Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

GCleaner is a type of malware loader that has the capability to deliver numerous malicious software programs, which differ based on the location of the targeted victim. This malware is commonly spread through fraudulent websites that advertise free PC optimization tools
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
19 September, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
19 September, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 807
807
 0
0

 488
488
 0
0

 2743
2743
 0
0
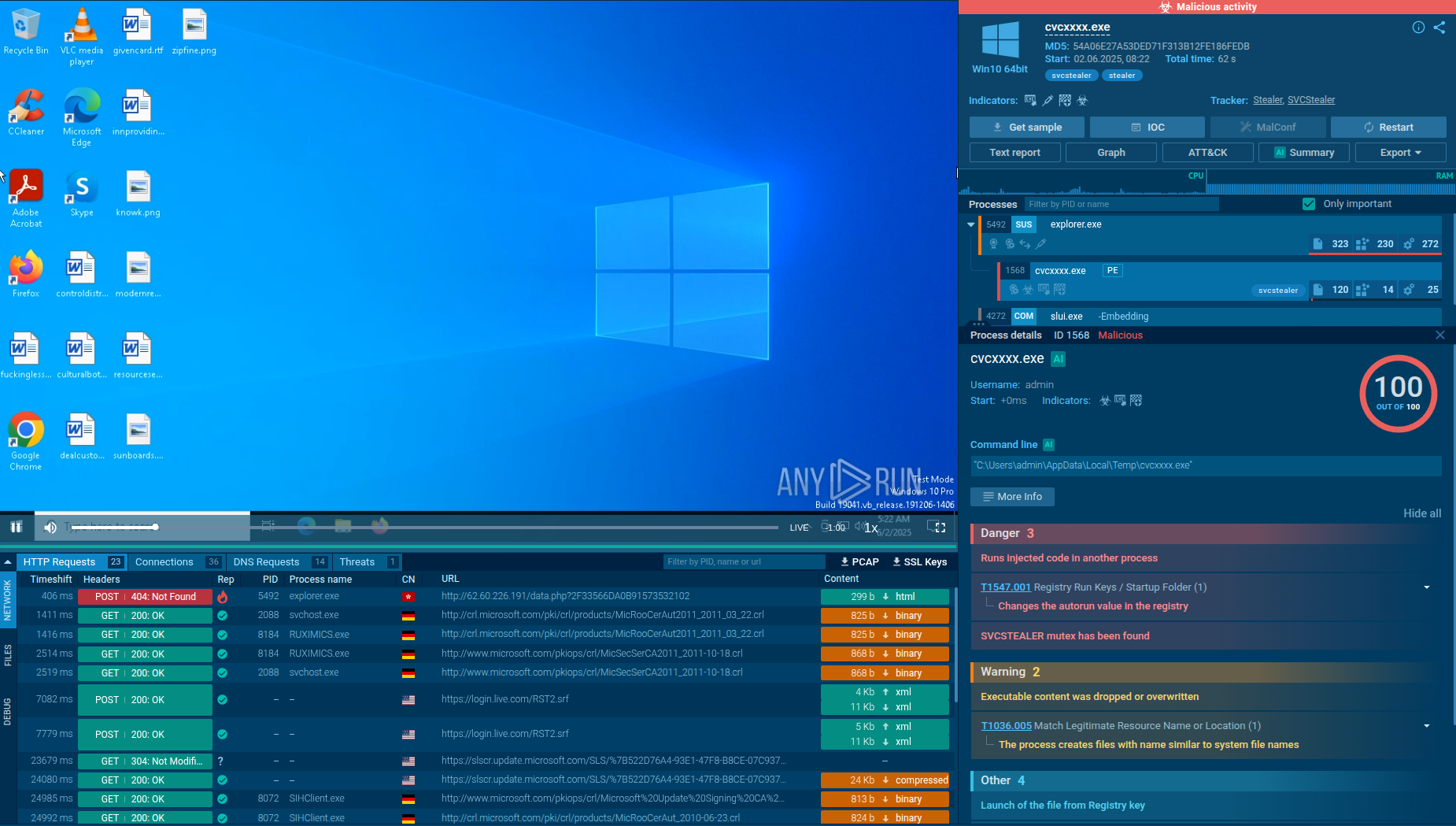
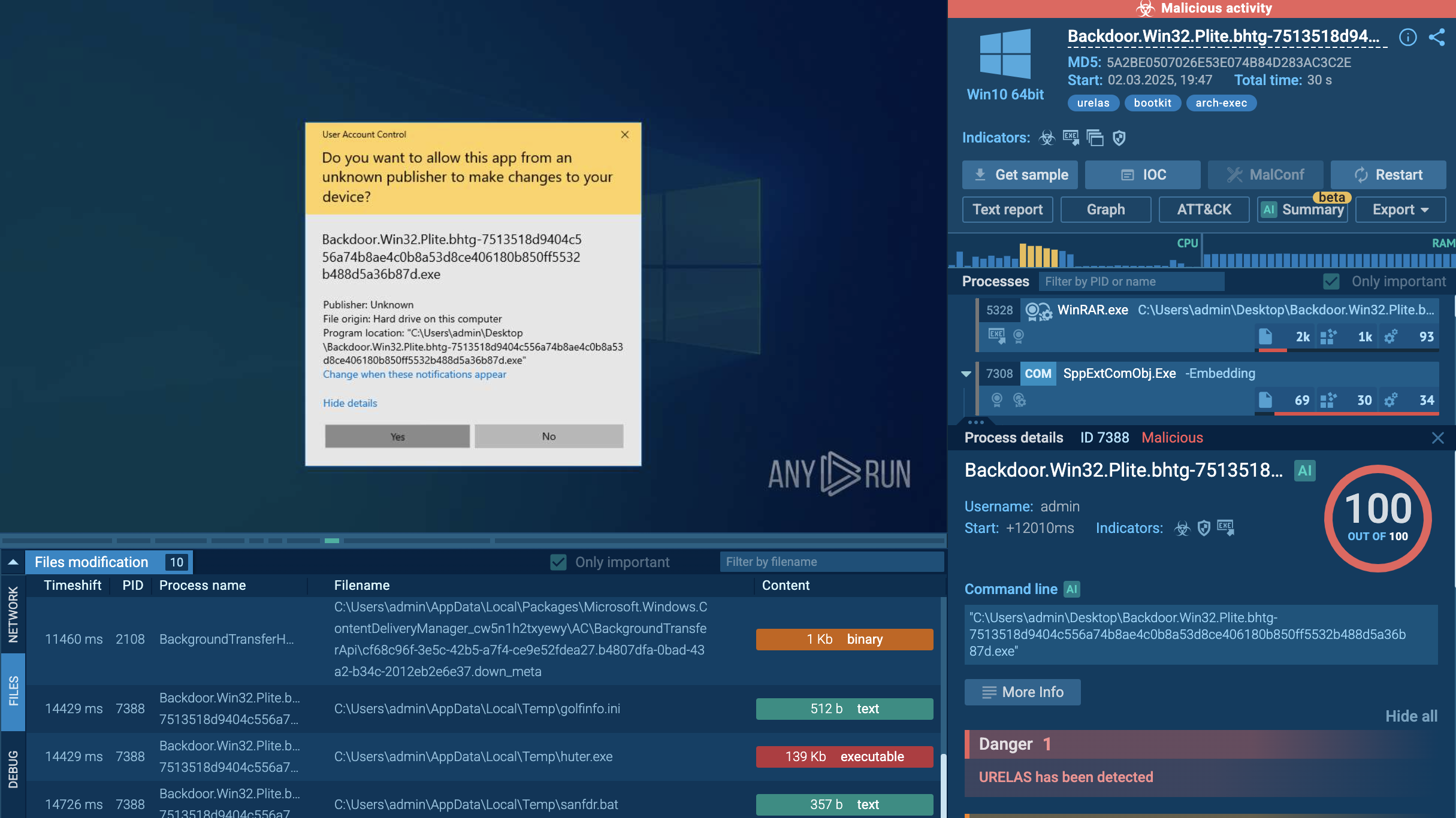
The system optimizer market has for a long time been a breeding ground for all kinds of malicious software masking as legitimate to dupe users into downloading and installing it. G-Cleaner, also known as GCleaner, is a notable example of a fake PC optimization program, appearing to be genuine at first glance. In reality, it is a loader designed with one purpose: to get hold of victims’ sensitive data.
