Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


DarkSide ransomware is a novel ransomware strain involved in high-profile incidents. Its attacks lead to data theft and encryption, causing significant damage to victims.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
10 August, 2020
First seen
:
|
6 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
10 August, 2020
First seen
:
|
6 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 396
396
 0
0

 2171
2171
 0
0

 4243
4243
 0
0
DarkSide is a cybercriminal group — and a ransomware of the same name — believed to have originated from Eastern Europe.
DarkSide operates as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) — essentially, it is offered to affiliates who then conduct the attacks. These affiliates, vetted through an interview process, reportedly agree to a revenue split of 25% for ransoms under $500,000, and 10% for amounts exceeding $5 million. In exchange, they gain access to the control panel.
The DarkSide's code is not publicly accessible and bears similarities to another notorious ransomware threat — REvil. This correlation could suggest that DarkSide is either a derivative or a partner of REvil. Both groups have their origins in the ex-USSR, employ similar techniques and tactics, and use similarly structured ransom notes.
Like most threats originating from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), DarkSide conducts a pre-attack check to ensure that the potential victim is not located in ex-USSR territories or Arabic states. This is achieved by accessing the system languages. The kill switch is activated if the language setting is set to:
Note that ANY.RUN interactive cloud sandbox enables you to set system language —among other settings — before launching a virtual machine. This can help to observe how DarkSide behaves under different device configurations.
