Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


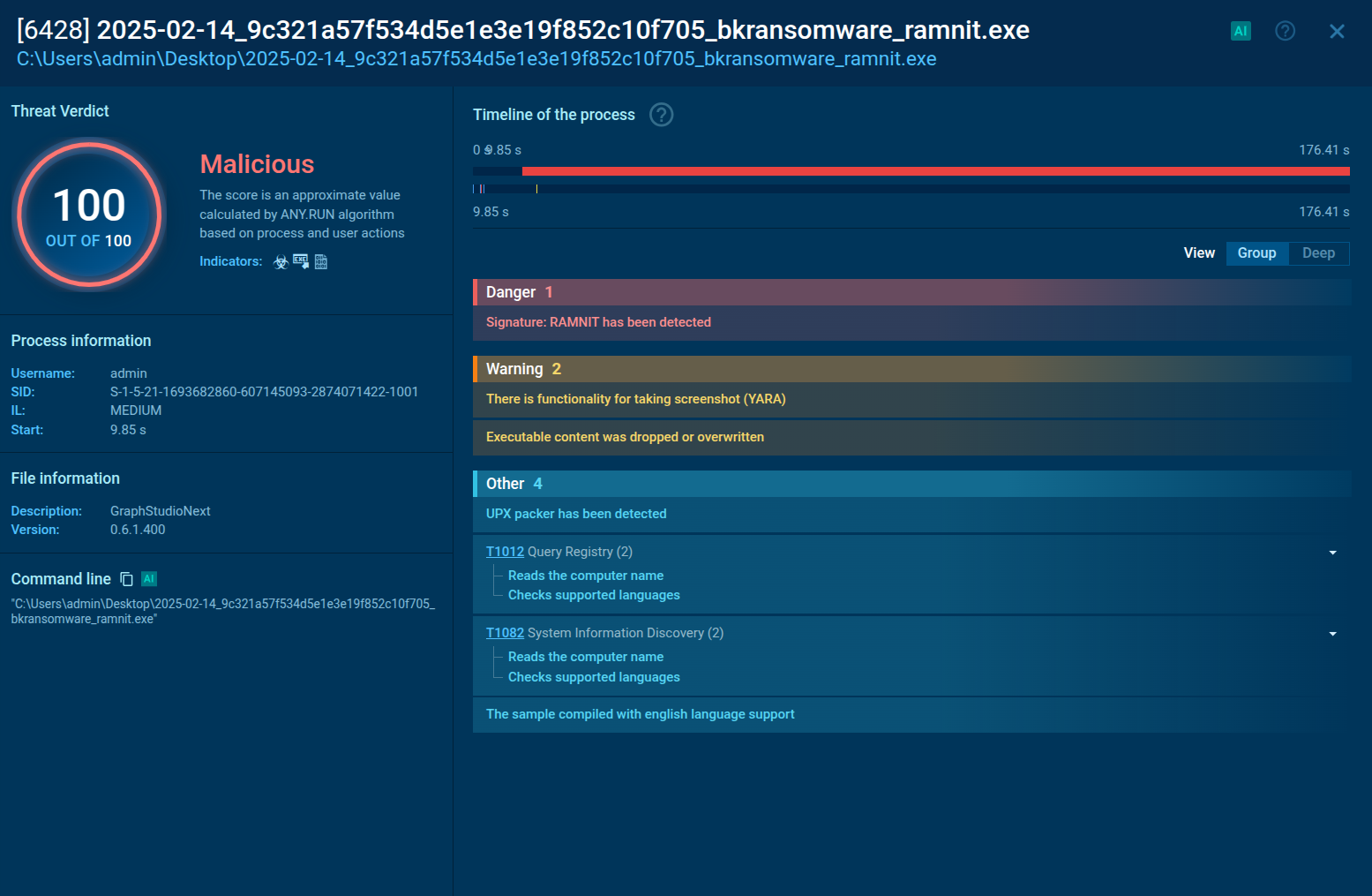
Rhadamanthys is a C++ information-stealing malware that extracts sensitive data from infiltrated machines. Its layered operational chain and advanced evasion tactics make it a major risk in cybersecurity landscapes.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
26 September, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
26 September, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
First observed in late 2022, Rhadamanthys is an advanced info-stealer that targets Windows platforms. It is distributed through the malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model. This, in conjunction with its extremely robust and diverse malicious capabilities contributes to the rising popularity of this malware.
