Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


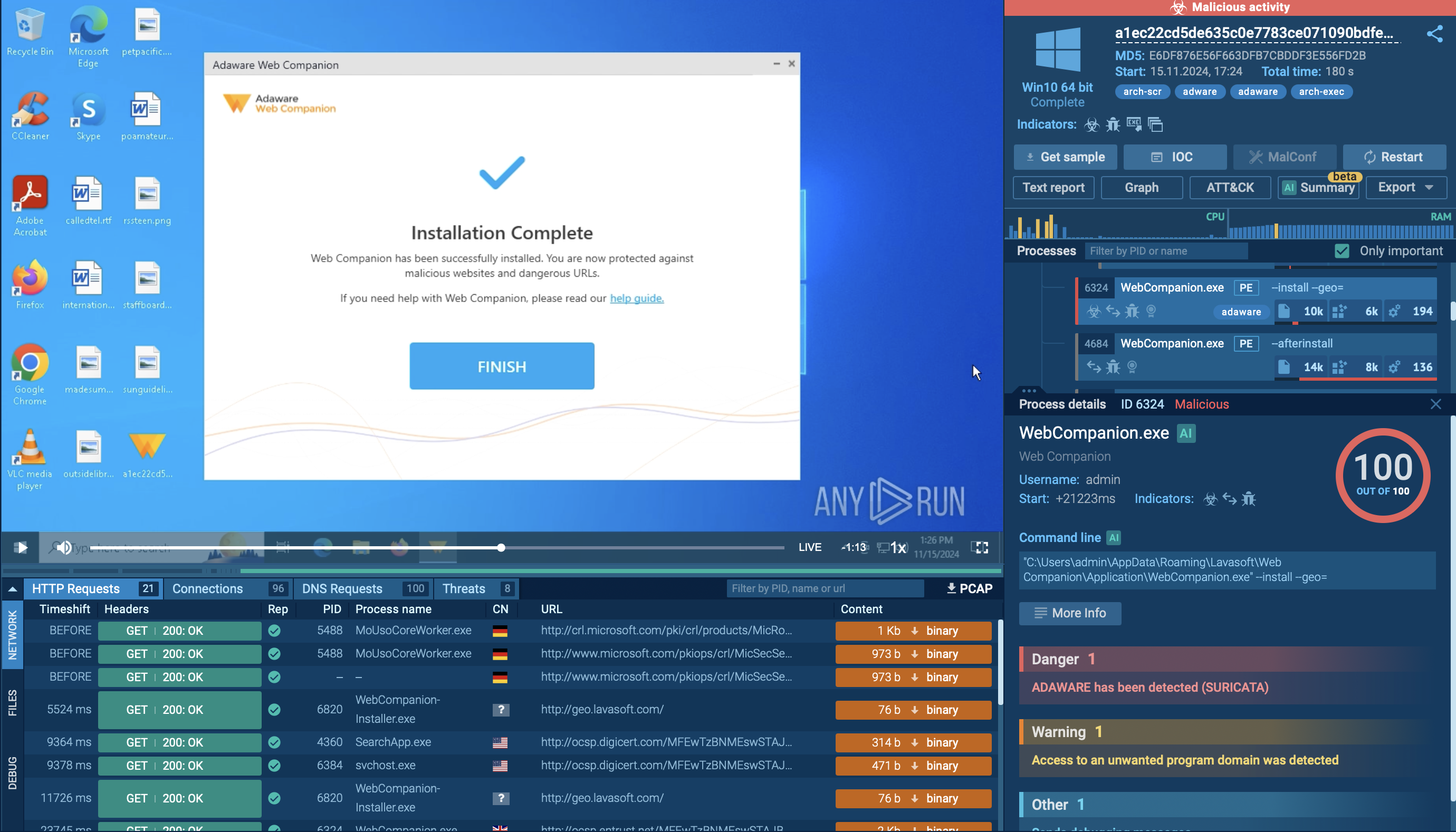
Netwire is an advanced RAT — it is a malware that takes control of infected PCs and allows its operators to perform various actions. Unlike many RATs, this one can target every major operating system, including Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2012
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2012
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 433
433
 0
0

 2286
2286
 0
0

 4434
4434
 0
0
Netwire is a remote access trojan-type malware. A RAT is malware used to control an infected machine remotely. This particular RAT can perform over 100 malicious actions on infected machines and can attack multiple systems, including Windows, Apple’s MacOS, and Linux.
