quickly analyze any suspicious file or link to spot threats.
Let’s upload a sample of DBatLoader to ANY.RUN and study its behavior.
In this task, DBatLoader was distributed as an executable file with a name mimicking the title of a document, attempting to trick users into opening the file and executing the malicious code. Upon execution, DBatLoader downloads and injects the Formbook malware into the Control and Explorer system processes, enabling its malicious activity.
Analyze malware for free in a fully interactive cloud sandbox – sign up now!
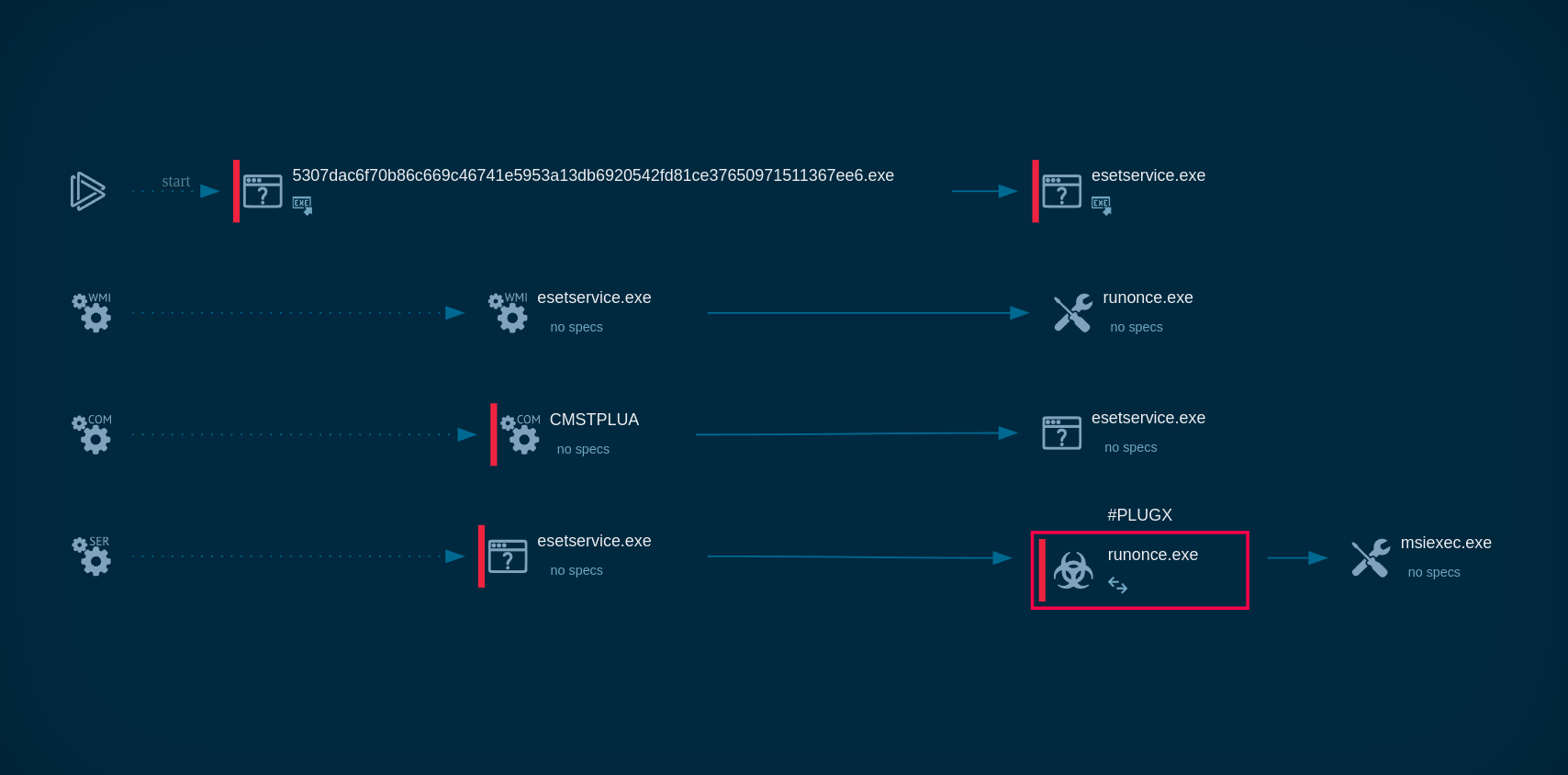
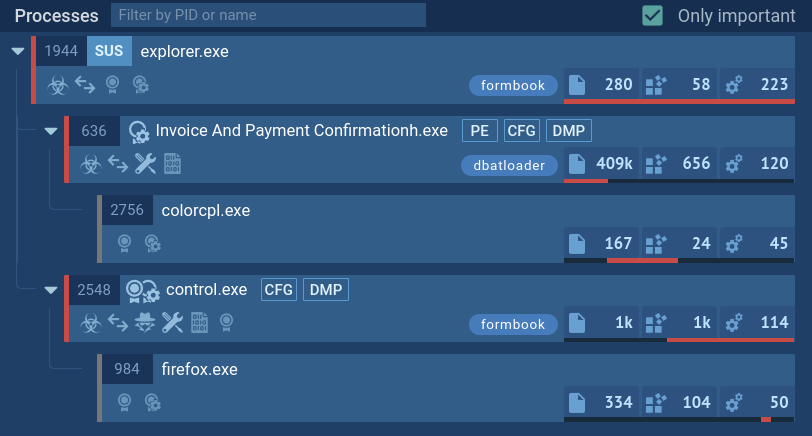 DBatLoader's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
DBatLoader's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
In addition, this loader can be used in more sophisticated attacks, such as exploiting vulnerabilities to penetrate the system. These can be familiar vulnerabilities like CVE-2017-11882, as well as lesser known ones. On top of that, DBatLoader can also make use of system utilities in its attacks. In this task, a whole arsenal of system utilities is actively used, such as cmd, ping, and xcopy, including for the purpose of lateral movement. Eventually, DBatLoader drops Remcos that instantly begins its operation.
Phishing campaigns constitute the most common vector of attack involving DBatLoader. Emails sent by the operators of the malware target different organizations and are masqueraded as genuine messages. In many cases, criminals even use legitimate email addresses they manage to hijack or gain access to.
The subject of such emails concerns different business-related matters, such as payments and other arrangements. For example, attackers may send fake invoices as Microsoft Office or PDF files. These files usually contain a link that, once clicked, can trigger the infection leading to DBatLoader being dropped on the computer and the eventual deployment of the final payload.
DBatLoader remains an active threat commonly used by criminals in their attacks on various types of organizations. To keep your infrastructure safe, it is essential that you have strong security measures in place, especially when it comes to software for detecting and inspecting threats.
Use the ANY.RUN sandbox as a reliable tool for analyzing emails you receive to safely determine if they pose any danger. ANY.RUN’s interactive cloud environment makes it easy to investigate the most advanced phishing campaigns and uncover multi-stage attacks in minutes. The service provides you with convenient text reports containing all the relevant information on the files and links you submit, including fresh IOCs.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!