Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


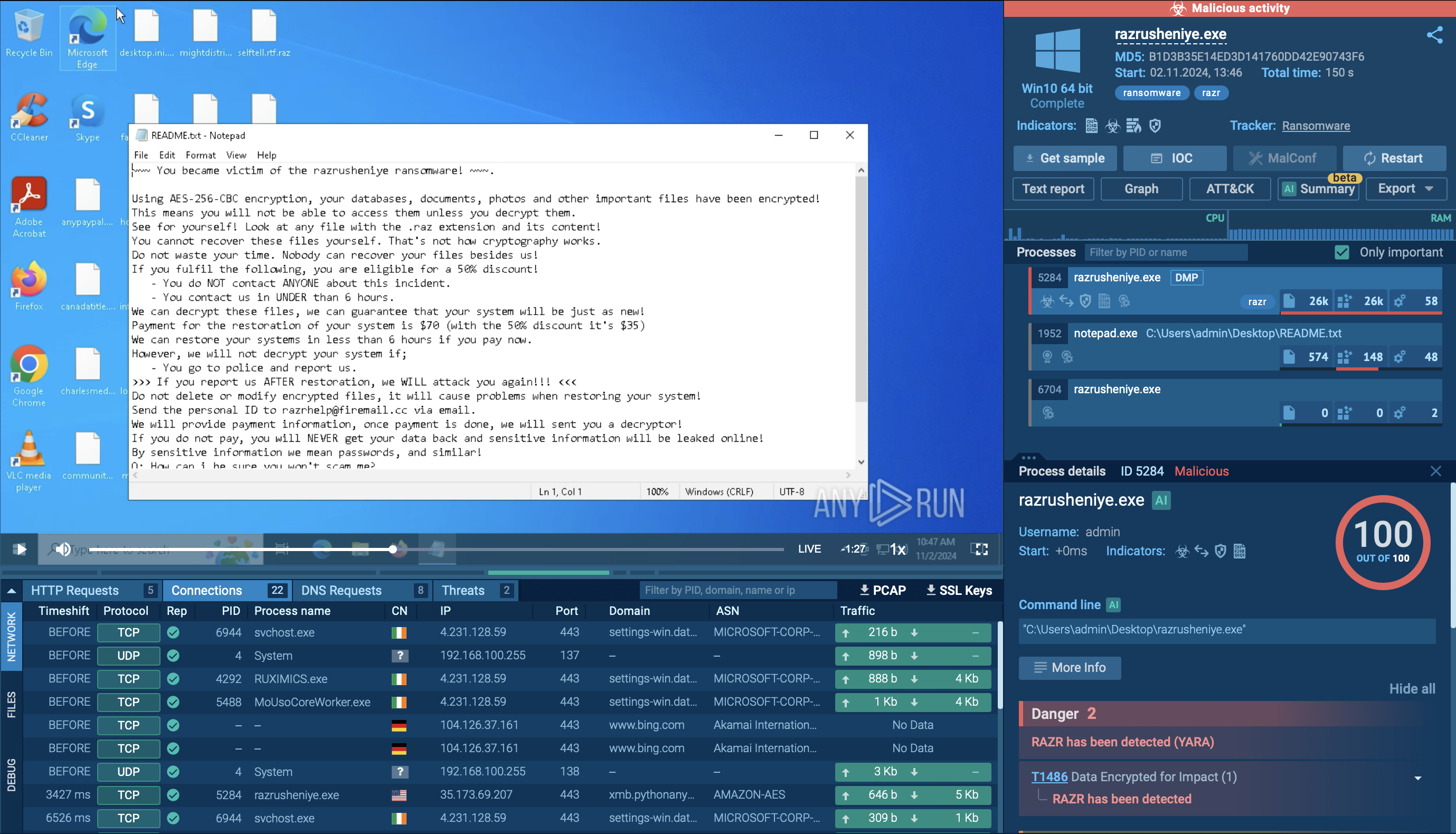
PureLogs is a stealer that collects a wide range of data from infected systems, including browser data, crypto wallets, PC configuration details, etc. It is delivered by PureCrypter, another malware that belongs to the Pure malware family. PureLogs is distributed based on a subscription model, allowing any threat actor to utilize it in their attacks.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2022
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2022
First seen
:
|
4 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 165
165
 0
0

