Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Mamba 2FA is an advanced phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform designed to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and target Microsoft 365 accounts. It focuses on intercepting authentication flows in real-time and enables threat actors to hijack user sessions and access sensitive systems even when additional security measures are in place.
|
Phishingkit
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Mamba 2FA is part of a growing class of malware that specifically targets multi-factor authentication mechanisms. It is a sophisticated phishing toolkit that leverages AiTM techniques to intercept user credentials and MFA tokens in real time.
The malware, which has been scrutinized and investigated by multiple researchers, including ANY.RUN's analyst team, mimics legitimate Microsoft services, such as OneDrive, SharePoint, and voicemail systems, using highly convincing fake login pages. It is marketed on Telegram and sold for as low as $250 per month, making it accessible to a wide range of threat actors, from novices to seasoned cybercriminals. Its infrastructure has evolved since its first documentation to include proxy servers and regularly updated phishing URLs to evade detection.
It typically operates by injecting malicious code into browsers, intercepting authentication tokens, or manipulating session cookies. Some variants also incorporate phishing components and man-in-the-browser (MitB) capabilities. Mamba 2FA attacks are highly targeted and often occur during high-value transactions or sensitive logins, making them especially dangerous for businesses, financial services, and critical infrastructure.
Mamba 2FA primarily targets users of Microsoft 365, including both enterprise and consumer accounts. Organizations relying on non-phishing-resistant MFA methods, such as one-time passwords (OTPs) and app notifications, are particularly vulnerable.
Industries with heavy Microsoft 365 usage, such as finance, healthcare, and technology, are prime targets due to their valuable data and reliance on cloud-based services. The platform’s ability to customize phishing pages to reflect corporate branding makes it especially effective against employees who may not recognize the signs of phishing.
Geographically, campaigns have been observed in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, often coinciding with politically or economically motivated attacks.
While Mamba 2FA itself is not a traditional malware that installs malicious code on endpoint devices, its impact is significant. Once a user enters credentials and MFA tokens on a phishing page, attackers gain immediate access to the victim’s account. This can lead to:
Unauthorized Access: Attackers can log into Microsoft 365 accounts, accessing sensitive emails, files, and data stored in OneDrive or SharePoint.
Data Theft: Sensitive information, such as financial records or intellectual property, can be exfiltrated.
