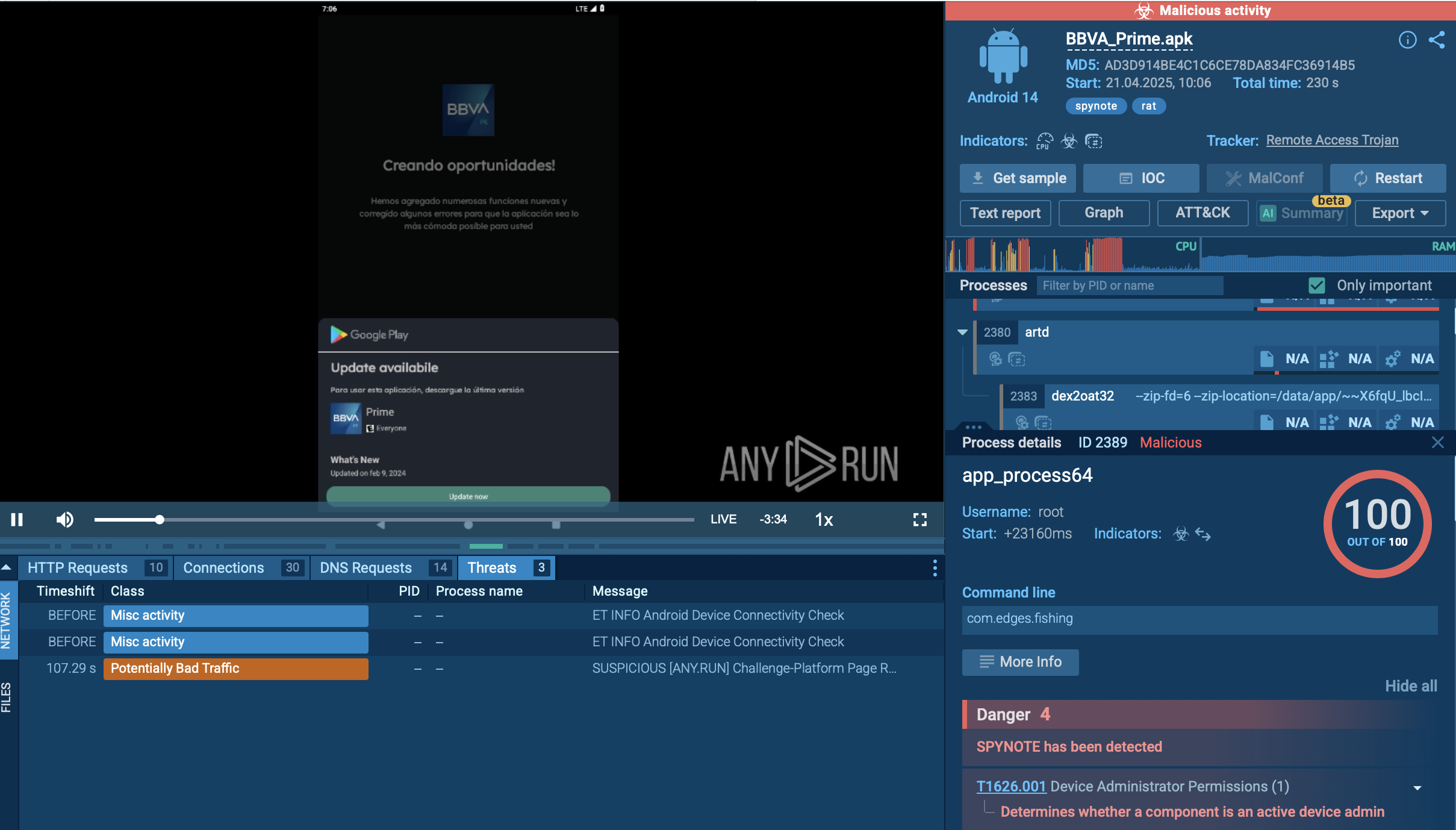
Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


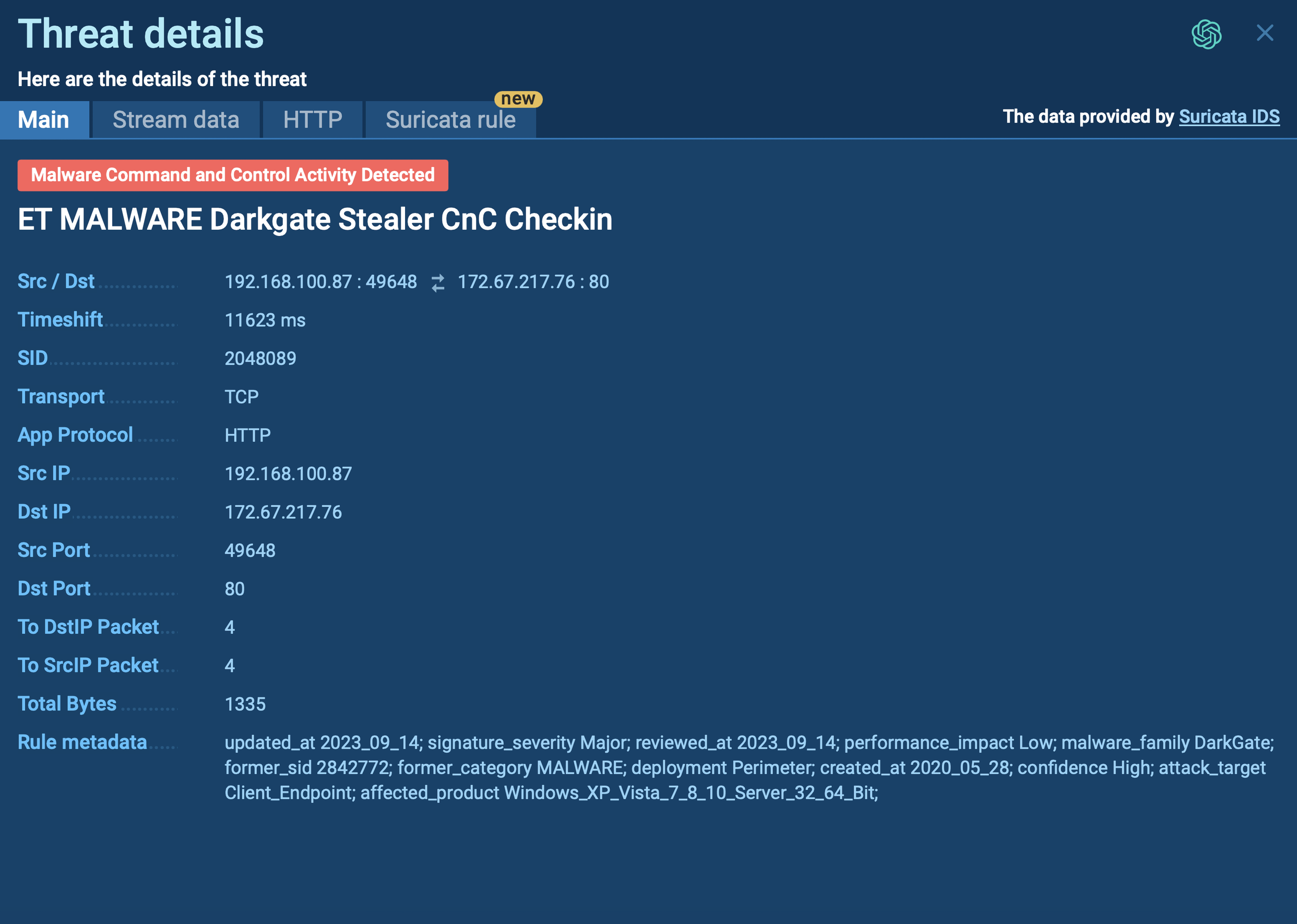
Pikabot is a trojan malware with a focus on loader capabilities. Pikabot is also used for other activities, such as executing commands on the infected system. The earlier versions of the malware made use of extensive code obfuscation to evade detection. Upon infection, it collects system information and sends it to command-and-control servers.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2023
First seen
:
|
18 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2023
First seen
:
|
18 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Pikabot, a loader malware, made its first appearance in the cybersecurity realm in February 2023. This malicious software is recognized for its wide array of anti-analysis features and flexible capabilities that have made it a popular choice among many attackers.
The malware functions through two key modules: the loader and the core. The loader initiates the malware's operations, while the core houses its primary functionalities. Pikabot shows signs of continuous evolution, as its latest version appeared in February 2024, exhibiting notable differences from its original builds.
The resemblances between Pikabot and Qakbot have led to assumptions that they could be the work of the same malware developers. Pikabot has also been utilized in campaigns orchestrated by the threat actor TA577, where it was disseminated in conjunction with the DarkGate malware.