 448
448
 0
0

 1911
1911
 0
0
PureLogs is a stealer malware that is part of the Pure ecosystem of products. This malware family, which includes PureCrypter and other tools, was first distributed in March 2021. It is offered as malware-as-a-service (MaaS) meaning that different threat actors can freely purchase access to this malware
The Pure malware family products are sold openly on the developer’s website and forums. Despite being promoted as software for testing purposes, it is widely employed for malicious activities.
PureCrypter, another tool in the Pure ecosystem, is often used in conjunction with PureLogs. PureCrypter is tasked with encrypting malicious payloads and delivering them to the victim’s system.
PureLogs Stealer is designed to collect a wide range of data from infected systems:
The malware uses PureCrypter, a loader that is capable of delivering staged and stage-less payloads. The loader has also been observed to drop third-party malware, such as AgentTesla.
Learn more about the Pure Malware family in ANY.RUN’s article “A Full Analysis of the Pure Malware Family: Unique and Growing Threat”.
The malware can gain persistence on the system via Registry Run Keys. It is also capable of removing itself via a PowerShell command.
PureLogs Stealer uses TCP/IP communication with its Command and Control (C2) server. It encrypts the data which it exfiltrates from the infected system.
We can conduct an in-depth analysis of a PureLogs sample in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
PureLogs begins its execution chain by infecting a host machine, typically through phishing emails or malicious downloads.
Once on the host, it unpacks itself to deploy the payload, often avoiding detection by employing techniques such as encryption or obfuscation.
The stealer then scans the infected system for valuable data, such as credentials, financial information, and other sensitive personal data. This information is extracted and often encrypted to ensure it is securely transmitted back to the command and control (C2) server. Throughout this process, PureLogs maintains communication with the C2 server to receive further instructions and update its operational parameters.
Finally, the stolen data is utilized by the attackers for various malicious purposes, including identity theft, financial fraud, or selling on the dark web
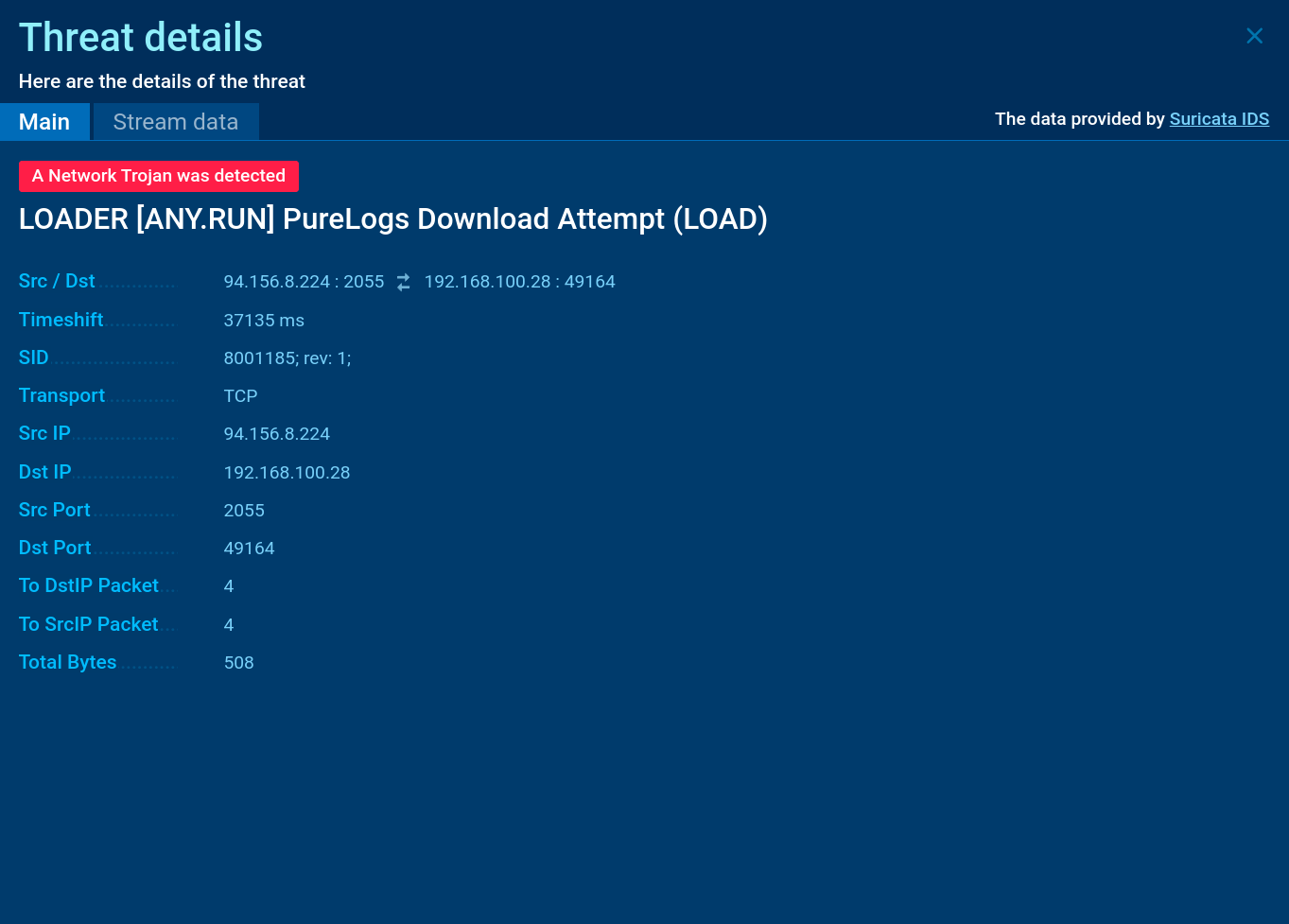 PureLogs Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
PureLogs Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
Since PureLogs is a MaaS stealer, different threat actors utilize their own methods for infecting victims’ devices.
Similar to Gh0stRAT and LimeRAT, some cybercriminals employ a tactic of renaming the malicious files associated with PureLogs Stealer infection to popular legitimate software and video games to trick unsuspecting users into downloading and installing the malware.
PureLogs Stealer's ability to collect a vast array of sensitive data coupled with a relatively low barrier to acquire it presents a significant risk to individuals and organizations. When used together with PureCrypter, this malware becomes even more challenging to detect, making it easier for cybercriminals to infect systems and compromise sensitive information.
To prevent infection, it is crucial to have a robust security infrastructure that includes sandboxing capabilities to analyze any suspicious files and links that enter the organization. By taking proactive measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to PureLogs Stealer and other malware threats.
ANY.RUN, a cloud-based sandbox, provides the tools for quick, easy, and conclusive analysis of PureLogs Stealer, as well as dozens of other malware families. Thanks to ANY.RUN’s interactive approach, users can engage with the virtual environment and perform any actions needed to study the threat comprehensively. The service provides threat reports on each analyzed sample that feature indicators of compromise, TTPs, and other info that can empower users to make informed security decisions.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!