Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


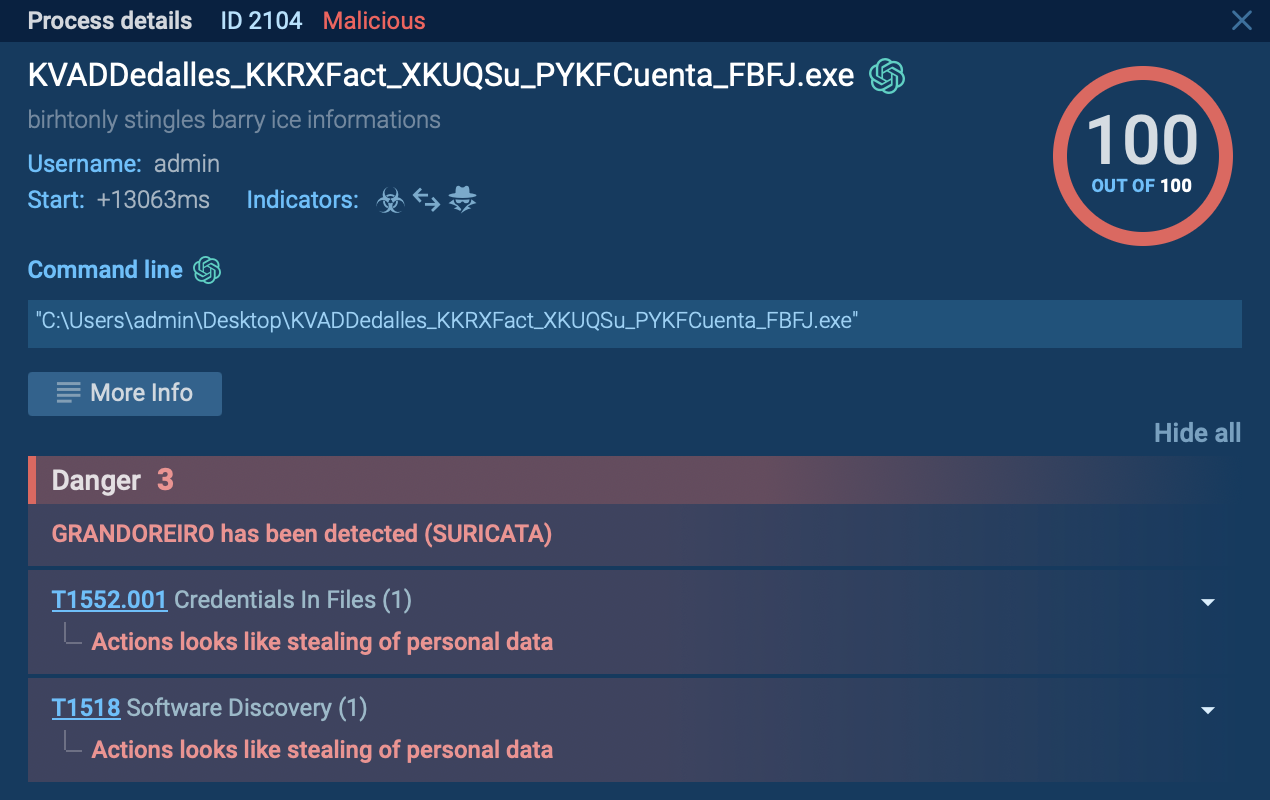
Medusa is a ransomware malware family targeting businesses and institutions. Medusa encrypts crucial data, rendering it inaccessible, and attempts to pressure users to pay to regain control of their information. The group behind this malicious software hosts a TOR website where it shares the list of the organizations whose infrastructure has been compromised. This malware utilizes various tactics, including exploiting vulnerabilities and employs a unique file extension (".MEDUSA") to mark encrypted files.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
5 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
5 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 461
461
 0
0

 2383
2383
 0
0

 4604
4604
 0
0
Medusa Ransomware is a type of malicious software employed by cybercriminals for extortion purposes. This tool is used in offensive campaigns that involve the encryption of critical data belonging to organizations, followed by a ransom demand for its decryption.