Similar to threats like RedLine or Raccoon, utilizing this new strain, threat actors can extract user passwords and exfiltrate sensitive data from infiltrated systems. The info-stealer also presents a significant threat to various cryptocurrency platforms, where it's employed to seize user credentials and wallets.
Certain indicators suggest that Rhadamanthys stealer has the potential to evolve into a pervasive threat. Notably, the malware's initial launch demonstrated signs of meticulous planning. The individual who first introduced it on an underground forum, operating under the pseudonym "kingcrete2022", began building his account's reputation well in advance of the release announcement. This proactive strategy aimed to establish credibility and set the stage for the malware's introduction.
The tactic proved successful, as the debut post, which promoted Rhadamanthys as a "first-class" stealer, quickly gained momentum and attracted attention in the underground community.
As it stands, Rhadamanthys indiscriminately attacks targets worldwide, even reaching into the territories of the former USSR. The malware has been identified in several malicious spam and Google Ads campaigns, but more on this later in the article.
It should be noted, that Rhadamanthys stealer employs a design philosophy that aims to incorporate an expansive list of features. These features are not strategically targeted but rather prioritize extensive capability. For example, malware is, rather unnecessarily, equipped with capabilities to steal data from web browsers such as KMeleon and Pale Moon, and to steal cryptocurrency from obscure browser extensions like Firefox's Auvitas Wallet.
In terms of system information extraction, Rhadamanthys can capture a wide array of data. This includes:
-Computer name, username, RAM capacity, CPU cores, screen resolution
-Installed software, cookies, browsing history
-Saved credit cards and other sensitive information
Furthermore, Rhadamanthys targets credentials from a vast range of sources: FTP clients like Cyberduck and TotalCommander, mail clients such as Outlook and Thunderbird, and password managers like RoboForm and KeePass. It also has the capacity to extract information from VPN services, note-taking applications, messenger applications, and other services like Steam, TeamViewer, and SecureCRT.
Rhadamanthys shows a particular interest in cryptocurrency. One of its version updates had nearly half of its new features dedicated to exfiltrating and cracking cryptocurrency wallets. The list of targeted wallets is quite extensive and includes Auvitas, BitApp, Crocobit, Exodus, Finnie, ICONex, Metamask, and more.
In addition to the automatic actions, Rhadamanthys also allows for direct intervention by attackers. The malware offers a functionality to push new configurations to the “file grabbing” module, allowing specific files to be exfiltrated. For a more hands-on approach, attackers can execute hand-crafted PowerShell scripts on the victim machine. This added flexibility provides a high degree of control over the infected system.
Written in C++, Rhadamanthys employs a number of sophisticated techniques to ensure its stealth and efficacy. Its operational chain is usually divided into three components:
-the Dropper,
-the Rhadamanthys Loader (second shellcode)
-and the Rhadamanthys Stealer (Nsis module).
