Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


LostTrust is a ransomware that has been active since March 2023. It is a multi-extortion malware, meaning that it not only encrypts data on the compromised system and demands a ransom, but also exfiltrates some of the critical files to the attacker. The criminals publish the stolen data on a special website, where dozens of companies are listed as victims of the malware.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2023
First seen
:
|
15 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2023
First seen
:
|
15 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 868
868
 0
0

 515
515
 0
0

 2802
2802
 0
0
LostTrust is a multi-extortion ransomware. The creators of this malware claim to be former cybersecurity specialists who turned to malicious software due to low compensation. They present their actions as a service.
LostTrust is believed to be linked to MetaEncryptor, another ransomware that emerged a year prior. Additionally, both programs’ characteristics closely resemble those of Sfile and Mindware.
The group behind LostTrust openly shares information about their victims, which includes companies from various sectors, including healthcare. They even go as far as publishing some of the stolen data.
The ransom demanded from victims as part of an attack starts from $100,000, with the exact amount depending on each targeted organization. This is in stark contrast to more common ransomware families such as Wannacry, whose amounts usually do not surpass the $1000 mark.
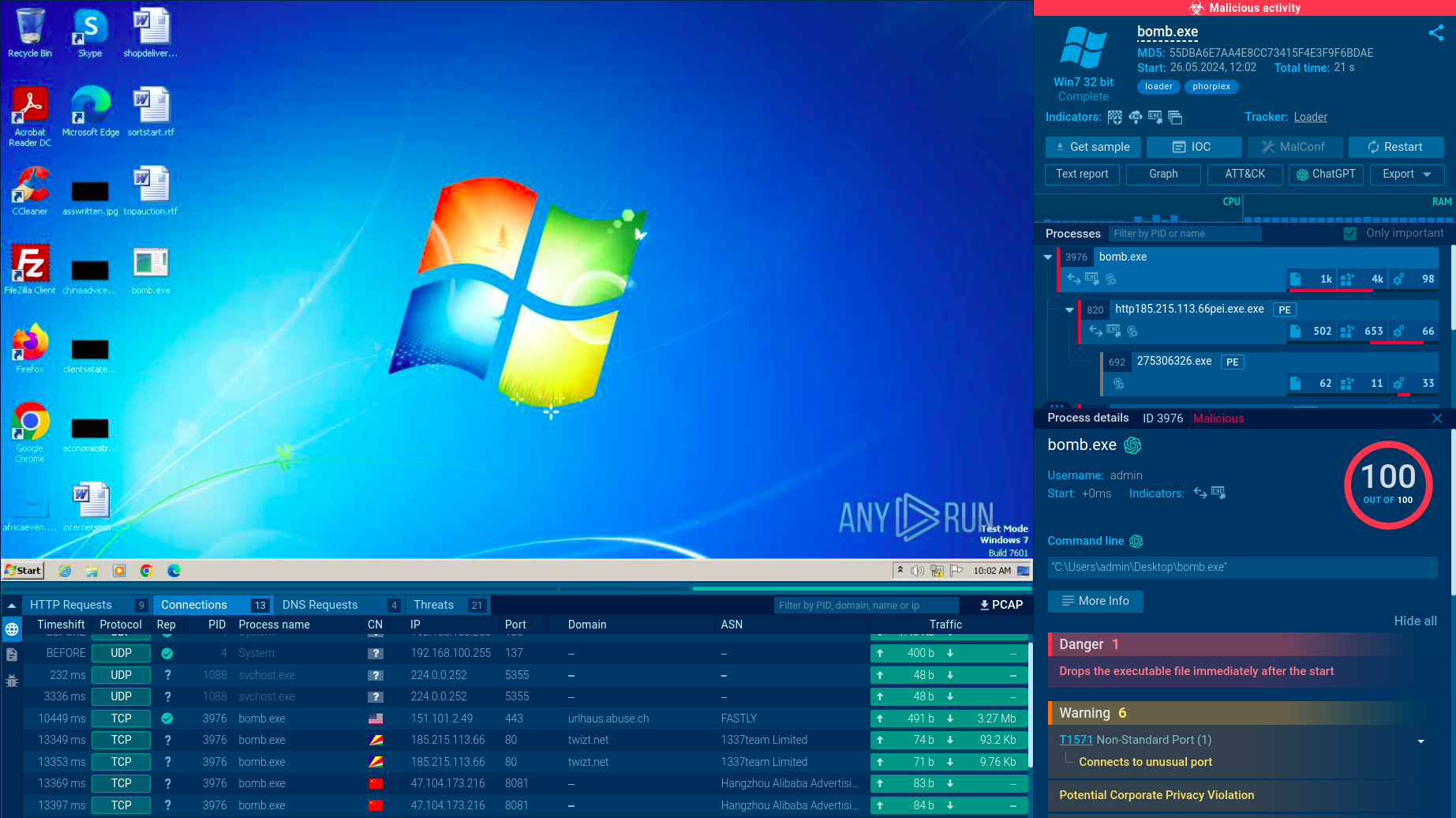
As mentioned above, the LostTrust operation largely resembles that of MetaEncryptor. The malware is capable of both encrypting the files on the compromised system and transferring some of the most critical data to the attacker’s server. The program adds the .losttrustencoded extension to the files that have been subjected to modification.
