Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


PlugX is a remote access trojan that is used extensively by Chinese APTs. The malware is primarily employed for spying on victims and can perform a variety of malicious activities, such as logging users’ keystrokes and exfiltrating information from browsers.
|
Backdoor
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
16 January, 2008
First seen
:
|
13 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
China
Origin
:
|
|
16 January, 2008
First seen
:
|
13 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 868
868
 0
0

 515
515
 0
0

 2802
2802
 0
0
PlugX is a remote access trojan (RAT) family used to gain access to and control computers. It has been around since 2008 and continues to be exploited today by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups, including Mustang Panda.
The malware is often employed for spying on victims, as it possesses a considerable set of tools that make it a go-to-option for attackers. Among other things, it can be utilized to log users’ keystrokes and exfiltrate sensitive information. As a result, PlugX has been involved in numerous attacks on organizations, primarily in Asia. However, there are also instances of attacks on private companies.
Due to the fact that PlugX has been around for over a decade, the malware has undergone numerous iterations, and multiple variants have been created as a result. However, in most cases, they share similar functionality, which includes:
PlugX has been known to leverage DLL side-loading to execute its malicious payload. DLL side-loading is a technique employed by malware to evade detection by traditional security measures. It involves injecting malicious code into a legitimate DLL (Dynamic Link Library) file, which is then executed by a trusted application.
Another persistence mechanism used by PlugX is the modification of the Windows Registry to kickstart its execution during every system booting.
Similar to njRAT and LimeRAT, PlugX makes use of USB-based propagation. It enables the malware to spread to other systems via infected USB devices.
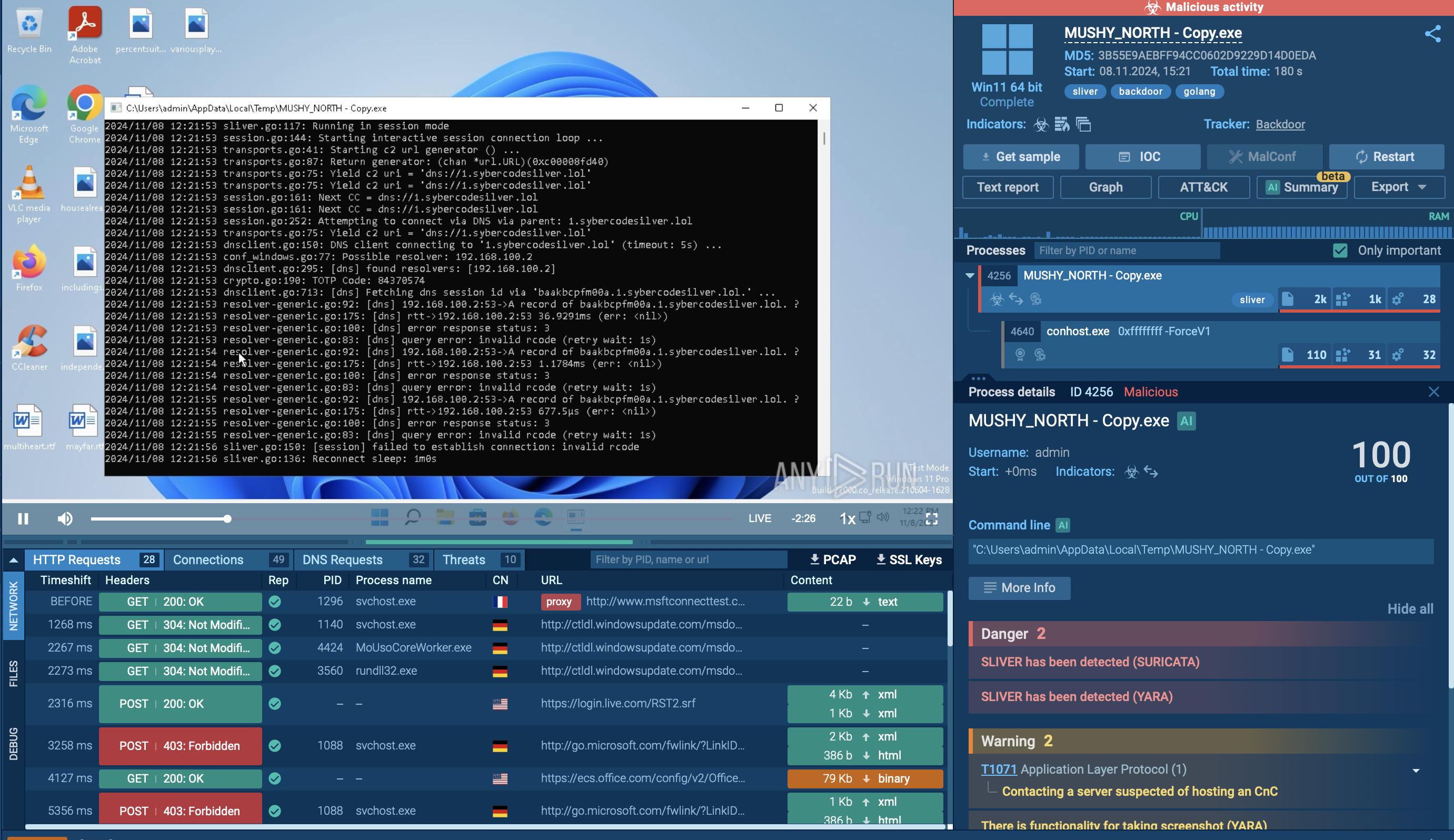
We observe the entire execution chain of PlugX in ANY.RUN by submitting its sample for analysis.
PlugX is known for utilizing system applications and legitimate files in its attempts to evade defense mechanisms. In our example, the malware drops a legitimate ESET EHttpSrv.exe file (renamed as esetservice.exe) that is exploited to load the http_dll.dll. This DLL file has the capability to collect files from the infected system.
The Remote Access Trojan (RAT) also exploits the dllhost process and runs an esetservice process as a service. Following privilege escalation, PlugX injects run once, establishing a connection to a Command and Control (C2) server and awaiting commands for subsequent malicious activities.
