Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


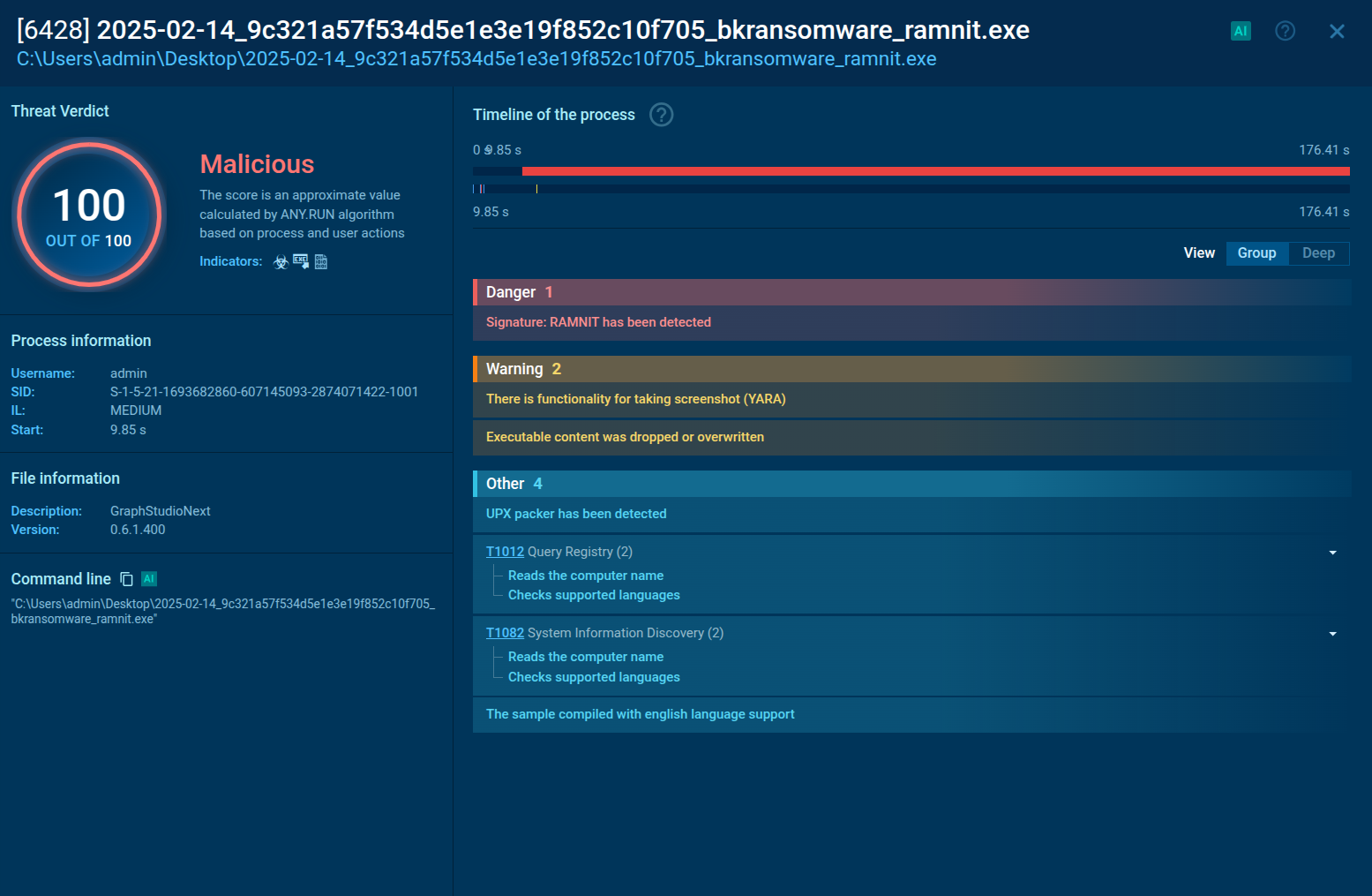
Parallax RAT is a versatile malware capable of stealing credentials, recording keystrokes, capturing screenshots, and exfiltrating sensitive data. It hides under legitimate processes like Notepad, uses diverse communication channels, and establishes persistence to maintain control over infected machines.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
16 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
16 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 453
453
 0
0

 2365
2365
 0
0

 4575
4575
 0
0
Parallax RAT, a remote access Trojan (RAT) active since December 2019. It has gained notoriety for its evasion techniques, such as process hollowing, and extensive data exfiltration capabilities.