Medusa Ransomware first emerged in June 2021 and has since targeted various industries, including the education sector. In 2023 alone, it is reported to have affected over 70 organizations globally, operating under the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) business model.
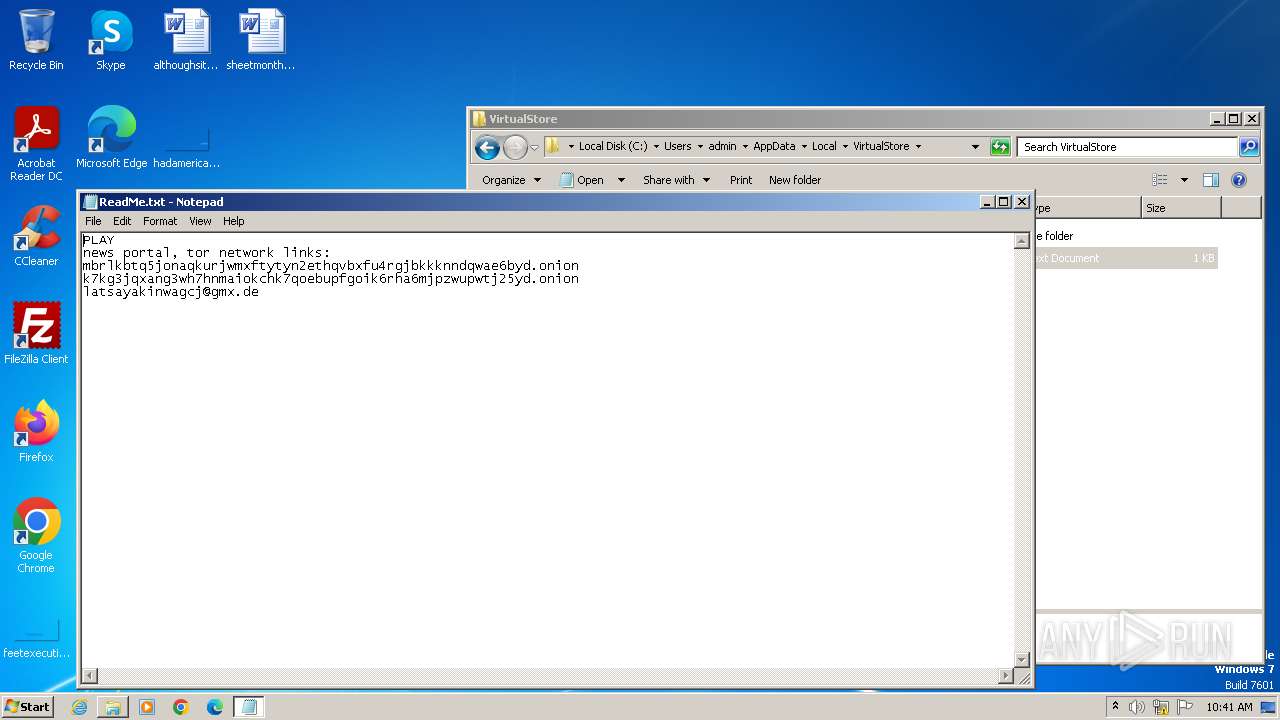
The cybercriminals behind Medusa Ransomware maintain a dedicated TOR website where they publish information about their victims, accompanied by a countdown clock indicating the time left before the data is released.
To prevent data leaks, victims are typically presented with three options. They can extend the time limit, pay a fee to have their stolen data deleted, or opt to download the compromised data, essentially buying back their own information.
One notable incident involving Medusa Ransomware took place in 2023. The group successfully infiltrated Toyota's European division, demanding a substantial ransom of $8 million. When negotiations broke down, the attackers proceeded to release the stolen data on their dark web portal.
