Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


SVCStealer is an information-stealing malware targeting sensitive user data through spear-phishing email attachments. It systematically extracts credentials, financial data, and system information from various applications, including browsers and messaging platforms.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2025
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2025
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
SVCStealer, an information-stealing malware, was first identified in late January 2025 by SEQRITE researchers. It is written in Microsoft Visual C++ and designed to harvest sensitive data from compromised systems:
SvcStealer focuses both on individuals and on business sectors with valuable data, such as finance, telecommunications, and healthcare. It primarily gains access through spear phishing attacks, where malicious email attachments trick users into executing the malware. These attachments often masquerade as legitimate files to exploit user trust. Social engineering is also engaged with messages posing as legitimate communications, often mimicking trusted entities like Google Meet or medical centers.
Once executed, the malware establishes a foothold on the victim's system and connects to C2 servers to receive further instructions or exfiltrate data. It does not rely on complex network infiltration but uses phishing as the primary vector.
SvcStealer maintains persistence by continuously beaconing to its C2 server, awaiting further commands, which may include downloading additional payloads.
It does not rely on traditional persistence mechanisms like registry modifications or scheduled tasks but ensures ongoing communication with its C2 server using backup IP addresses if the primary connection fails.
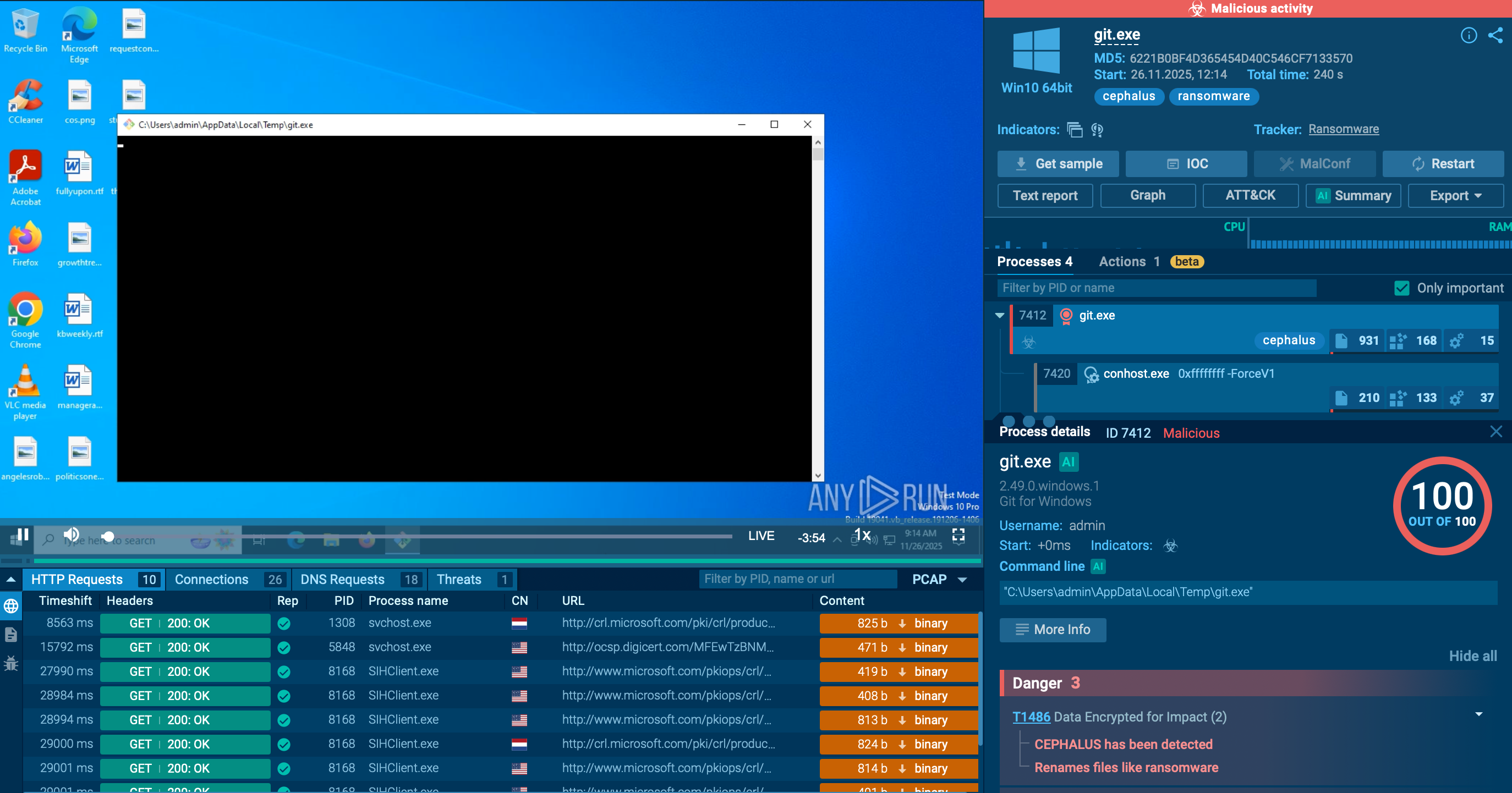
In spite of being quite recently discovered, SVCStealer has already been actively researched by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox users including over 500,000 threat analysts and 15,000 SOC businesses. We can choose a public analysis session of the stealer’s sample and watch its execution chain:
View the analysis and gather actionable data.
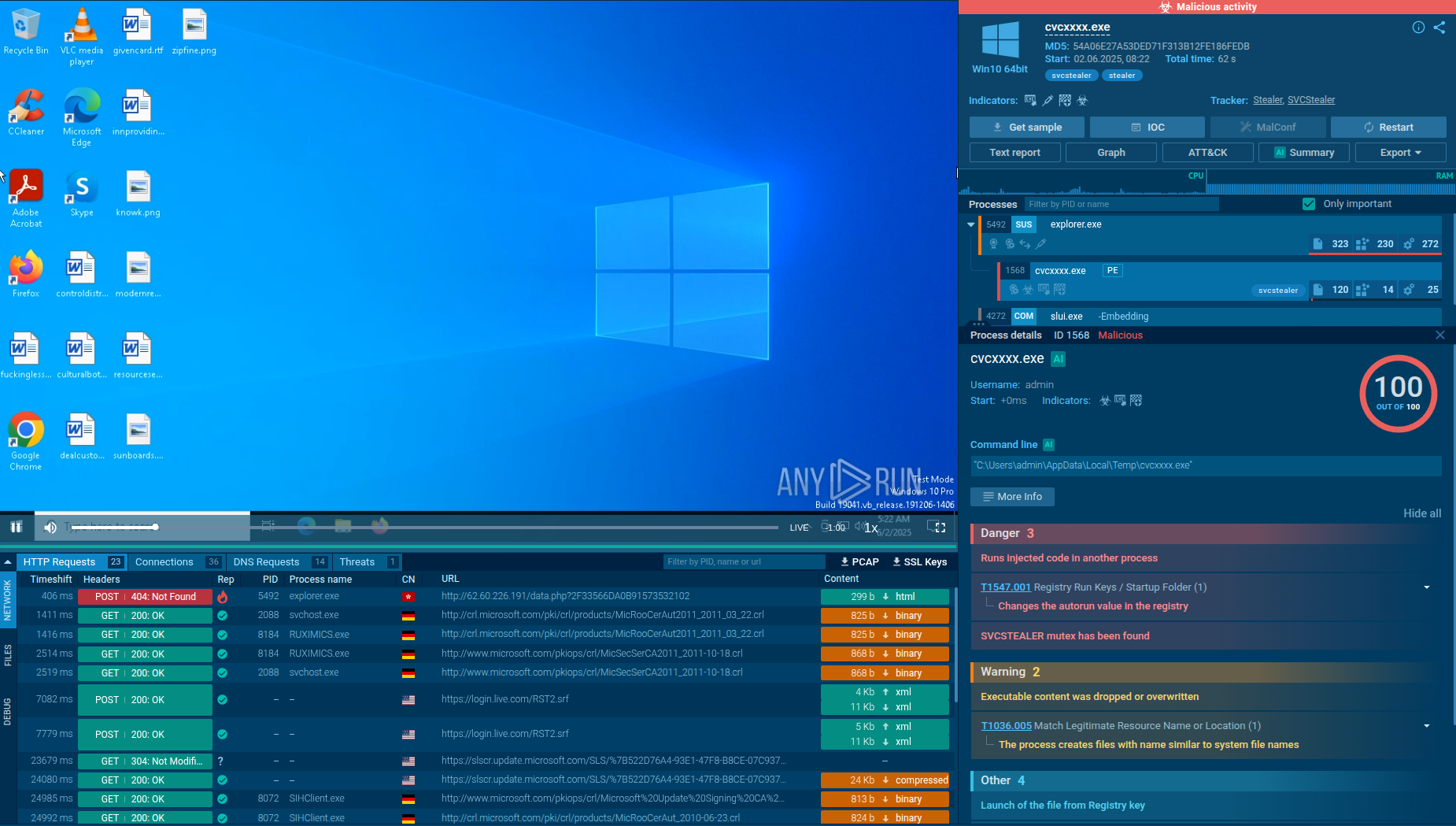 SVCStealer sample in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
SVCStealer sample in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
SvcStealer is primarily distributed via spear-phishing emails that contain malicious documents or executables. When executed, it generates a unique 11-character alphanumeric folder name derived from the volume serial number of the infected system’s root