The malware has been widely used by various APTs around the world, including in attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic. ParallaxRAT has also been linked to the activity of the advanced persistent threat (APT) named TA2541 that has been targeting aviation and defense industry actors since 2017.
Parallax RAT’s architecture enables attackers to engage in diverse malicious activities. The most common of them are:
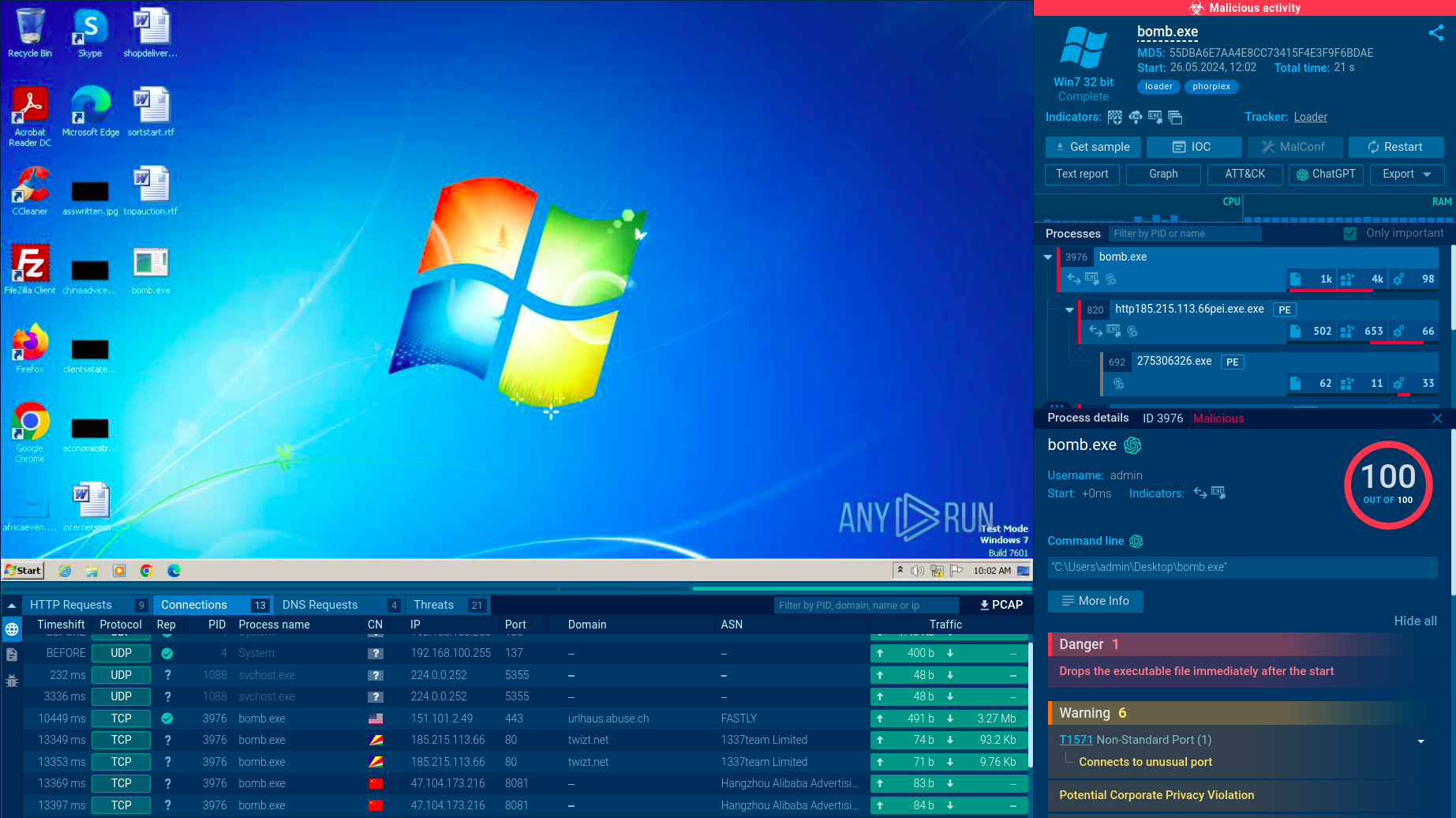
Similar to other malware families, such as WarzoneRAT and DarkGate, Parallax RAT utilizes a sophisticated process-hollowing technique. It injects its malicious payload into a legitimate Windows process (e.g., pipanel.exe), leveraging the process's existing privileges to bypass security checks and remain undetected.