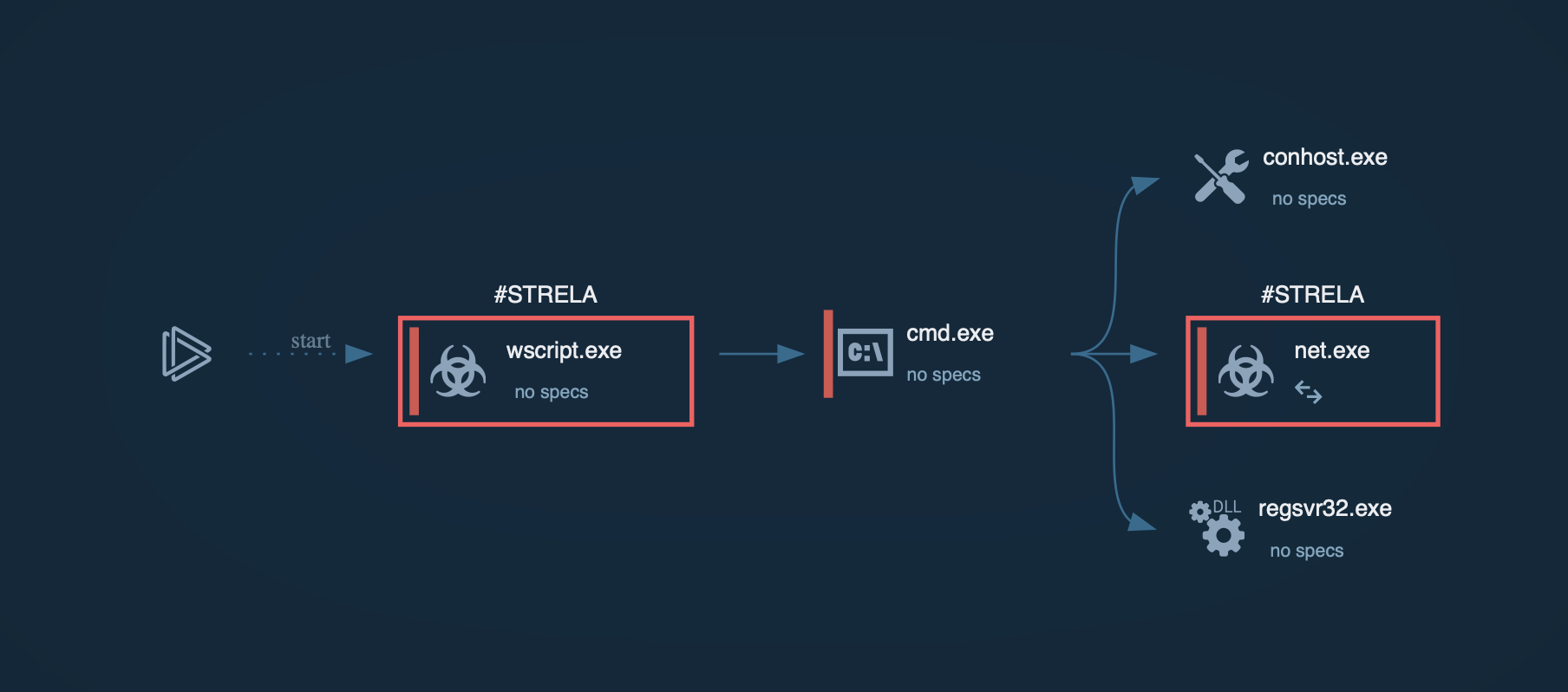
One of the primary signs of a Medusa ransomware attack is the addition of the ".MEDUSA" extension to encrypted files. However, this malware has been known to use various other extensions such as .1btc, .mylock, and .key1.
The variety of file extensions linked to Medusa ransomware indicates the existence of several versions. The ransom notes can appear in either TXT or HTML format (in newer versions). The note contains a unique 32-character hash value used for communication with the attackers.