GCleaner is a loader, which was first spotted in early 2019. It is capable of a wide variety of malicious activities depending on the payload it is equipped with. Analysts have observed it to drop malware such as AZORult, the Raccoon info stealer, Smoke Loader, RedLine Stealer, and other popular families, depending on the victim’s geographic location.
The GCleaner malware is primarily known as one of the most widespread fake Windows utilities that is intended for targeting both organizations and individuals. It attempts to capitalize on the popularity of system cleaning tools by taking advantage of people’s negligence.
The identity of the individuals responsible for developing the G-Cleaner malware remains a mystery. Nonetheless, experts in the field of cybersecurity suspect that the creation of this malicious software was the work of a highly skilled and organized criminal organization.
Once G-Cleaner is installed on a computer, it extracts a malicious file in the system's temporary files folder and downloads a payload. For instance, GCleaner often drops AZORult and RedLine, stealers that scan the system for any type of personal information, which from now on becomes known to the attackers, including:
Although each malware family may exploit different types of vulnerabilities, in most cases, the process involves hijacking the victim’s web browser and then recording their keystrokes.
GCleaner makes use of different persistence mechanisms. For instance, after installation, it creates a number of new processes running in the background. The malware also writes data to a remote process, which is typically a legitimate Windows process. This makes it difficult for antivirus software to detect and remove the malware.
GCleaner attempts to stay hidden by using rootkit capabilities, which allow it to hide its presence from the operating system. As an extra layer of protection, it implements encryption to obfuscate its code, rendering it unreadable and harder for researchers to analyze.
Anti-debugging is also on the menu, which hinders reverse engineering efforts, making it challenging for analysts to debug the code and understand how it works.
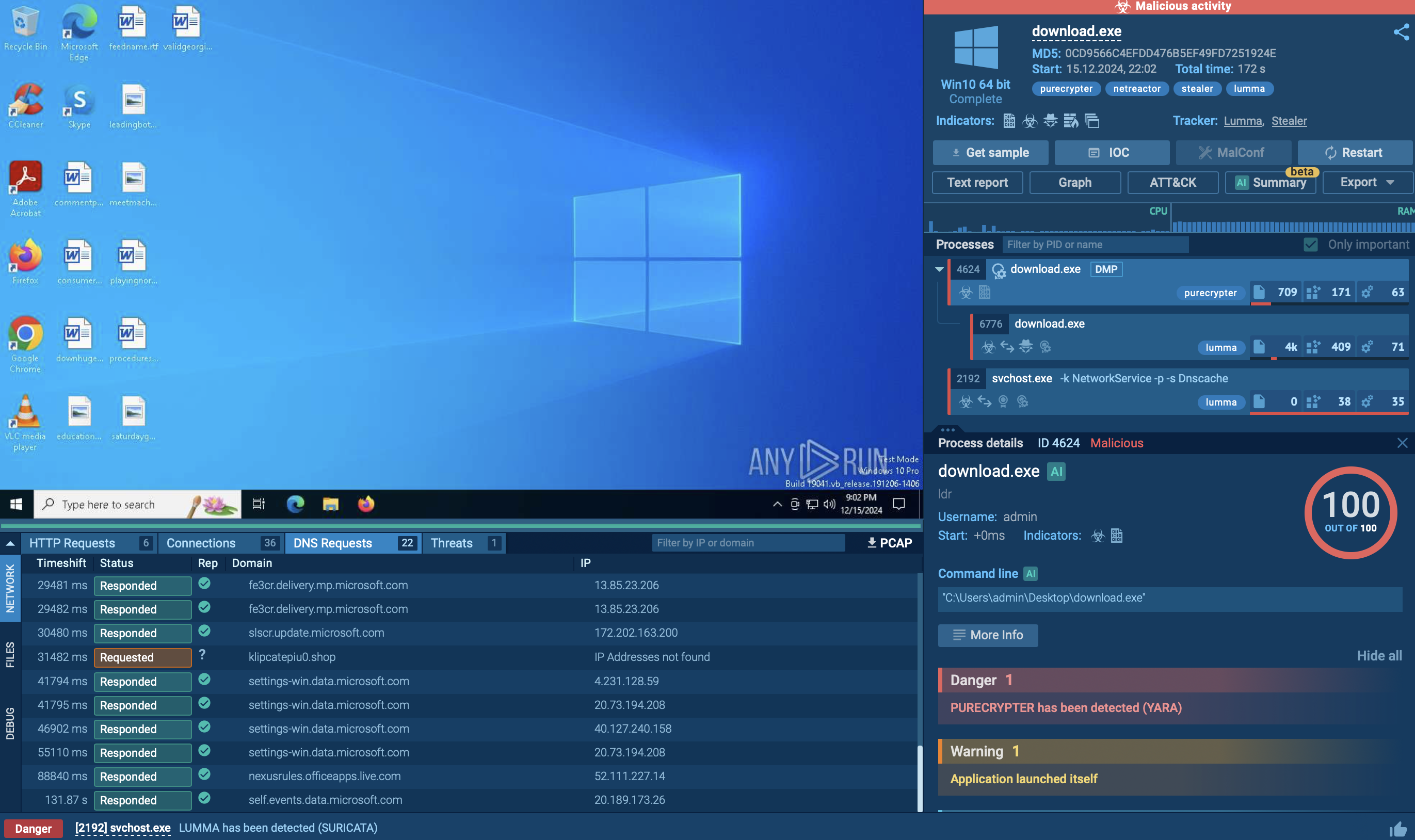
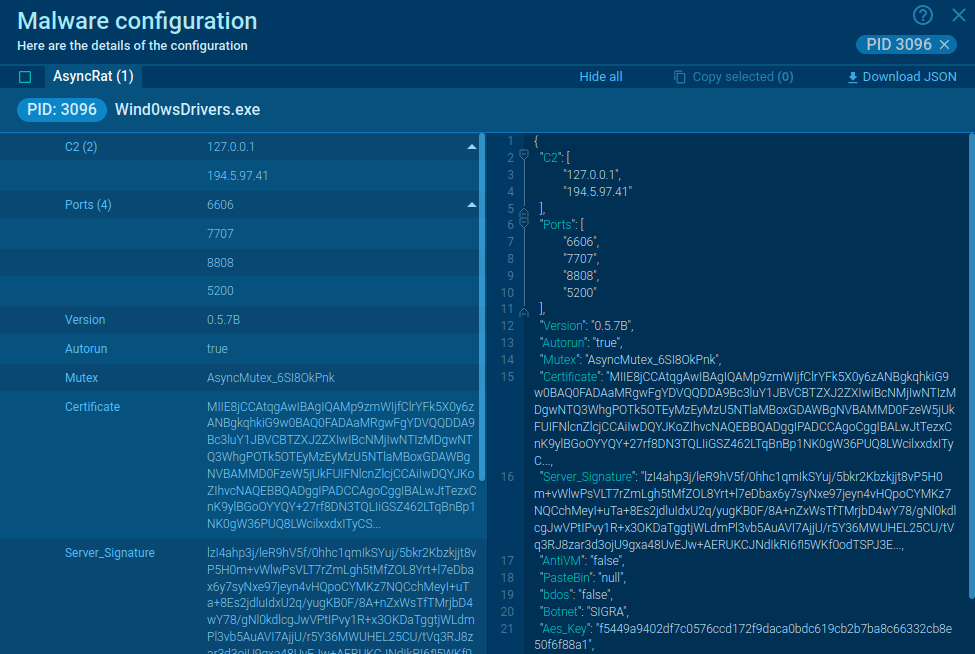
By utilizing ANY.RUN, we can track the entire execution path of G-Cleaner and retrieve its config automatically. Here is a sample of the malware analyzed in our sandbox.