When it comes to victim geography, DarkSide primarily targets the US, with Canada, France, Belgium, and other Western European countries following closely. This threat is notorious for executing high-profile attacks across various business sectors. It's worth noting, however, that DarkSide steers clear of targeting charitable organizations, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and non-profits, presumably adhering to an internal code of conduct.
Some of the most notable incidents DarkSide was involved in include the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in May 2021. This attack led to a voluntary shutdown of a pipeline supplying 45% of fuel to the East Coast of the United States. The group extorted about 75 Bitcoin, nearly $5 million. Another notable incident includes the Ransomware attack on IT managed services provider CompuCom in March 2021. This attack resulted in over $20 million in restoration expenses, causing significant financial damage to the company.
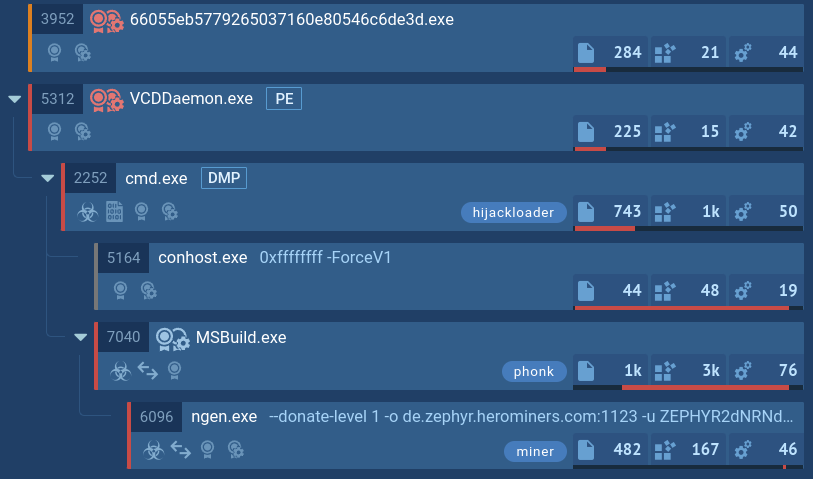
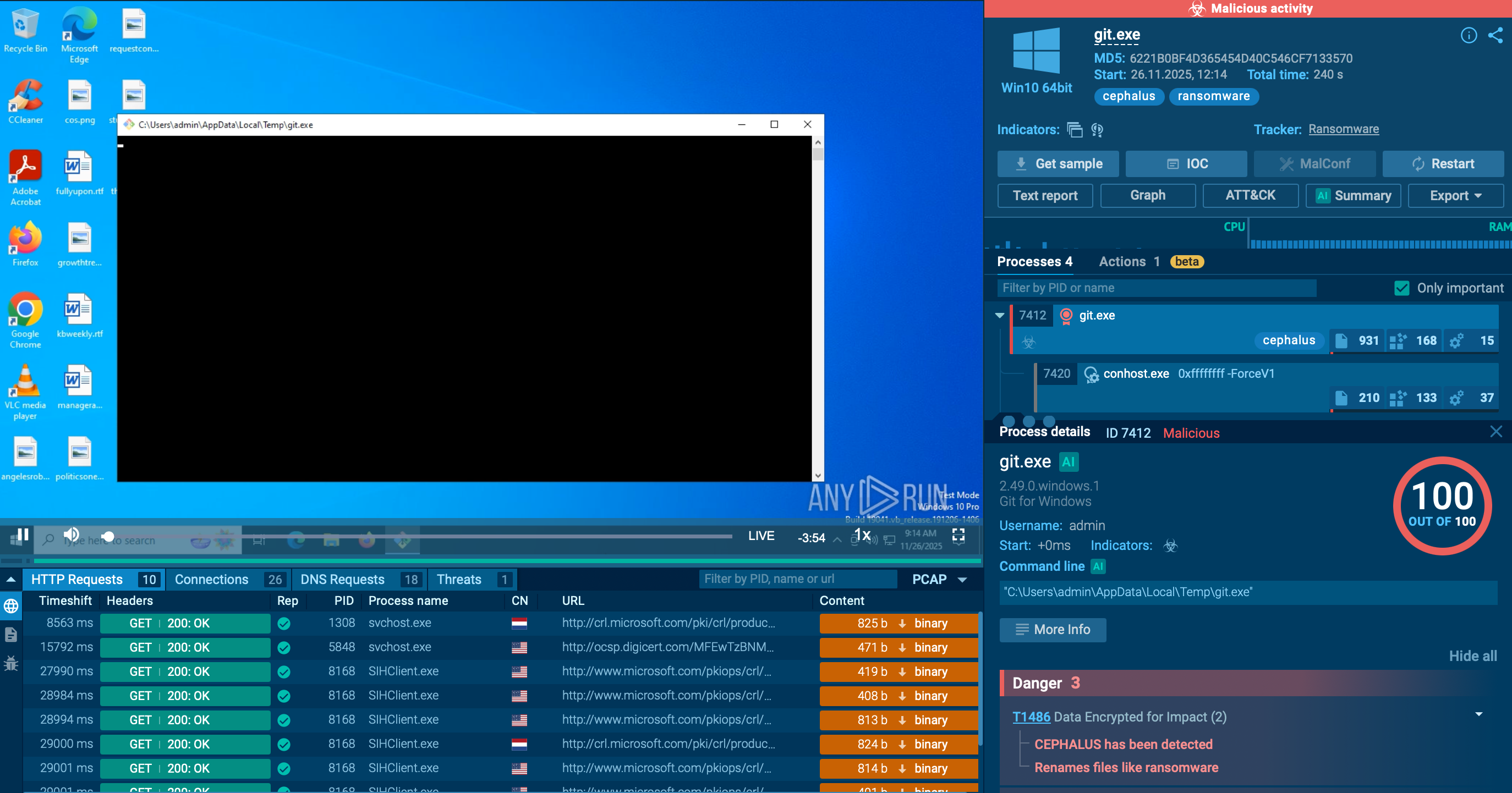
After DarkSide ransomware gains initial access, it establishes command and control primarily through an RDP client over port 443, routed through TOR. Some samples may use Cobalt Strike as a secondary command and control mechanism, with customized stagers deployed on targeted devices.
The group uses various tools such as Advanced IP Scanner, psexec, and Mimikatz to scan networks, run commands, and steal credentials. After a reconnaissance phase, an Active Directory reconnaissance tool is used to gather additional information about users, groups, and privileges.
The attackers mine credentials from user profile folders and use a script named Invoke-mimikatXz.ps1 to extract credentials from servers. Once domain admin credentials are obtained, they perform a DCSync attack to replicate AD information, gaining access to password data for the entire domain.
The group uses an active Windows server as a hub to store data before exfiltration. Data from servers is compressed into 7zip archives with a simple naming convention. They also relax permissions on file systems to access files with any domain user account.
