Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Grandoreiro is a Latin American banking trojan first observed in 2016. It targets mostly Spanish-speaking countries, such as Brazil, Spain, Mexico and Peru. This malware is operated as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), which makes it easily accessible for cybercriminals. Besides, it uses advanced techniques to evade detection.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2017
First seen
:
|
20 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2017
First seen
:
|
20 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 405
405
 0
0
 6830
6830
 0
0

 615
615
 0
0
Grandoreiro is a sophisticated banking trojan first observed in 2016, primarily targeting users in Latin America, including countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina.
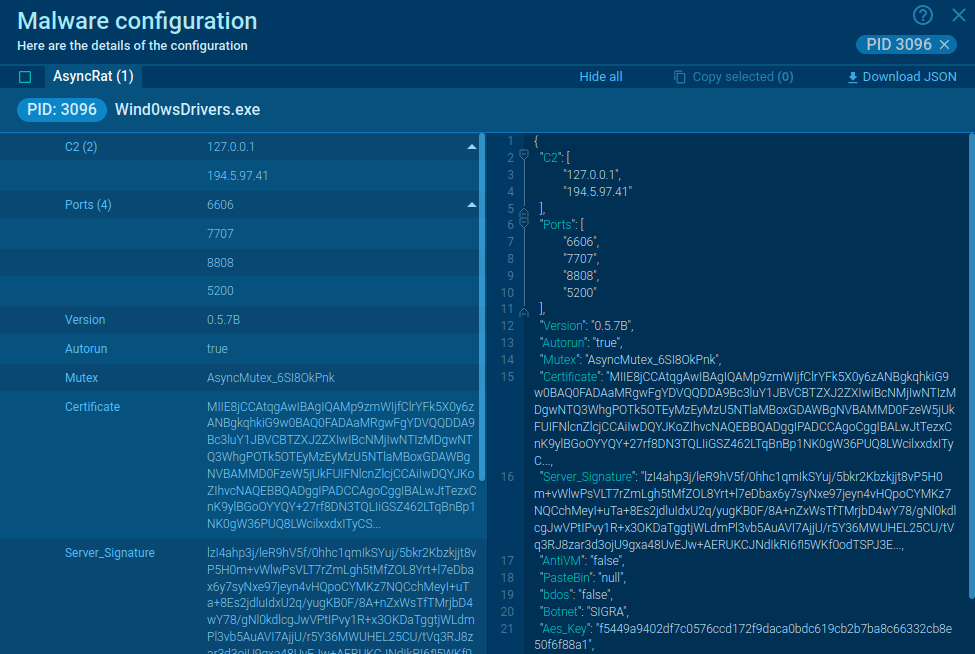
Grandoreiro is known for its advanced evasion techniques, including various string encryption methods, and the use of a domain generation algorithm (DGA) that enables it to communicate with multiple command-and-control (C2) servers.
In March 2024, the Grandoreiro banking trojan launched a massive attack targeting over 1,500 banks' applications worldwide, expanding beyond its usual Latin American focus to regions in Central and South America, Europe, Africa, and the Indo-Pacific.
Attacks usually begin with phishing campaigns impersonating government entities, tricking recipients into downloading the malware. Once deployed, Grandoreiro targets specific banking applications, allowing attackers to steal credentials and execute fraudulent transactions.
Key technical features of Grandoreiro include its ability to evade detection, verify victims to avoid sandbox environments, and more. The malware’s sophisticated structure and its ability to adapt to different regions and targets make it a significant threat in financial cybercrime.
The main functionality of Grandoreiro malware is to steal sensitive financial information of users by targeting banking applications.
Some of the key capabilities of the Grandoreiro malware include:
Grandoreiro is a complex malware with over 10,000 strings, which would be easily detectable if left unencrypted. To avoid detection, it uses a sophisticated multi-step decryption process. This involves custom encoding and decryption using the same key as the loader, followed by AES decryption, and then further decoding to finally reveal the plaintext strings, making the malware harder to detect and analyze.
To see how Grandoreiro operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox for analysis.