Netwire malware is available for purchase on the darknet in the underground hacking communities, where attackers can buy this RAT for the price of 40 to 140 USD. In addition, Netwire can be purchased on the surface internet for a price of 180 USD. Notably, in 2016 Netwire received an update that added the functionality to steal data from devices connected to the infected machine, such as USB credit card readers, allowing Netwire to perform POS attacks.
Netwire Trojan core functionality allows this malware to take remote control of infected PCs, record keyboard strokes and mouse behavior, take screenshots, check system information, and create fake HTTP proxies.
The keylogger functionally allows Netwire to record various personal data imputed on a computer connected to the internet or a corporate network. Combined with the ability to steal credit card information and operate undetected for extended periods of time, Netwire RAT is truly capable of inflicting serious dangers to organizations.
In some malicious campaigns, the Netwire trojan was used to target healthcare and banking businesses. The malware was also documented as being used by a group of scammers from Africa who utilized Netwire to take remote control of infected machines.
Netwire RAT creators have put in a lot of work to ensure that researchers have a hard time analyzing this malware, as many precautions are taken to complicate the research process, including techniques like multiple data encryption layers and string obfuscation. In addition, the malware uses a custom C2 binary protocol that is also encrypted, and so is the relevant data before transmission.
During one campaign, researchers have observed Netwire being distributed as “TeamViewer 10” – named so in an effort to trick victims into thinking that they have downloaded the legitimate remote assistance software. Once the execution process began, this version would drop an .EXE file and start establishing persistence right away. The malware created a Windows shortcut in the Startup menu to ensure that the Netwire trojan would always run when the user logged into the system. Interestingly, another trick designed to keep the malware hidden actually gave it away during this particular campaign. The malware would inject its code into the Notepad.exe, unveiling its presence since it’s not normal for the notepad to have an always active network connection. Only after decoding the data prepared for transmission to the C2, the sensitive nature of the stolen information was discovered. Unfortunately, researches did not reveal what the organization was targeted in this particular attack.
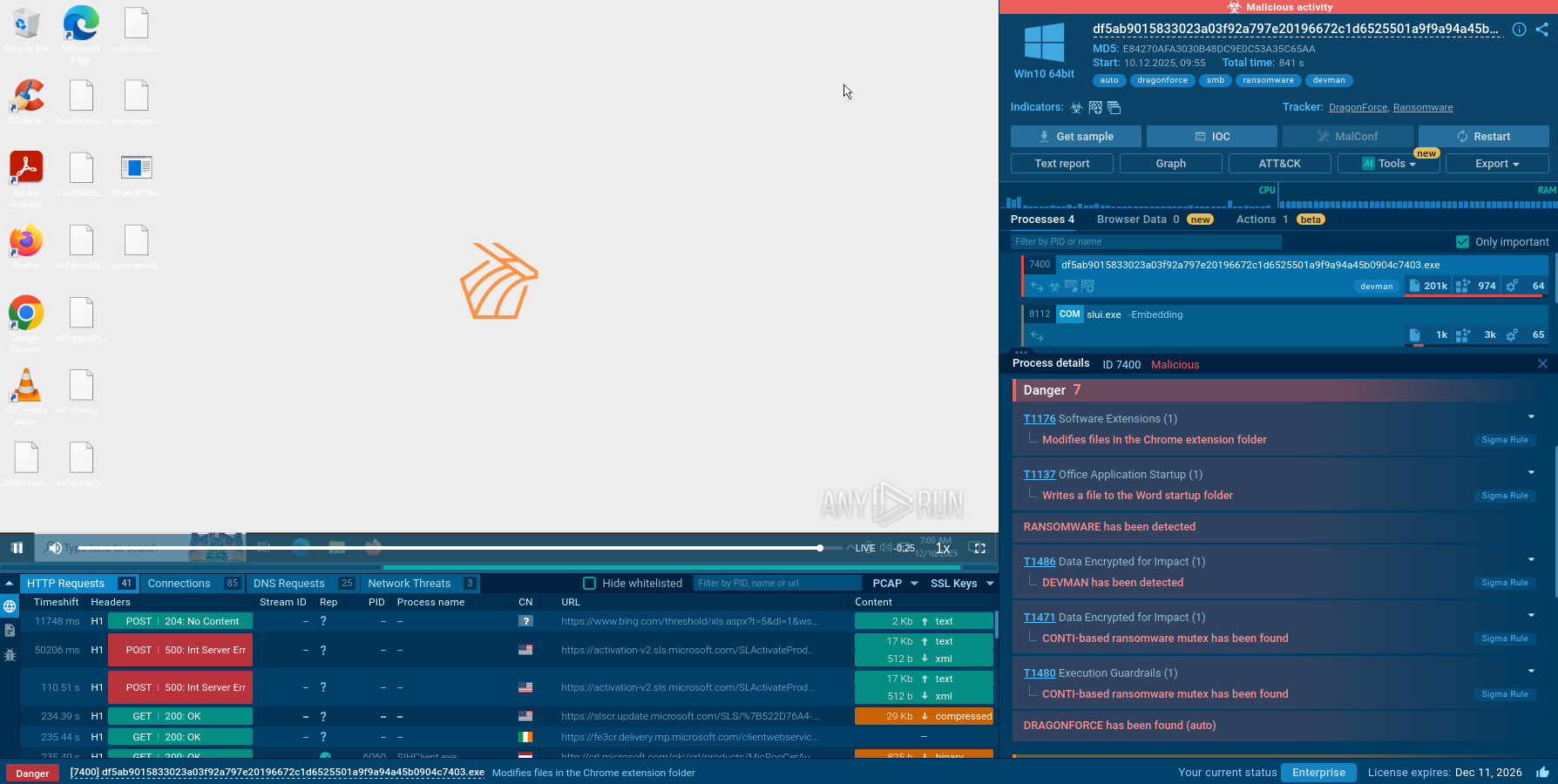