For the encryption process, Medusa utilizes the strong AES256 algorithm, making decryption without the proper key extremely challenging. Additionally, the key used for encryption is itself encrypted using an RSA public key, further securing the encrypted data.
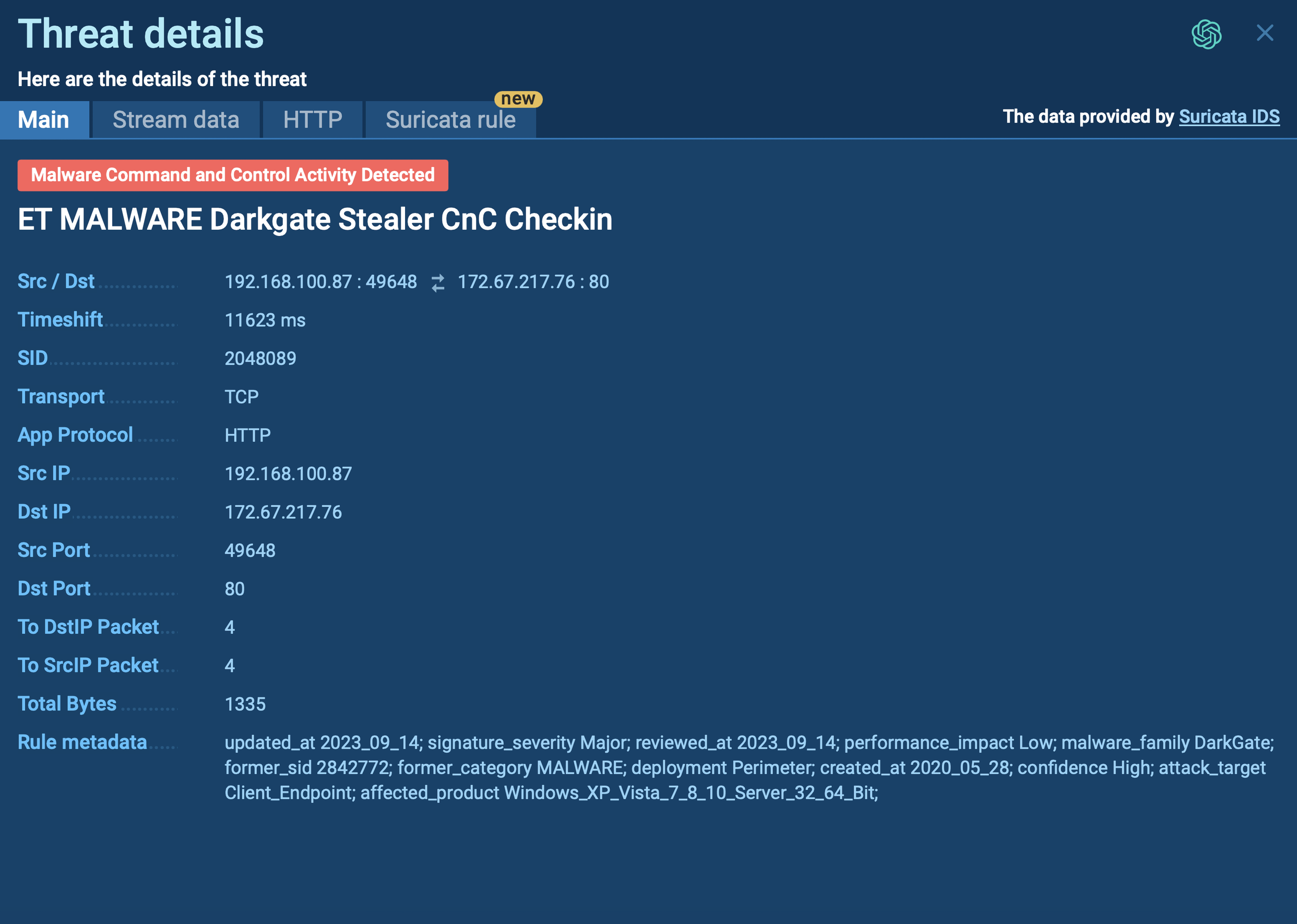
Medusa often infiltrates systems by exploiting existing vulnerabilities. In the past, it has targeted weaknesses such as CVE-2022-2294 and CVE-2022-21999 to deliver its payload.