Account Takeover: Attackers can change account settings, lock out legitimate users, or use the account for further malicious activities, such as sending phishing emails to other users.
Lateral Movement: Compromised accounts can serve as entry points for broader network attacks, potentially leading to ransomware or data breaches.
Mamba 2FA poses a severe threat to businesses due to its ability to bypass MFA, a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. The platform’s low cost and ease of use democratize advanced phishing capabilities, enabling even low-skill attackers to execute sophisticated campaigns. Key threats include:
Typically, this malware:
Core operations are organized through a two-layer infrastructure:
The platform supports non-phishing-resistant MFA methods, integrates with Entra ID, AD FS, and third-party SSO providers, and instantly transmits stolen credentials and cookies via Telegram bots. It also employs sandbox detection to block automated security scans, enhancing its stealth.
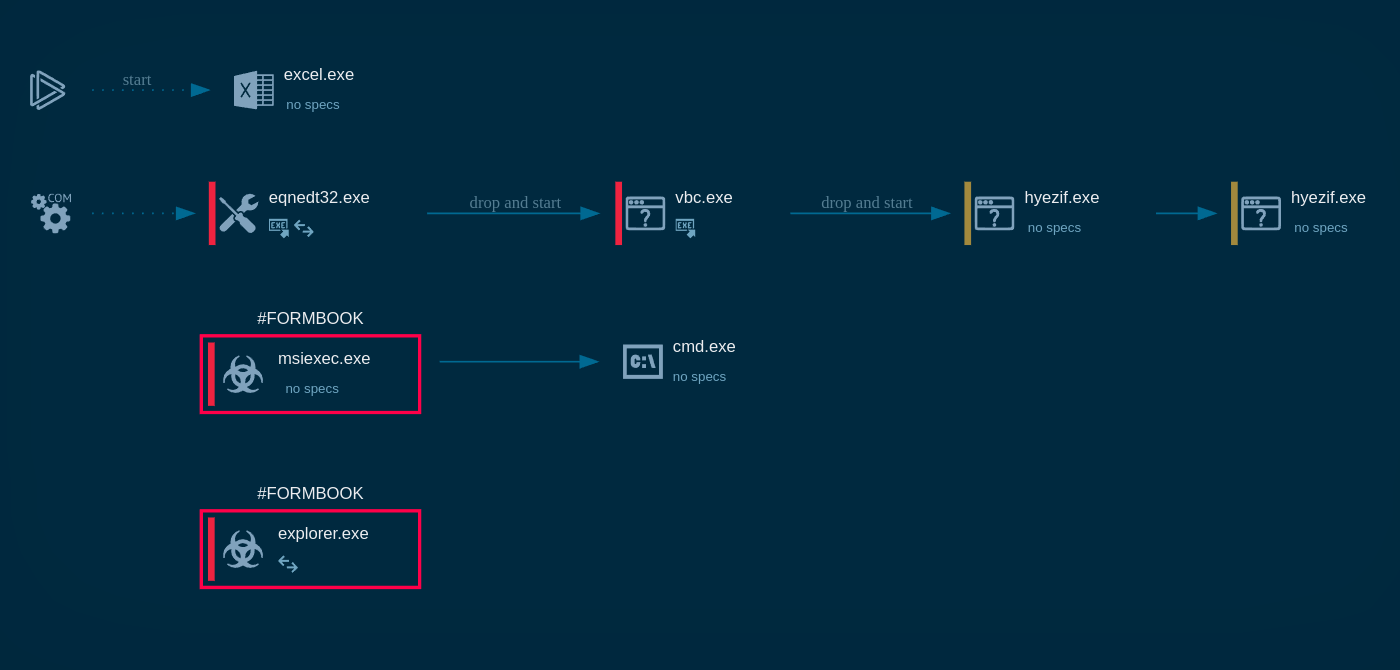
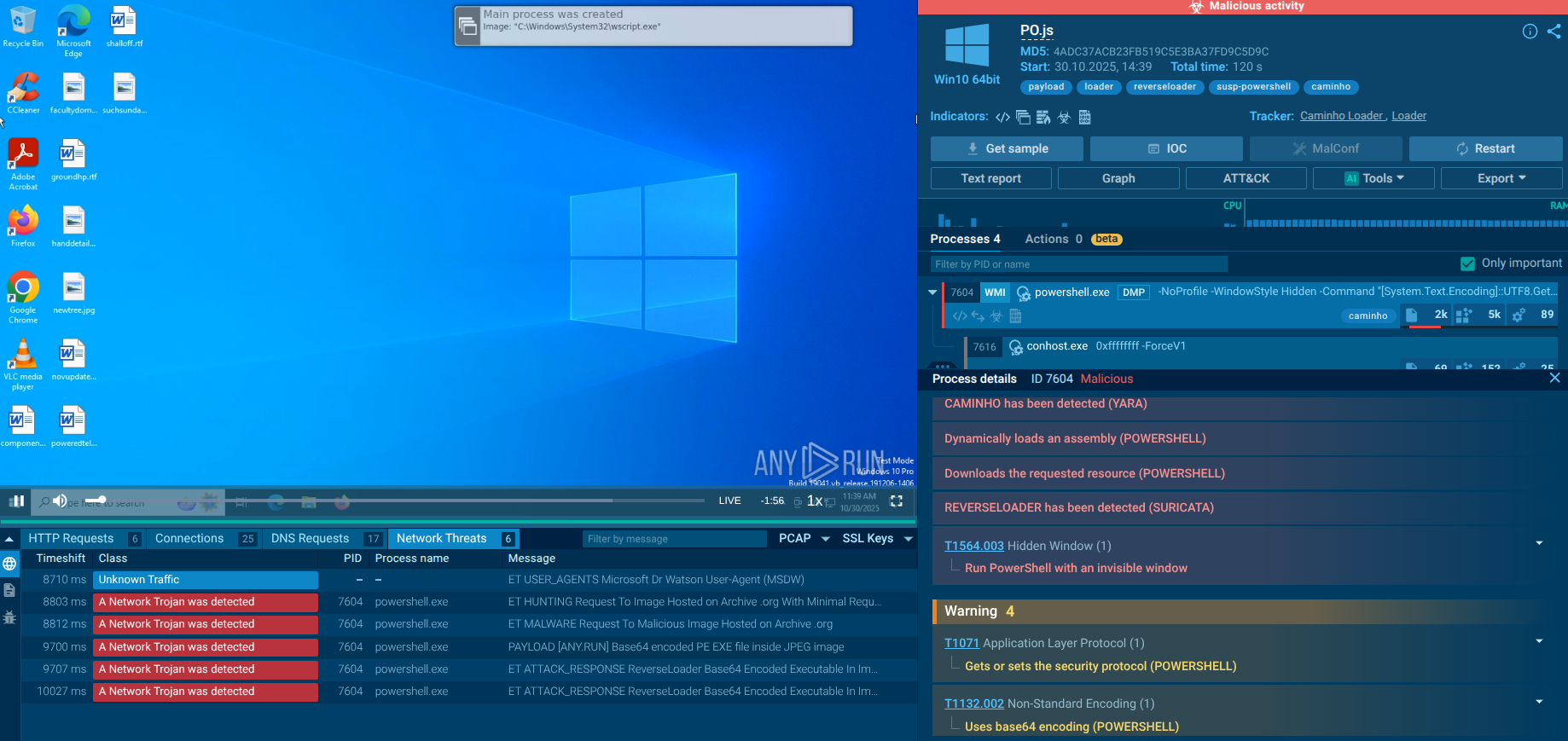
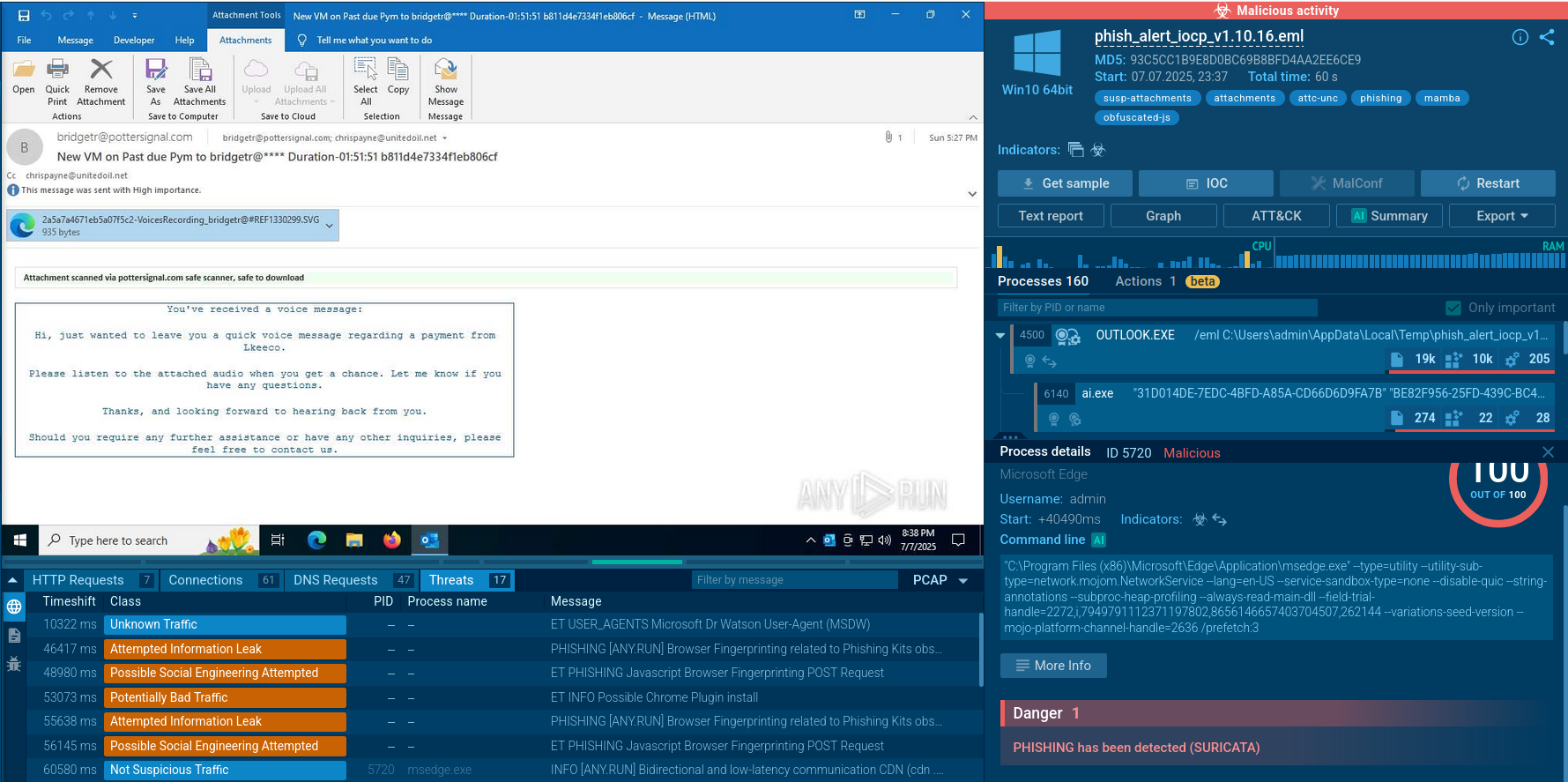
The primary attack vector for Mamba 2FA is phishing emails, which serve as the initial point for luring victims outside the secure perimeter of corporate environments. The HTML attachments contain obfuscated JavaScript code that redirects users to phishing pages, often hosted on services like Cloudflare R2 or IPFS.