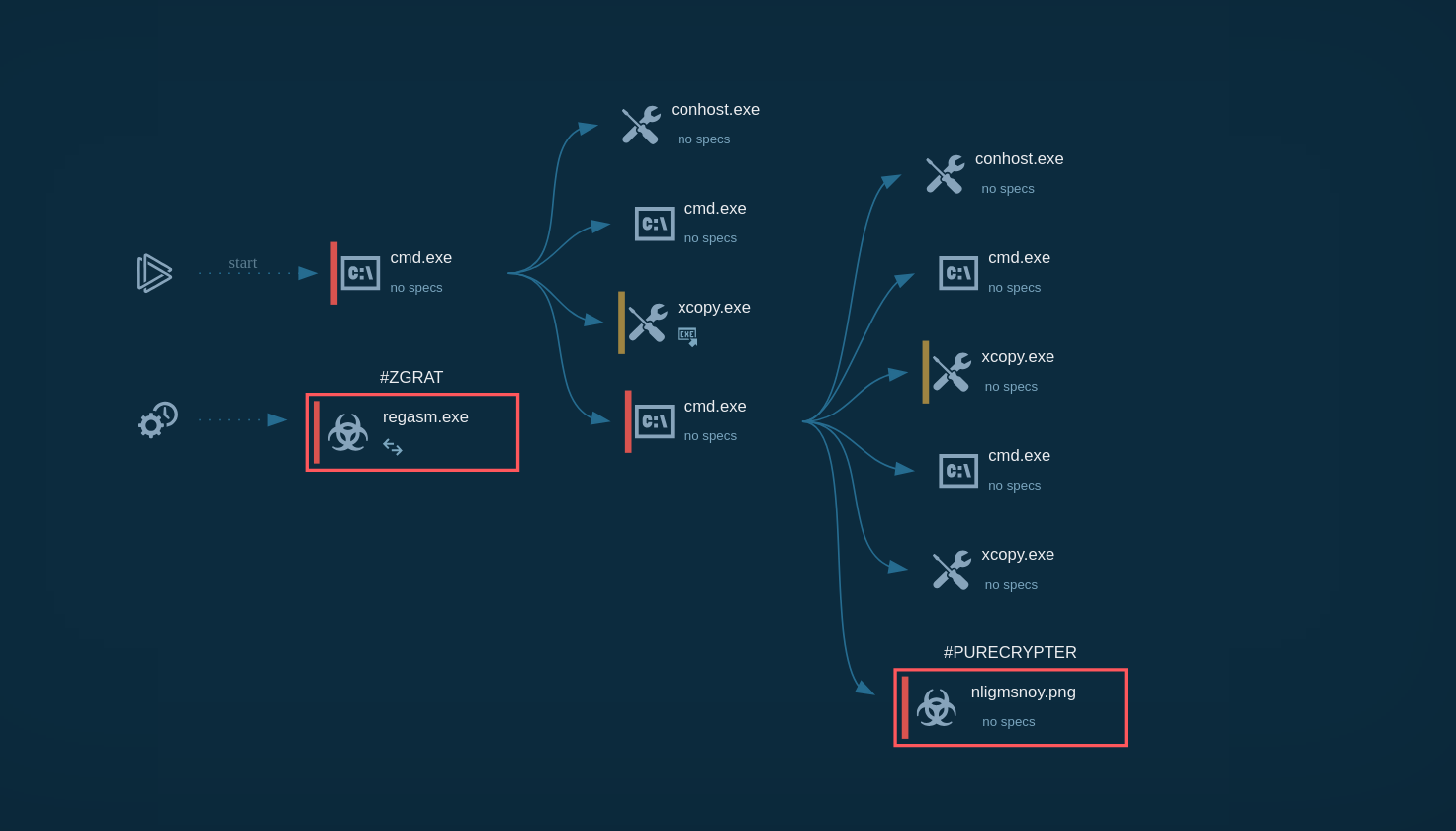
In one attack observed the wild, the Dropper initiated the process by executing the shellcode through a callback function. This bypassesed common security measures that track shellcode execution methods like CreateThread or CreateRemoteThread.
Next, the Rhadamanthys Loader, or the second shellcode, comes into play. This shellcode uses several evasion methods. It manipulates exception handling to maintain low visibility, creates a Mutex to simulate legitimate processes, and unhooks API calls to avoid detection. In addition to these, it is responsible for decrypting the malware configuration and managing its network functions.
Lastly, the Rhadamanthys Stealer, or the Nsis module, is activated. Some samples have the ability to manipulate AVAST’s AMSI-related modules to avoid detection. It is this component that ultimately executes the data theft.