LostTrust also can kill many of the system processes and services, such as those related to Tomcat, SharePoint, MSSQL, and PostgreSQL, in order to ensure unimpeded encryption. It does it via Command Prompt by launching multiple sessions running in the background. At the same time, the malware makes the execution of its payload visible to the victim using a separate command window.
To prevent the user from recovering data, the malware removes Windows Event Logs and shadow copies.
Once the encryption process is finished, users are shown a note where they are instructed to communicate with the hackers through a designated website chat. They are given a 72-hour timeframe to respond before their files are leaked to the public.
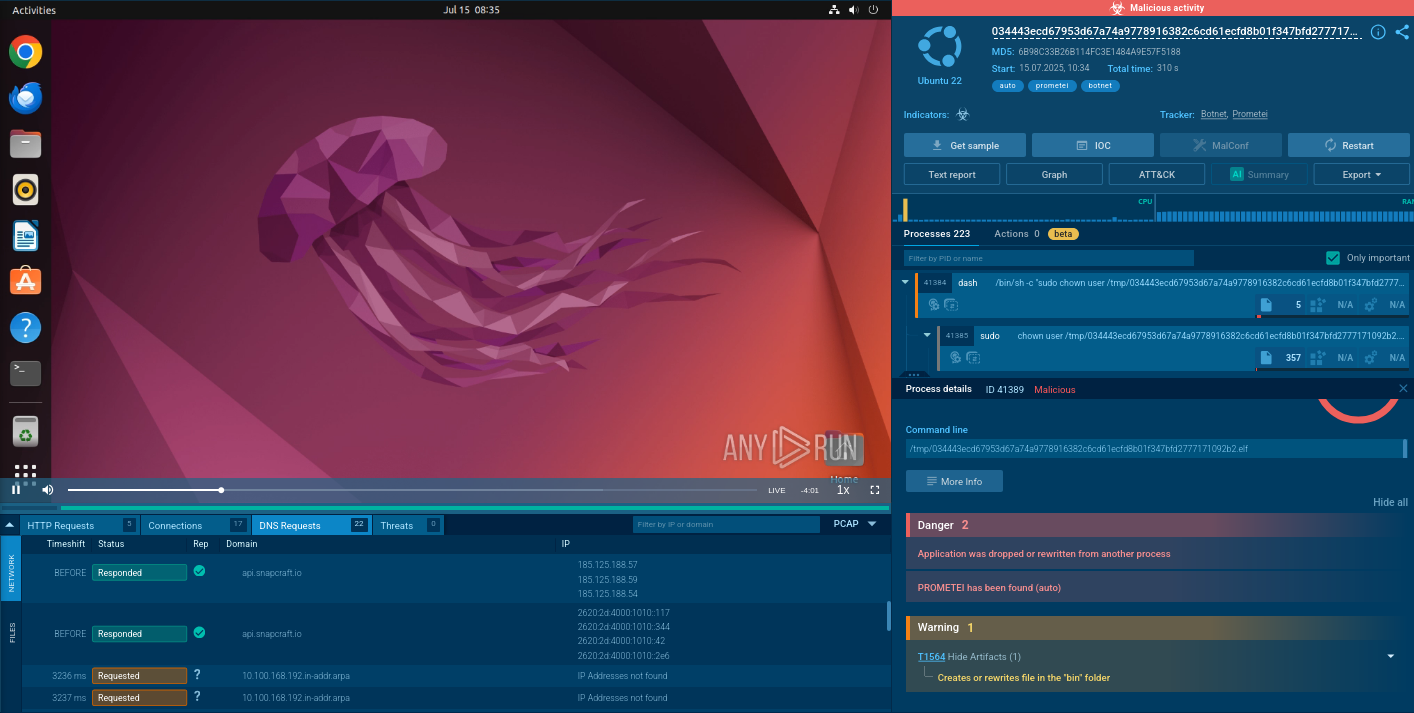
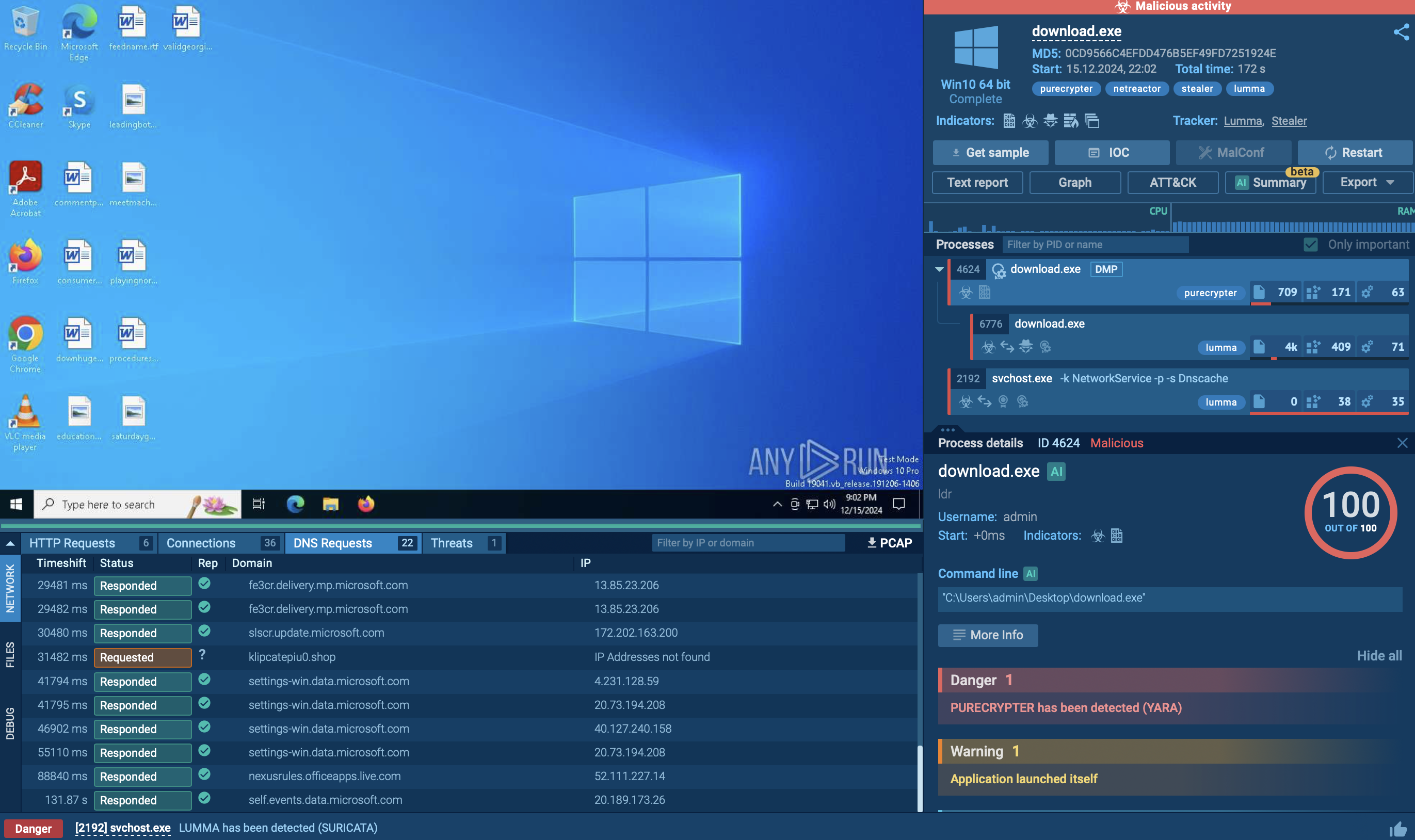
By uploading a sample of LostTrust to the ANY.RUN sandbox we can gain a better look at the malware execution process and collect essential threat intelligence.
