Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

SquirrelWaffle is a dropper that distributes Qbot and Cobalt Strike, in addition to other malware families. It leverages malicious documents that are part of compromised emails to drop second-level payloads to affected devices.
|
Dropper
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
8 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Dropper
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
8 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 165
165
 0
0

 448
448
 0
0

 1911
1911
 0
0
Discovered in September 2021, SquirrelWaffle is a loader/dropper malware strain designed to infect systems with malicious payloads. Security professionals speculate that it emerged as a replacement for Emotet after law enforcement dismantled the notorious botnet. It remains unclear whether the same group is responsible for this new threat, or if a different crew has stepped in to capitalize on the void left by the infamous malware.
The Squirrelwaffle payload, a PE DLL, is dropped on infected systems and executed using either rundll32.exe or regsvr32.exe, depending on the maldoc initiating the infection process. For instance, the payload can be executed using rundll32.exe with the following syntax: cmd.exe /c rundll32.exe C:\ProgramData[DLL FILENAME],ldr.
Primarily functioning as a malware loader, the DLL allows for deploying additional malware, with Qbot and Cobalt Strike installations often observed following the initial compromise. The DLL contains an IP blocklist in its configuration to further evade automated analysis platforms and security research organizations.
One of the the DLL's functionalities involves encoding and decoding information to enable communication between the victim system and the C2 infrastructure. The malware communicates with the C2 over HTTP POST requests containing obfuscated data, which is XOR-obfuscated and Base64-encoded.
The URL used for victim-C2 communication comprises a random alphanumeric string and the victim's IP address. The HTTP POST request body contains information about the victim system, such as %APPDATA% configuration, host name, username, and workstation configuration.
The C2 server responds with a status code and the previously sent beacon information obfuscated using the same method. This C2 channel can also deliver secondary payloads as per the attacker's discretion.
It is also worth noting that threat actors use compromised web servers, primarily running WordPress 5.8.1, for file distribution and deploy "antibot" scripts to avoid white-hat detection.
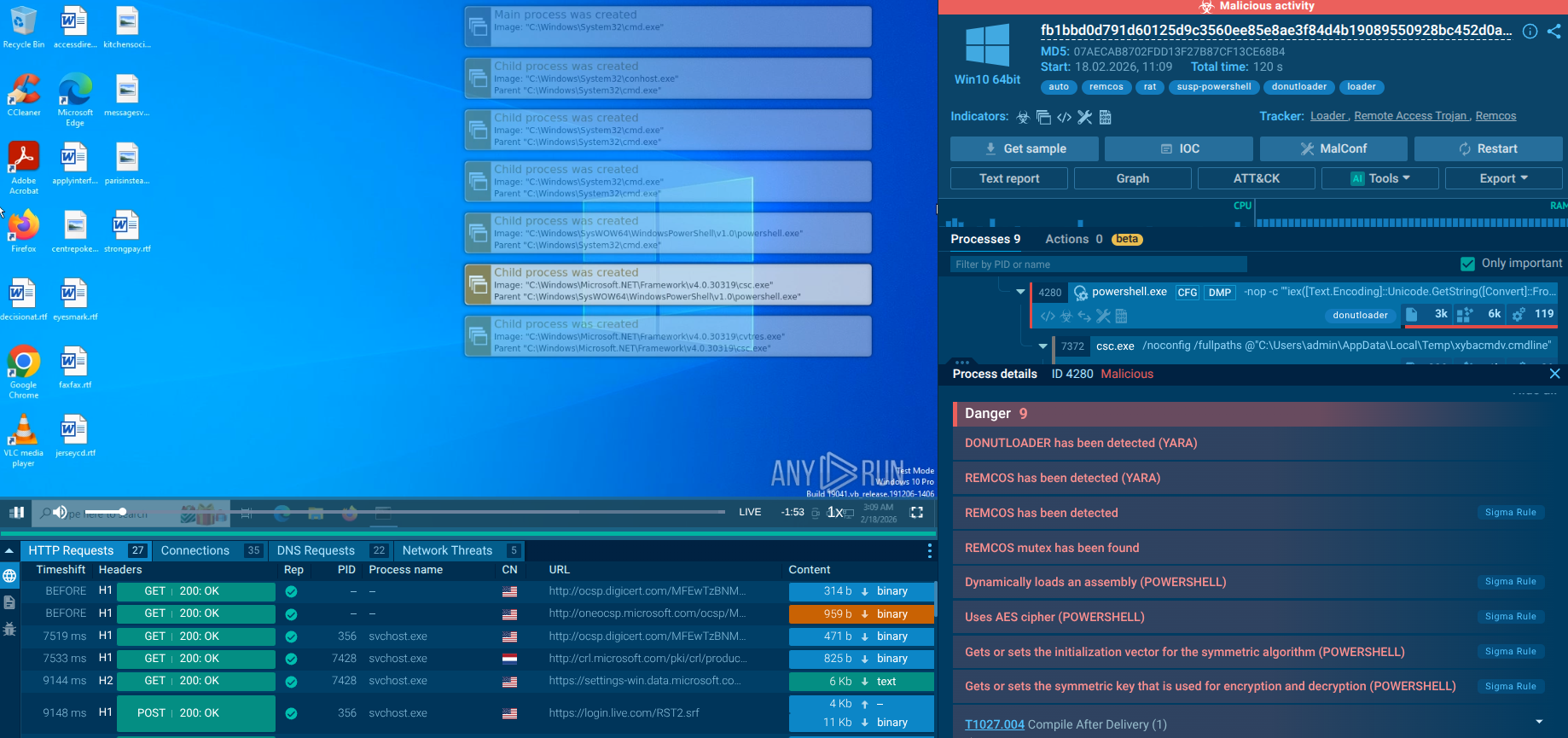
ANY.RUN's cloud-based interactive sandbox facilitates seamless analysis of SquirrelWaffle samples for malware analysts. The platform efficiently compiles and displays execution data in accessible formats while gathering artifacts and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) in real time.