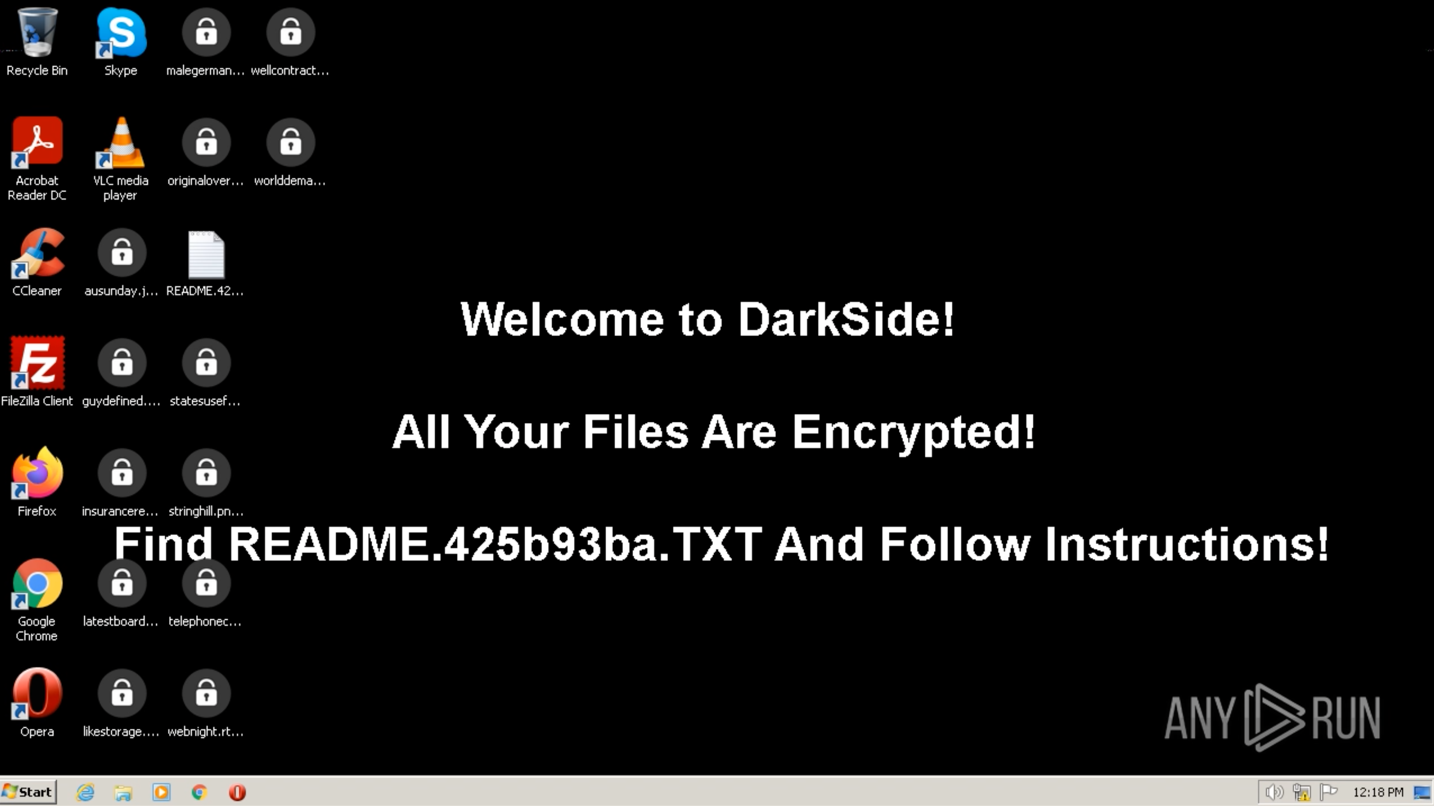
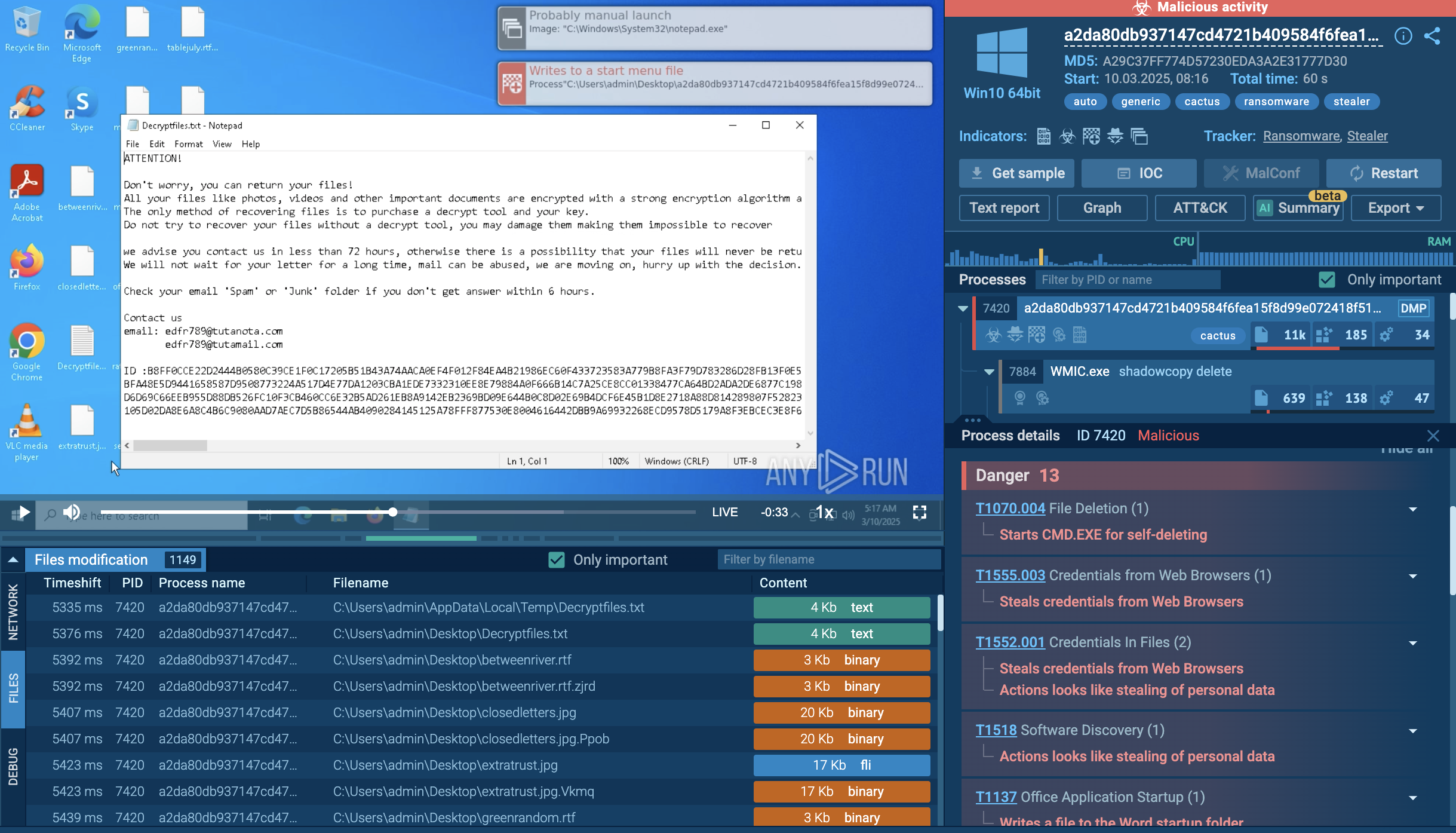
Workstation’s desktop after the DarkSide infection
Before deploying ransomware, DarkSide maps the environment, exfiltrates data, gains control of privileged accounts, and identifies backup systems, servers, and applications. The ransomware code is delivered through established backdoors and is customized for each victim. The ransomware evades signature-based detection mechanisms by using unique executables and extensions and employs anti-forensics and anti-debugging techniques.