The malware usually establishes persistence by adding itself to the startup folder and creating scheduled tasks. Afterwards, Parallax RAT opens communication channels with the attacker's command-and-control (C2) server. One of the standout features of the malware is the use of Windows Notepad for communication with the victim. In many instances, attackers used this way of connecting with the victims to instruct them to visit the criminals’ Telegram channel.
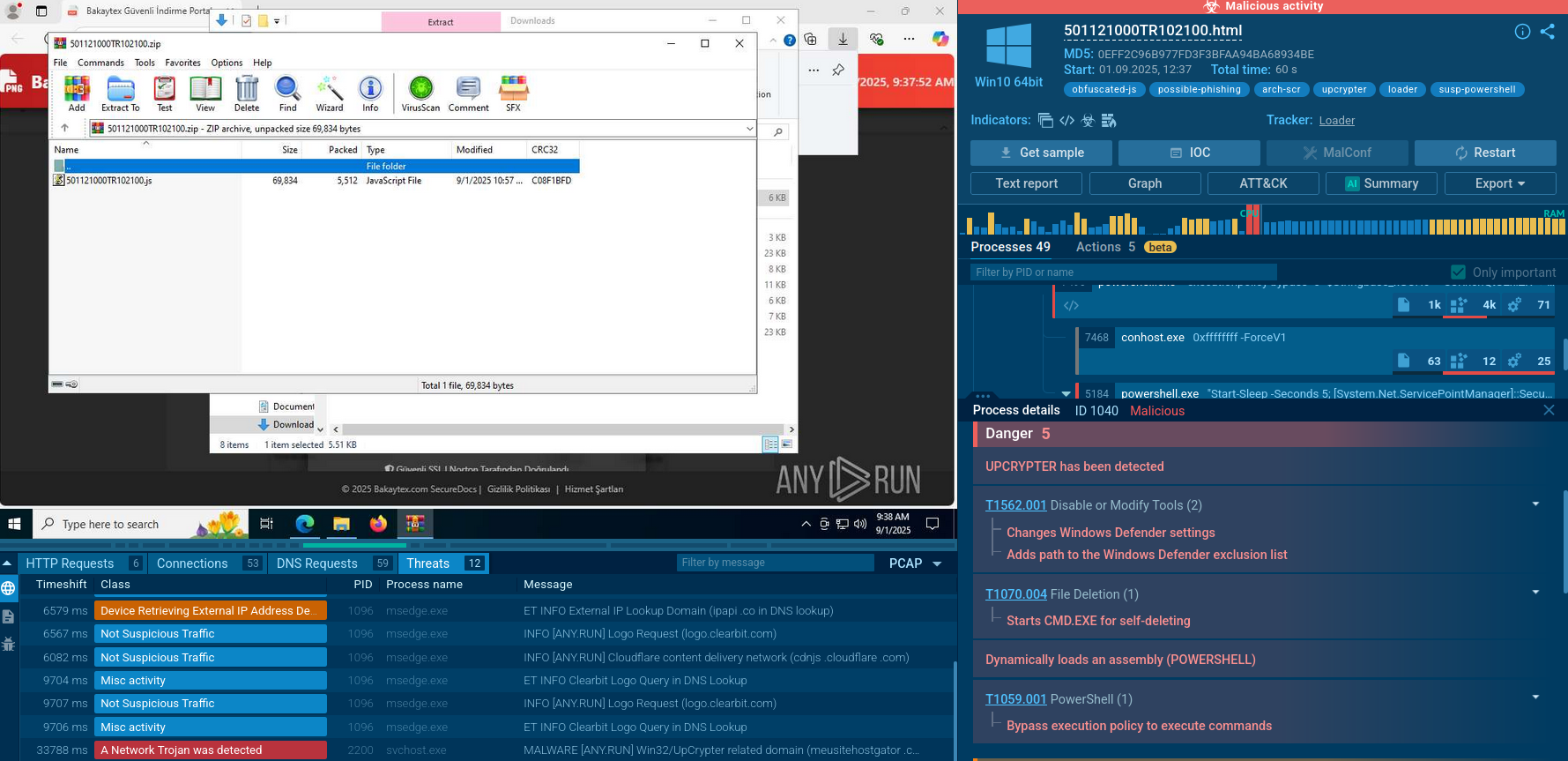
Parallax RAT often employs a multi-stage delivery chain to evade detection. Initial stages might involve seemingly harmless files like weaponized Microsoft Word documents with embedded macros. Triggering these macros can download and execute the next stage payload, often a malicious DLL.