Analyze malware for free in a fully interactive cloud sandbox – sign up now!
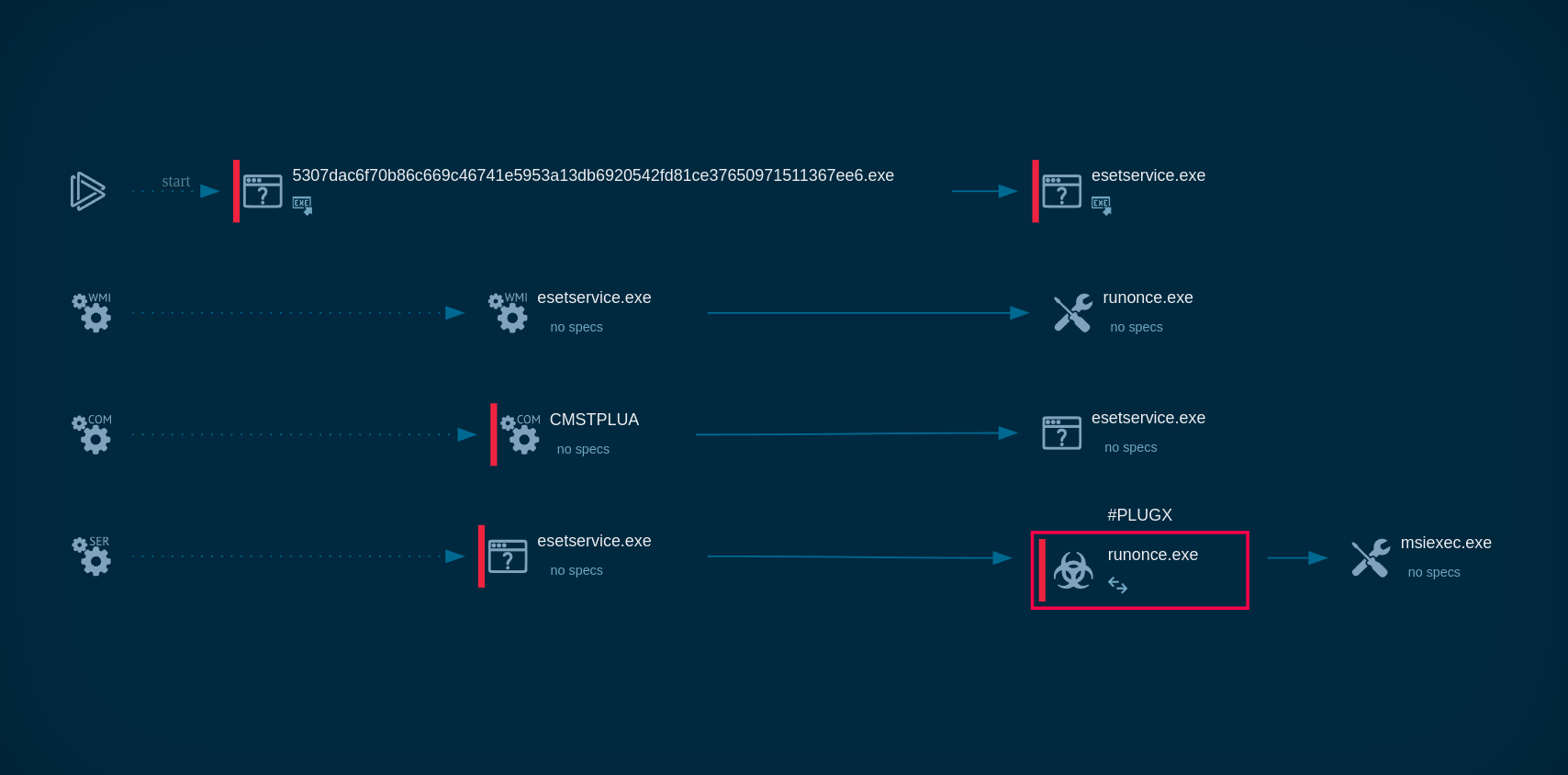
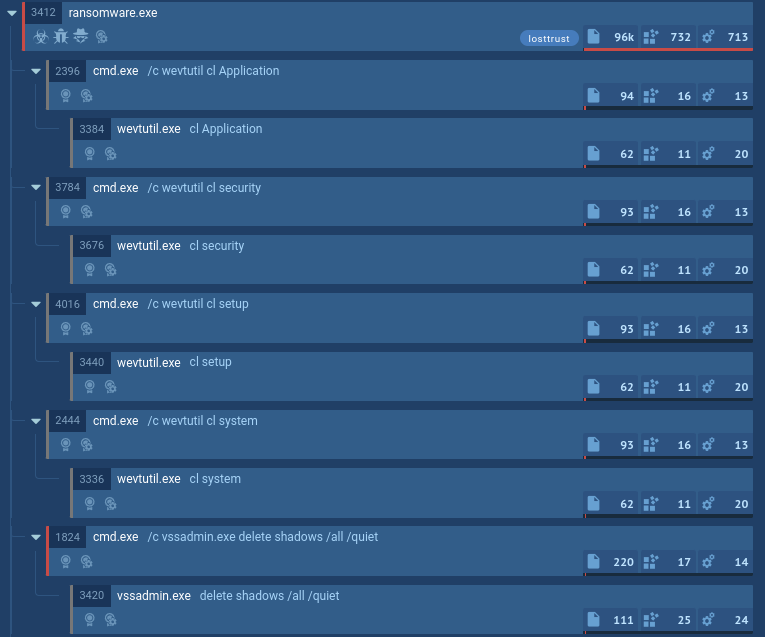 LostTrust's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
LostTrust's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
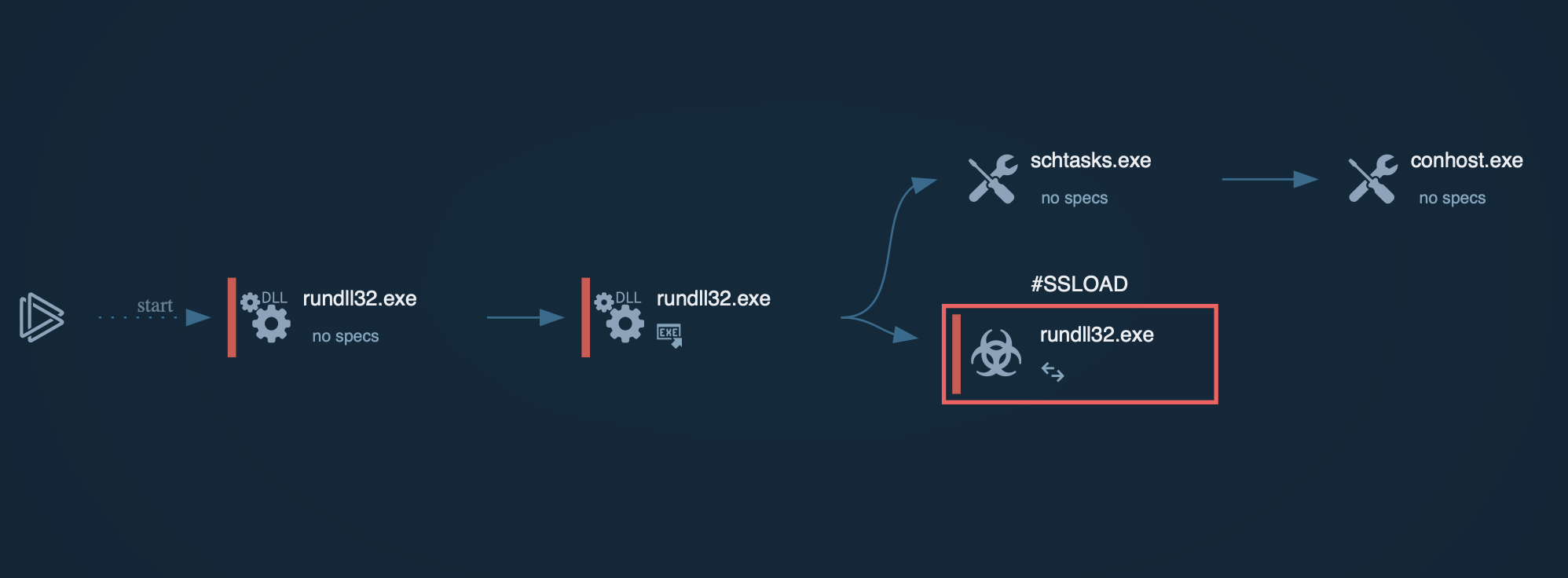
Upon execution, LostTrust ransomware, like any malware of its kind, immediately begins encrypting files on the infected system. A distinctive feature of LostTrust is its initiation of numerous