Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Metamorfo is a trojan malware family that has been active since 2018. It remains a top threat, focusing on stealing victims’ financial information, including banking credentials and other data. The malware is known for targeting users in Brazil.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2018
First seen
:
|
30 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2018
First seen
:
|
30 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 399
399
 0
0

 2185
2185
 0
0

 4261
4261
 0
0
Metamorfo, also known as Casbaneiro, is a trojan malware family used for exfiltrating financial information. The operators behind the malicious software spread it primarily via phishing campaigns. While initially, users living in Brazil were the core victims of the malware, the attackers later expanded the list of targeted countries.
Keylogging serves as the main method of collecting information from the infected devices. To facilitate the process, Metamorfo can display fake bank forms requesting users’ credentials. At the same time, the malware can also be employed to steal other sensitive data, as well as take screenshots.
One of the ways Metamorfo manages to collect users’ login banking info is by first killing all the browser processes and then modifying the registry to disable auto-complete and auto-suggest. This is done to force the user to enter their login and other form details manually, allowing Metamorfo’s keylogging capability to record the keys they press.
Metamorfo also can scan the clipboard and replace any saved crypto wallet address with that of the attacker. As a result, victims may unknowingly send their funds to criminals.
On top of that, the malware can search for certain files on the infected device using specific keywords and exfiltrate them to the attacker. Metamorfo can also download additional files from its C2, meaning that it can update itself and install other malicious software.
Many attacks involving the malware have been observed to implement DLL hijacking. This technique enables Metamorfo to