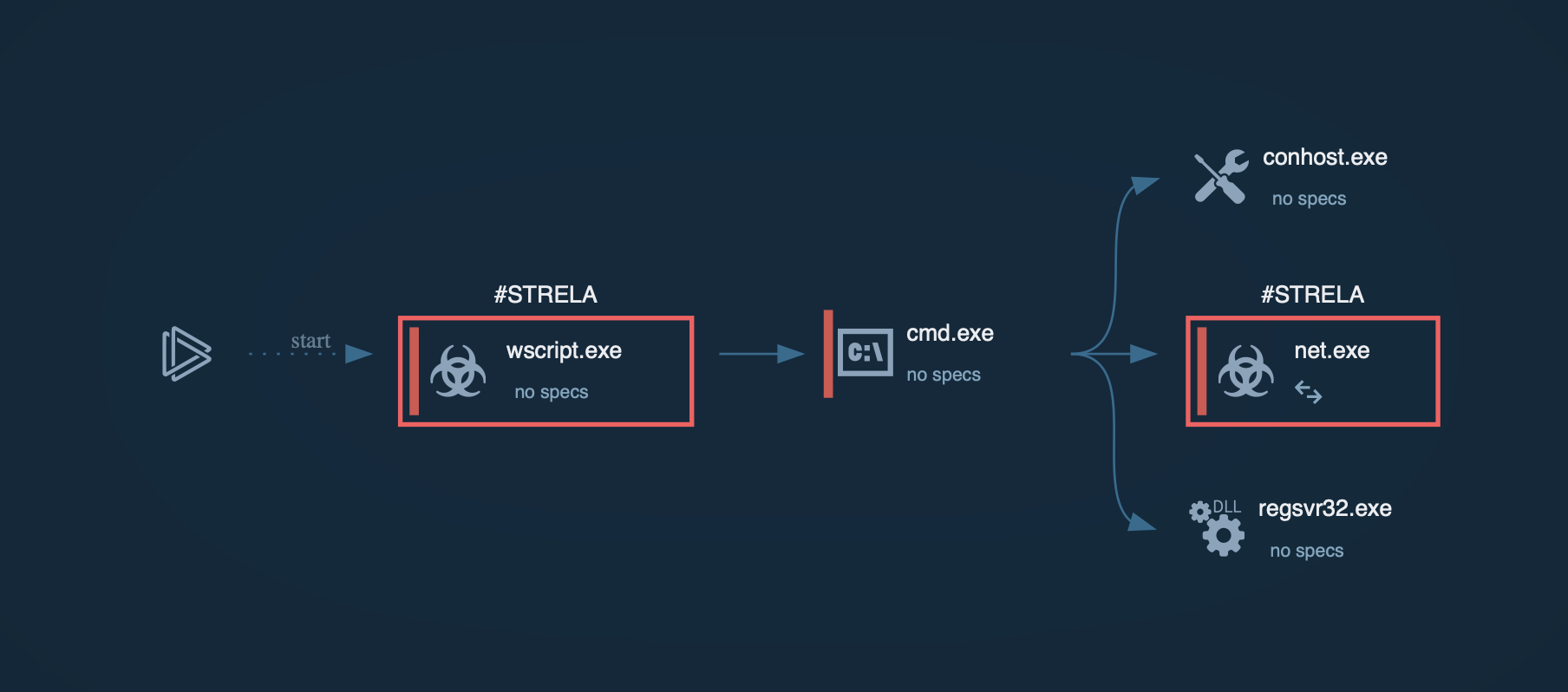
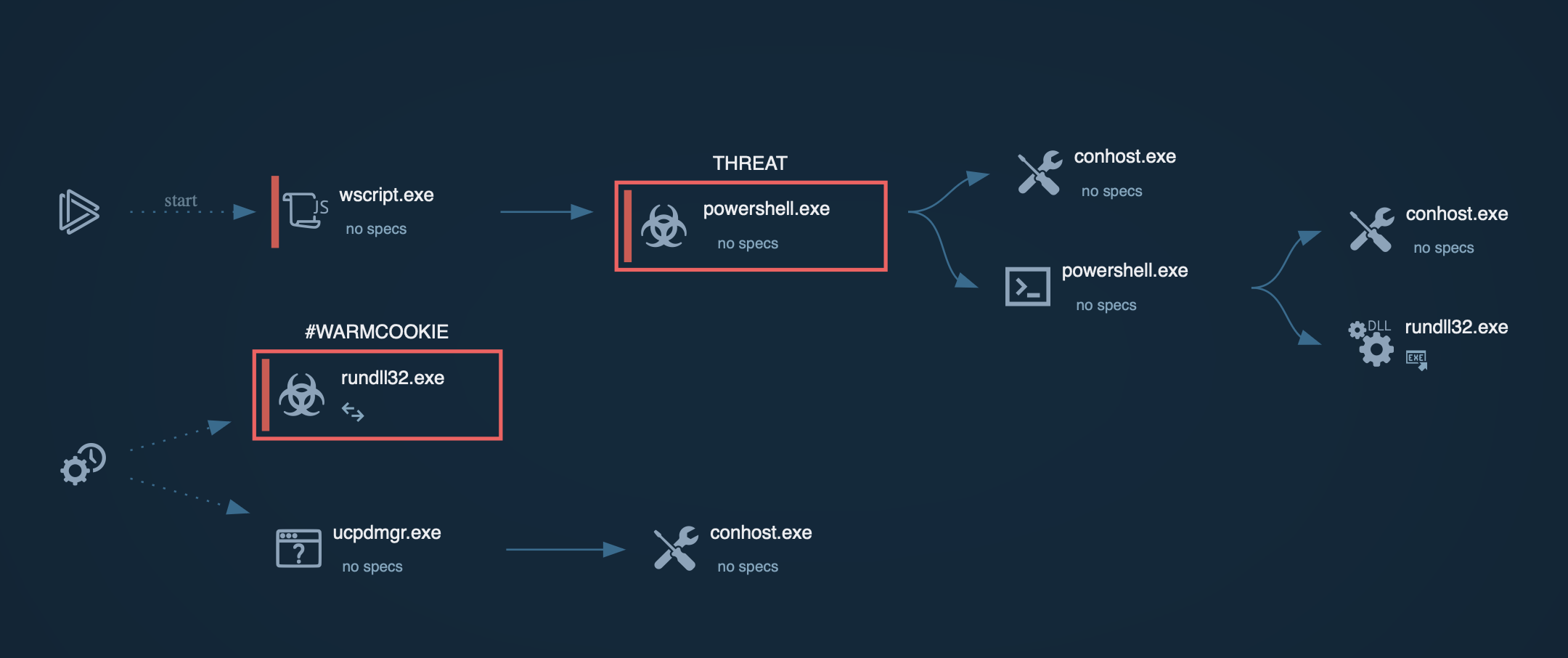
Grandoreiro is typically delivered through phishing emails containing malicious links or attachments. These emails often impersonate legitimate organizations, such as government agencies, to deceive victims. Clicking on the link or opening the attachment downloads a malicious ZIP file containing the Grandoreiro loader, disguised as a PDF or another benign file.