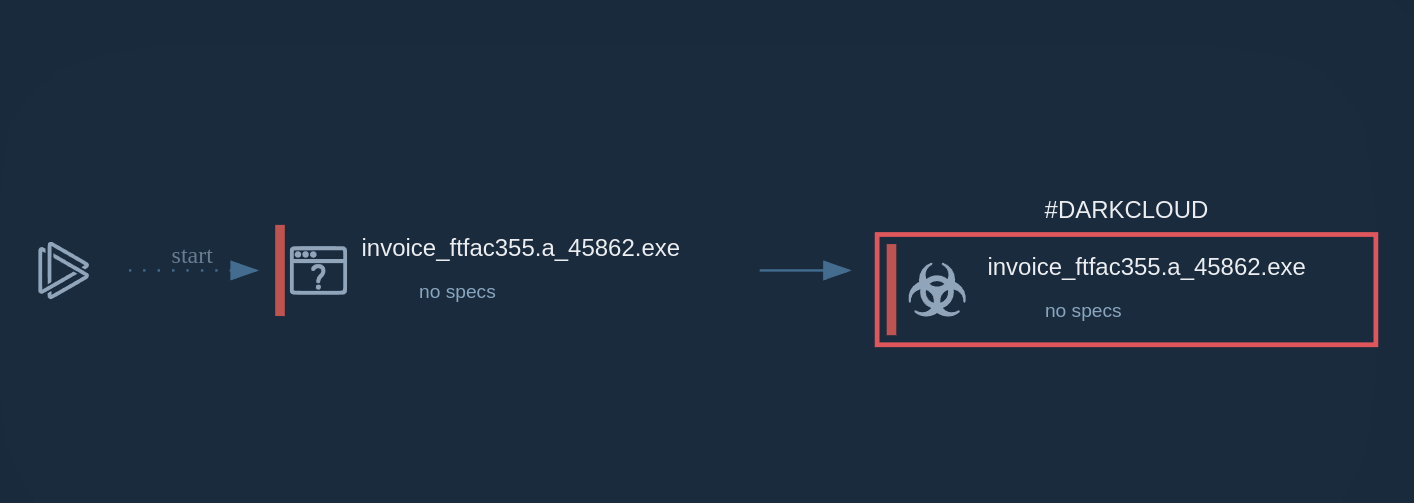
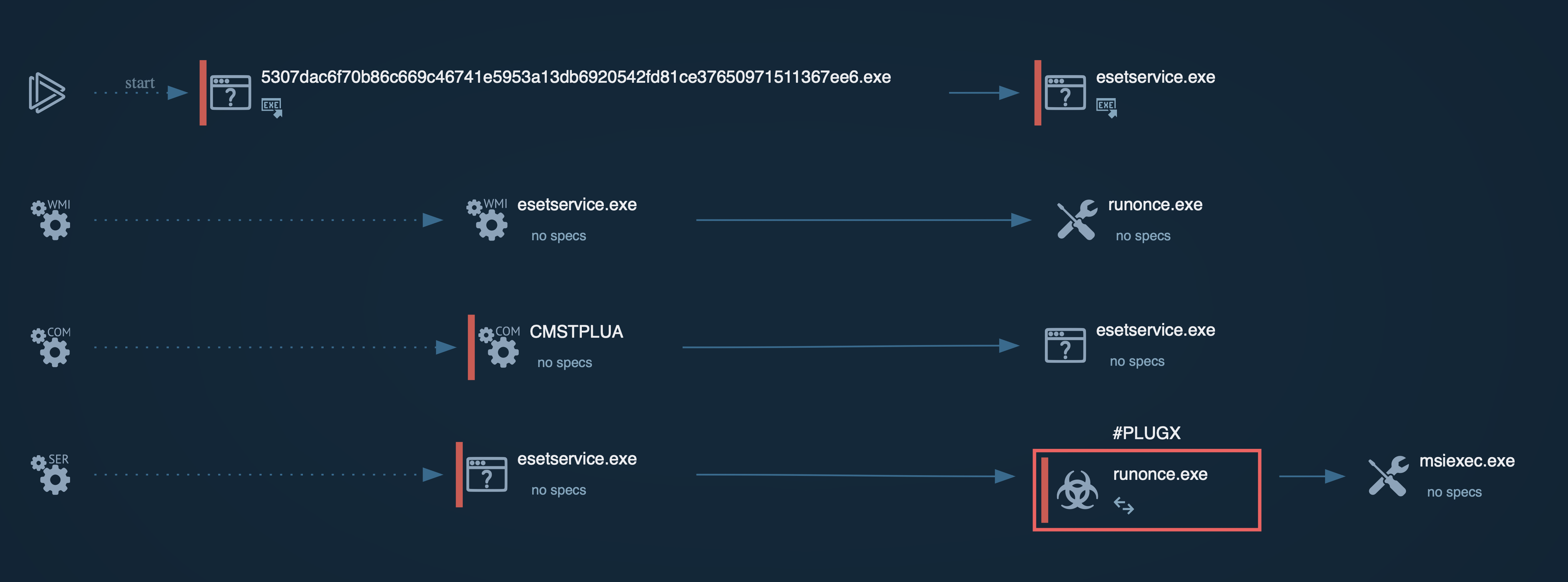 PlugX`s process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
PlugX`s process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Apart from USB-based distribution, PlugX is most often spread via phishing emails. Attackers usually place the malware inside an archive which is sent to victims in the form of an attachment. Once they open and launch the files inside the archive, the execution process begins.
PlugX is one of the most persistent threats in the world that has been actively used since 2008. Despite its long history, it regularly evolves, gaining new capabilities and features that allow it to beat defense systems. To make sure your organization remains safe from a PlugX infection, it is vital to keep up with the latest samples of the malware and its behavior. To this end, you can use ANY.RUN.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based malware analysis sandbox that lets you investigate any threat to unveil its TTPs and collect IOCs. Thanks to its advanced interactivity, ANY.RUN makes it possible to conduct malware analysis by engaging with the malware and the infected system just like on a standard computer.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!