To see how Parallax RAT infection takes place and collect its indicators of compromise, we can use ANY.RUN. Let’s submit a PrallaxRAT sample for analysis.
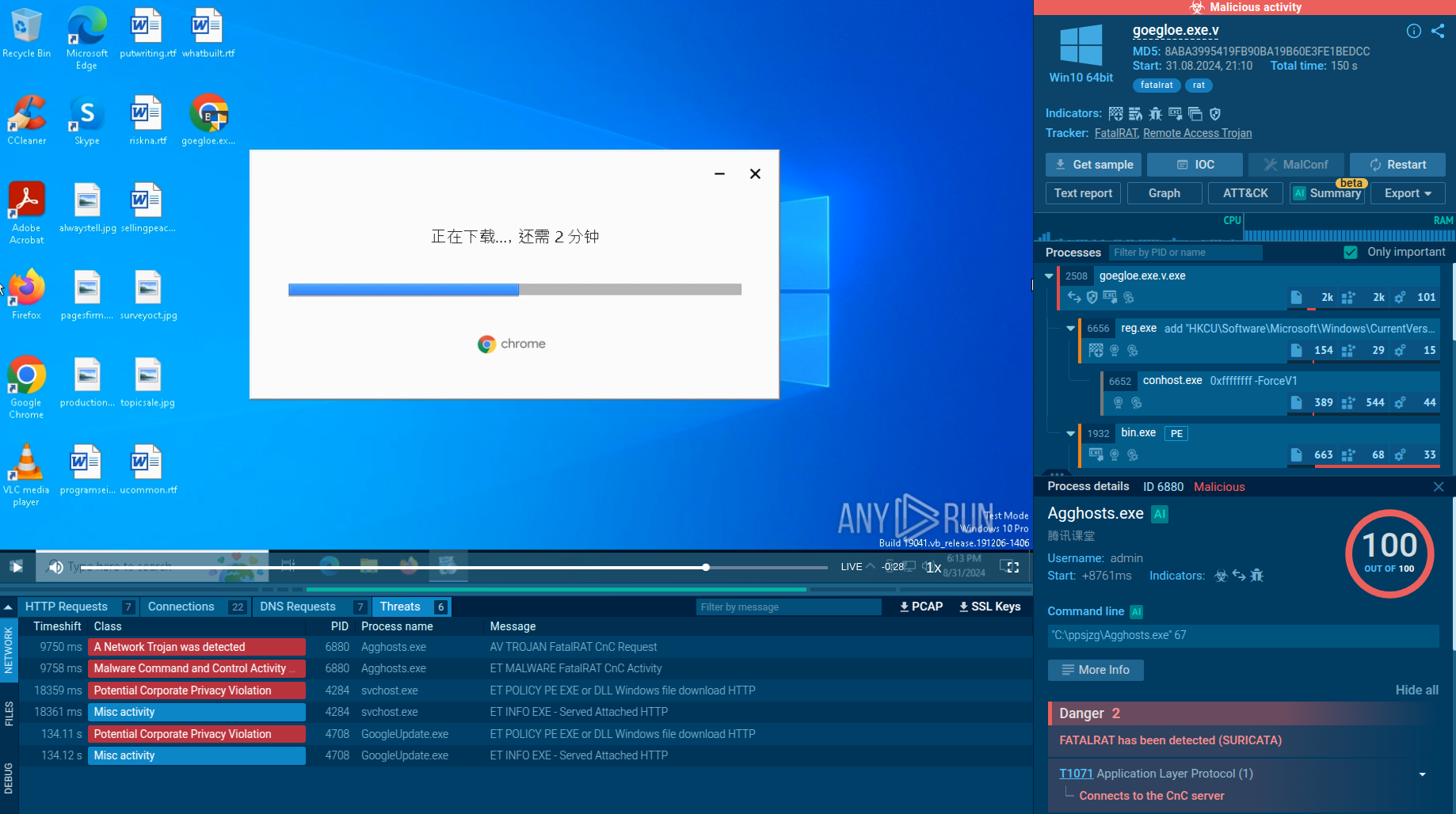
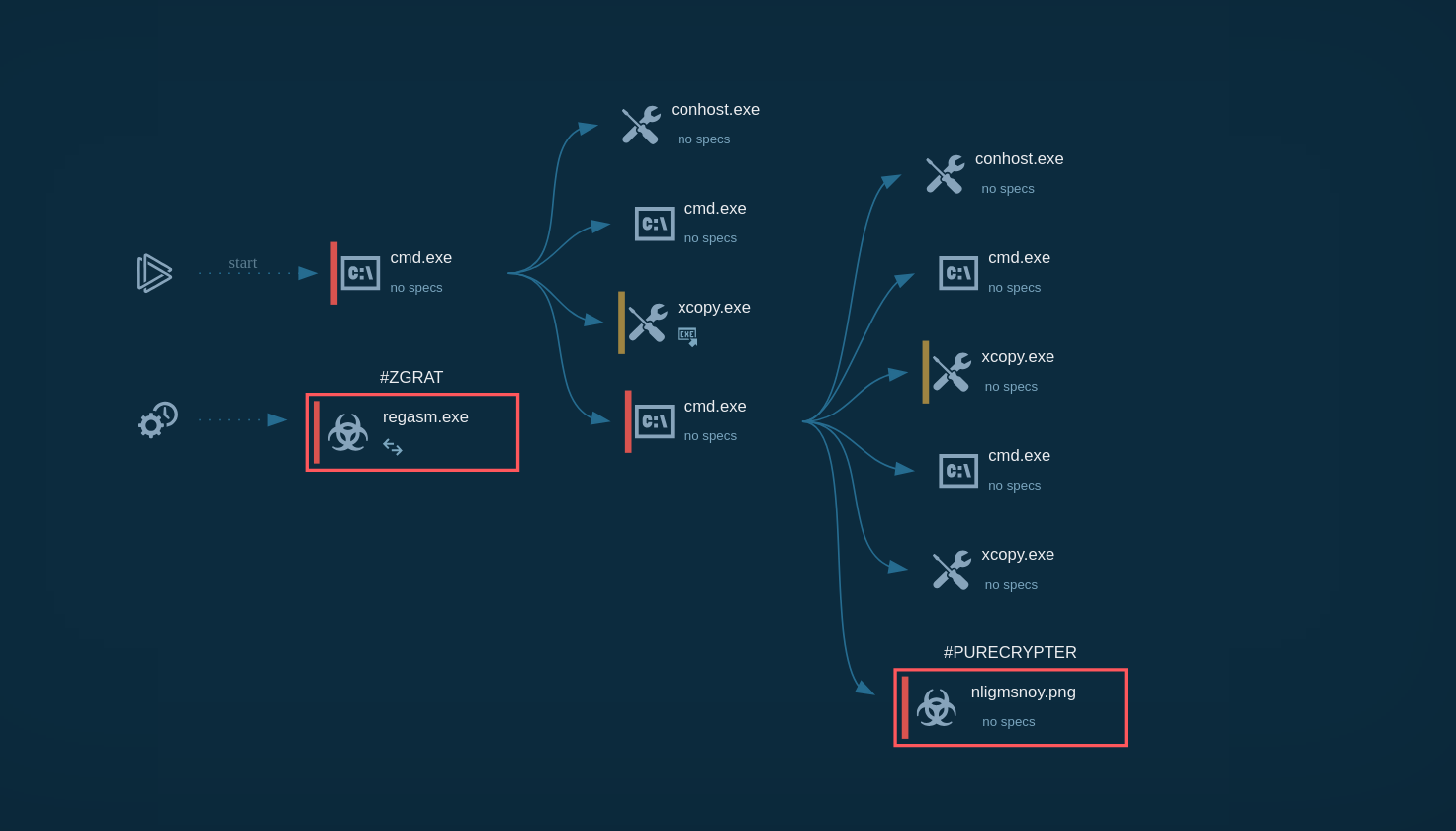
Parallax utilizes various techniques to infect targeted systems and establish persistence within them. In our analysis, it's evident that this malware generates a child process that promptly initiates malicious activities, including the theft of personal data, execution of injected code in a separate process, and the creation of files in the startup directory. Parallax employs injection techniques to conceal itself within legitimate processes, rendering detection challenging. In this instance, it is injected into the Explorer.exe system process. Furthermore, the Remote Access Trojan (RAT) also establishes connections to a Command and Control (C2) server to receive additional instructions.