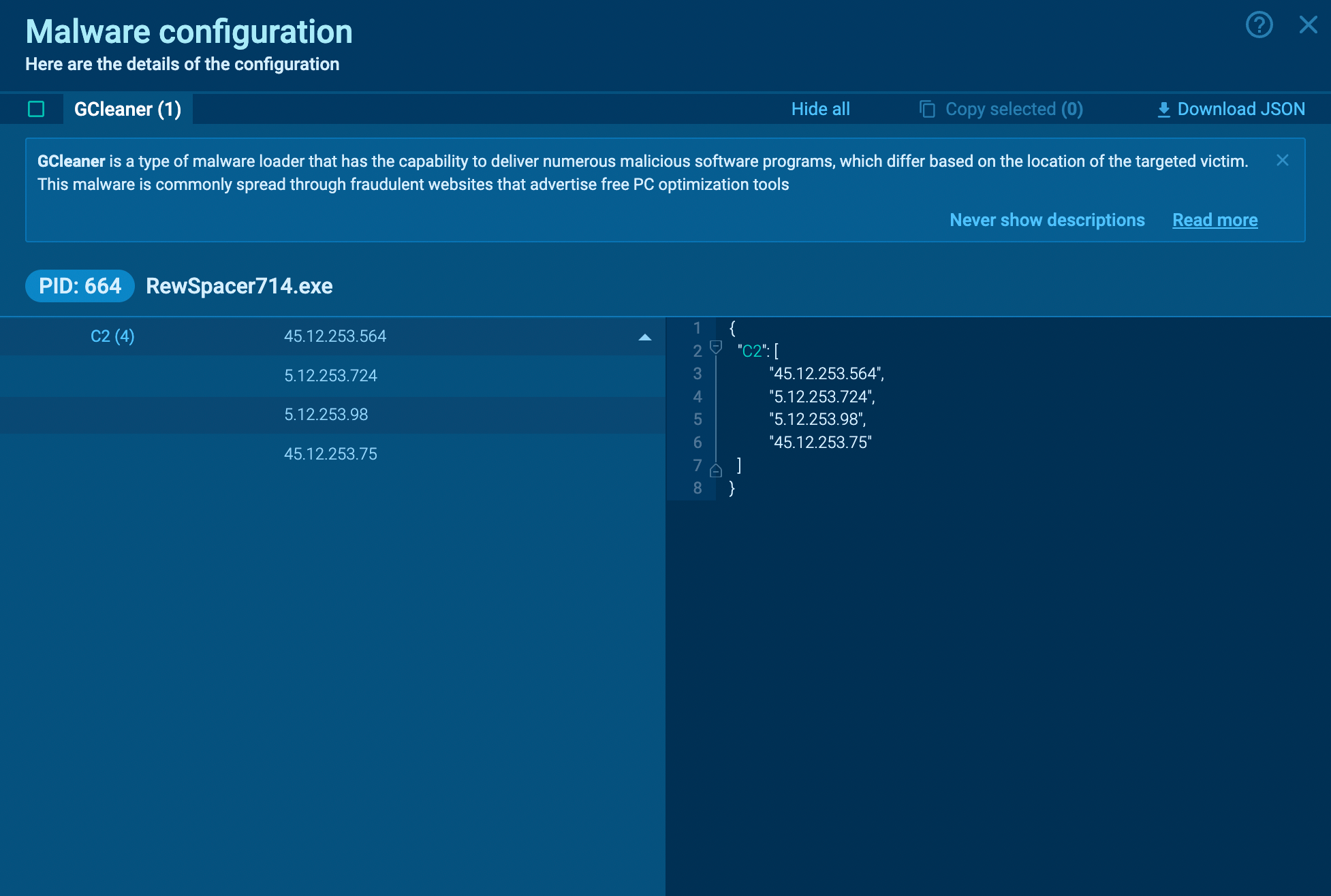 Gcleaner's configuration extracted by ANY.RUN
Gcleaner's configuration extracted by ANY.RUN
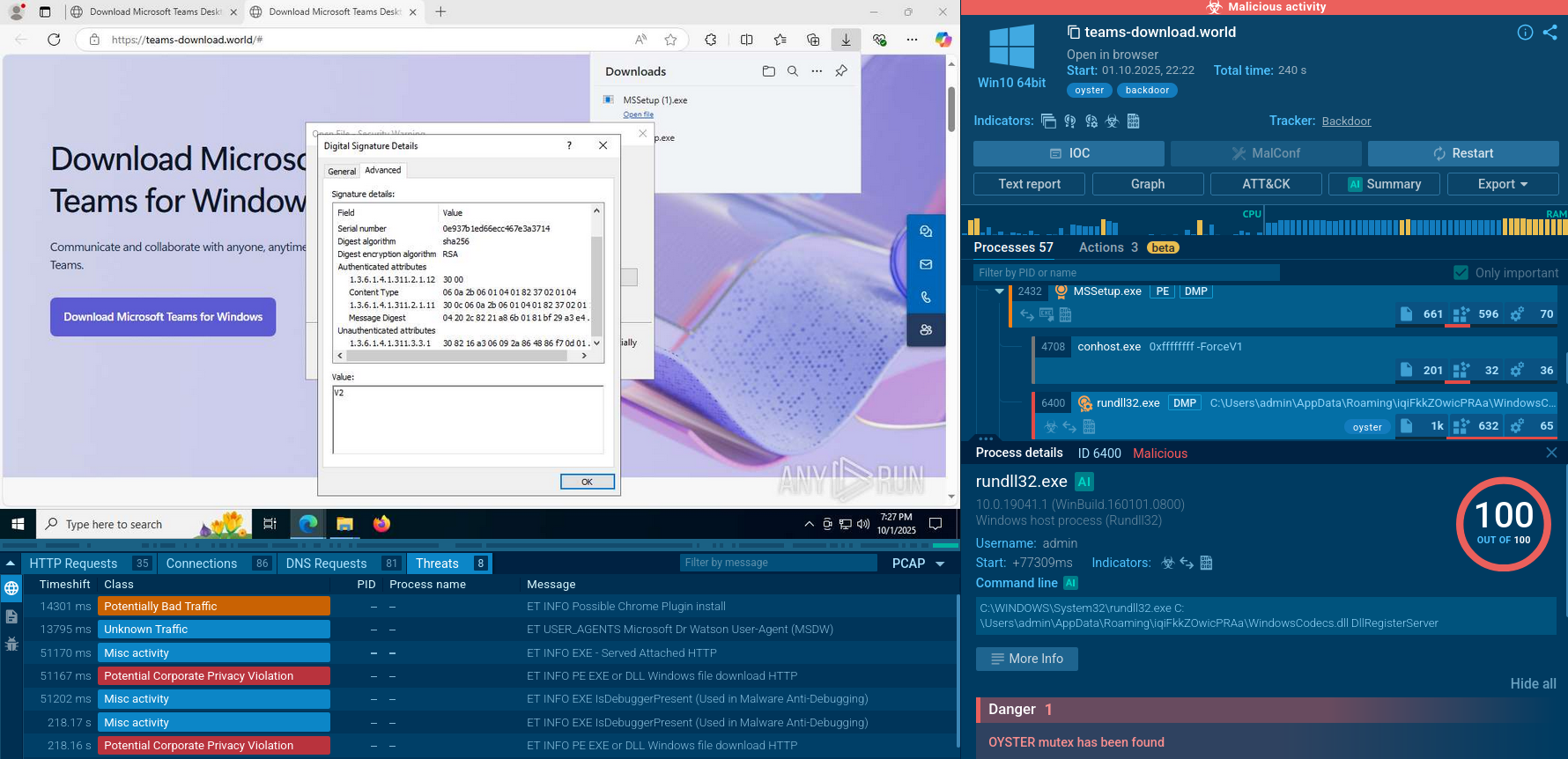
Since GCleaner is a loader, its main purpose is to download other malware families. As a result, the execution flow varies from one version to another and can include the use of different tools. Overall, after it starts, the loader simply reruns itself under a different name from one of the "Program Files" directories. After that, it mostly attempts to download malware onto the infected system. In our case, GCleaner downloaded Redline.
