Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Blank Grabber is an infostealer written in Python. It is designed to steal a wide array of data, such as browser login credentials, crypto wallets, Telegram sessions, and Discord tokens. It is an open-source malware, with its code available on GitHub and regularly receiving updates. Blank Grabber builder’s simple interface lets threat actors even with basic skills to deploy it and conduct attacks.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 966
966
 0
0

 568
568
 0
0

 2918
2918
 0
0
Blank Grabber is an infostealer that has been openly distributed through Github since 2022. According to its developer, the software is intended for educational purposes only. However, this does not prevent threat actors from using it in malicious activities to infect devices and steal victims’ credentials, crypto wallets, and other sensitive data.
Currently, the original Blang Grabber GithHub repository is no longer active due to the author’s withdrawal from the project, but the official Blank Grabber fork is actively maintained and regularly receives new updates.
The stealer is written in Python, which lets attackers abuse legitimate services such as the Python Package Index by uploading malicious packages containing Blank Grabber.
Due to the open-source nature of the malware, threat actors can create different versions and add new components. It is also relatively simple to deploy and offers a graphical interface builder, allowing even low-skilled individuals to leverage it to conduct attacks.
Blank Grabber can steal a wide range of data, including:
Blank Grabber also employs the WMIC tool to gather details about the infected system, such as operating system, hardware specifications (CPU, GPU, memory), and software versions. It is equipped with the capabilities to take screenshots and webcam images.
The malware is particularly popular among criminals targeting gamers. This is why it is widely utilized for stealing victims’ Roblox and Minecraft files, as well as Steam, Epic Games, and Uplay data.
Blank Grabber possesses built-in features for evading detection. The code of the program is often obfuscated to make it harder for security researchers to analyze. Attackers also can enable anti-sandboxing to stop the malware’s execution from running in a virtual environment.
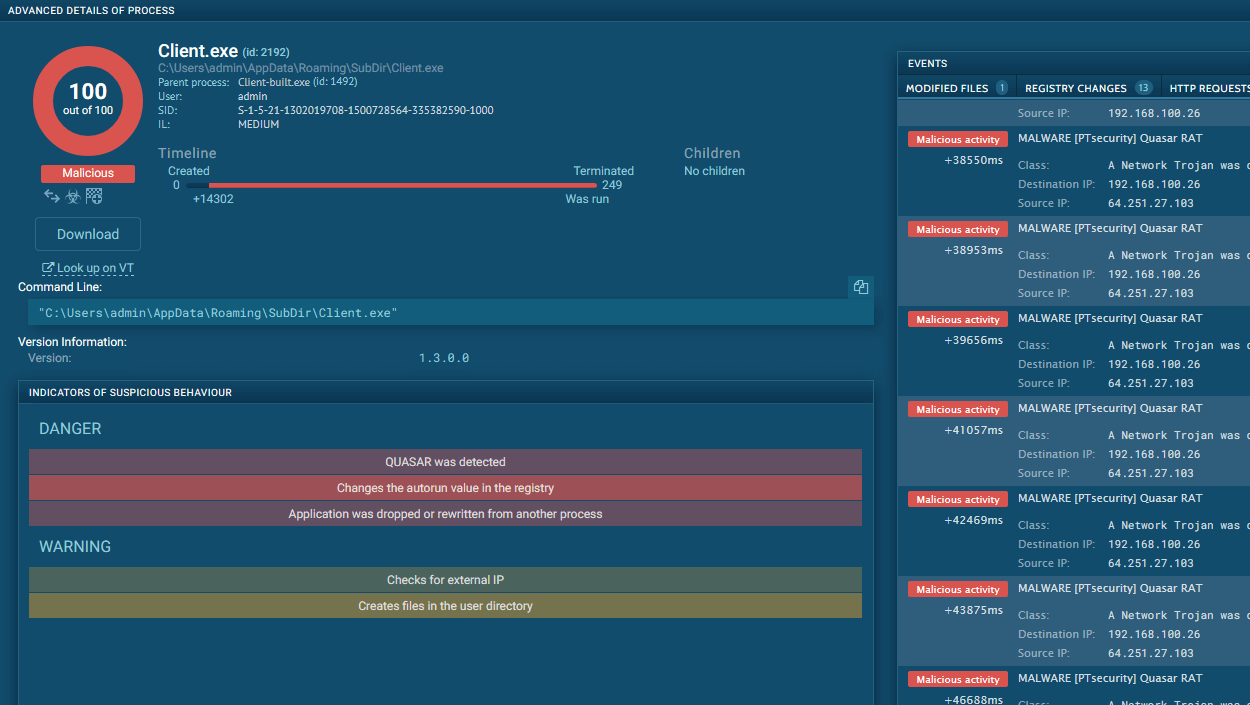
Blank Grabber can disable Windows Defender and bypass User Account Control (UAC) on Windows systems, gaining elevated privileges.