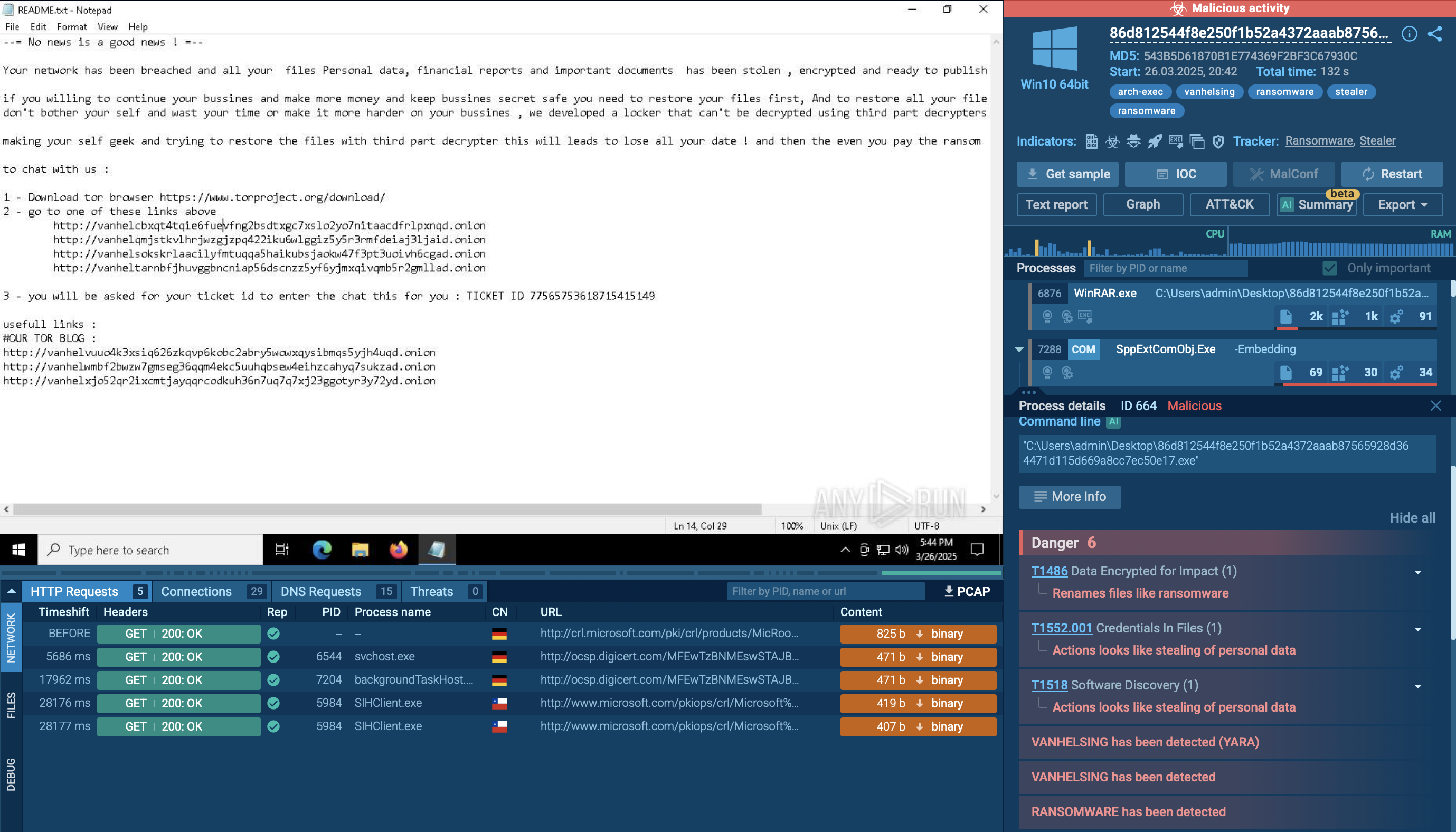
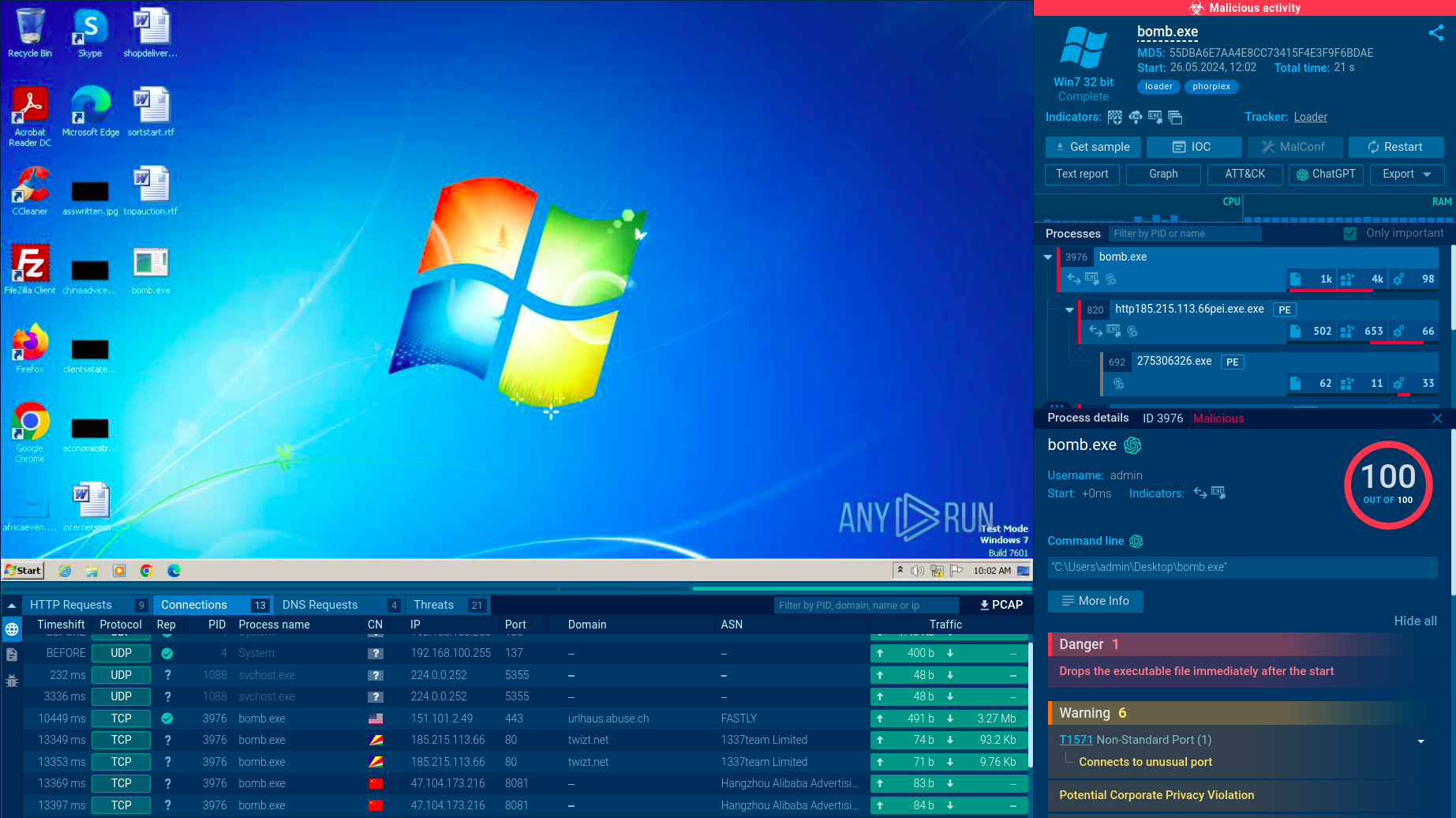
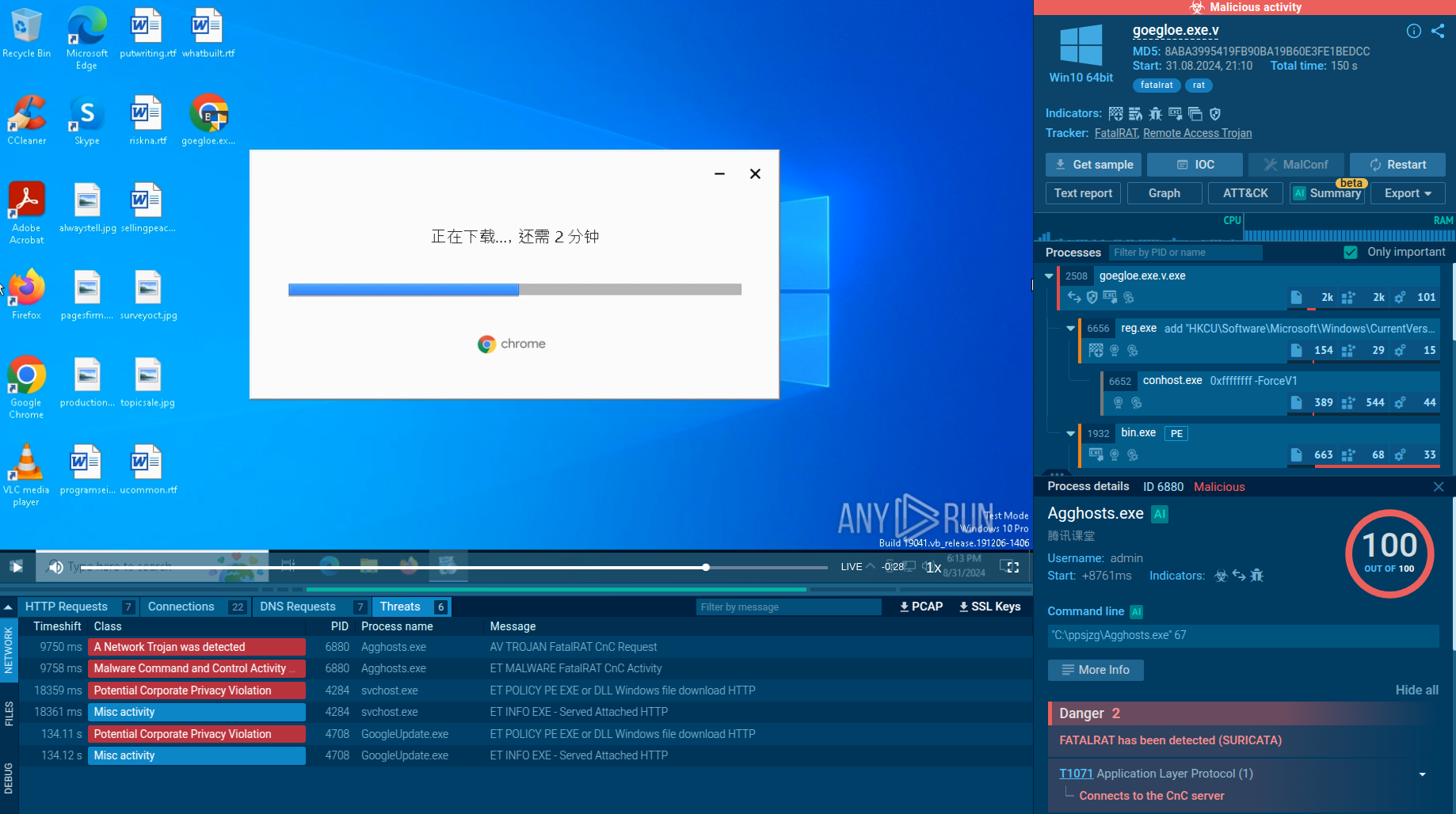