Common lures include:
Voicemail notifications, often with an SVG file.
File access notifications for OneDrive/SharePoint.
Payment or invoice receipts.
Password expiration notices.
Each of these delivery methods can be detonated and effectively analyzed in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox service using its ML functionality.
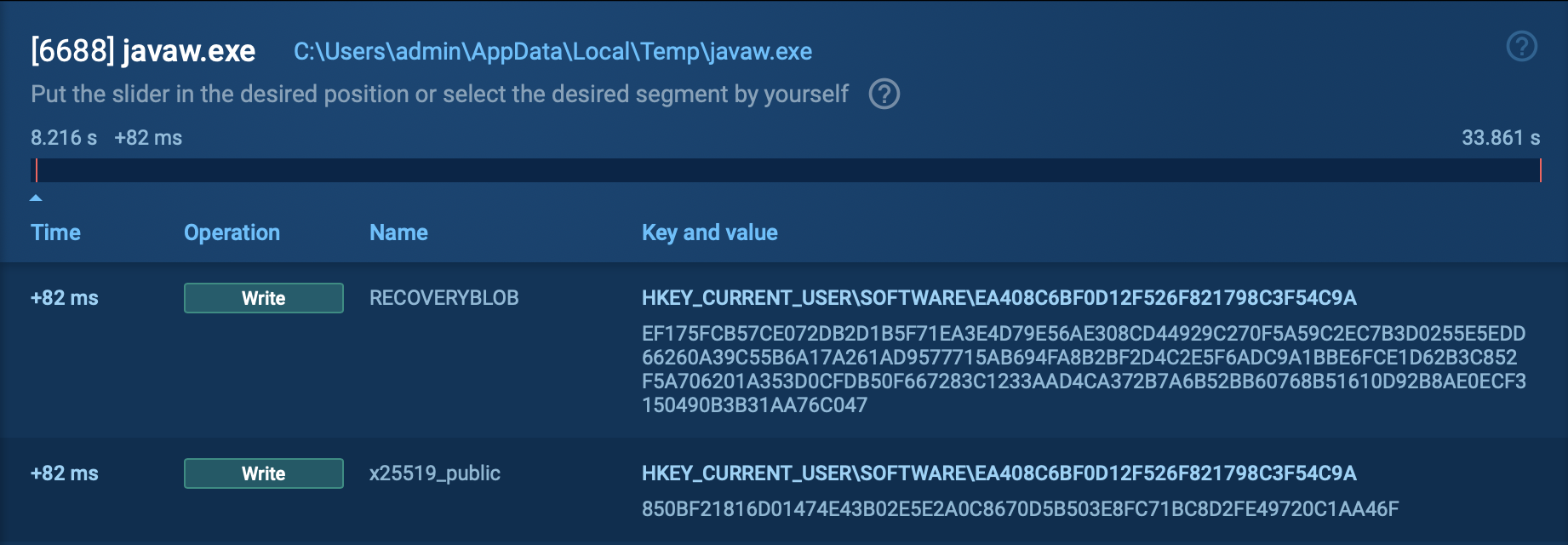
Sandbox analysis of Mamba 2FA sample with a voice message notification
Mamba 2FA analysis in the Sandbox
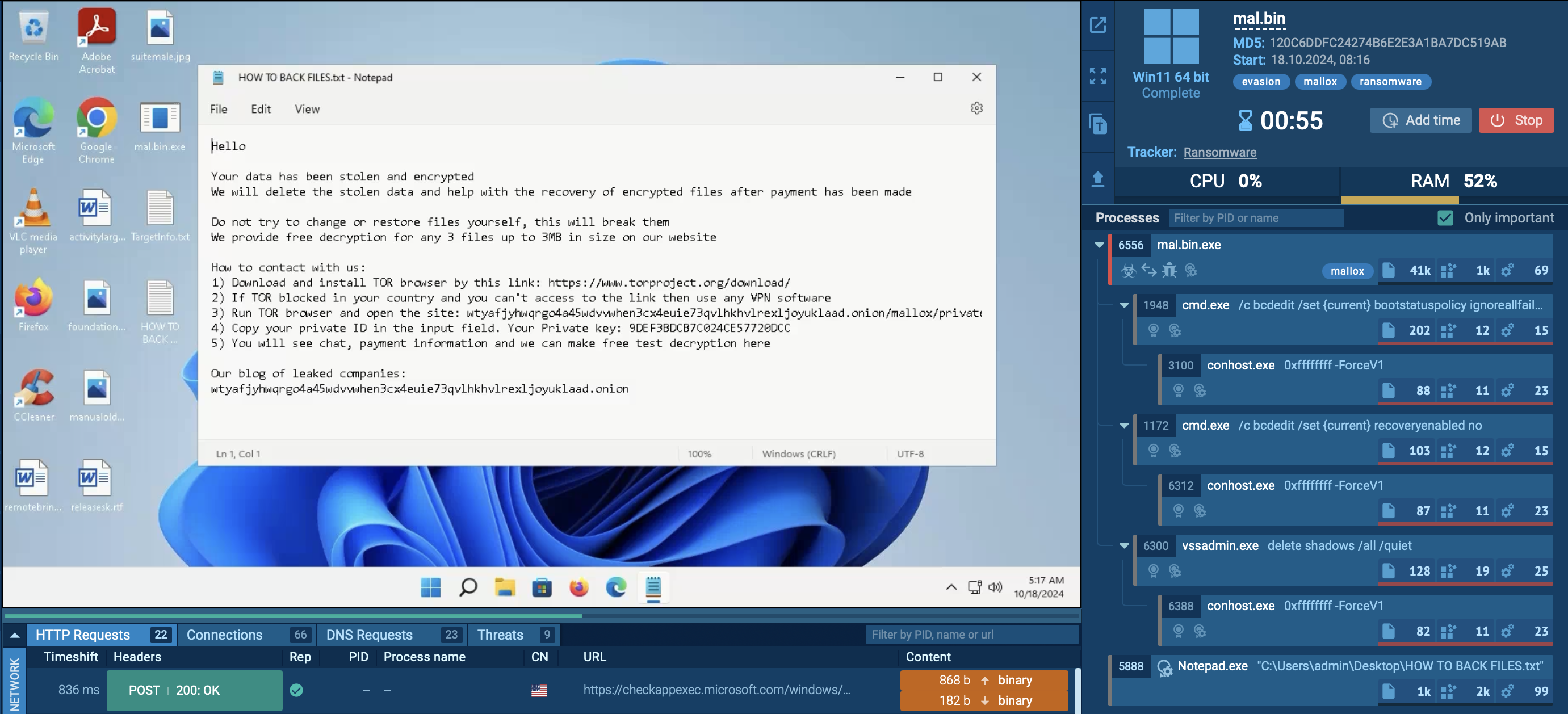