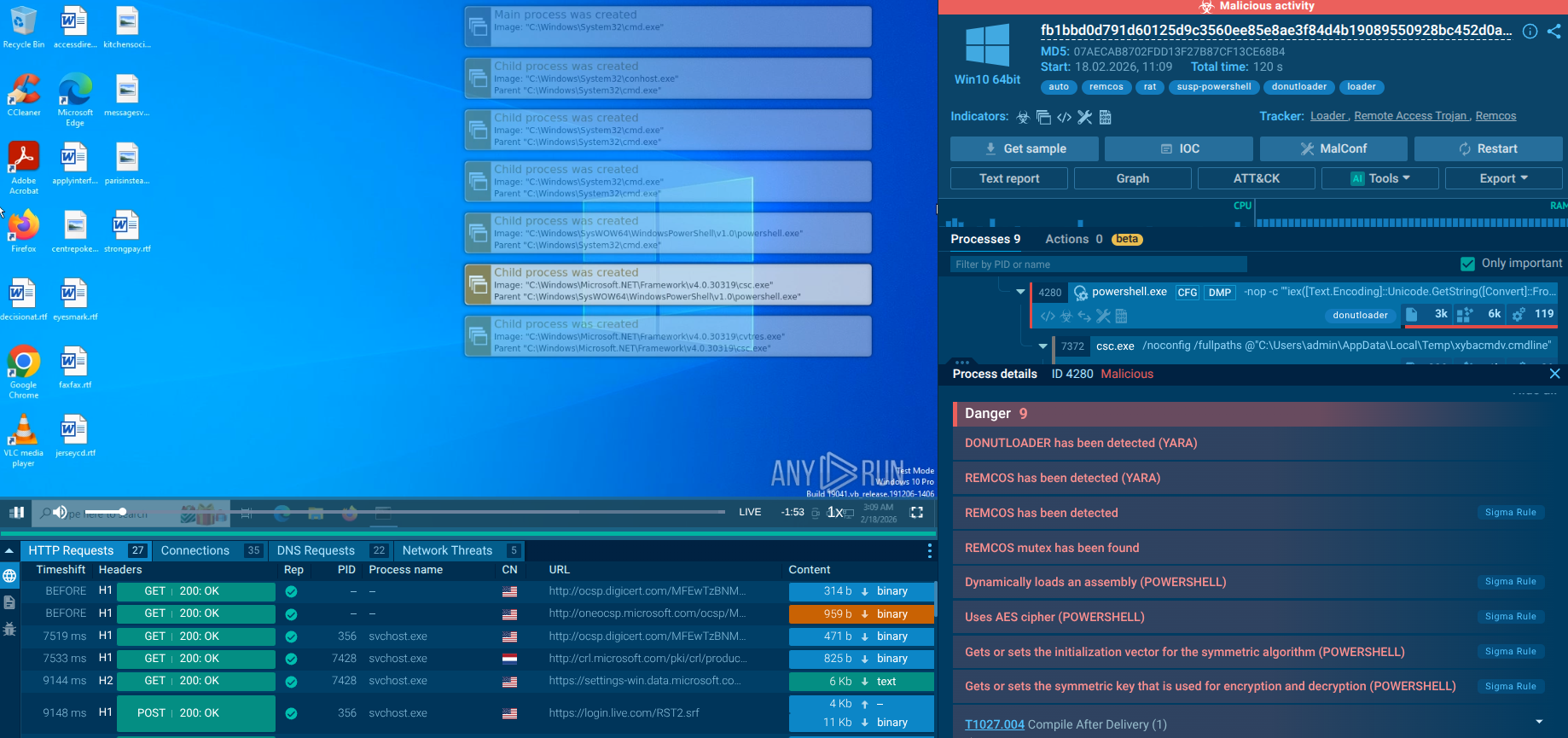
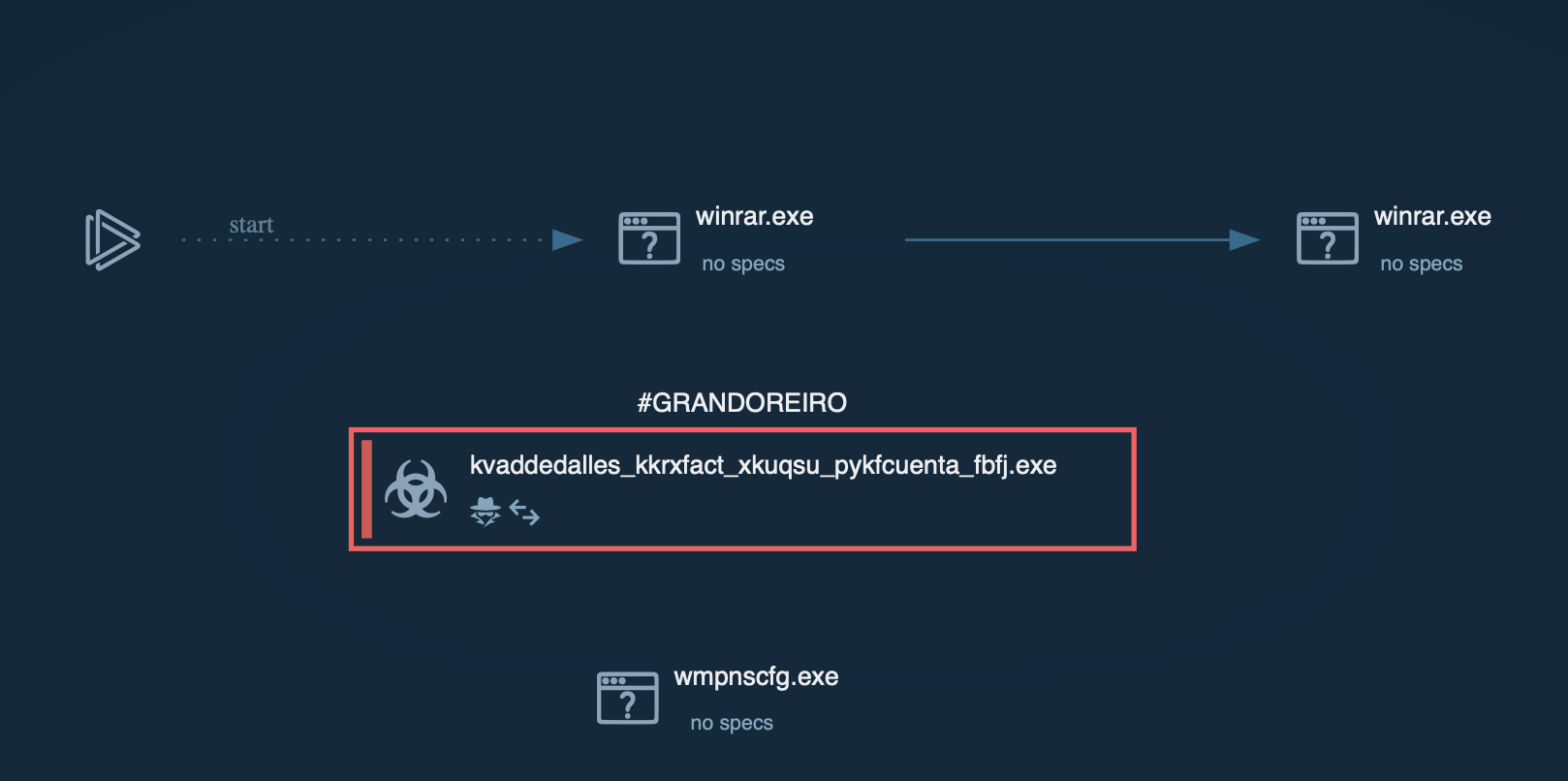 Grandoreiro process graph displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Grandoreiro process graph displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
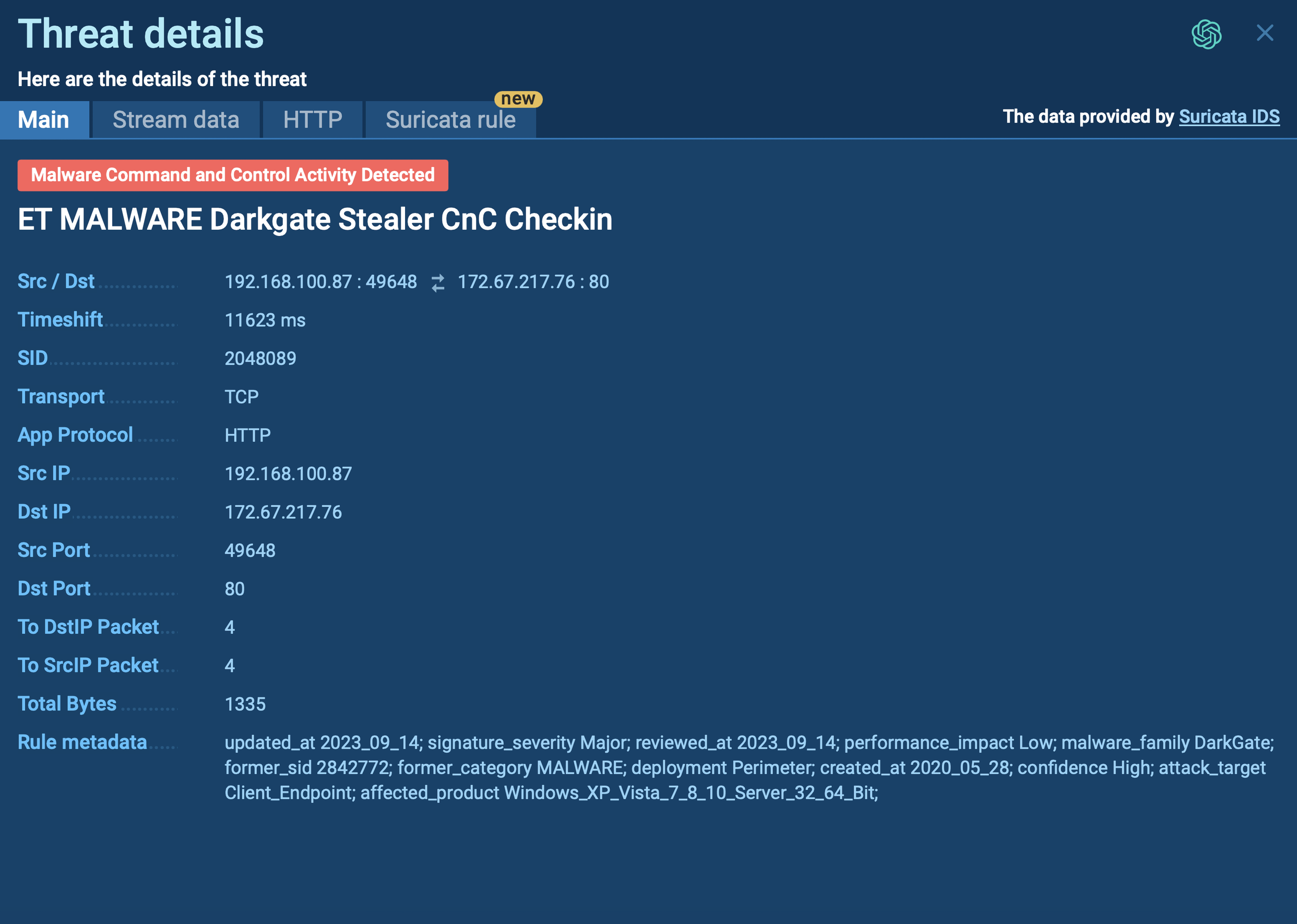
Once executed, the loader performs anti-analysis checks to detect sandboxes and virtual environments. It collects victim information, including IP address, operating system details, installed software, and more. The loader then decrypts a URL using XOR-based decryption and sends a GET request to retrieve the final payload download URL.
The loader downloads the final Grandoreiro payload from the retrieved URL as a large ZIP file. This ZIP file contains a massive executable disguised as an image or PDF file. Then, the loader extracts and renames the executable to a random name with an .exe extension. This renamed executable is the full Grandoreiro banking trojan payload, often signed with a legitimate digital certificate to appear trustworthy and evade detection.