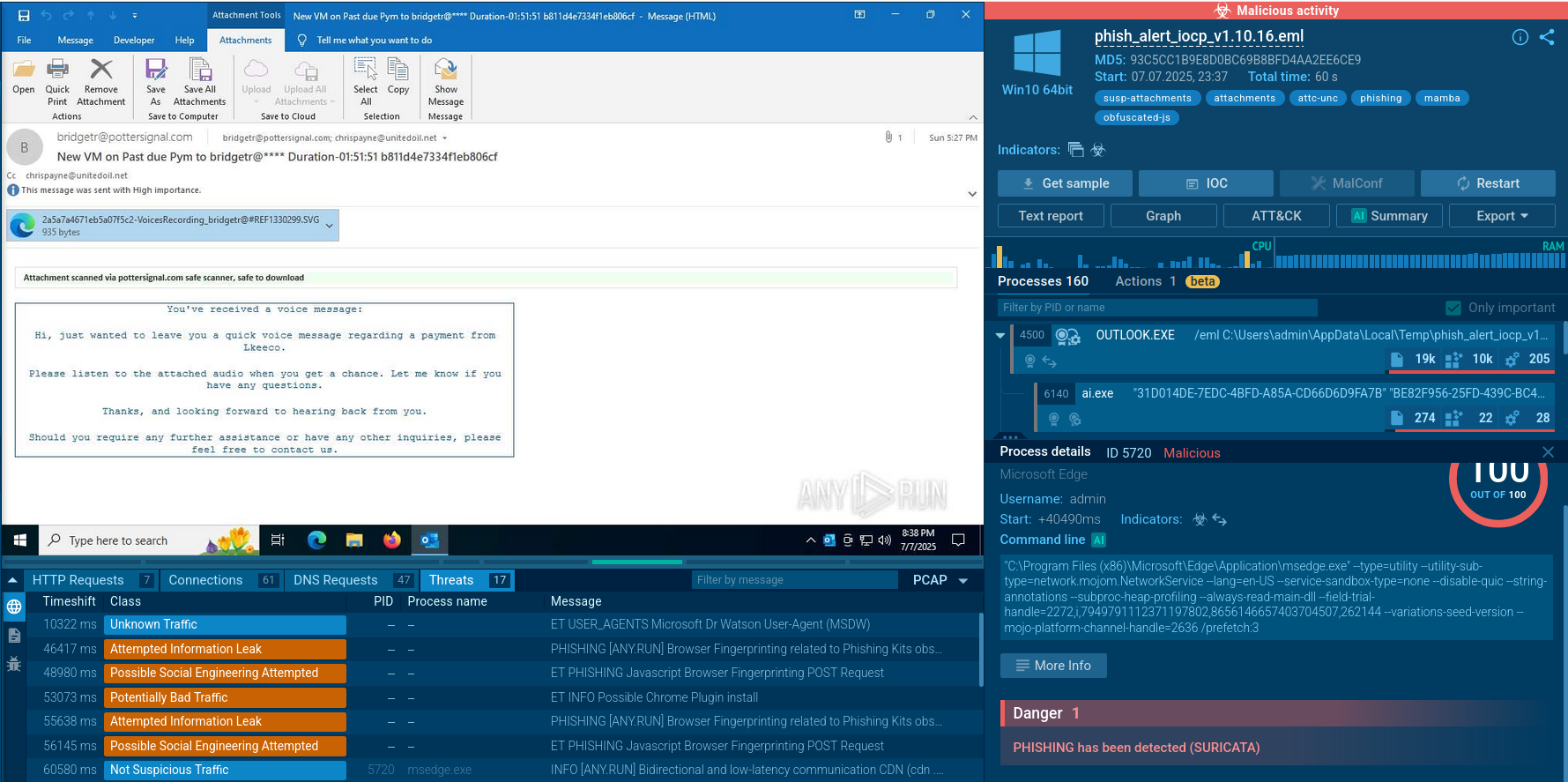
Being a stealer, Rhadamanthys tries to operate as secretively as possible, remaining under the radar and avoiding detection. The malicious activity starts right after infection — Rhadamanthys extracts information from the system and tries to send it to the Command & Control servers.