child processes for carrying out additional malicious activities. System utilities are launched to halt system and network processes, services, and application processes, as well as to remove shadow copies and perform other disruptive actions. The encrypted files receive the ".losttrustencoded" extension, and "!LostTrustEncoded.txt" files are created containing ransom demands and instructions.
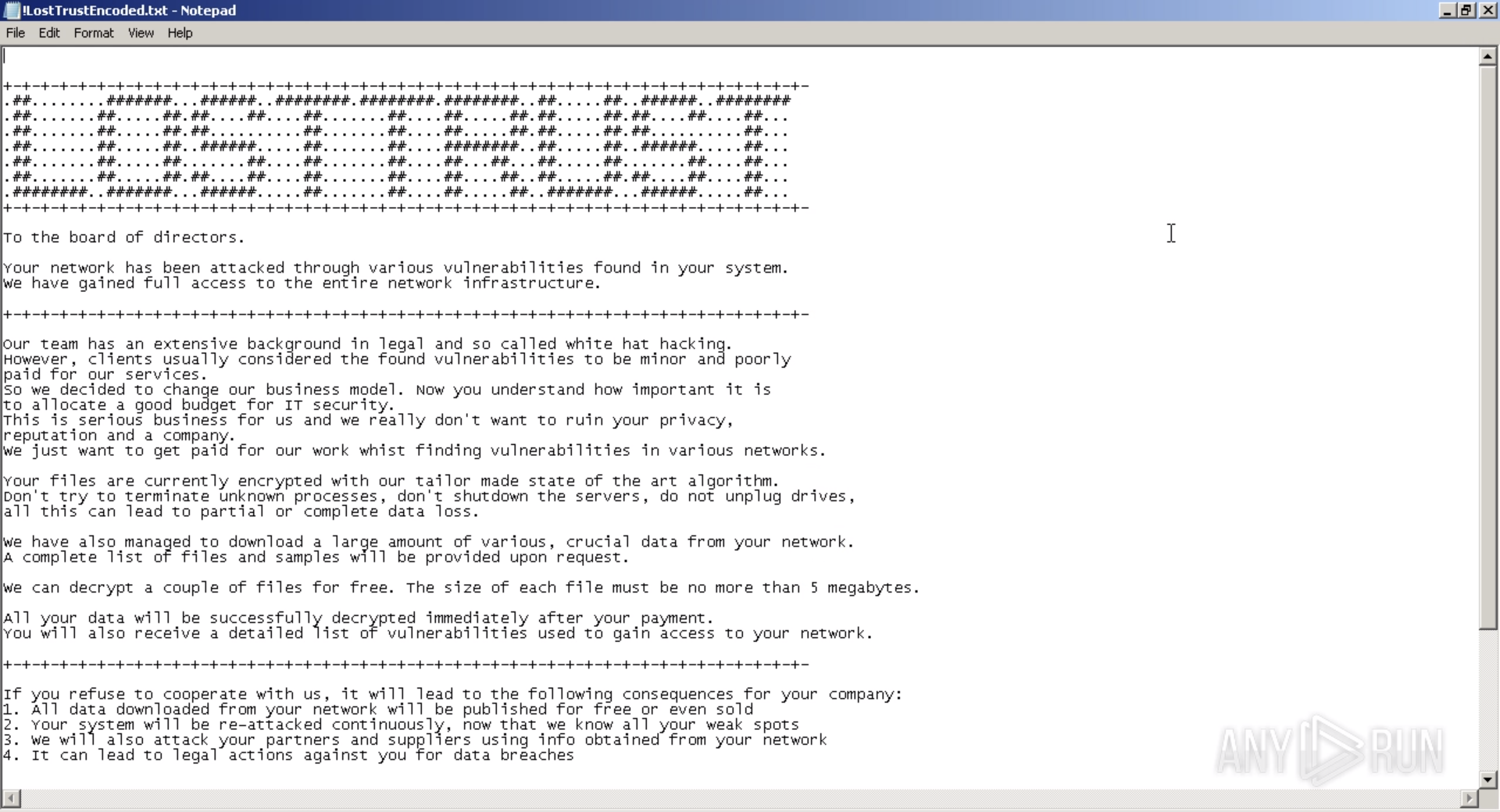 LostTrust ransom note
LostTrust ransom note