Attackers employing the Blank Grabber malware leverage Discord and Telegram webhooks for communication and extraction of stolen information. With this approach, conventional Command and Control (C2) infrastructure is no longer required, which lowers the entry barrier for less experienced threat actors to carry out such cyber attacks.
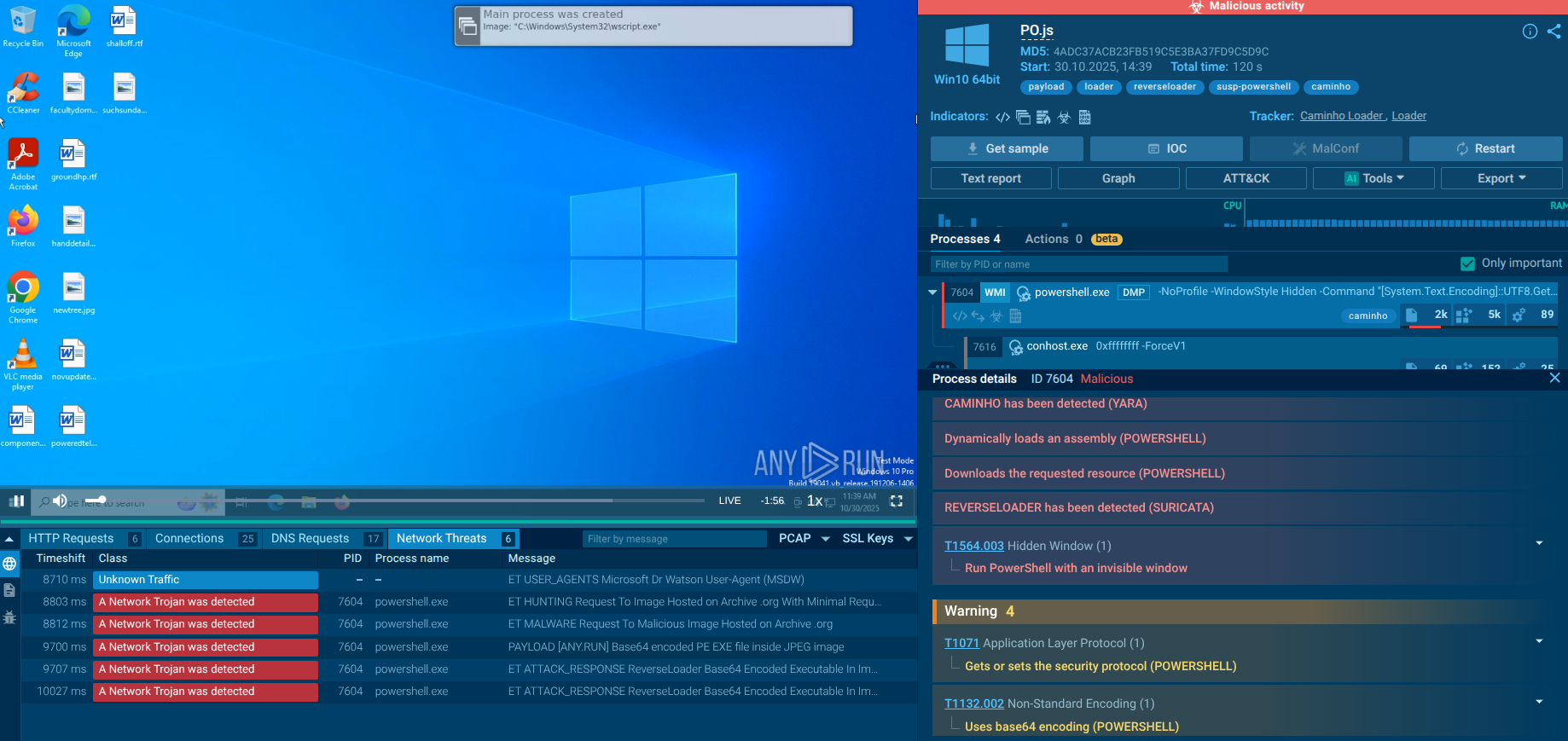
Let’s analyze a sample of Blank Grabber in the ANY.RUN sandbox to see how it operates.
The execution chain of Blank Grabber often involves one or two processes that carry out all the malicious activities themselves. However, it can be very complex and may involve the use of system utilities.
The execution chain of Blank Grabber begins with the delivery of a malicious payload through a phishing email or compromised website. Once the payload is executed, Blank Grabber injects itself into legitimate processes to evade detection. It then establishes persistence by creating registry entries or scheduled tasks. Next, it communicates with a command-and-control server to receive instructions and updates. Blank Grabber then scans the infected system for sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, and personal information. Finally, it exfiltrates the collected data to a remote server controlled by the attackers for further exploitation.
In this analysis session in the ANY.RUN malware sandbox, Blank Grabber executes a series of commands:
The sandbox detects the malicious behavior of Blank Grabber, indicating it with the tags “blankgrabber” and “stealer”.