directory. This folder is created in either the “C:\ProgramData” or “%AppData%” path. This method ensures that only one instance of the malware runs on the system. If the folder already exists, SvcStealer terminates itself to prevent multiple infections, functioning similarly to a mutex.
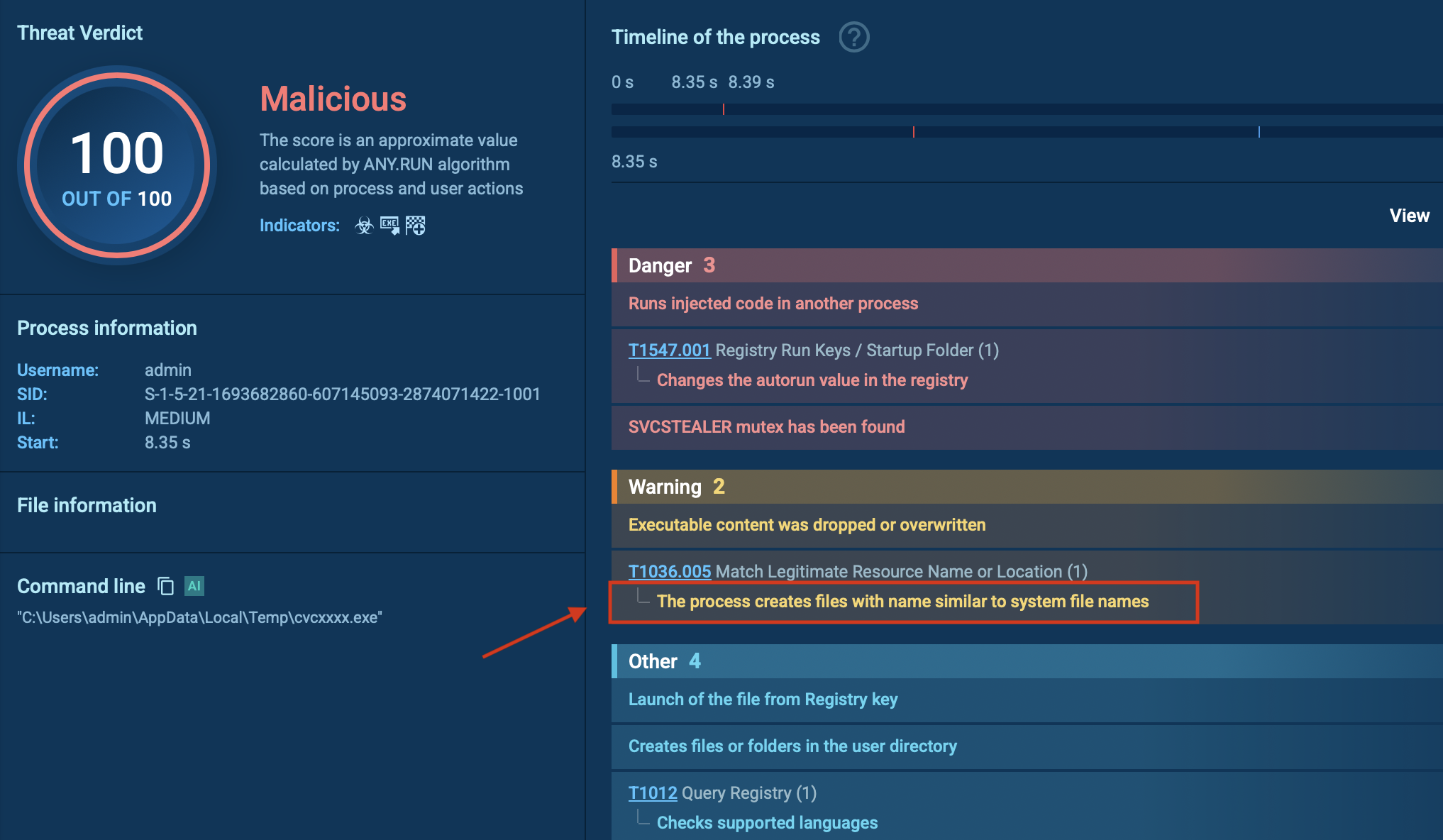 SVCStealer creates the folder with name similar to system name
SVCStealer creates the folder with name similar to system name
Once active, SvcStealer attempts to evade detection by terminating common system monitoring and analysis tools. It targets processes such as Taskmgr.exe, ProcessHacker.exe, procexp.exe, and procexp64.exe. This prevents administrators and security software from identifying its activity.
The malware then begins harvesting sensitive information from the victim’s machine. It collects cryptocurrency wallet data stored in a dedicated “Wallets” folder, along with credentials and data from messaging applications like Discord, Telegram, 64gram, and Tox.
Browser data is also targeted, including content from Google Chrome, Opera, Microsoft Edge, Brave, and other browsers. This browser data often includes saved passwords, credit card details, browsing history, and other stored information. In addition, SvcStealer gathers system information, lists of installed applications, running processes with their process IDs, screenshots of the desktop, and files with specific extensions such as .jpg, .pdf, .docx, and .wallet.
After completing data collection, the malware compresses the harvested information into a ZIP archive within the generated folder. It then attempts to connect to its Command and Control (C2) server over HTTP using port 80. The stolen data is typically exfiltrated via HTTP POST requests. Once the transmission is successful, SvcStealer deletes the ZIP file and other artifacts to cover its tracks and minimize detection.
SvcStealer’s primary focus is data theft rather than extensive lateral movement. However, it can facilitate lateral movement by downloading additional tools or malware (e.g., via C2 commands) that enable network reconnaissance or privilege escalation. Its ability to act as an entry point for secondary payloads suggests potential for lateral movement if instructed by the attacker, though no specific lateral movement tactics are documented.
Leverage threat intelligence solutions like ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup to gather indicators of compromise associated with SvcStealer campaigns and block them in your network. You can start your research with the malware’s name and further investigate found IOCs with over 40 search parameters in TI Lookup.