A video simulation recorded on ANY.RUN enables researchers to study the lifecycle of the Netwire in a lot of detail and works like a tutorial.
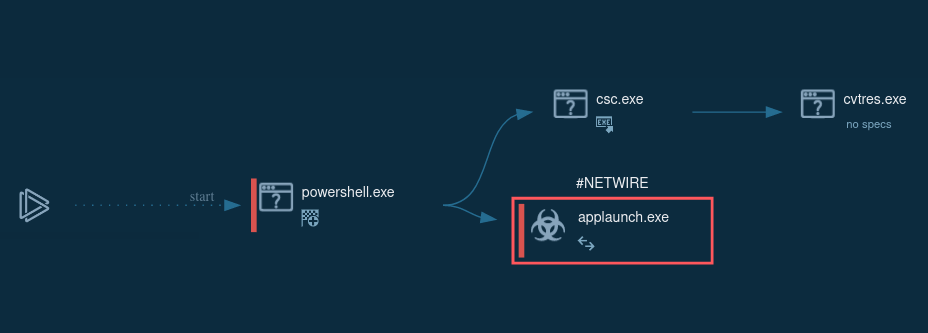 Figure 1: Process graph generated by ANY.RUN allows visualizing the life cycle of Netwire
Figure 1: Process graph generated by ANY.RUN allows visualizing the life cycle of Netwire
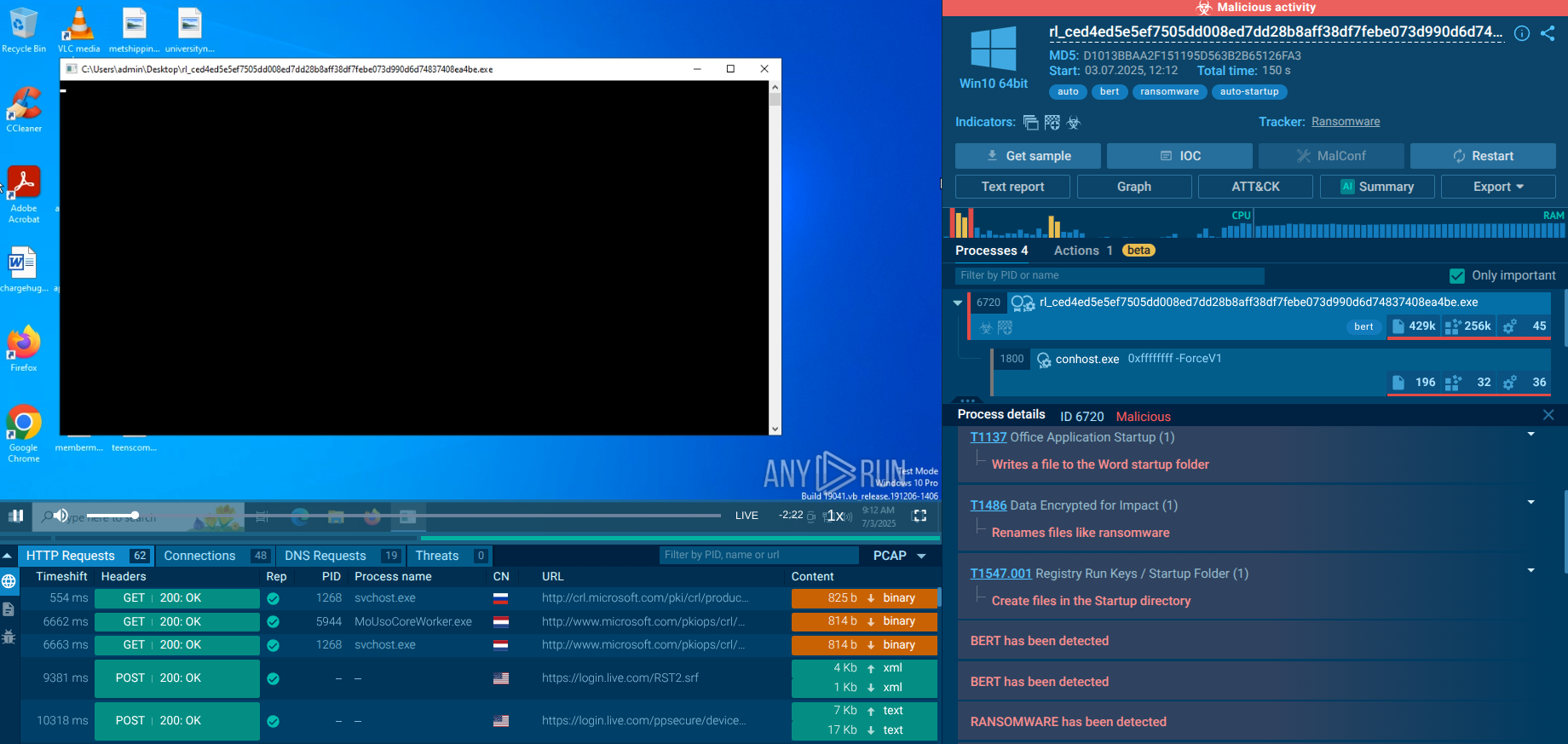
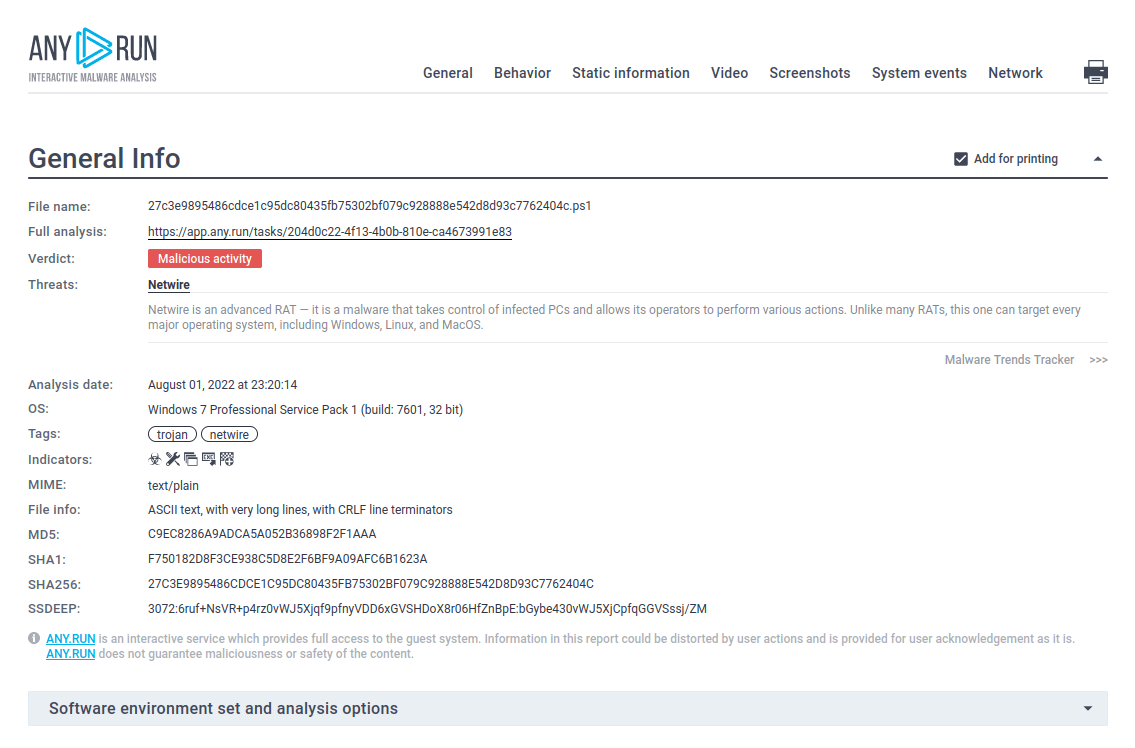 Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN is a great tool to share the research results
Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN is a great tool to share the research results
Netwire isn't as exciting as some other malicious programs can be as far as malware execution goes. It makes its way into the device, mostly in the form of a payload.
The user receives a spam email with an attached Microsoft Word file. After the user downloads and opens this file, the executable is dropped or downloaded onto the machine. After that, the executable starts performing the main malicious activity such as writing itself in autorun, connecting to C2 servers, and stealing information from an infected device. Netwire also has the ability to inject into unsuspicious processes from which it can perform malicious activities.