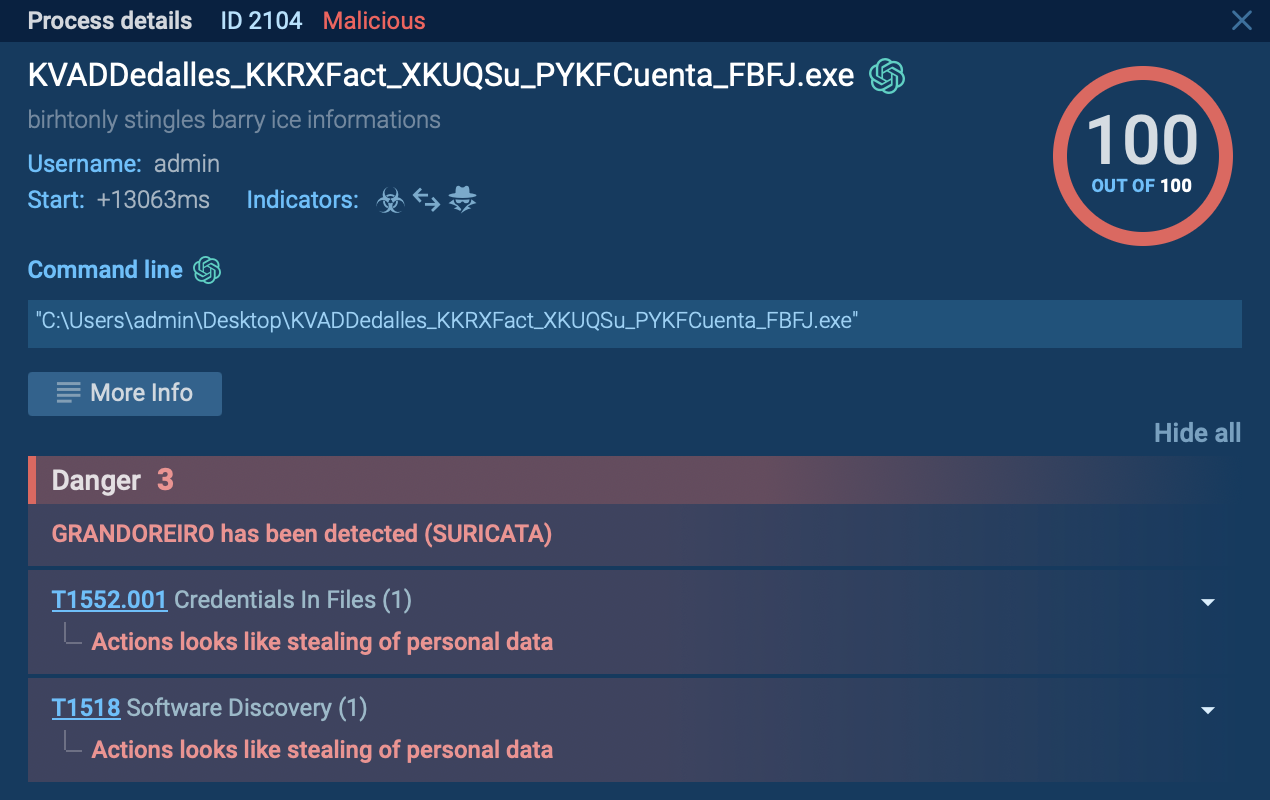 Malicious process related to Grandoreiro analyzed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Malicious process related to Grandoreiro analyzed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Grandoreiro establishes persistence via the Windows registry, ensuring it launches upon user login. It collects more detailed information and sends a POST "check-in" request to the command and control (C2) server with the gathered data. The trojan then proceeds to carry out a range of malicious activities, including browser session hijacking, credential theft, and banking fraud.
Grandoreiro malware is primarily distributed through phishing campaigns.
Attackers often send emails that impersonate legitimate government entities or financial institutions, tricking recipients into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments. These emails may claim to contain important documents, such as tax notices or account statements, which, when opened, initiate the download of the malware.
In addition to phishing emails, Grandoreiro may also be spread through malicious websites that prompt users to download fake software updates or security tools, which actually install the malware.
The impact of the Grandoreiro campaign has been devastating, leading to widespread financial fraud and significant monetary losses. This malware has infiltrated multiple sectors, including banking, finance, manufacturing, public administration, telecommunications, and energy. Its ability to steal sensitive financial information and perform fraudulent transactions has caused severe disruption and harm to countless organizations and individuals, making it one of the most dangerous banking trojans in recent years.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based service that allows anyone to safely analyze suspicious files and URLs. It enables you to observe malware behavior and collect indicators of compromise in a secure environment. By using ANY.RUN, you can gain valuable insights into Grandoreiro's tactics and improve your defenses against it.