Sandbox analysis of Mamba 2FA sample with a password expiration notice
Another Mamba 2FA sample detonated in the Sandbox
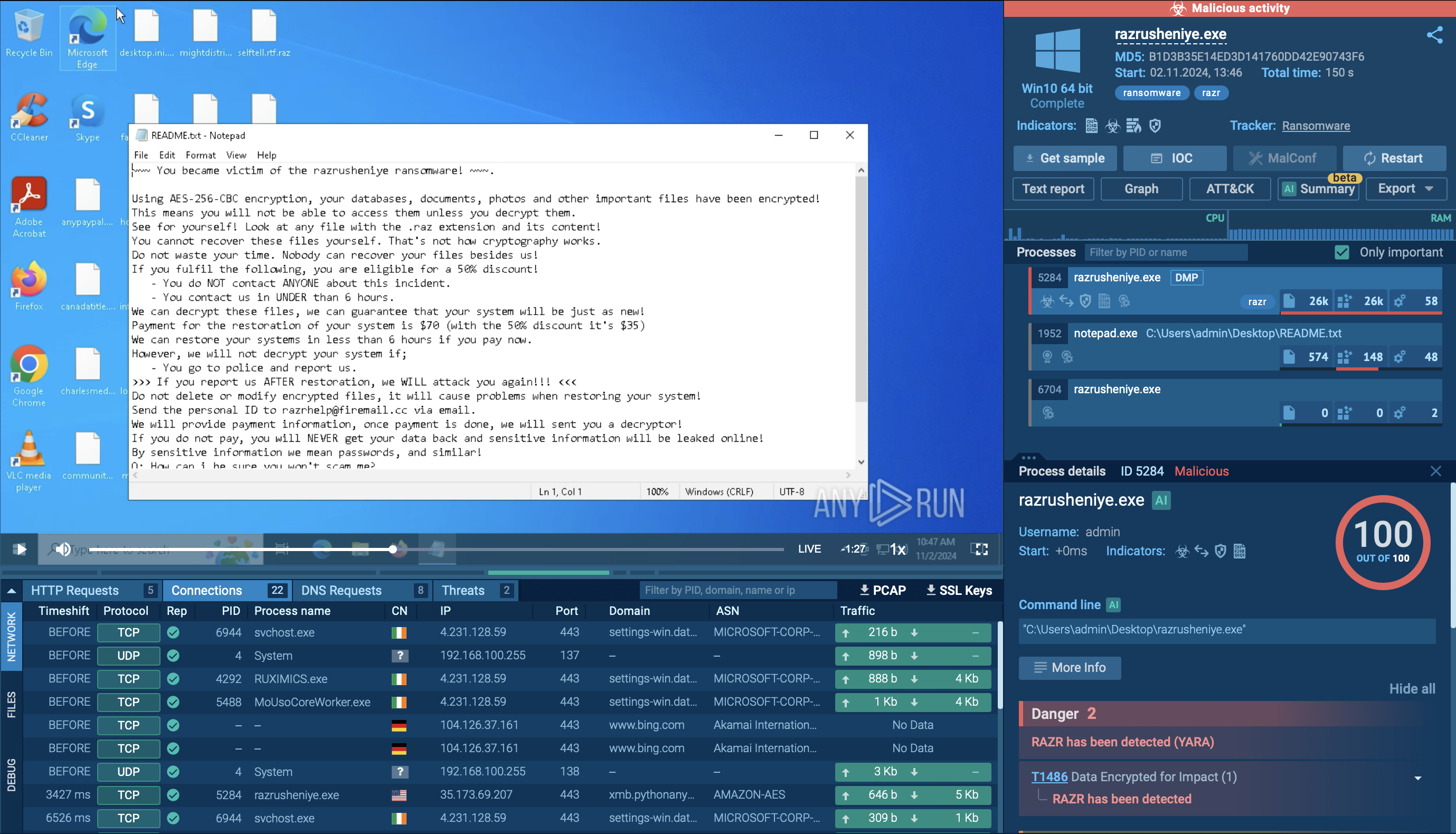
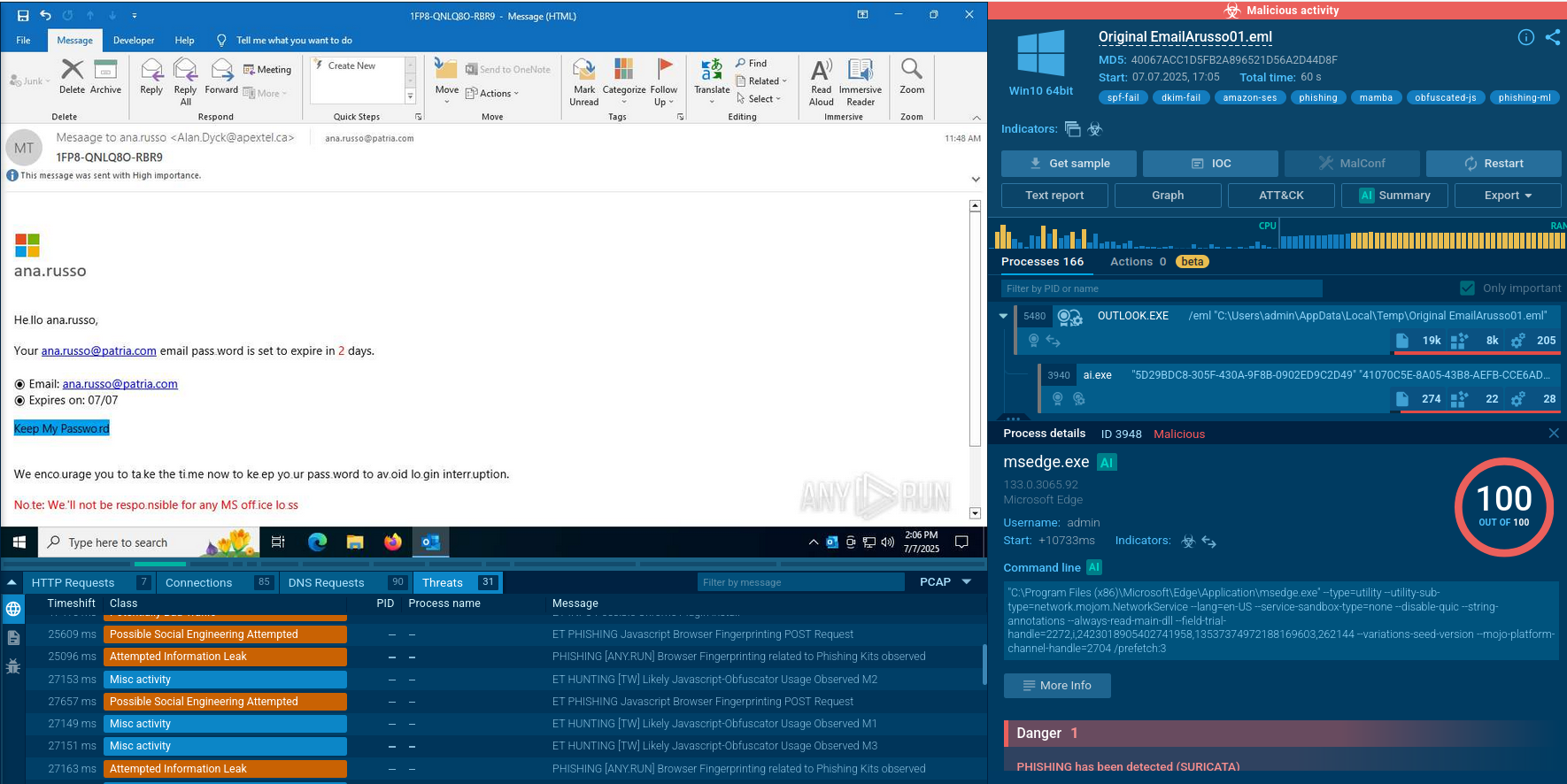
Mamba 2FA uses a fingerprinting mechanism to filter users before redirecting to either a phishing or benign page. After clicking the link from the phishing email, the victim lands on a filtering page that collects device and browser data. This data is sent to a server that decides whether to redirect the user to a phishing page mimicking Microsoft services or