To maintain persistence on the infected system, Medusa copies an executable file, usually named "svhost.exe" or "svhostt.exe", to a specific directory within the user's profile. This executable is then scheduled to run at regular intervals, ensuring the continued operation of the ransomware.
Medusa targets and terminates processes associated with security software. By doing so, it aims to disable potential detection and data recovery mechanisms.
Another strategy employed by Medusa is the deletion of Volume Shadow Copies, a Windows feature that creates backups of files at specific points in time. By eliminating these copies, Medusa removes a potential recovery method for victims.
Medusa Ransomware can be analyzed in the ANY.RUN sandbox. To do this, we can upload its sample to the service.
Medusa ransomware typically infiltrates a system through phishing emails or malicious downloads, exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software or weak security measures. Once executed, it stealthily encrypts files using strong encryption algorithms, rendering them inaccessible to the user. Medusa then displays a ransom note, usually demanding payment in cryptocurrency, in exchange for a decryption key. The ransom note often includes instructions on how to make the payment and how to contact the attackers. Meanwhile, Medusa may also attempt to spread laterally across the network, infecting other connected devices. Finally, the attackers await payment confirmation before providing the decryption key, although there's no guarantee they will uphold their end of the bargain. As a common activity for ransomware, Medusa halts system services and deletes shadow volumes.