Criminals leverage Pikabot for various harmful activities which include:
In its earlier iterations, the Pikabot trojan utilized a combination of AES-CBC and RC4 key to encrypt strings. The new version demonstrates a shift towards less complex obfuscation and only occasional use of RC4.
Another notable difference between the early variants of the malware and its newest form is the approach to storing a configuration. While the first builts contained hardcoded configs, the newer iterations tend to download them from the command and control (C2) server.
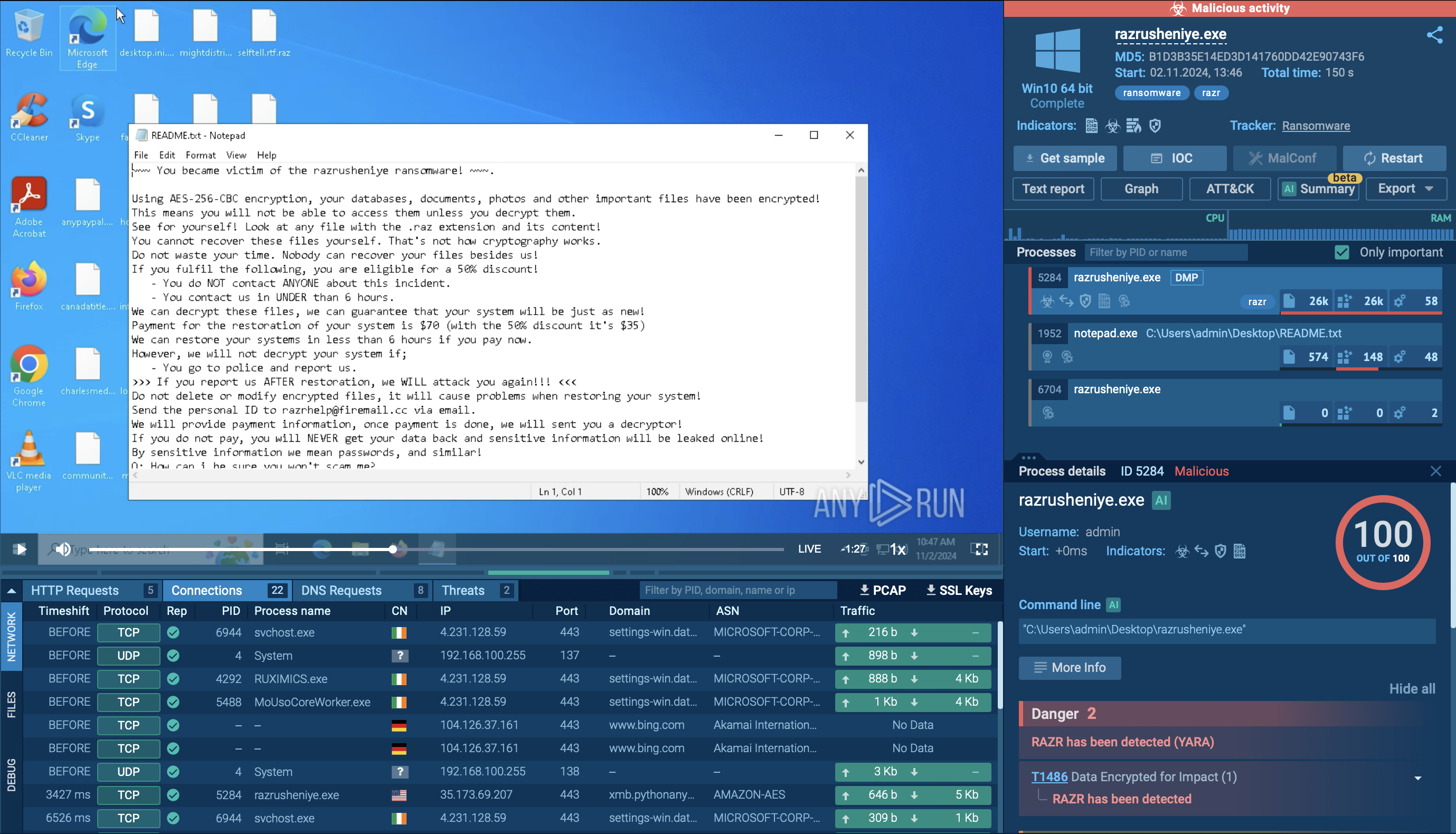
The Pikabot malware is particularly skilled at evading sandbox detection. One way it does this is by postponing its execution until the sandbox analysis period has expired. The malware also integrates junk code among legitimate instructions to further complicate analysis.