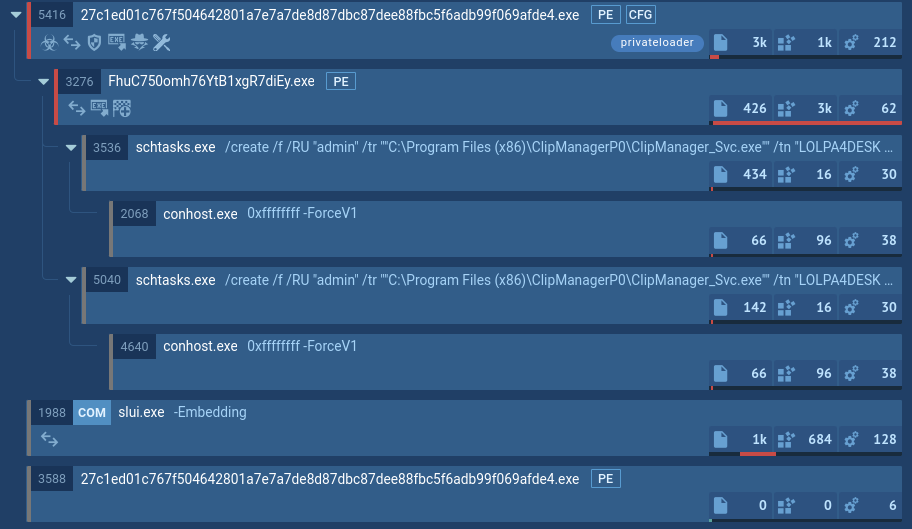
Due to the specific traits inside its POST requests, SquirrelWaffle may be detected by network activity. On the screenshot below, loader was detected by a Suricata rule.
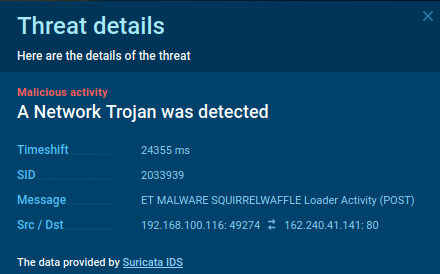 The SquirrelWaffle’s network activity with a detected loader
The SquirrelWaffle’s network activity with a detected loader
In order to be as inconspicuous as possible, Squirrelwaffle execution flow is simple. The loader often sneaks into the systems after a user opens a malicious document. Then the payload is downloaded, and it starts execution. While active, Squirrelwaffle connects to the Command & Control server to download the next-step payload.
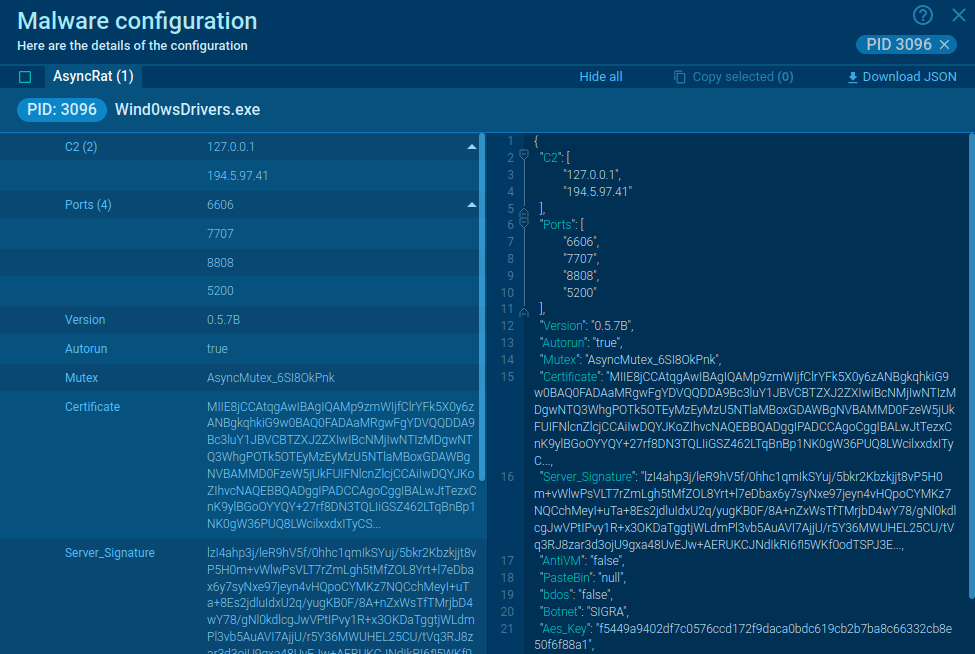
Checked out a sample we've analyzed.