to a safe dead-end page. Fingerprinting transmission can be tracked through the Suricata rule "ET PHISHING Javascript Browser Fingerprinting POST Request".
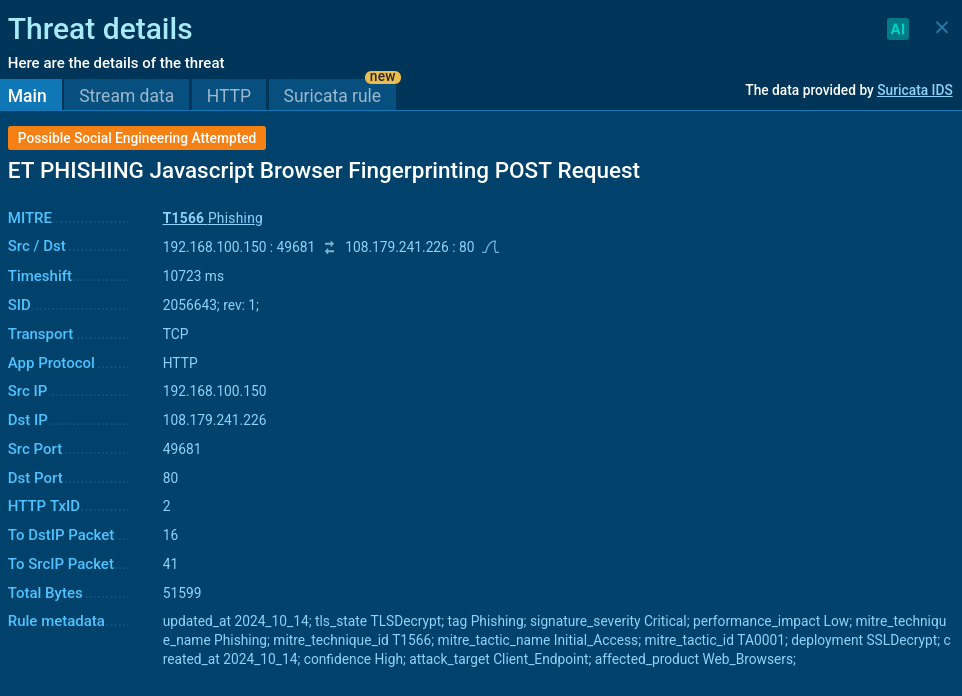
Fingerprinting request in Mamba 2FA activity
After passing filtering, the user is redirected to a phishing page created based on templates that mimic Microsoft authorization pages, including OneDrive and SharePoint. For corporate accounts, Mamba 2FA pulls backgrounds and icons corresponding to the target organization's branding using legitimate Microsoft CDNs, which increases the page's credibility. The phishing page URL typically contains a domain/base64 pattern, where parameters such as IP address, victim's email address, service identifier (e.g., Office 365), campaign, or unique user identifier are encoded in Base64 format for masking and complicating analysis.
In implementing the "Adversary-in-the-Middle" (AiTM) technique, Mamba 2FA uses the Socket.IO JavaScript library to organize real-time communication through WebSocket, which is one of the main differences from other phishing kits.