Pikabot uses regex to dynamically generate file names and other data. This lets the malware hide its code and evade detection by security tools that rely on signatures.
Pikabot initiates its operations by registering the compromised host with the C2 servers. This process involves gathering system information and submitting it to the C2 server via an HTTPS POST request. The gathered data encompasses. The data collected by Pikabot is encoded using standard Base64 and then encrypted using AES. The malware collects the following information about the system:
Let’s upload a sample of Pikabot to the ANY.RUN sandbox to conduct a Pikabot malware analysis sessions and observe its execution process in detail.
Pikabot malware initiates its execution chain by leveraging phishing emails or malicious downloads to infiltrate a system. Once inside, it employs PowerShell scripts or macros to download additional payloads from a remote server.
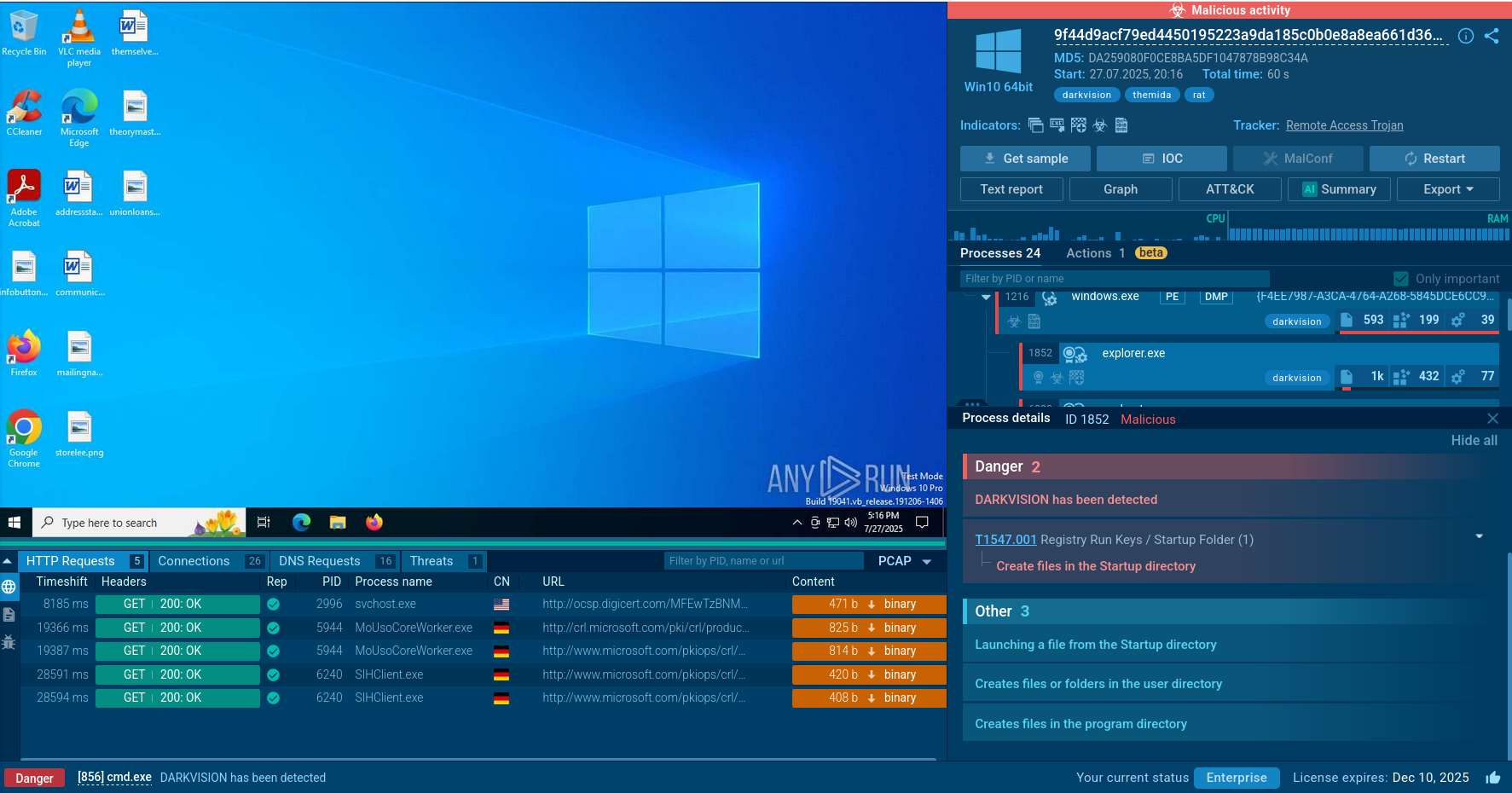
Pikabot then uses living-off-the-land techniques, such as exploiting legitimate system processes like "ctfmon.exe," to evade detection and maintain persistence. This process, commonly used for language and input services, is hijacked to execute malicious code while appearing benign.