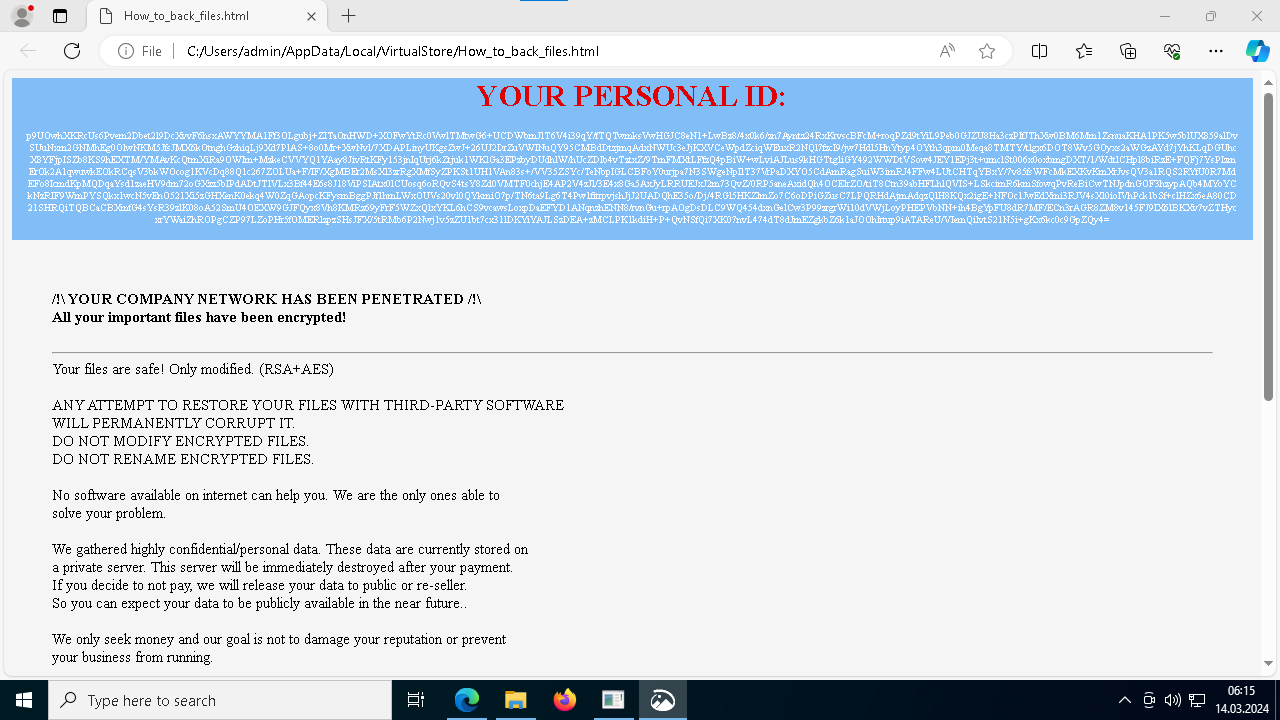 Medusa ransom note demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Medusa ransom note demonstrated in ANY.RUN
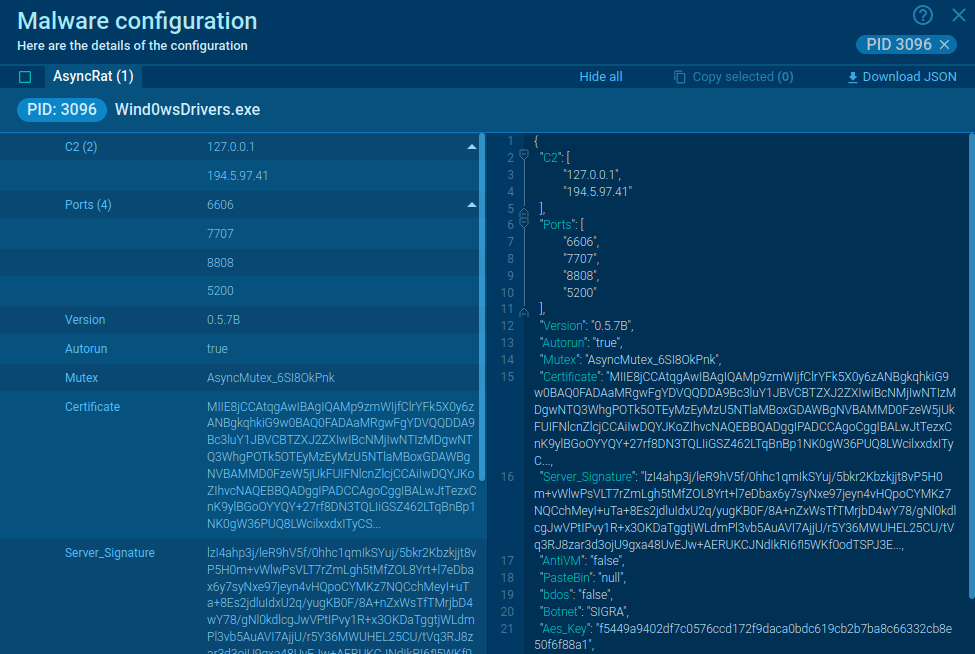
Similar to other malware, such as AsyncRAT and Remcos, phishing is one of the primary distribution methods employed by Medusa ransomware operators. Attackers send deceptive emails to potential victims, often disguising themselves as legitimate organizations or individuals. These emails typically contain malicious attachments or links, which, when clicked or downloaded, initiate the ransomware installation process.
Medusa ransomware's ability to compromise sensitive data poses a threat to businesses and individuals. The consequences of a successful attack can be severe, ranging from financial losses due to ransom demands to reputational damage caused by leaked information. Prioritizing preventive measures, such as learning about the malware’s TTPs and collecting its indicators of compromise (IOCs) can prove invaluable for any organization’s security posture. ANY.RUN is an online sandbox that enables users to do just that.
This interactive sandbox environment allows users to safely explore potential malware and quickly receive detailed technical reports. By leveraging this service, users can collect important information for making decisions needed for safeguarding their systems from harm.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!