The execution chain may vary a little — some versions of the Trojan have the ability to inject into system processes, while others simply execute themselves.
It also may delay execution and sleep for some time after infection or use utilities like PowerShell to run commands.
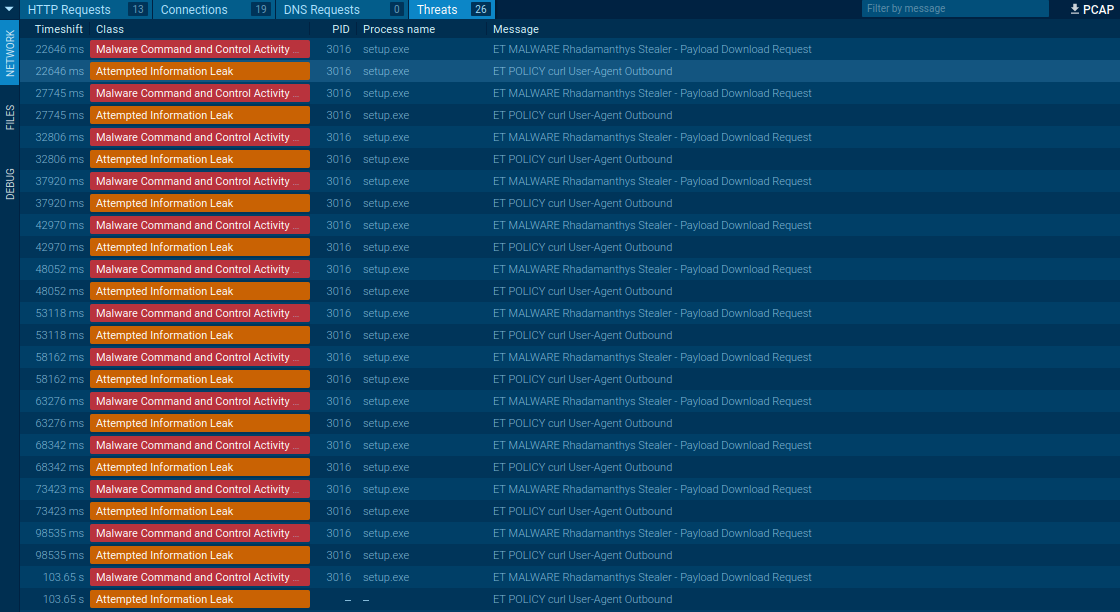 Rhadamanthys’s network traffic
Rhadamanthys’s network traffic
Thanks to the network packets structure, Rhadamanthys can be detected by Suricata rules.
Rhadamanthys info-stealer employs a couple of key strategies to infiltrate systems. One of its infamous шstribution techniques involves hijacking Google ads, where it covertly replaces the original content with a link to the malware.
It also uses phishing webpages and malicious spam for propagation. In malspam campaigns, a PDF file triggers victims to download the malware. The PDF file was observed presenting a fake Adobe Acrobat DC software update prompt which, when clicked, initiates the execution of the malware.
In phishing-based distribution, the malware creators build fake webpages mimicking legitimate services like Zoom or AnyDesk. Links to these fraudulent sites are then spread via Google ads. These malicious sites facilitate the download of the Rhadamanthys infostealer disguised as a legitimate installer. Consequently, the target unknowingly downloads the malware without noticing the infection.
Boasting an extensive stealing feature set that may well be unmatched among similar types of malware, Rhadamanthys has the potential to emerge as a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape. We strongly recommend analysts to delve into this threat while it's still relatively new on the scene.
Conveniently, dynamic analysis of Rhadamanthys can be easily carried out on platforms such as ANY.RUN — our cloud interactive sandbox allows for a deeper understanding of its execution process and facilitates the collection of valuable Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
Investigating the nuances of Rhadamanthys not only aids in its containment but also prepares us for future threats that may adopt a similar design strategy.