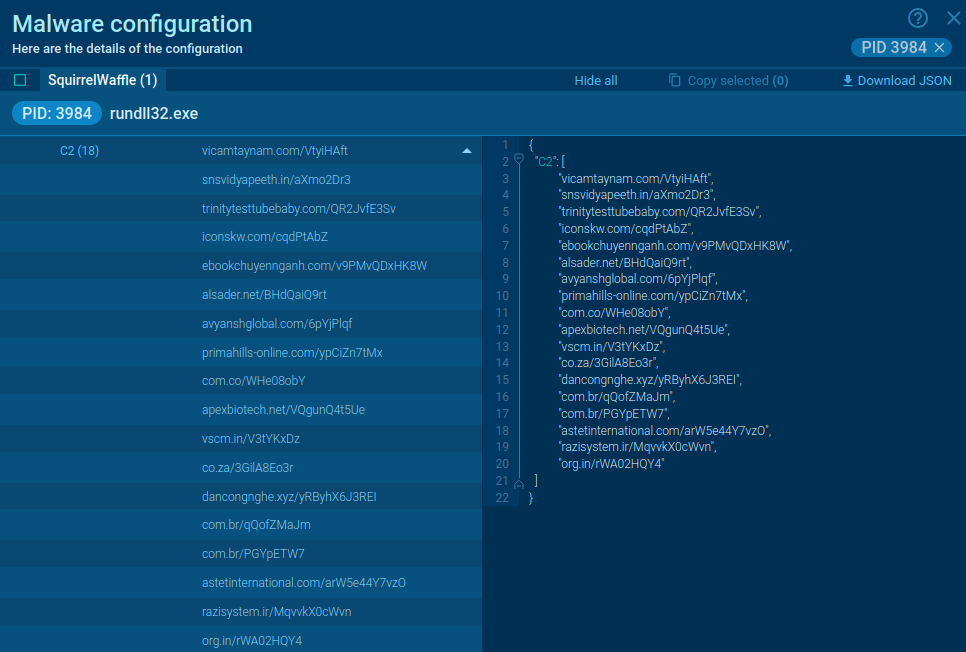 Malware configuration extracted from SquirrelWaffle
Malware configuration extracted from SquirrelWaffle
SquirrelWaffle is primarily delivered through malicious documents in phishing campaigns, often employing stolen reply-chain attacks for distribution. This method involves hijacking an existing account to send phishing emails, rather than fabricating an account or creating a new one.
This technique boasts a high success rate, as it is challenging to defend against. By gaining access to email history, adversaries can craft convincing messages and continue existing conversation. This leaves few discernible phishing indicators. Researchers note that SquirrelWaffle-distributing emails are well-composed, and the attackers adeptly mimic the style of prior correspondence, regardless of the language.
While the malware predominantly targets English-speaking users, campaigns in French, German, Dutch, and Polish have also been detected — though they account for less than 30% of the total volume at the time of writing.
The malicious emails typically contain hyperlinks to infected ZIP archives hosted on attacker-controlled servers. These emails usually include a malicious .doc or .xls attachment, which triggers the execution of malware-retrieving code when opened.
The attackers fake the DocuSign signing platform, persuading recipients to enable macros in their MS Office suite. The embedded code employs string reversal for obfuscation, creates a VBS script in %PROGRAMDATA%, and then executes it.
This process retrieves Squirrelwaffle from one of five hardcoded URLs and delivers it as a DLL file to the compromised system. Subsequently, the Squirrelwaffle loader deploys malware such as Qakbot or the often-misused penetration testing tool, Cobalt Strike.
In the wake of Emotet's disruption, it was inevitable that threat actors would devise a substitute. It may be premature to declare SquirrelWaffle as the definitive replacement, but it possesses the fundamental attributes needed to potentially become the next prominent dropper and assume Emotet's role.
We recommend that organizations and researchers examine the TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures) utilized by this malware operation while it is still in the (relatively) early stages of gaining traction.