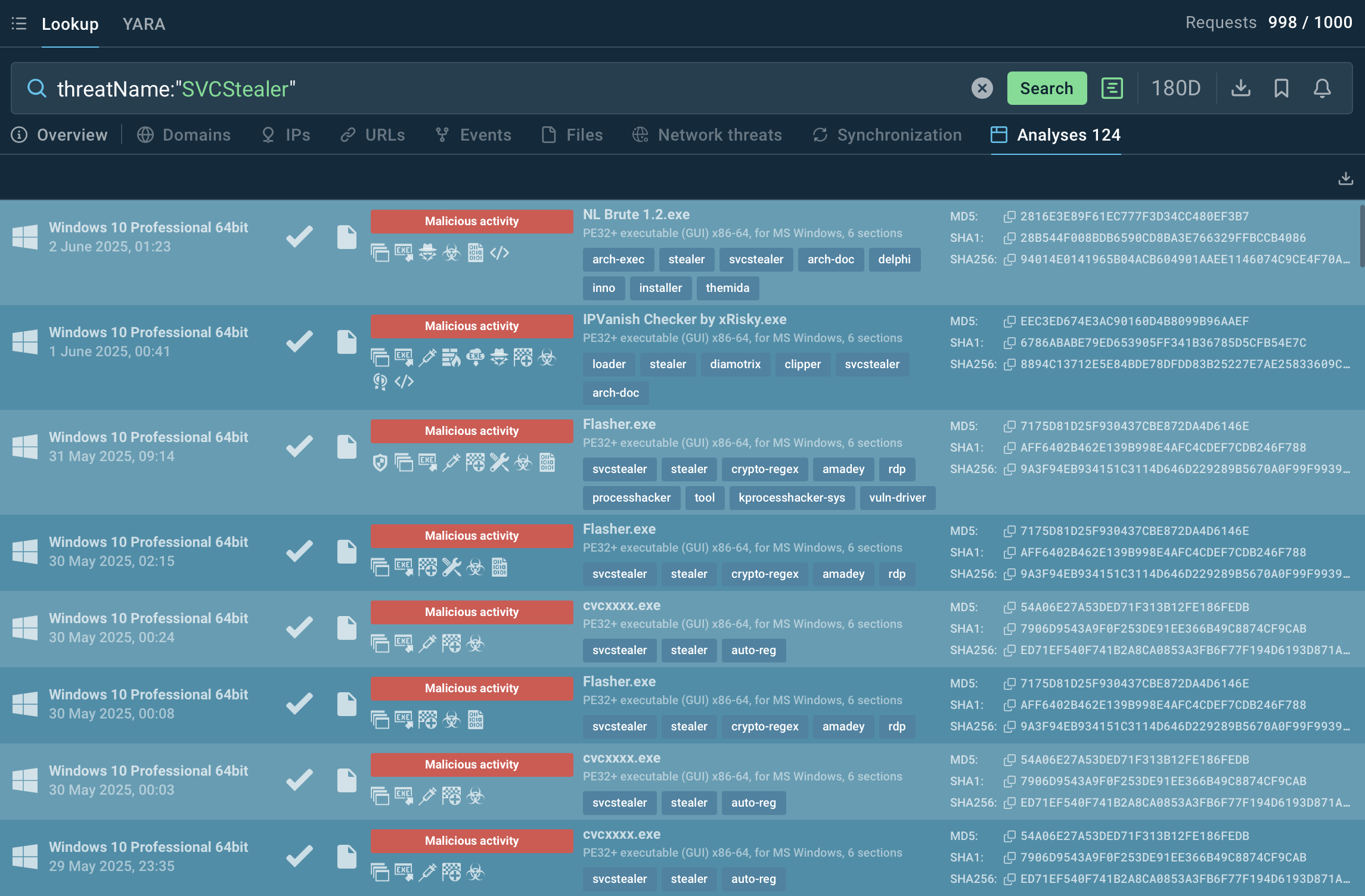 Analyses of SVCStealer samples found via TI Lookup
Analyses of SVCStealer samples found via TI Lookup
SVCStealer is a dangerous info-stealer with advanced evasion techniques, primarily targeting credentials and financial data. Defending against it requires a mix of endpoint security, network monitoring, and user awareness. Organizations should employ threat intelligence to stay updated on new variants and attack methods.