The ransomware first copies itself to a temporary path and injects its code into the existing process. If it detects debugging or VM, it stops. The ransomware then dynamically loads its libraries to avoid detection by AV and EDR solutions.
The malware deletes the shadow copies on the victim device using an obfuscated PowerShell command. After the deletion, the malware closes specific processes to avoid locked files and begins its encryption routine, appending an 8-character string to the end of the encrypted file names. It avoids encrypting files with certain extensions and creates a ransom instructions file for decryption.
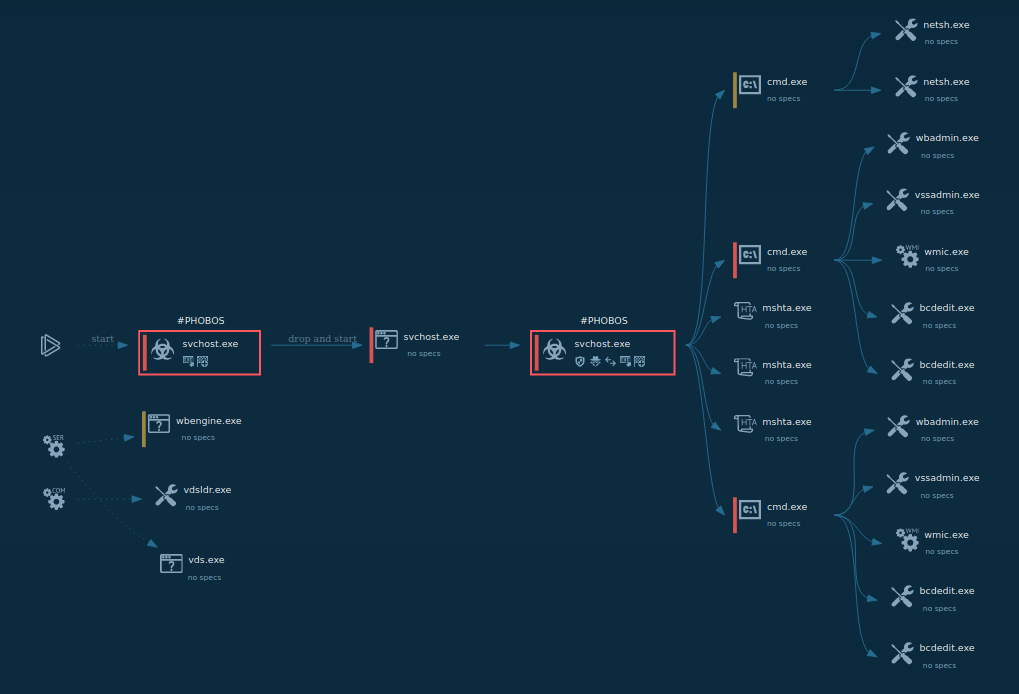
The execution process of DarkSide is typical for ransomware. For comparison, you may take a look in most popular ones - Phobos or Maze. First, the executable file makes its way into the infected system and runs, then the main malicious activity begins. After the start of execution, the ransomware may delete shadow copies and stop execution of the security software. When all targeted files get encrypted, DarkSide drops a ransom note and changes wallpaper on the desktop, like in the following sample.