run its code with the help of legitimate processes, which allows it to stay undetected by traditional security solutions.
The malware can also display fake security pop-ups of popular Brazilian banks, informing the users that their account has been compromised. The next window then requests the victim to share their login credentials.
Metamorfo gains persistence on the system by creating a task that launches the malware at every new startup.
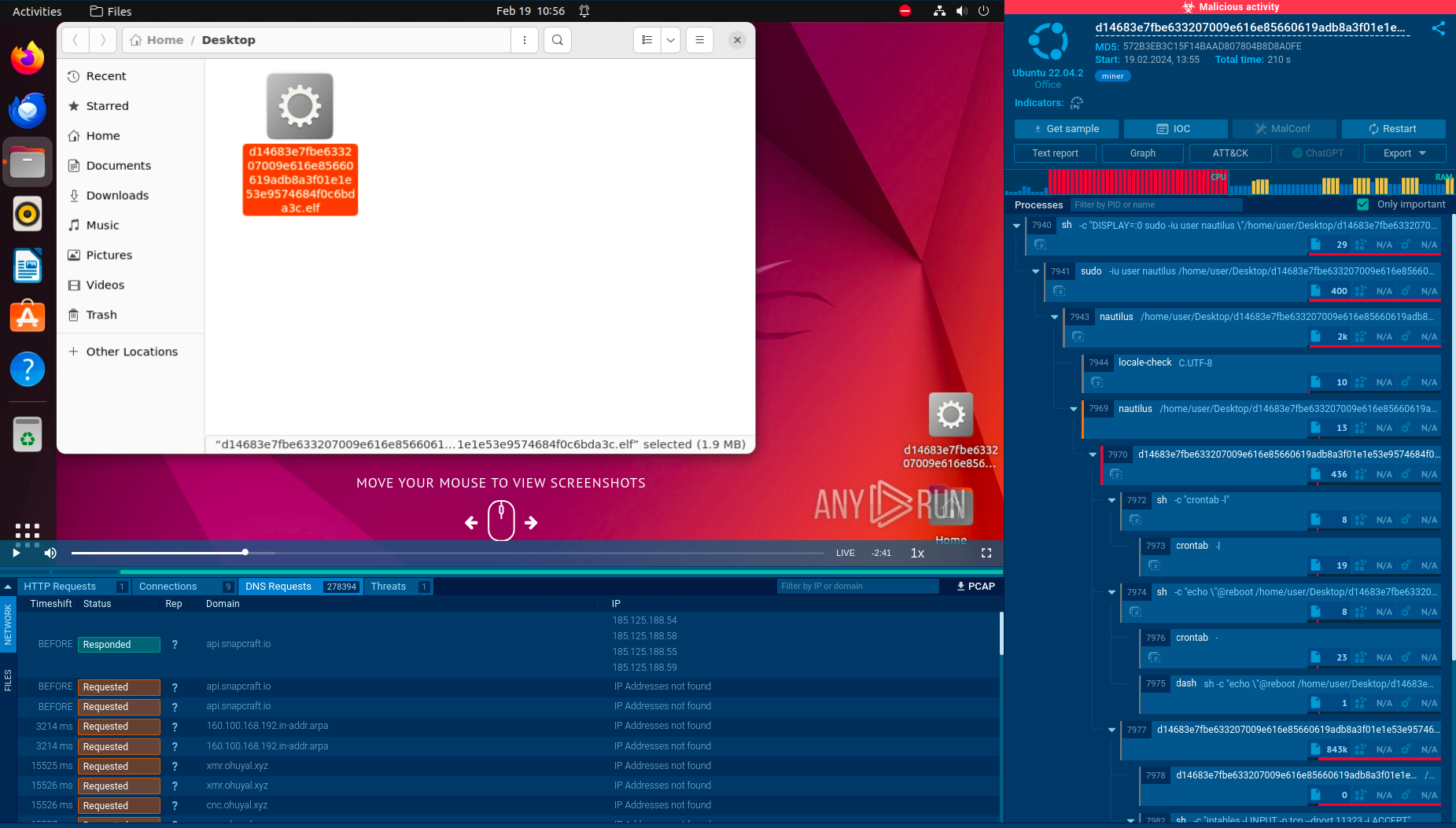
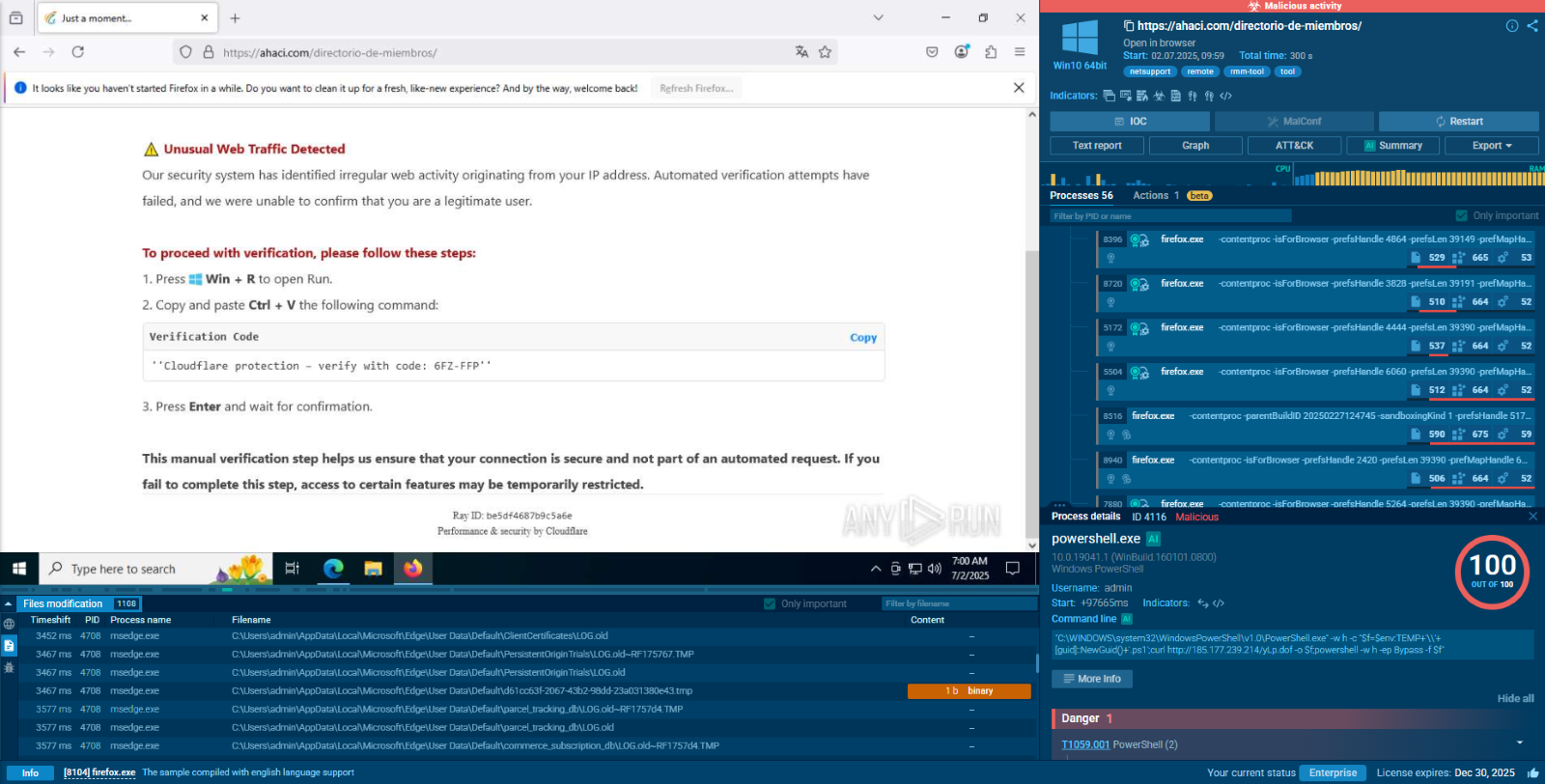
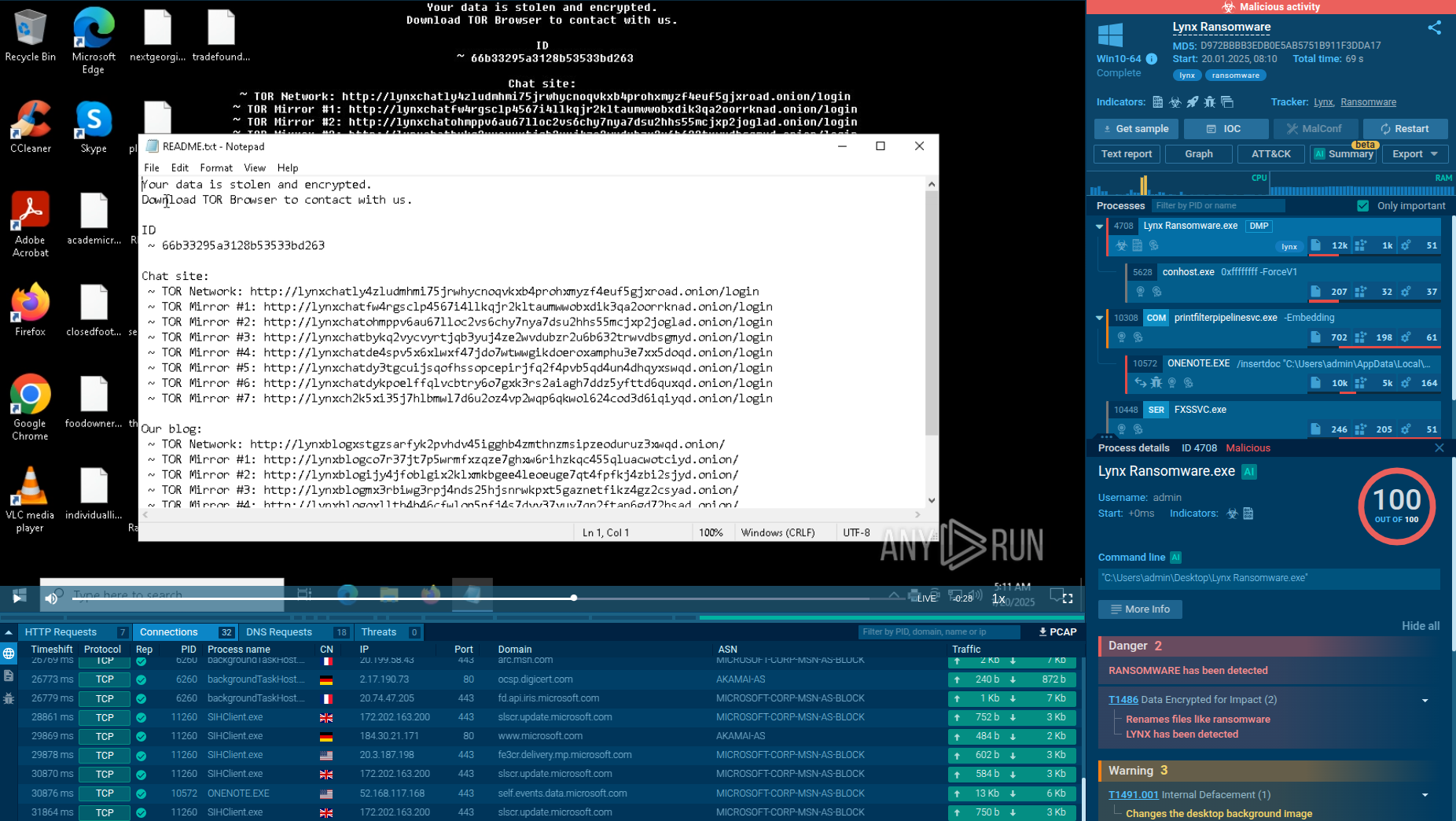
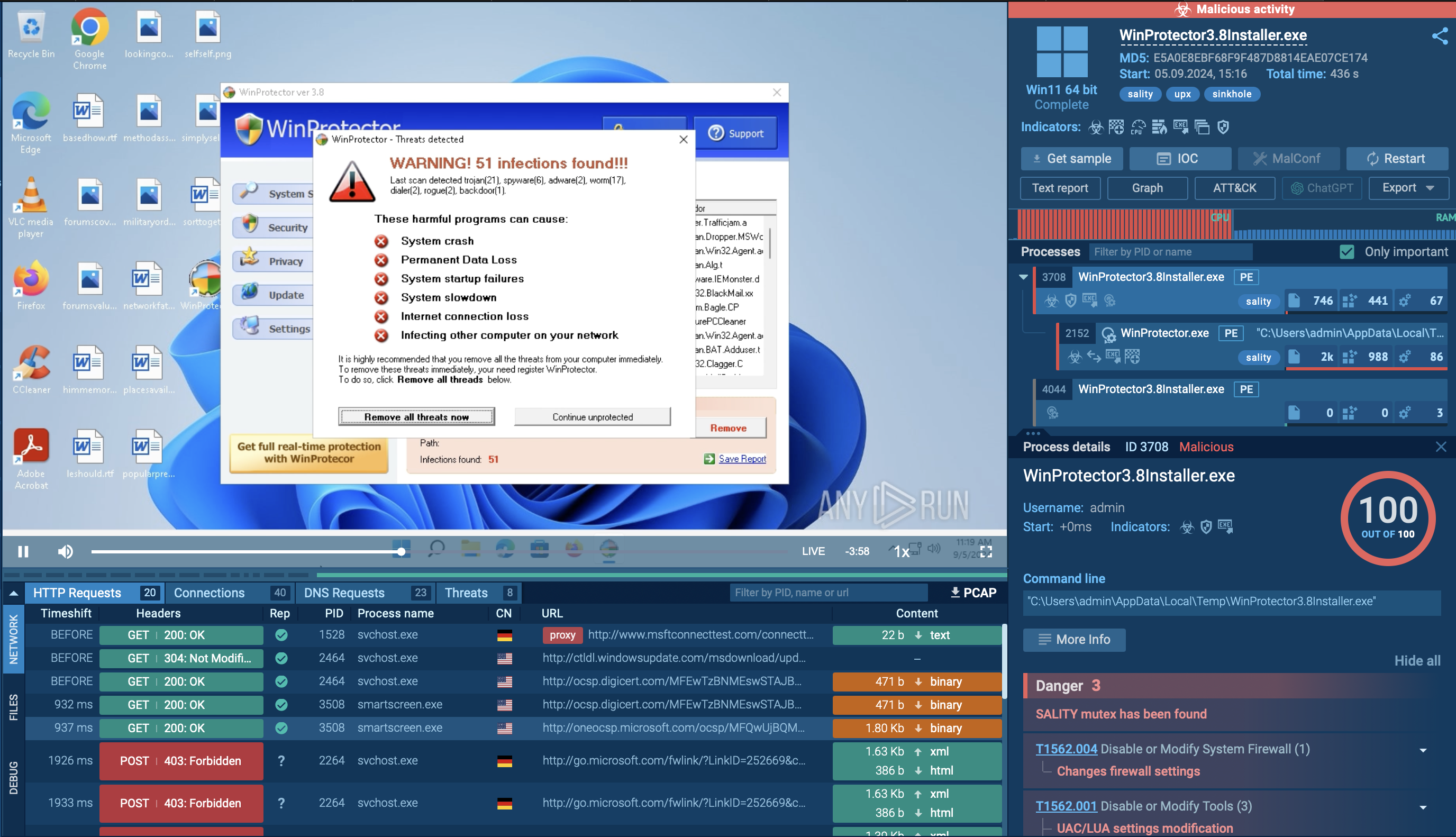
Let’s upload a sample of Metamorfo to the ANY.RUN sandbox to explore its execution chain.