In their attacks, criminals employ a variety of methods to distribute LostTrust. However, just like most ransomware, including such notable examples as LockBit, LostTrust is usually delivered in the form of malicious email attachments. Attackers design phishing campaigns that exploit social engineering tactics to trick users into downloading and running payloads that hijack and compromise their systems.
LostTrust is one of the key emerging ransomware threats of 2023, which means that companies must be equipped with the necessary capabilities to detect and prevent infection. One way they can ensure protection is by uploading any suspicious email to ANY.RUN to determine if it is malicious or not.
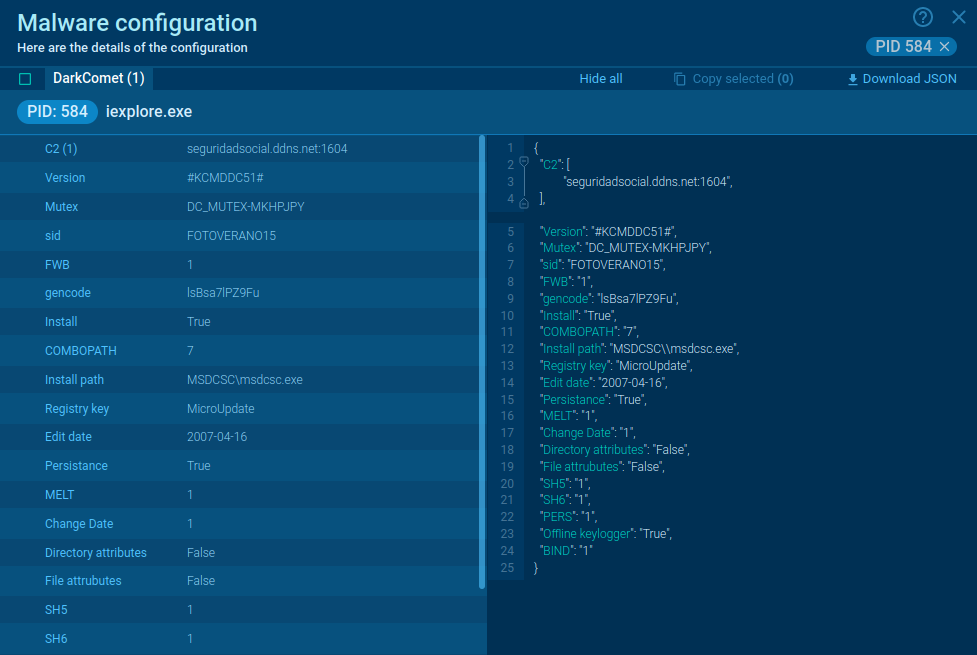
ANY.RUN is fully interactive and lets you engage with the infected system like you would on your own computer but in a safe cloud environment. The service automatically generates a comprehensive report on the analyzed file or link and presents its verdict as well as IOCs and malware config.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!