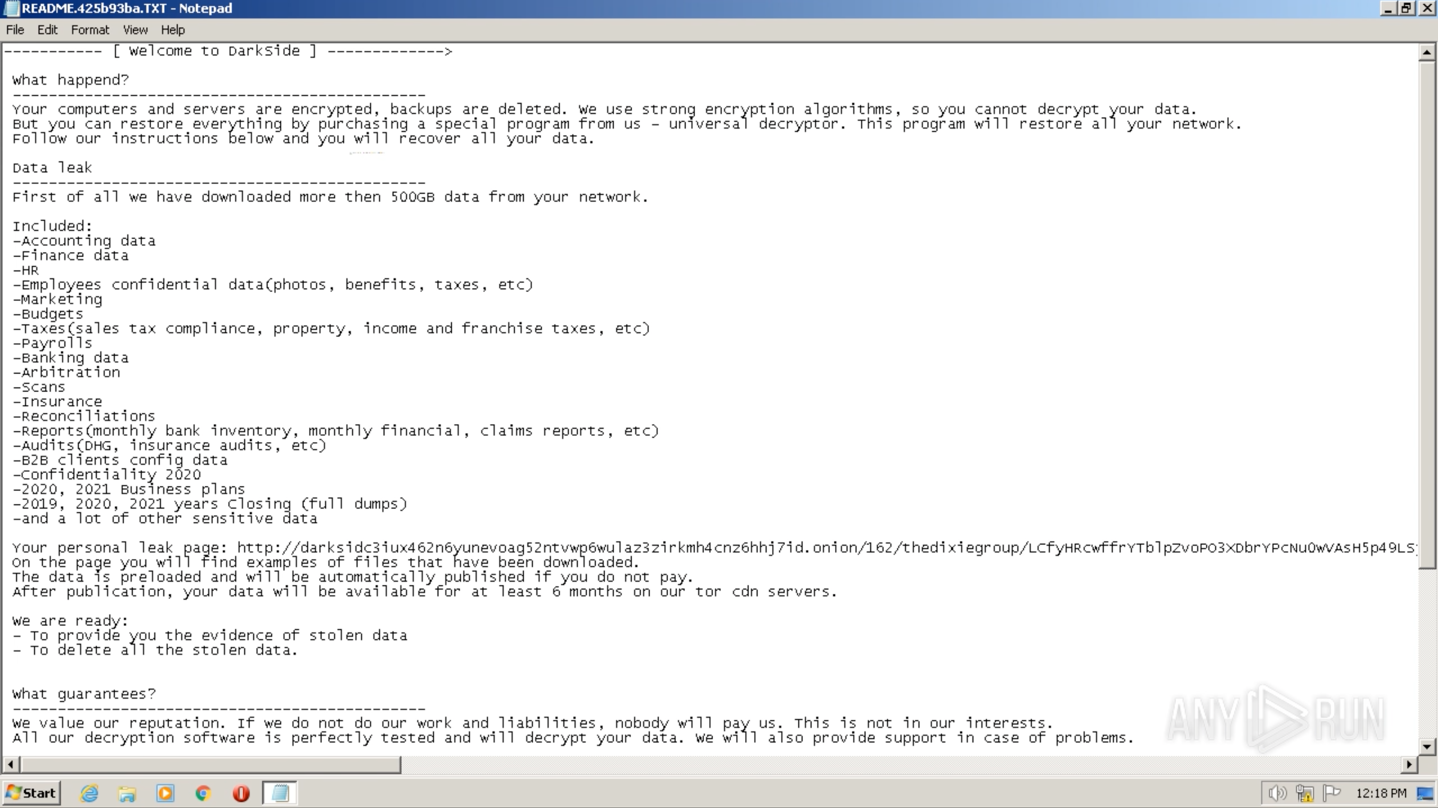
DarkSide’s ransom note
DarkSide ransomware primarily distributes through phishing campaigns and leverages Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) abuse and known vulnerabilities for initial access.
Ransomware operators employ social engineering and highly targeted spear phishing campaigns to trick users into downloading malicious content. Alternatively, they are known to exploit weakly secured RDP endpoints. The group also targets unpatched servers and remotely exploitable systems, sometimes accessing Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) via compromised contractor accounts.
As early as May 2021, the DarkSide group announced that they had lost access to part of their hacking infrastructure due to "significant pressure from the U.S.," pledging to shut down their operations.
However, if the similarities with REvil (and by extension, GandCrab its precursor) indeed indicate a connection between these groups, it is highly improbable that DarkSide's ransomware activities will diminish.
We will likely continue to observe the use of this ransomware code, making the study of the tactics and techniques deployed by this operation vitally important.
To expedite your results — like acquiring strings and malware configurations — consider analyzing DarkSide samples in ANY.RUN. Our cloud malware sandbox can detect this threat and extract its configuration automatically, saving you hours of manual deobfuscation and code reversal. You can also experiment with system configurations to observe how this threat behaves under different conditions.
Ready to give it a shot? Create a free ANY.RUN account a free ANY.RUN account.