This particular Trojan family often employs a deceptive strategy of embedding itself into installers that unsuspecting users download in the hopes of installing legitimate software. Our analyzed sample, also in MSI format, deviates from this common modus operandi by employing more sophisticated installation techniques. Instead of relying on fake installer windows to blend in, it utilizes a combination of a hidden window and the header "Installation Database" to conceal its installation process.
Upon execution, the downloaded sample establishes a connection to a remote server to retrieve the primary payload, Metamorfo. Once Metamorfo is downloaded, it is launched, initiating a series of malicious activities. These activities include creating a file in the startup directory to ensure its persistent operation and, to evade detection, subsequently removing this file from the startup registry.
Once established, the dropped file, SlimBoat, takes center stage, orchestrating a coordinated attack on the compromised system. It loads additional modules, establishes a connection to the remote server, and embarks on the primary objective of exfiltrating sensitive information.
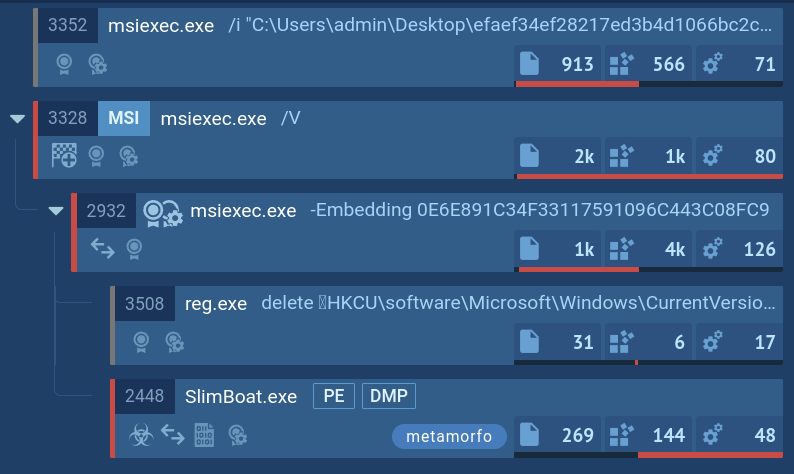 Metamorfo's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Metamorfo's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Similar to other trojan malware families like Agent Tesla and Remcos, Metamorfo is distributed using phishing emails with malicious attachments in the form of archives with an .MSI file inside and PDFs. In some attacks, criminals also send links. The subject of the email usually concerns finance, asking the recipient to conduct an invoice payment.
Despite being active since 2018, Metamorfo continues to pose a major threat to users in Brazil and other countries, including the United States. Organizations without reliable security measures in place are particularly vulnerable to such attacks. As Metamorfo typically spreads through emails, checking all the incoming files and links should be top priority for organizations that do not wish to fall victim to the malware.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based malware analysis sandbox that lets you quickly analyze any suspicious file and URL to determine whether it is malicious. The service also generates reports on the threats identified, containing all the necessary intelligence, including indicators of compromise (IOCs).
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!
.png)