Threat intelligence is critical in combating Mamba 2FA by providing real-time insights into its infrastructure, tactics, and IOCs. It enables organizations to:
Services such as Threat Intelligence Lookup from ANY.RUN allow identifying and blocking Mamba2FA infrastructure, including domains and IPs, at the network perimeter.
Start gathering IOCs and behavioral data with the malware name search request to Threat Intelligence Lookup:
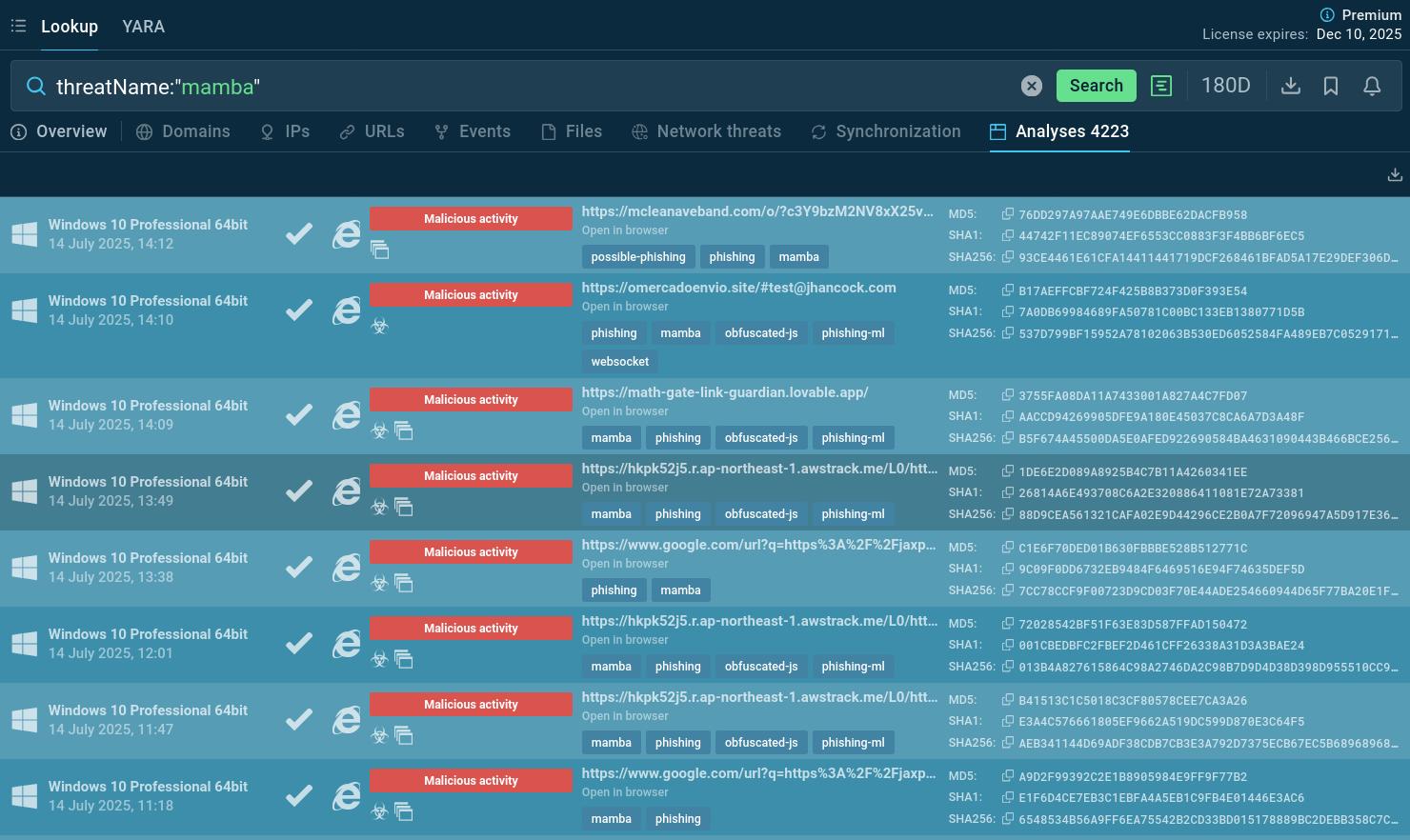 Mamba 2 FA samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
Mamba 2 FA samples recently analyzed in the Sandbox
Mamba 2FA represents a growing class of post-authentication threats capable of undermining modern security infrastructures. As more organizations adopt MFA, attackers evolve to bypass it. Understanding how Mamba 2FA works and using threat intelligence to detect and disrupt its lifecycle is essential for proactive defense. Organizations must pair robust technical controls with actionable data to stay ahead of these advanced threats.
Gather fresh actionable threat intelligence via ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup: start with 50 trial requests.