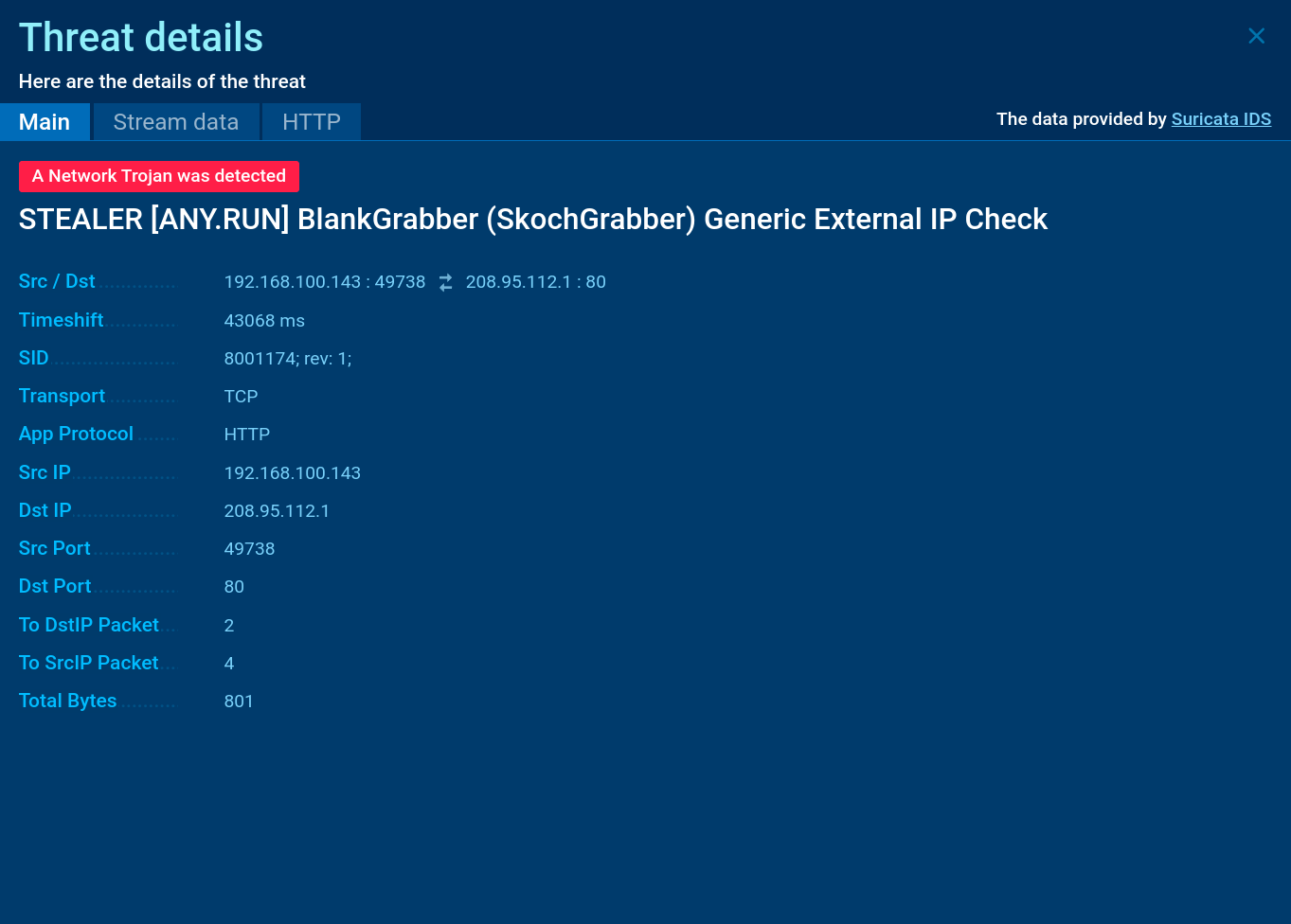 Blank Grabber Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
Blank Grabber Suricata rule shown in ANY.RUN
Unlike some of the popular infostealers, such as FormBook and RisePro, Blank Grabber is rarely distributed via phishing emails. Instead, attackers prefer to mask it as software for gamers, hosting it on GitHub and similar platforms. There are also instances when the malware was found in legitimate repositories. Another common way of spreading Blank Grabber is via direct message on Discord.
Blank Grabber’s advanced features, evasion mechanisms, and wide accessibility make it a significant threat to user data. To prevent infection, it is crucial for organizations and individuals to analyze any suspicious files and links using a reliable security tool.
The ANY.RUN sandbox delivers safe and reliable virtual environments for conducting extensive malware behavior analysis and produces reports with critical information, like IOCs and TTPs. Analysts can use the analysis results to make well-informed decisions and improve their security against threats like Blank Grabber.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!