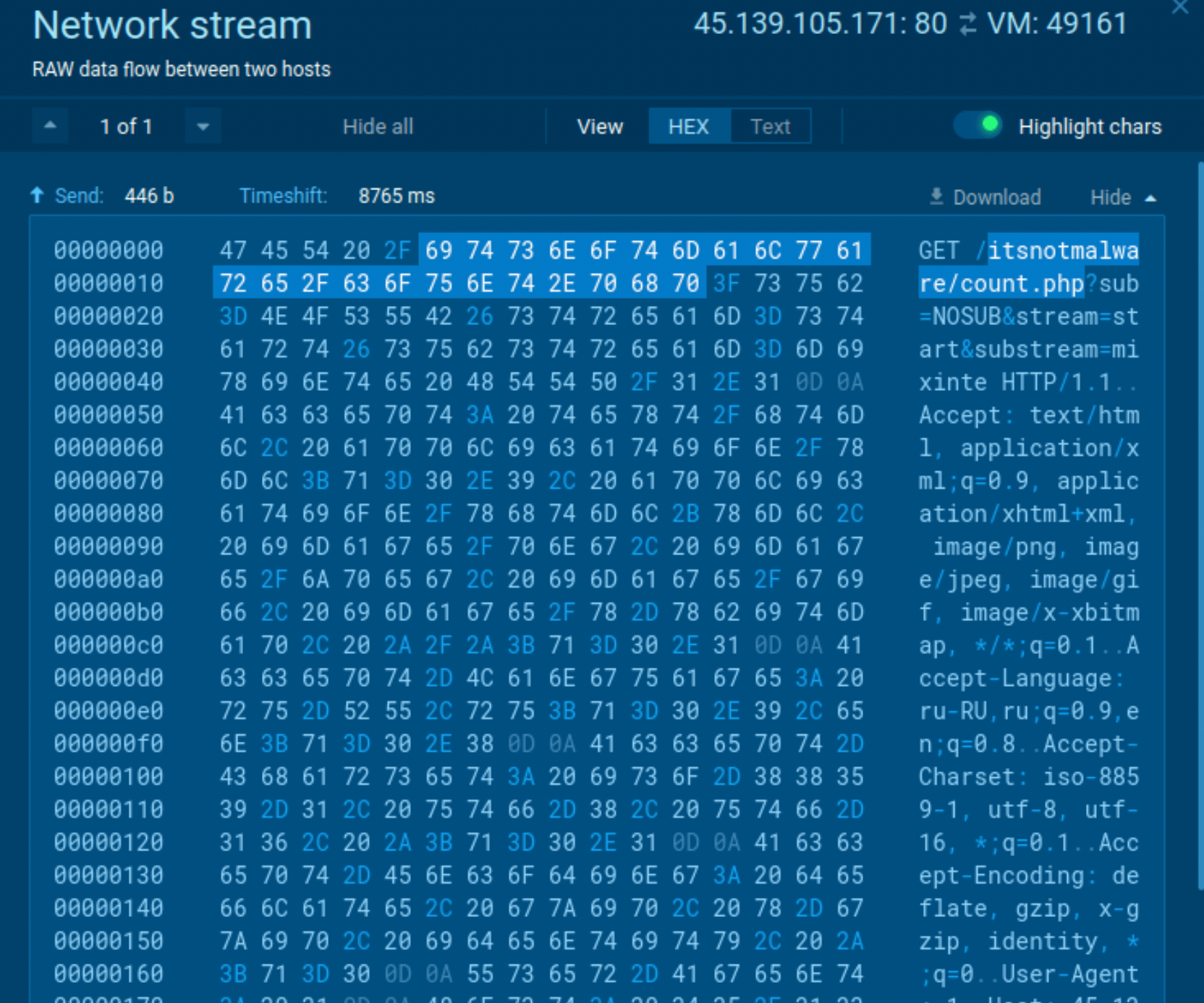 Gcleaner's network traffic
Gcleaner's network traffic
Some samples of GCleaner may be detected by the malware’s network traffic. To do so, just look at the network stream. If you find "itsnotmalware/count.php" there, you can be pretty sure that it is GCleaner.
G-Cleaner has several channels for finding its way to users’ systems:
The most common one is through a website promoting a free optimizer. In fact, such was the first instance of this malware being discovered in 2019. The design of the page is reminiscent of those of CCleaner and other trusted providers, which is how criminals trick users into downloading malware.
Another widespread distribution method for G-Cleaner is through spam emails disguised as legitimate messages from international brands. In such cases, attackers utilize social engineering techniques to get users to install email attachments.
Alternatively, GCleaner can be masked as files not related to PC optimization. These may include game modes, patches, and other types of software.
G-Cleaner is a loader capable of introducing a range of malicious software onto the victim's computer. Generally, it is disseminated through fake websites advertising free PC performance optimization tools or via spam emails.
To prevent GCleaner and other malware from posing a risk to your organization’s infrastructure, you can conveniently scrutinize any questionable files using the ANY.RUN interactive malware analysis sandbox to quickly identify harmful code, study its behavior, and collect IOCs.