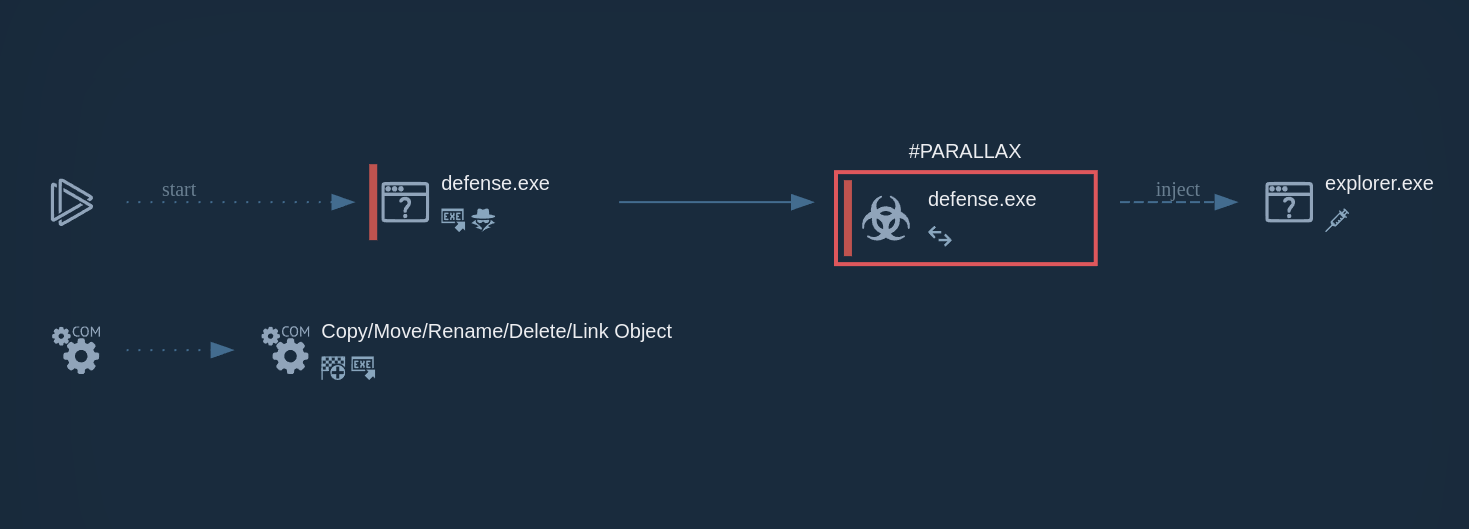 ParallaxRAT's process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
ParallaxRAT's process graph demonstrated in ANY.RUN
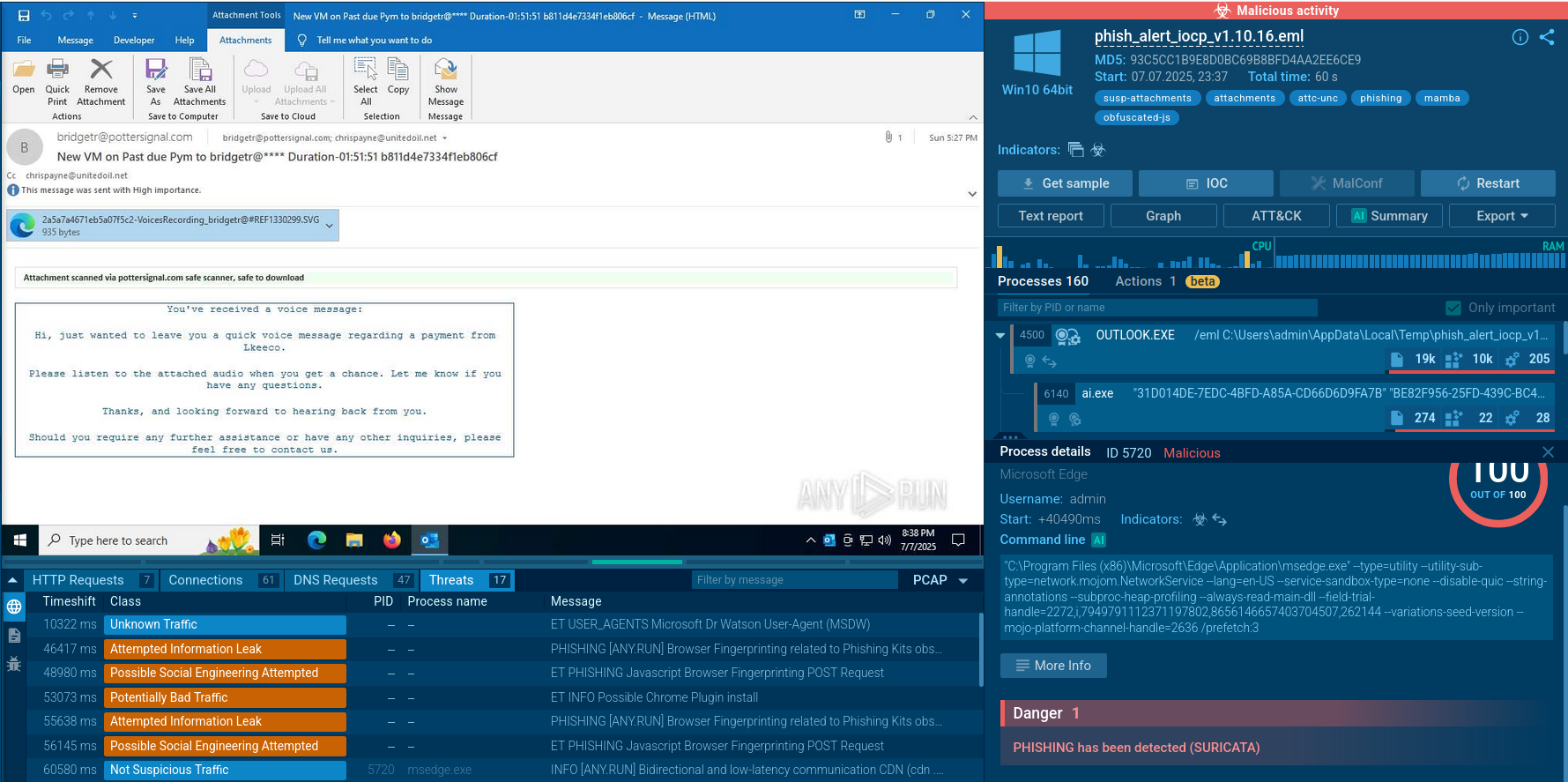
Attackers that engage in the distribution of Parallax RAT typically leverage phishing campaigns. They use emails impersonating trusted entities (e.g., banks) with malicious attachments or links. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many ParallaxRAT campaigns involved sending victims messages with attached archives that contained files responsible for further infection of the victim’s device.
Parallax RAT's reliance on email-based social engineering makes it crucial for organizations to ensure that there are appropriate mechanisms in place to prevent infection. One of the essential elements of a layered defense strategy is a malware analysis sandbox. It offers an isolated environment for safely executing any file or opening a link to determine if it poses a danger.
ANY.RUN is a malware analysis sandbox that provides an effortless cloud-based experience for analyzing files and links. The service swiftly identifies ParallaxRAT and dozens of other malware families and provides users with conclusive reports on the threat, featuring the malware’s TTPs and IOCs.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!