Netwire RAT is usually being distributed in email phishing campaigns in the form of a malicious Microsoft Office document. The victim must enable macros for the RAT to enter an active state. The macros then proceed to download Netwire, allowing the malware to start the execution process.
If analysts want to do additional work with events from tasks or share them with colleagues for tutorials, they can export to different formats. Just click on the "Export" button and choose the most suitable format in the drop-down menu. Export of any kind of malware research is available including Predator the Thief or Qbot.
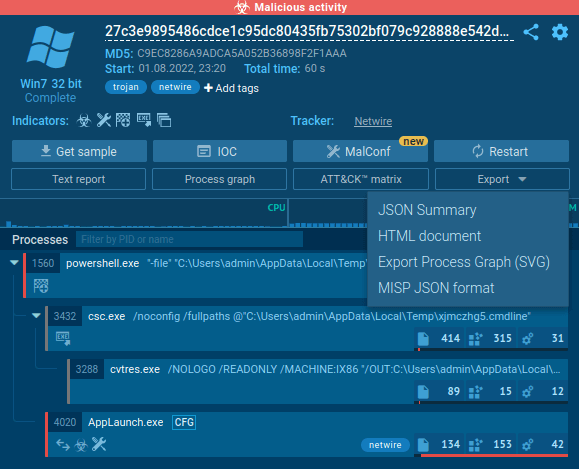 Figure 3: Export options for netwire malware
Figure 3: Export options for netwire malware
Diverse information stealing feature sets combined with the ability to target multiple operating systems and steal data from credit cards used in an infected system make Netwire Trojan a highly dangerous remote access trojan.
Despite its impressive functionality, the malware is fairly accessible, “retailing” on underground forums for as little as 40 dollars in some select cases. The situation is further worsened by the fact that creators of Netwire RAT have implemented several features designed to complicate the analysis as much as possible.
However, researchers can take advantage of interactive malware hunting services, such as ANY.RUN, which allows to influence the simulation at any point and get much purer research results.
.png)