The malware establishes communication with its command-and-control (C2) server, receiving instructions and exfiltrating sensitive data. It can also spread laterally across networks, exploiting vulnerabilities or using stolen credentials.
Throughout its execution, Pikabot employs various obfuscation and evasion techniques to avoid detection by security solutions.
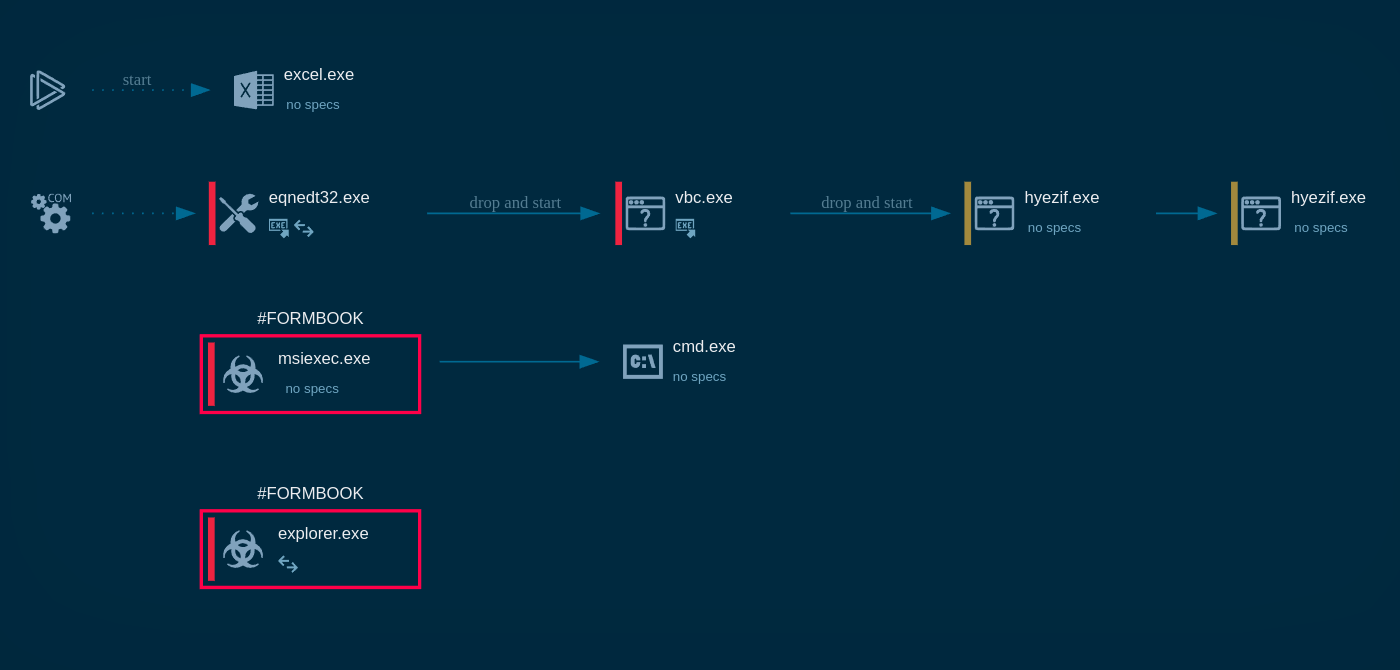
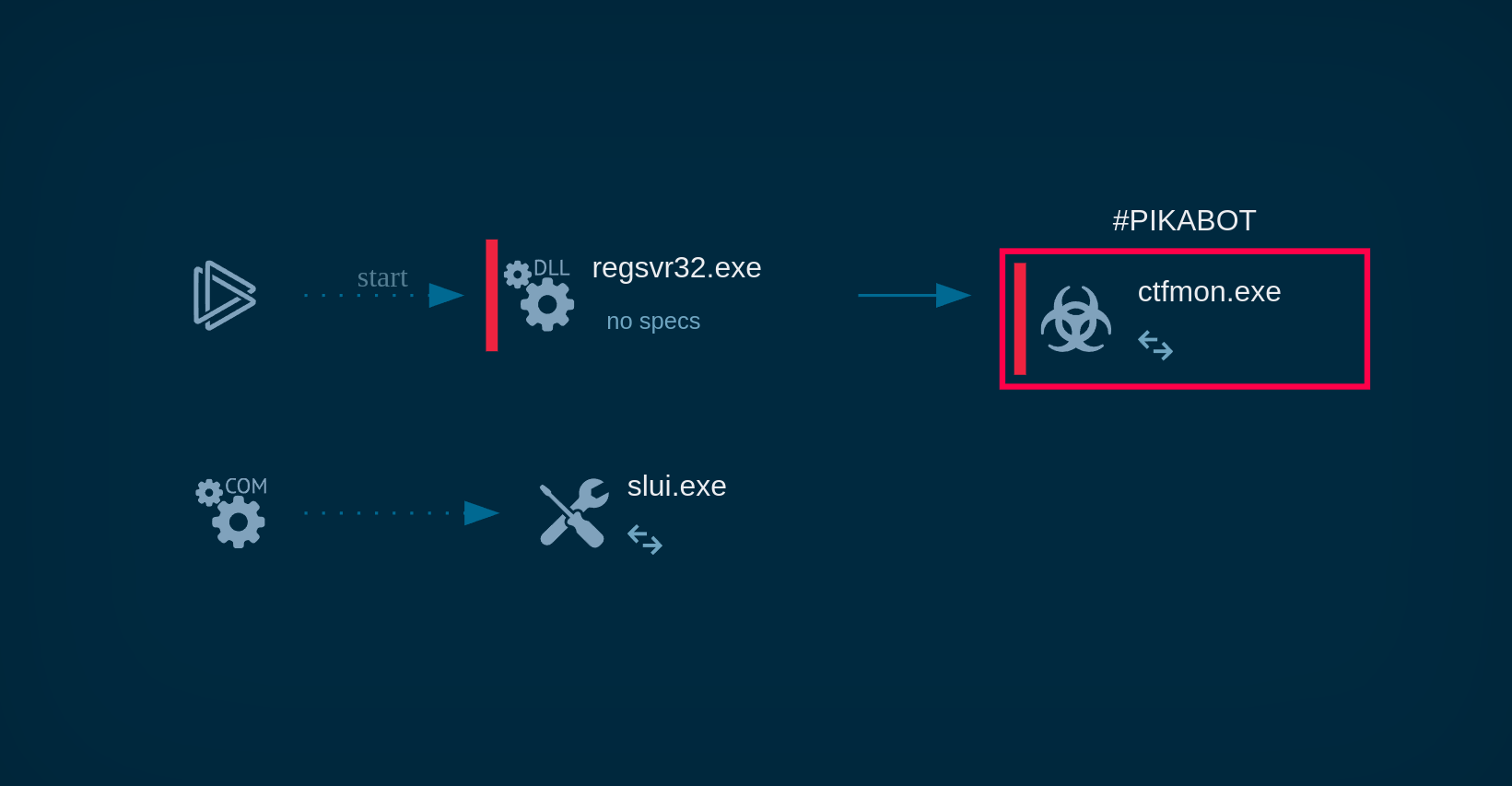 Pikabot process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Pikabot process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Just as in the case of other widespread malware, such as Remcos and NjRAT, Pikabot has been observed to be distributed primarily via phishing emails. Attackers usually employ multi-stage attacks that begin with an email that ask users to perform certain activities, such as clicking a link or opening a weaponized attachment. From there, the infection begins.
Another notable attack involving Pikabot occurred in 2023 when attackers utilized malvertising. As part of their campaign, they employed Google Ads to promote a fake website with a download link for AnyDesk, a remote desktop software. After running the installer file, the victim’s system became compromised and infected with Pikabot.
Pikabot is a sophisticated trojan malware that has the potential to significantly disrupt the affected infrastructure. Thanks to its anti-analysis features, it can be a challenge for certain security solutions to detect it. Therefore, it is impossible to use reliable solutions that timely implement updates to keep up with the new version of Pikabot.
Use ANY.RUN, a cloud-based sandbox, for analyzing suspicious files and links to identify Pikabot and other malware families. The service lets you gain an in-depth look at the behavior of any malware in a completely safe and secure environment. ANY.RUN generates detailed reports on the analyzed threats that contain all the essential information, including Pikabot IOCs (indicators of compromise) and TTPs, needed for making better security decisions.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!